Introduction to Organic Medicinal Chemistry
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
The practice of medicinal chemistry devoted to the discovery and development of new drugs
a. Organic chemistry
b. Inorganic chemistry
c. Organic biochemistry
d. Organic medicinal chemistry
d. Organic medicinal chemistry
Receptor is a relatively small region of macromolecule which can be:
a. Isolatable enzyme
b. Structural or functional component of cell membrane
c. Specific intracellular substances
d. a and c
e. All
e. All
What is the most stable form of morphine to bind to the mu receptor?
a. T-shaped conformation
b. L-shaped conformation
c. S-shaped conformation
d. R-shaped conformation
a. T-shaped conformation
What is the chemical bonding involved between protamine and heparin?
a. Neutralization
b. Oxidation
c. Reduction
d. Hydrolysis
a. Neutralization - specifically neutralization reaction
Selection of structural components, the steric, electronic, and solubility characteristics of a drug which makes it interchangeable with drugs of the same pharmacologic class.
a. Isomerism
b. Isosterism
c. Sterioisomerism
d. Geometric isomerism
b. Isosterism
Interchangeability of one molecule with another molecule.
a. Isomerism
b. Isosterism
c. Sterioisomerism
d. Geometric isomerism
b. Isosterism
Basis for alteration of pharmacokinetic and pharmacologic properties of drugs.
a. Isomerism
b. Isosterism
c. Sterioisomerism
d. Geometric isomerism
b. Isosterism
Compounds or group of atoms having the same number of arrangement of electrons.
a. Isomers
b. Isobars
c. Isotones
d. Isosteres
d. Isosteres
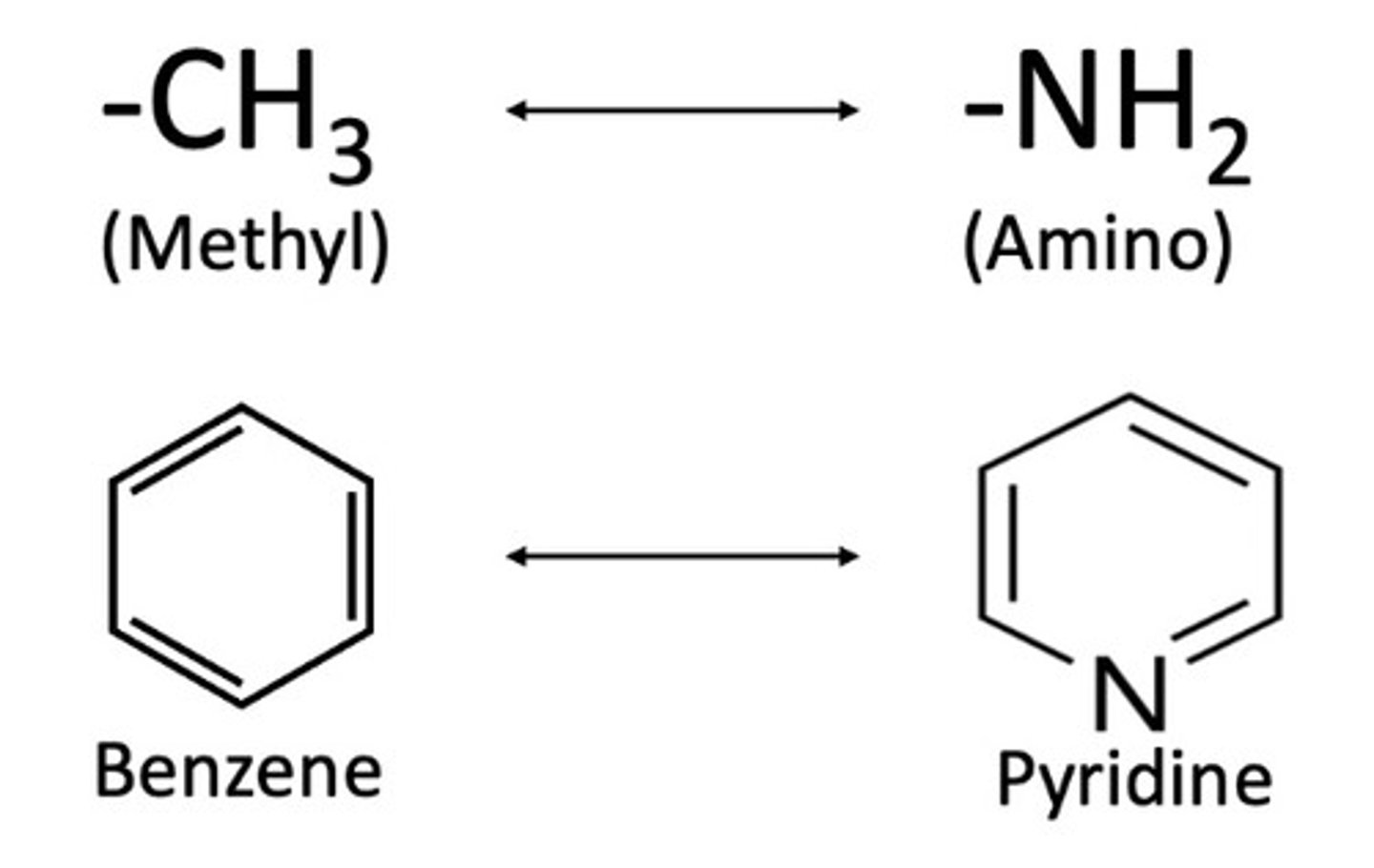
Concepts under SAR except:
a. Part responsible for mechanism of action
b. Part responsible for increased absorption
c. Part mainly metabolized
d. Part responsible for prolonged or shortened duration of action
e. None
e. None
R−N=N−R′
a. Azo
b. Hydrazo
c. Azido
d. Nitroso
e. Nitro
a. Azo
R−N-N−R′
a. Azo
b. Hydrazo
c. Azido
