Physics 2 - Lesson 7: Geometric Optics
1/34
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Physics 2 Lesson 7
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Lesson 7: Geometric Optics
Lesson 7: Geometric Optics
CRB Fill in the blanks: According to Rectilinear ______________, light traveling in a homogeneous medium will travel ________________.
(A) Parallax, adjacent to the expected path.
(B) Parallax, in a straight line.
(C) Propagation, adjacent to the expected path.
(D) Propagation, in a straight line.
(D) Propagation, in a straight line.
According to Rectilinear Propoagation, light traveling in a homogeneous medium will travel in a straight line.
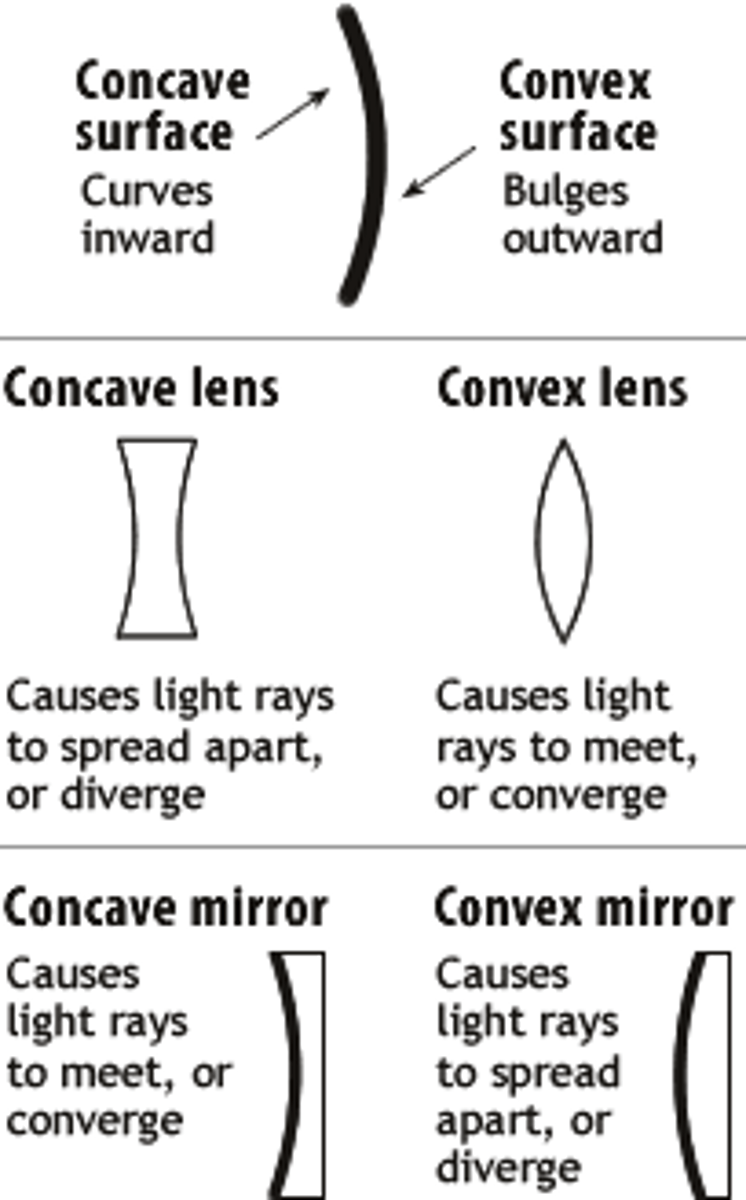
Draw a Convex vs. Concave Lens.

Contrast the effects of a Convex and Concave lens.