d. Nitroso
e. Nitro
b. Hydrazo
⁻N=N⁺=N⁻
a. Azo
b. Hydrazo
c. Azido
d. Nitroso
e. Nitro
c. Azido
N=O
a. Azo
b. Hydrazo
c. Azido
d. Nitroso
e. Nitro
d. Nitroso
-NO2
a. Azo
b. Hydrazo
c. Azido
d. Nitroso
e. Nitro
e. Nitro
HO-C-NH2
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Carbinolamine
c. Sulfoxide
d. Sulfone
e. Sulfonamide
b. Carbinolamine
HO-NH2
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Carbinolamine
c. Sulfoxide
d. Sulfone
e. Sulfonamide
a. Hydroxylamine
S=O
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Carbinolamine
c. Sulfoxide
d. Sulfone
e. Sulfonamide
c. Sulfoxide
O=S=O
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Carbinolamine
c. Sulfoxide
d. Sulfone
e. Sulfonamide
d. Sulfone
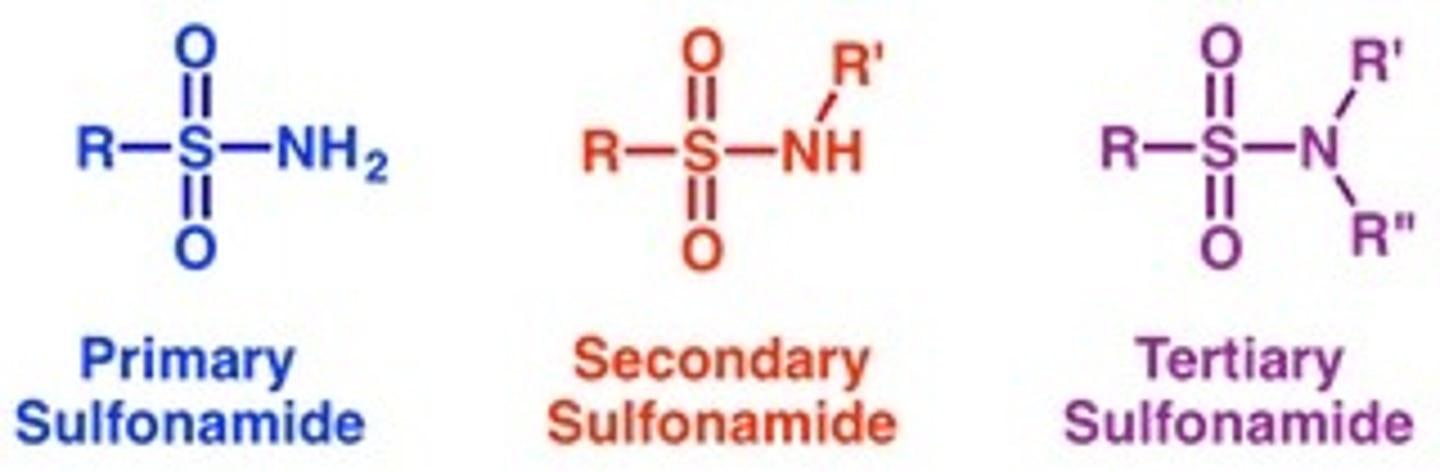
R−S(=O)2−NR'R"
a. Hydroxylamine
b. Carbinolamine
c. Sulfoxide
d. Sulfone
e. Sulfonamide
e. Sulfonamide
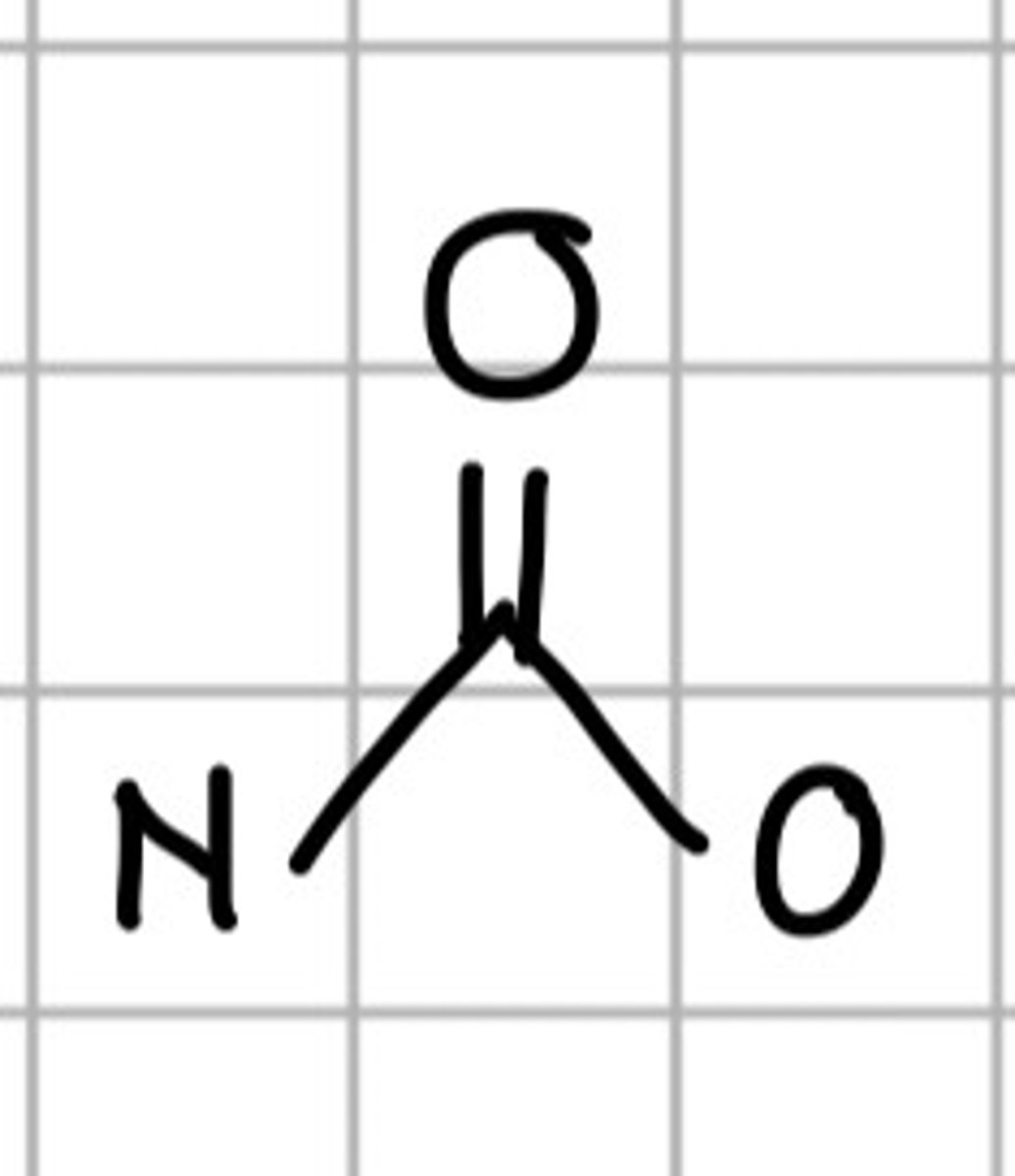
NC=OO
a. Carbamate
b. Urea
c. Guanidine
d. Sulfonamide
a. Carbamate
NC=ON
a. Carbamate
b. Urea
c. Guanidine
d. Sulfonamide
b. Urea
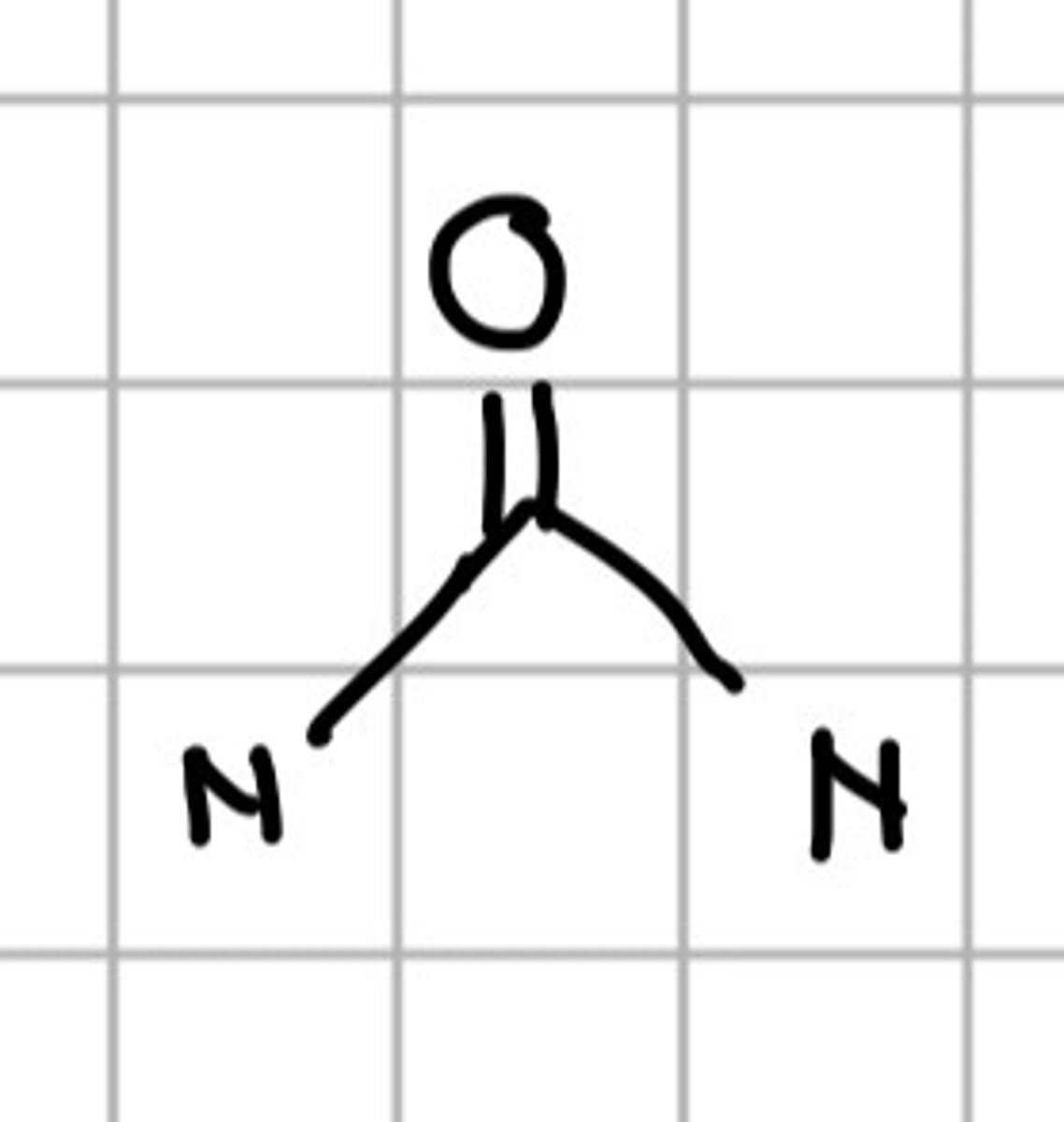
NC=NN
a. Carbamate
b. Urea
c. Guanidine
d. Sulfonamide
c. Guanidine
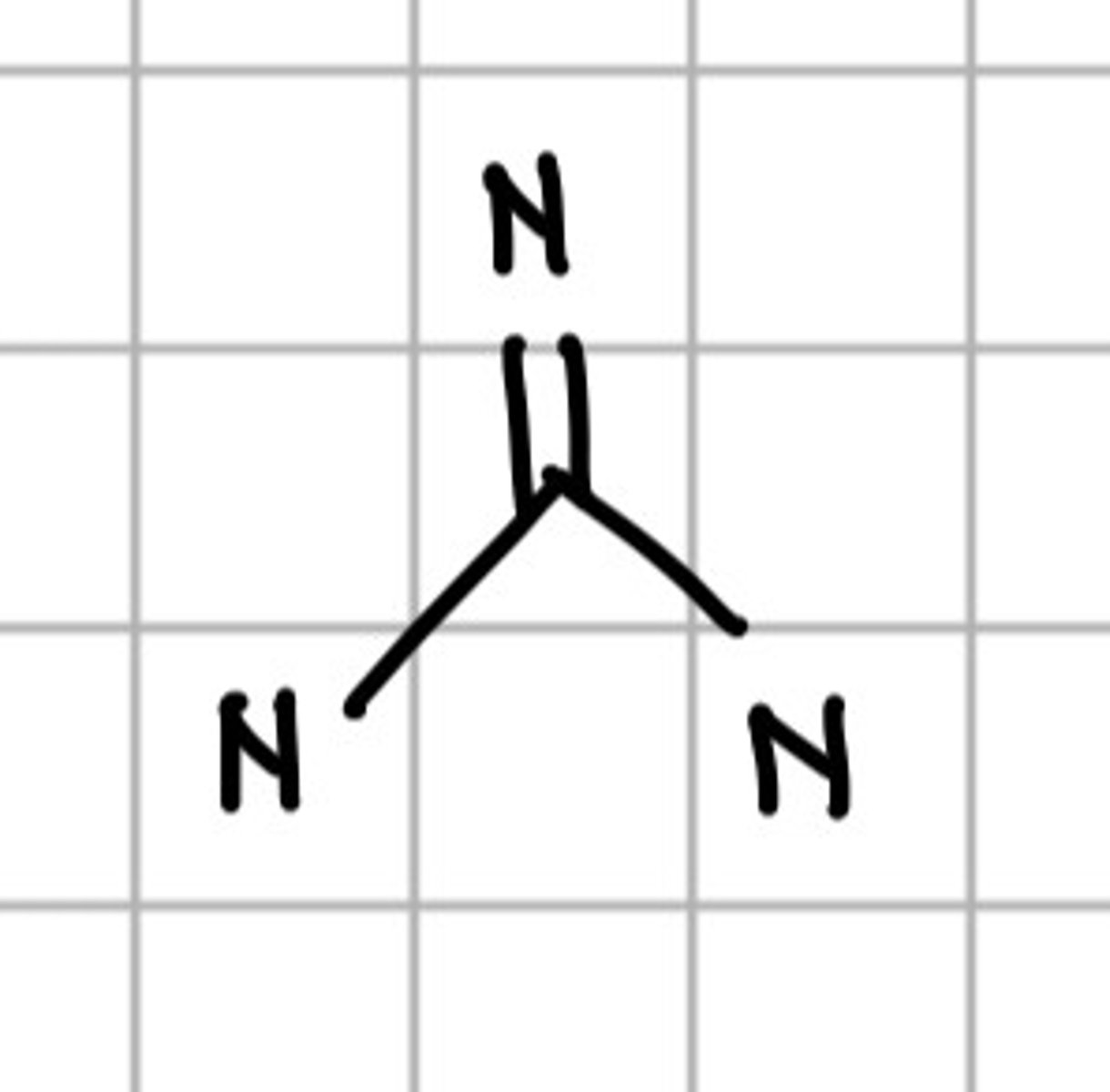
Nomenclature of heterocyclic compounds:
a. Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature
b. Common names
c. Replacement nomenclature
d. a and b
e. All
e. All
Oxiranes is an example of:
a. Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature
b. Common names
c. Replacement nomenclature
d. a and b
e. All
a. Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature
Ethylene oxide:
a. Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature
b. Common names
c. Replacement nomenclature
d. a and b
e. All
b. Common names
Oxacyclopropane:
a. Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature
b. Common names
c. Replacement nomenclature
d. a and b
e. All
c. Replacement nomenclature
Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature prefix for O.