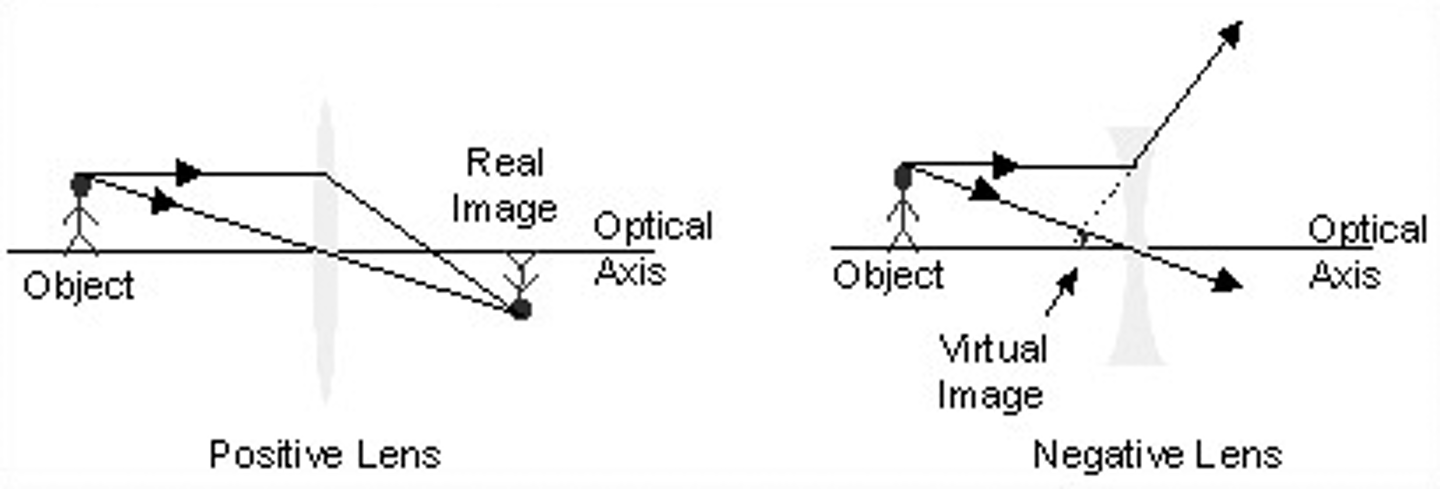
If an object is on the same side of a lens as the image, this is considered to be a ________ image. If an object is on the opposite side of a lens as the image, this is considered to be a ________ image.
(A) virtual, virtual
(B) virtual, real
(C) real, real
(D) real, virtual
(B) virtual, real
If an object is on the same side of a lens as the image, this is considered to be a virtual image. If an object is on the opposite side of a lens as the image, this is considered to be a real image.
CRB Fill in the blank: A ___________ Image will be formed whenever reflected or refracted rays _______________ to form the image.
(A) Virtual, Meet
(B) Virtual, do not meet
(C) Real, Meet.
(D) B and C
(D) B and C
A Virtual Image will be formed whenever reflected or refracted rays Do not meet to form the image.