a. Oxa-
b. Aza-
c. Thia-
d. Phospha-
a. Oxa-
Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature prefix for N.
a. Oxa-
b. Aza-
c. Thia-
d. Phospha-
b. Aza-

Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature suffix for 5-membered heterocyclic compound.
a. ir
b. et
c. ol
d. in
e. ep
c. ol
Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature suffix for 6-membered heterocyclic compound.
a. ir
b. et
c. ol
d. in
e. ep
d. in
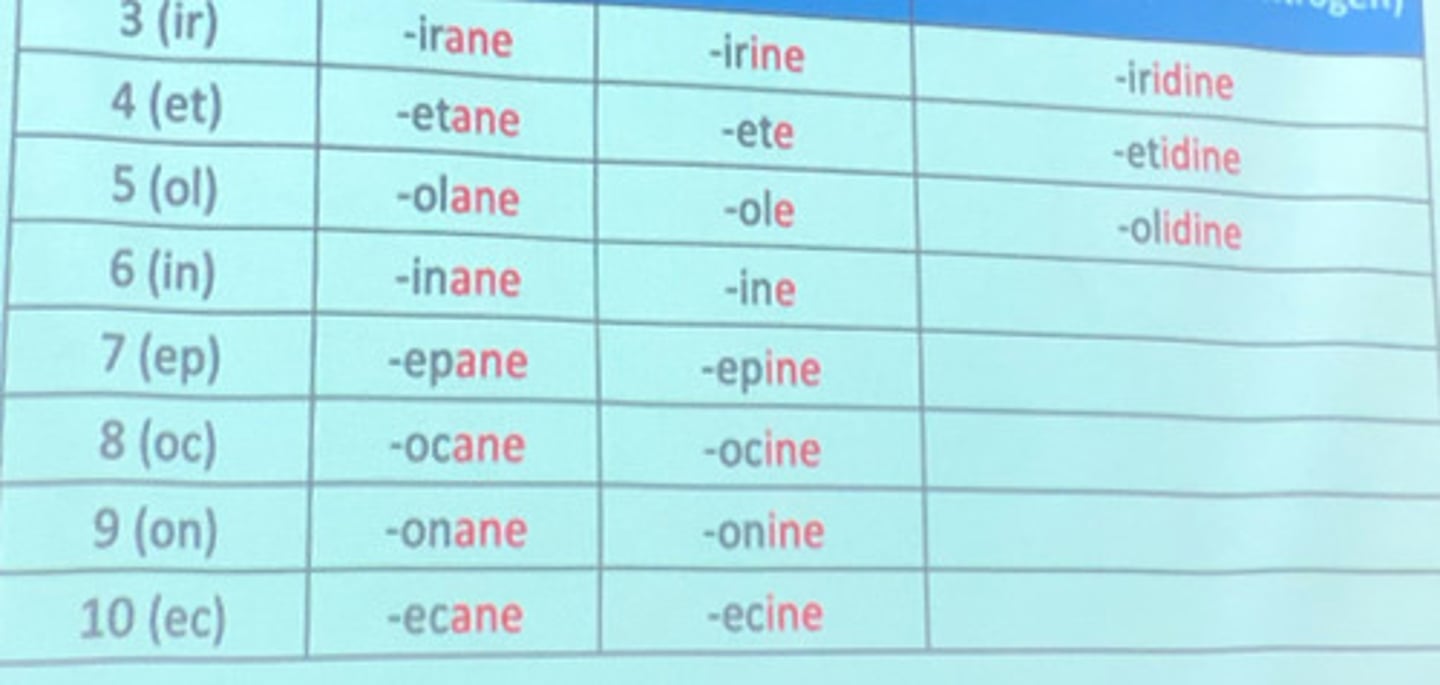
Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature suffix for 6-membered saturated heterocyclic compound.
a. irane
b. etane
c. olane
d. inane
e. epane
d. inane
Hantzsch-Widman nomenclature suffix for 5-membered saturated heterocyclic compound with nitrogen.
a. iridine
b. etidine
c. olidine
d. inane
e. epane
c. olidine
True about drug metabolism except:
a. Aim is to convert drug to polar, pharmacologically inactive, and excretable form
b. Some drugs are extensively metabolized
c. Most drug absorbed are lipophilic
d. All metabolites are detoxified or inactivated
e. None
d. All metabolites are detoxified or inactivated
NOT ALL.
The following undergo extensive first pass effect except:
a. Lidocaine
b. Nitrates
c. Morphine
d. Meperidine
e. None
e. None
Phenol hydrogen sulfate from metabolism of phenol:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
a. Inactive
Temazepam from hydroxylation of diazepam:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the main drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
b. Similar activity to the main drug
Oxazepam from N-demethylation of Temazepam:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the main drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
b. Similar activity to the drug
Isoniazid from N-Dealkylation of Ipronazid:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
c. Different activity
Phenetidine from metabolism of Phenacetin:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
d. Toxic metabolite
N-hydroxy phenacetin from metabolism of phenacetin:
a. Inactive
b. Similar activity to the drug
c. Different activity
d. Toxic metabolite
d. Toxic metabolite
Can be responsible for hepatotoxicity:
a. Phenacetin
b. N-hydroxy phenacetin
c. Phenetidine
d. Diazepam
b. N-hydroxy phenacetin
Can be responsible for methemoglobinemia:
a. Phenacetin
b. N-hydroxy phenacetin
c. Phenetidine
d. Diazepam
c. Phenetidine
Functionalization phase of metabolism:
a. Phase I
b. Phase II
a. Phase I
Polar functional group introduced during phase I metabolism except:
a. OH
b. COOH
c. NH2
d. SH
e. None
e. None
Enzyme system involved during phase I metabolism except:
a. Mixed function oxidases
b. Monooxygenases
c. CYP450
d. CYP3A4
e. None
e. None
Mixed function oxidases is aka monooxygenases or CYP450
Most dominant enzyme system involved during phase I metabolism.
a. CYP450
b. CYP3A4
c. MAO
d. COMT
a. CYP450
Dominant enzyme system involved during phase I metabolism inhibited by grapefruit.
a. CYP450
b. CYP3A4
c. MAO
d. COMT
b. CYP3A4
Mechanism of functionalization during phase I metabolism:
a. Direct introduction
b. Unmasking
c. Demethylation
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Demethylation is an example of unmasking.
Phase I metabolism reactions:
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Most common phase I metabolism reaction.
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
a. Oxidation
Phase I metabolism reaction for carboxylic acid derivatives.
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
c. Hydrolysis
The following undergo oxidation except:
a. Alcohols
b. Aldehydes
c. Olefins
d. Aromatic moieties
e. None
e. None
Product of oxidation of 1° alcohol.
a. Aldehdye
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
a. Aldehyde
Product of oxidation of 2° alcohol.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
c. Ketone
Product of oxidation of aldehyde under acidic condition.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
a. Carboxylic acid
Product of oxidation of aldehyde under alkali condition.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
e. Salt
Product of oxidation of olefin.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
b. Epoxide
Product of oxidation of arenes.
a. Carboxylic acid
b. Epoxide
c. Ketone
d. Arenol
e. Salt
d. Arenol
Oxidation of arenes at what position will produce arenol which usually favors excretion?
a. Meta
b. Ortho
c. Para
d. Any
c. Para
Undergo reduction reaction except:
a. Aldehydes
b. Ketones
c. Azo groups
d. Nitro grouos
e. Disulfides
f. None
f. None
Product of reduction of ketone.
a. 1° alcohol
b. 2° alcohol
c. Amine
d. Thiol
b. 2° alcohol
Product of reduction of aldehyde.
a. 1° alcohol
b. 2° alcohol
c. Amine
d. Thiol
a. 1° alcohol
Conversion of chloral hydrate to trichloroethanol involved what reaction?
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
b. Reduction
chloral hydrate (aldehdye) to trichloroethanol (1° alcohol)
Trichloroethanol is still active which can act as sedative hypnotic.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Chloral hydrate is a date rape drug.
a. True
b. False
a. True
Product of reduction of disulfide.
a. 1° alcohol
b. 2° alcohol
c. Amine
d. Thiol
d. Thiol
Final product of reduction of azo and nitro group.
a. 1° alcohol
b. 2° alcohol
c. Amine
d. Thiol
c. Amine
Product of reduction of azo group.
a. Nitroso
b. Hydroxylamine
c. Hydrazo
d. Amine
c. Hydrazo
Product of reduction of hydrazo group.
a. Nitroso
b. Hydroxylamine
c. Azo
d. Amine
d. Amine
Product of reduction of nitro group.
a. Nitroso
b. Hydroxylamine
c. Hydrazo
d. Amine
a. Nitroso
Product of reduction of nitroso group.
a. Nitro
b. Hydroxylamine
c. Hydrazo
d. Amine
b. Hydroxylamine
Product of reduction of hydroxylamine group.
a. Nitro
b. Nitroso
c. Hydrazo
d. Amine
d. Amine
Major pathway for acid derivatives.