A Real Image will be formed whenever reflected or refracted rays Meet to form the image.
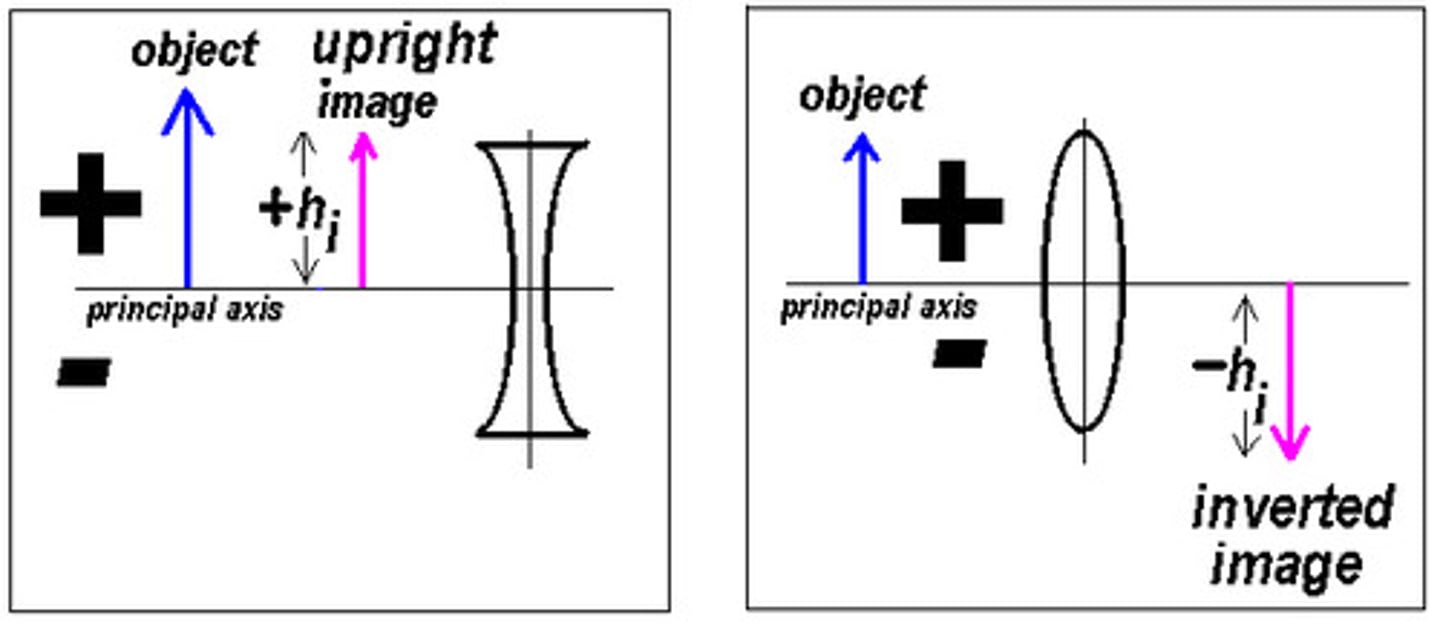
When is an image considered Upright vs. Inverted?
An image is considered to be Upright when it is above the horizonal axis/plane (the principal axis). An image is considered to be Inverted when it is below the horizonal axis/plane (the principal axis).
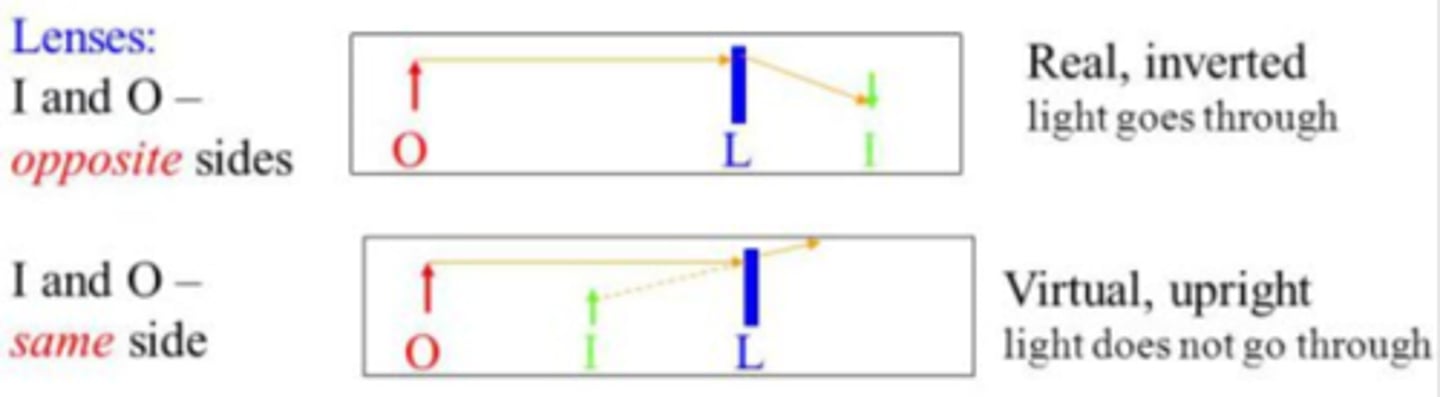
CRB True or false? When there is only a single mirror/lens in play, a Real image is always Inverted and a Virtual image is always Upright.
True. When there is only a single mirror/lens in play, a Real image is always Inverted and a Virtual image is always Upright.
CRB To really understand when lenses will lead to Virtual, Real, Upright and Inverted Images, Try drawing out Lens diagrams where there are Real Inverted images and Virtual Upright images. (Hint: Think of where the object and image must be!)
What equation can be used to relate object distance to image distance and focal length?
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/

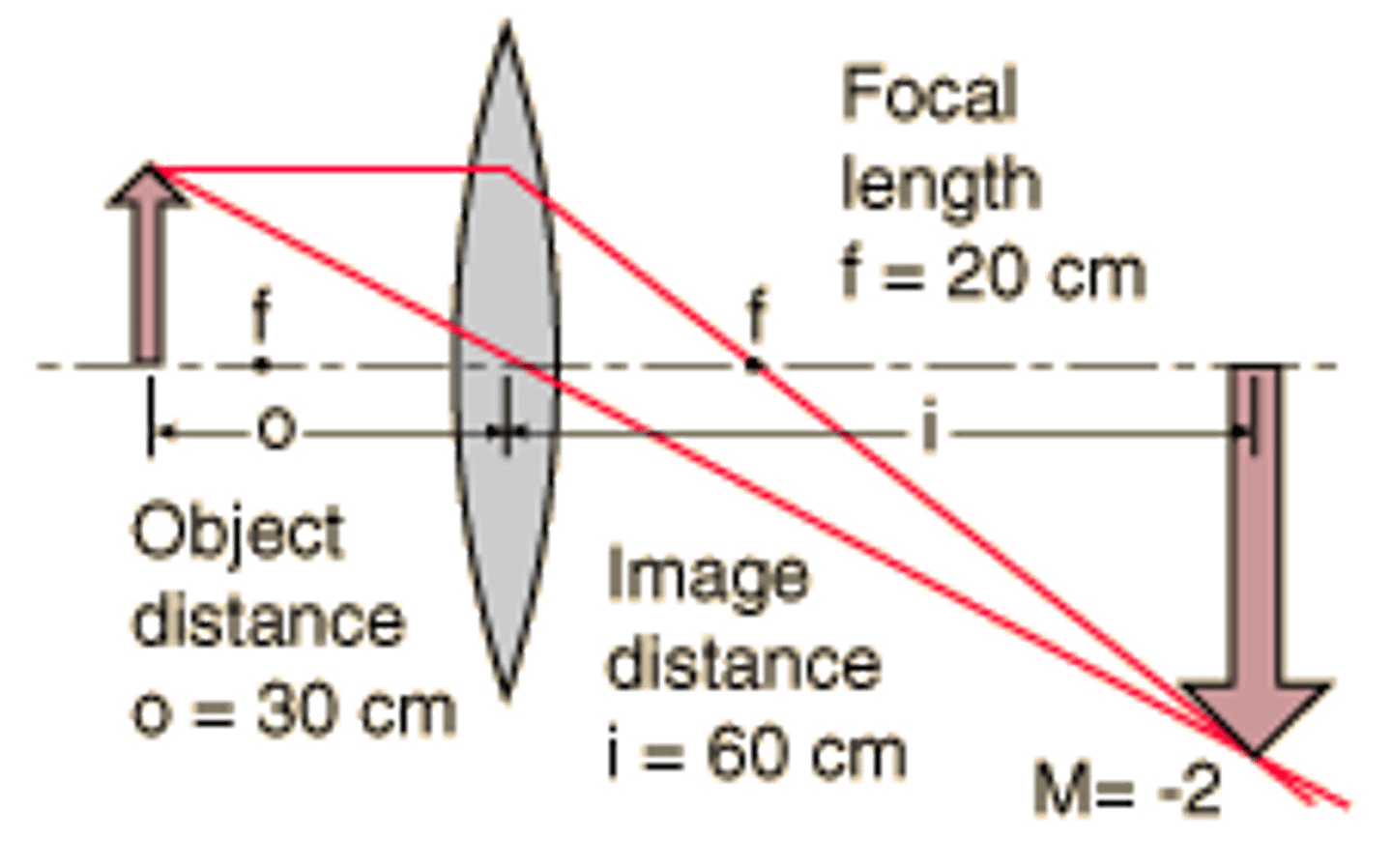
An object is at a distance of 30 cm from a convex lens with a focal length of 20 cm. What is the image distance (in cm) for this lens? Is the image inverted or upright? Is the image real or virtual?