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
c. Hydrolysis
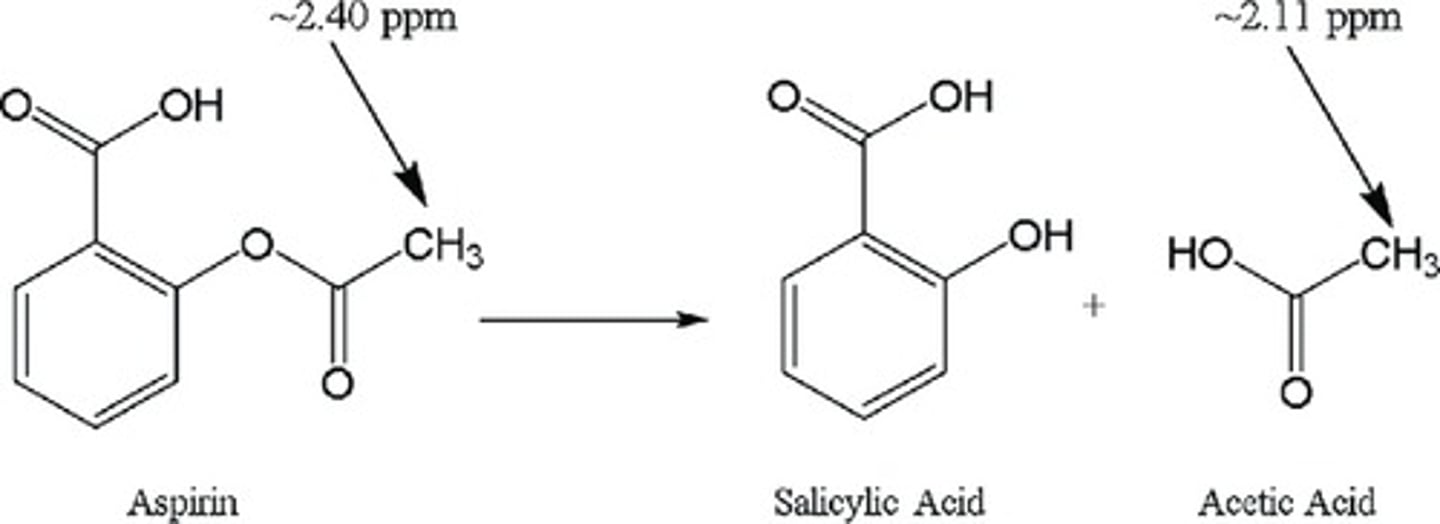
Reaction involved in metabolism of aspirin to salicylic acid and acetic acid.
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
c. Hydrolysis
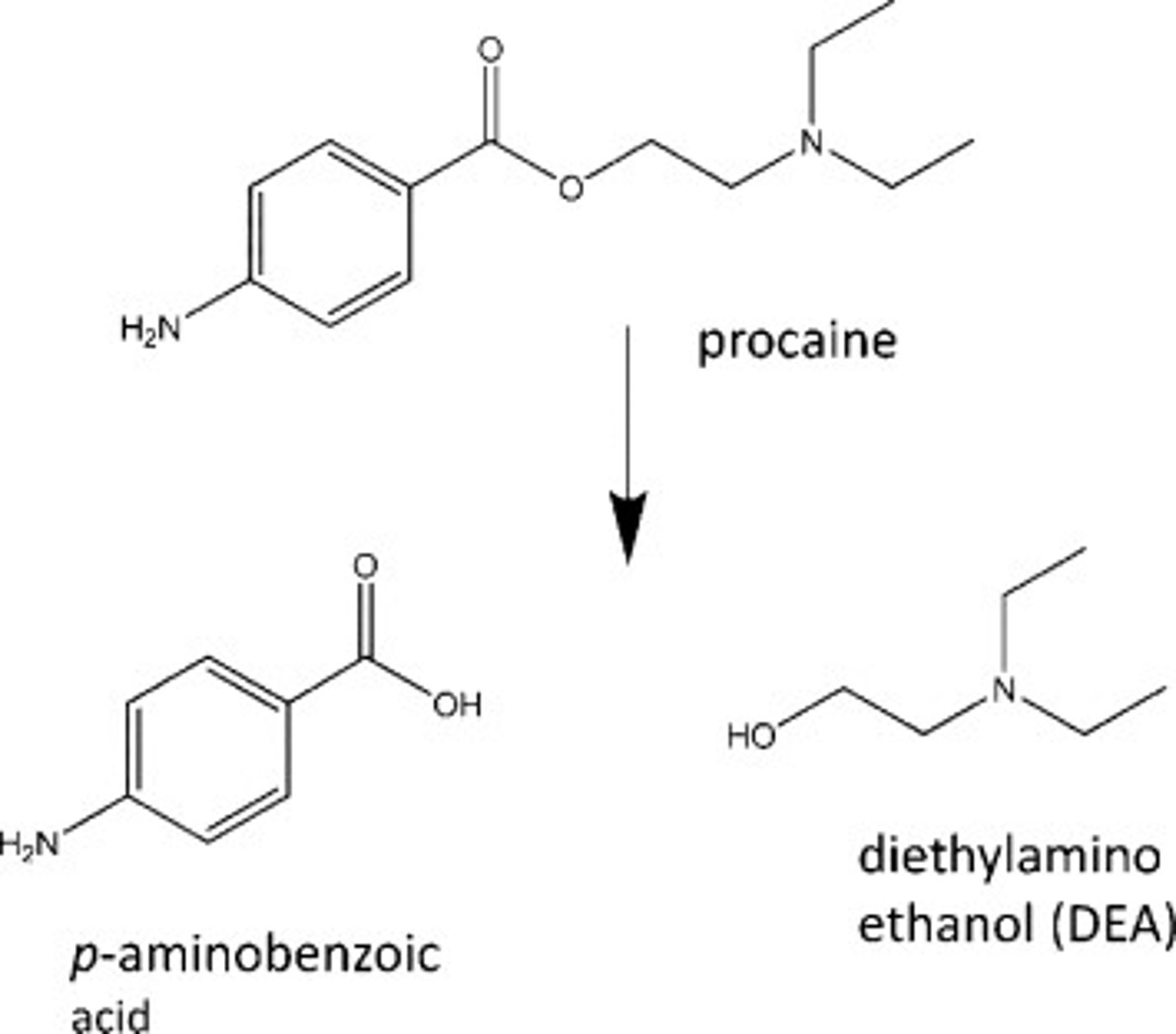
Reaction involved in metabolism of procaine to para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA).