(A) 90
(B) 60
(C) -60
(D) -90
(B) 60
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
1/20 = 1/30 + 1/i
i = 60
The image distance is 60 cm. The image is inverted and real.
NOTE: You can use the thin lens equation, but I find that it is much easier to simply draw it out and estimate the answer since exact numbers are not a requirement on the MCAT.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
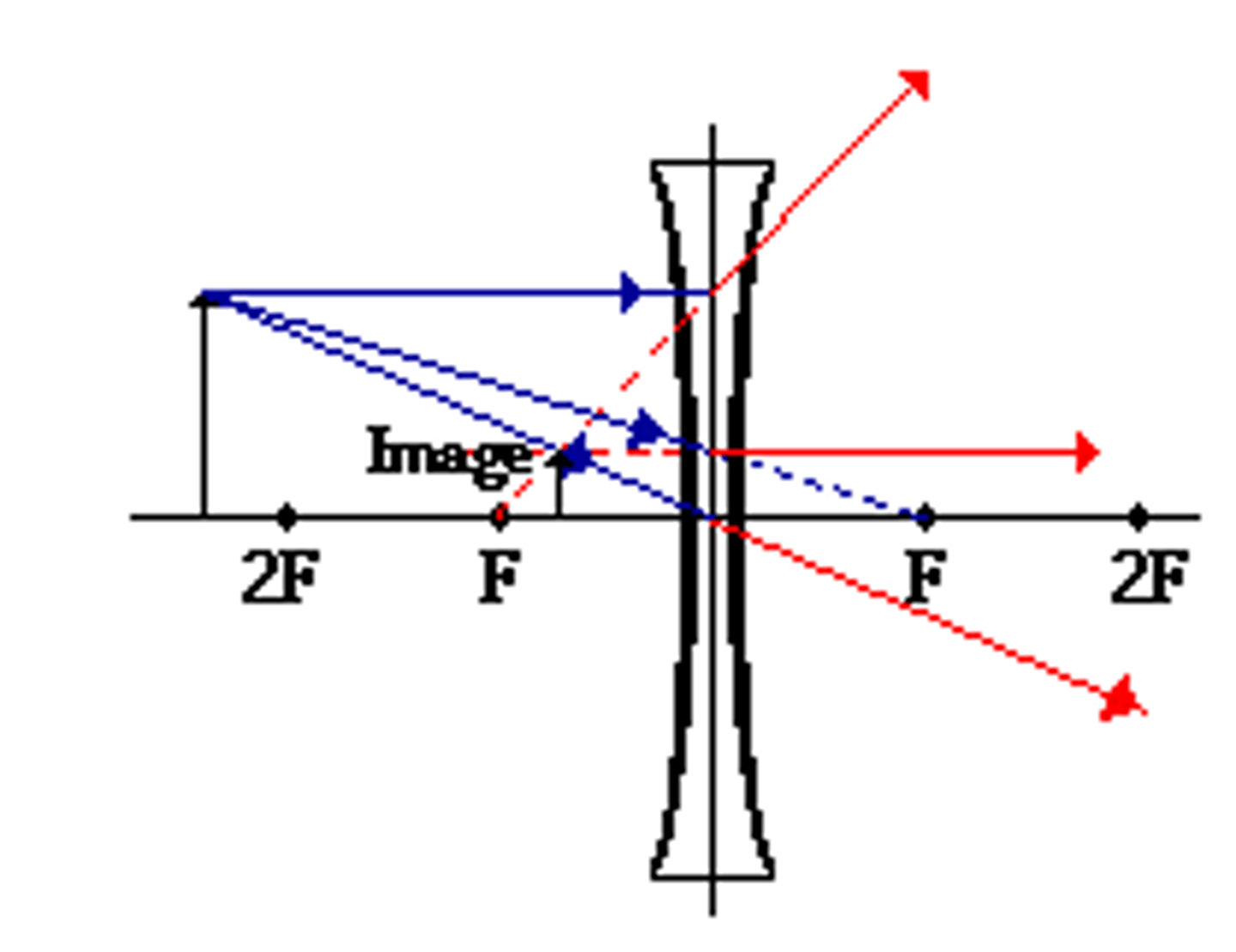
An object is at a distance of 126 cm from a concave lens with a focal length of 48 cm. What is the image distance (in cm) for this lens? Is the image inverted or upright? Is the image real or virtual?
(A) 82.45
(B) 34.76
(C) -34.76
(D) -82.45
(C) -34.76
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
1/-48 = 1/126 + 1/i
i = approx. -35 (actual: -34.76)
The image distance is -34.76 cm. The image is upright and virtual.
NOTE: You can use the thin lens equation, but I find that it is much easier to simply draw it out and estimate the answer since exact numbers are not a requirement on the MCAT.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
An object is at a distance of 45 cm from a convex lens with a focal length of 110 cm. What is the image distance (in cm) for this lens? Is the image inverted or upright? Is the image real or virtual?
(A) 76.15
(B) 34.54
(C) -34.54
(D) -76.15
(D) -76.15
1/f = 1/o + 1/i
1/110 = 1/45 + 1/i
i = approx. -75 (actual: -76.15)
The image distance is -76.15 cm. The image is upright and virtual.
NOTE: You can use the thin lens equation, but I find that it is much easier to simply draw it out and estimate the answer since exact numbers are not a requirement on the MCAT.
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
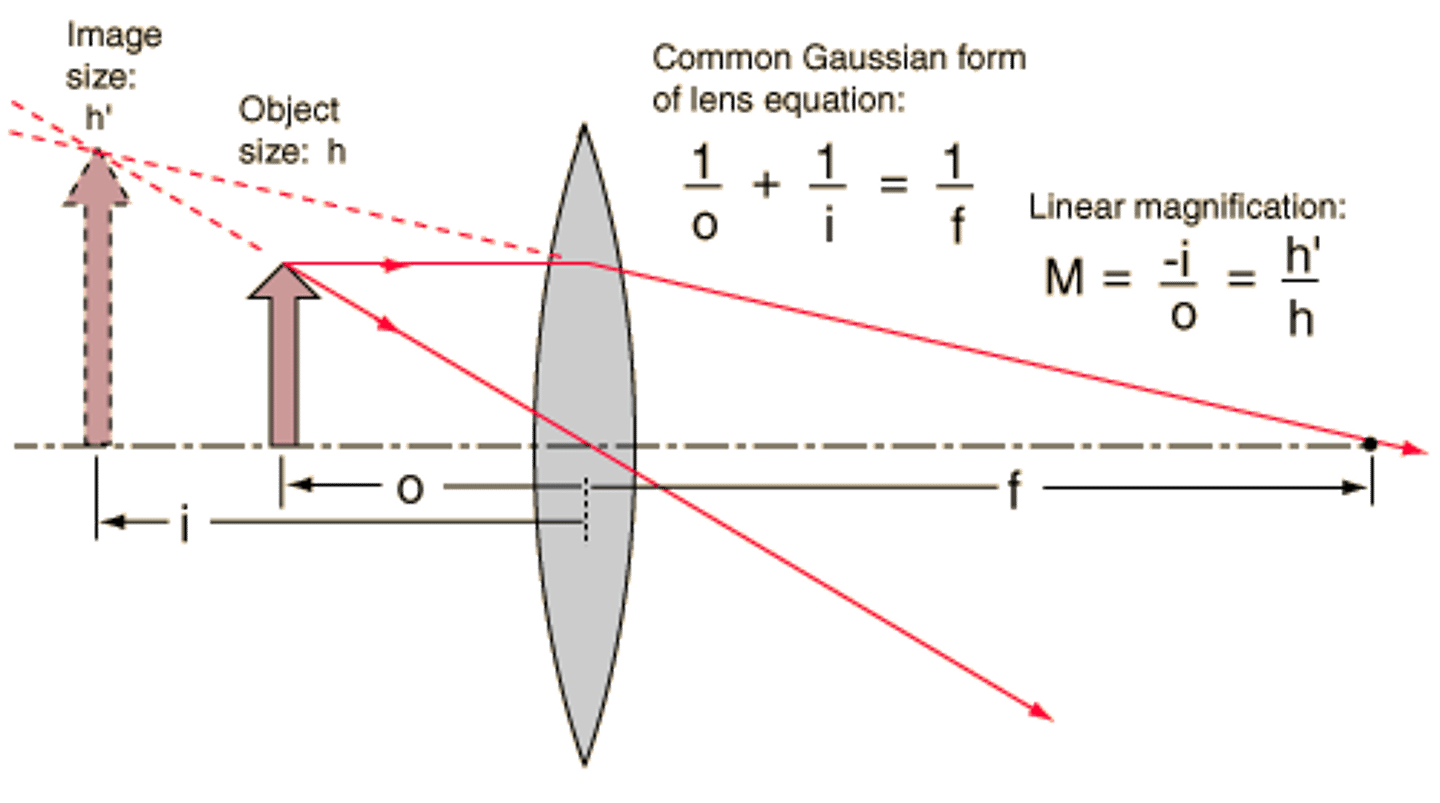
What equation can be used to relate the height of an image to the distance of an image from the lens? How does this equation relate to magnification?