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
c. Hydrolysis
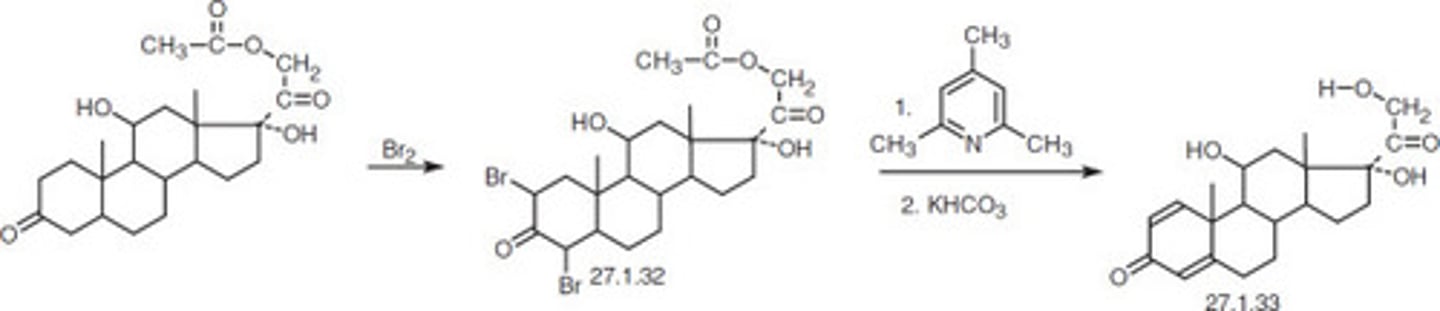
Reaction involved in metabolism of prednisone to prednisolone.
a. Oxidation
b. Reduction
c. Hydrolysis
b. Reduction
Phase of metabolism with goal to attach small , polar, ionizable endogenous compounds to functional handles produce water soluble conjugated products.
a. Phase II
b. Conjugation phase
c. Synthetic phase
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Phase II metabolism reaction that do not necessarily increase water solubility.
a. Methylation
b. Acetylation
c. Glutathione conjugaion
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
f. All
Terminate or attenuate biologically activity and not generally increase water solubility.
a. Methylation
b. Acetylation
c. Glutathione conjugaion
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
d. a and b
Methylation
Acetylation
Protect the body against chemically active compounds and metabolites.
a. Methylation
b. Acetylation
c. Glutathione conjugaion
d. a and b
e. b and c
f. All
c. Glutathione conjugaion
Phase II reactions except:
Glucuronidation
Sulfation
Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
Acetylation
Methylation
Glutathione conjugation
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Methylation
d. Glutathione conjugation
e. None
e. None
Most common phase II reaction.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Methylation
d. Glutathione conjugation
e. None
a. Glucuronidation
Not yet developed in neonates.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
a. Glucuronidation
Substrate are:
Alcohols
Phenols
Carboxylic acids
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
a. Glucuronidation
Substrate are mostly phenols.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
b. Sulfation
Substrate are:
Glycine: aromatic acid and arylalkyl acids
Glutamine: aryl acetic acids
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
Substrate are:
1° amines
Aromatic amines
Sulfonamides
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
d. Acetylation
Substrate are endogenous biogenic amines.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
e. Methylation
Substrate are electrophilic reactive species.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
f. Glutathione conjugation
Enzyme and cofactor for glucuronidation.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
Enzyme and cofactor for sulfation.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
Enzyme and cofactor for glycine and glutamine conjugation.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
c. N-acyl transferase
Enzyme and cofactor for glutathione.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
f. S-transferase
Enzyme and cofactor for methylation.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
Enzyme and cofactor for acetylation.
a. UDP-glucuronosyl acetyltransferases (UDP-glucuronic acid)
b. Sulfotransferases (3'Phosphoadenosyl-5'-phosphosulfate [PAPS])
c. N-acyl transferase (Gly,Glu)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
e. Methyltransferase (S-adenosylmethionine [SAM])
f. S-transferase (GSH)
d. N-acetyltransferase (Acetyl-CoA)
Reaction undergone by:
Paracetamol
Chloramphenicol
Bilirubin
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
a. Glucuronidation
Reaction undergone by benzoic acid.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
Main reaction undergone paracetamol in neonates.
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
b. Sulfation
Reaction undergone by:
Hydralazine
Isoniazid
Procainamide
Sulfonamide
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
d. Acetylation
Reaction important to relieve paracetamol poisoning
a. Glucuronidation
b. Sulfation
c. Glycine/Glutamine conjugation
d. Acetylation
e. Methylation
f. Glutathione conjugation
f. Glutathione conjugation