Both sides of the equation can be used to calculate the magnification!
A positive Magnification means that the image is __________. A negative Magnification means that the image is __________.
(A) upright, inverted
(B) inverted, upright
(C) virtual, real
(D) real, virtual
(A) upright, inverted
A positive Magnification means that the image is upright. A negative Magnification means that the image is inverted.
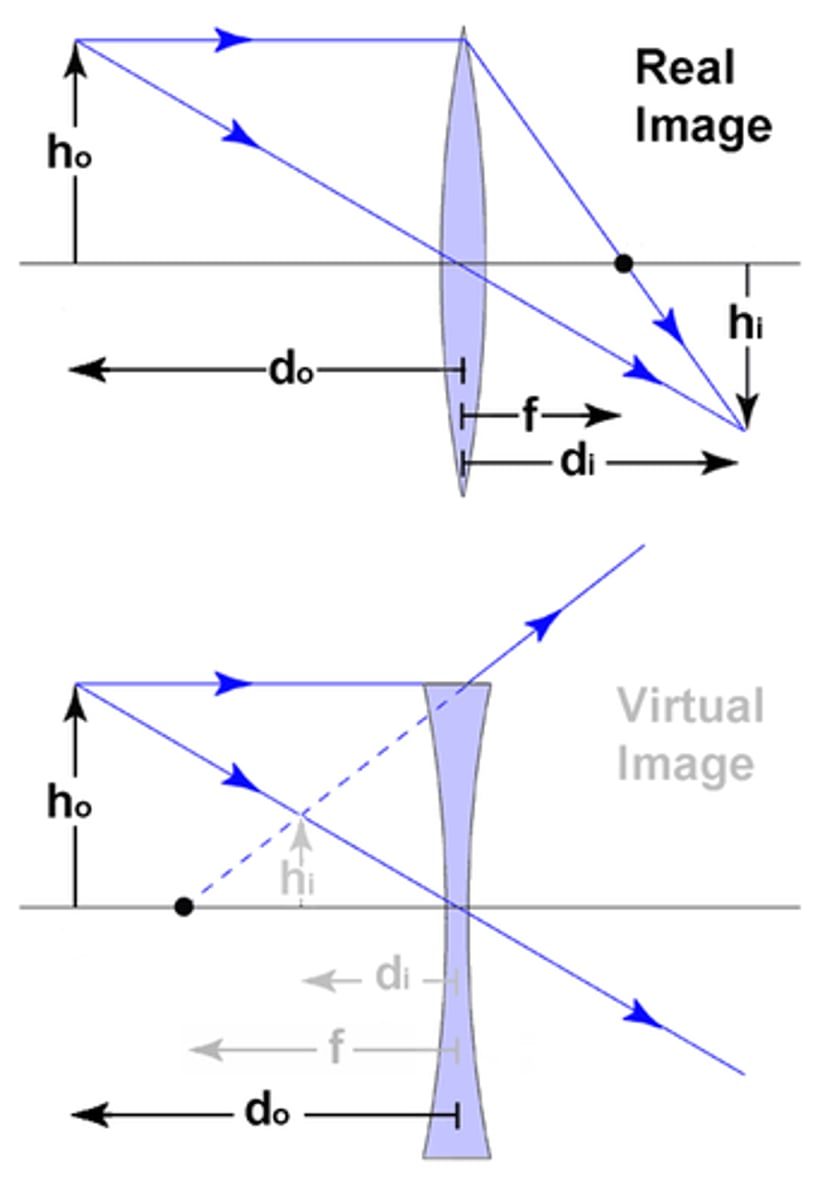
CRB Fill in the blanks: For an image to be enlarged, the Magnification must have __________________ greater than one; for an image to be reduced, the magnification must have ___________________ less than one.
(A) a value, a value
(B) a squared value, a squared value
(C) an absolute value, an absolute value
(D) None of the above
(C) an absolute value, an absolute value
For an image to be enlarged, the Magnification must have an absolute value greater than one; for an image to be reduced, the magnification must have an absolute value of less than one.
When is object distance considered to be a positive number for lenses? Negative number?
Object distance is always positive when dealing with a single lens.
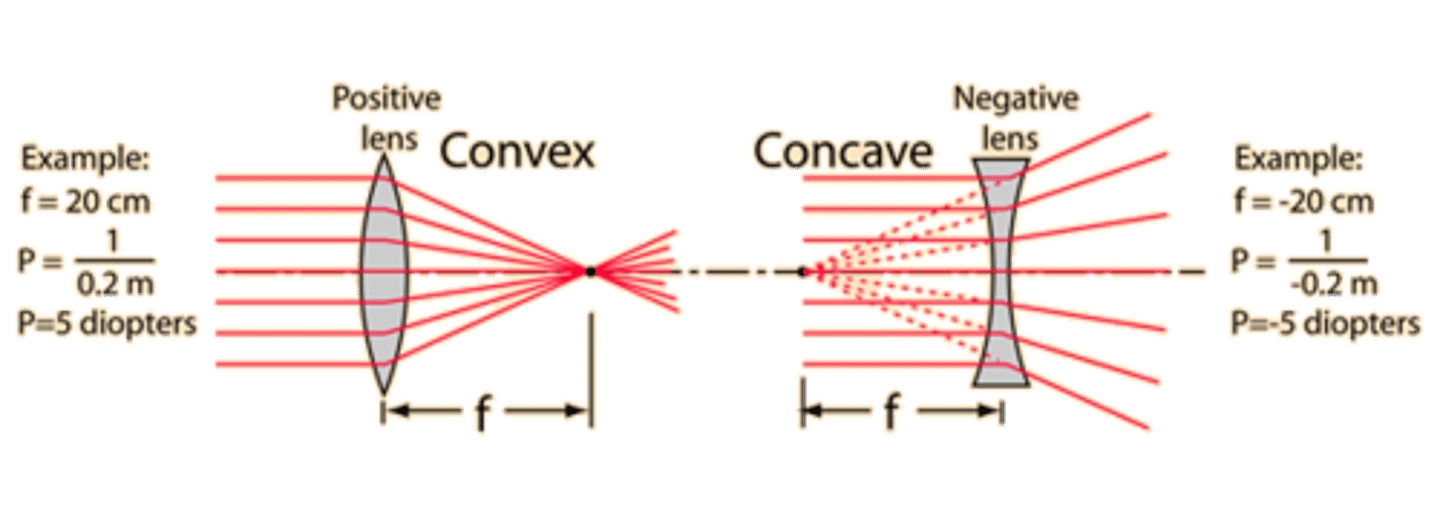
When is focal length considered to be a positive number for lenses? Negative number?
Focal length will be a positive number when you are using a convex/converging lens.
Focal length will be a negative number when you are using a concave/diverging lens.
When is image distance considered to be a positive number for lenses? Negative number?
Image distance will be a positive number when it is on the opposite side of the object.
Image distance will be a negative number when it is on the same side of the object.
You are in physics lab and your lab instructor tells you to use two lenses. The second lens that you use will have what as its object?
(A) The object from the first lens
(B) The image from the first lens
(C) The image from the second lens
(D) None of the above
(B) The image from the first lens
The first lens will produce an image, which will then be the object for the second lens.
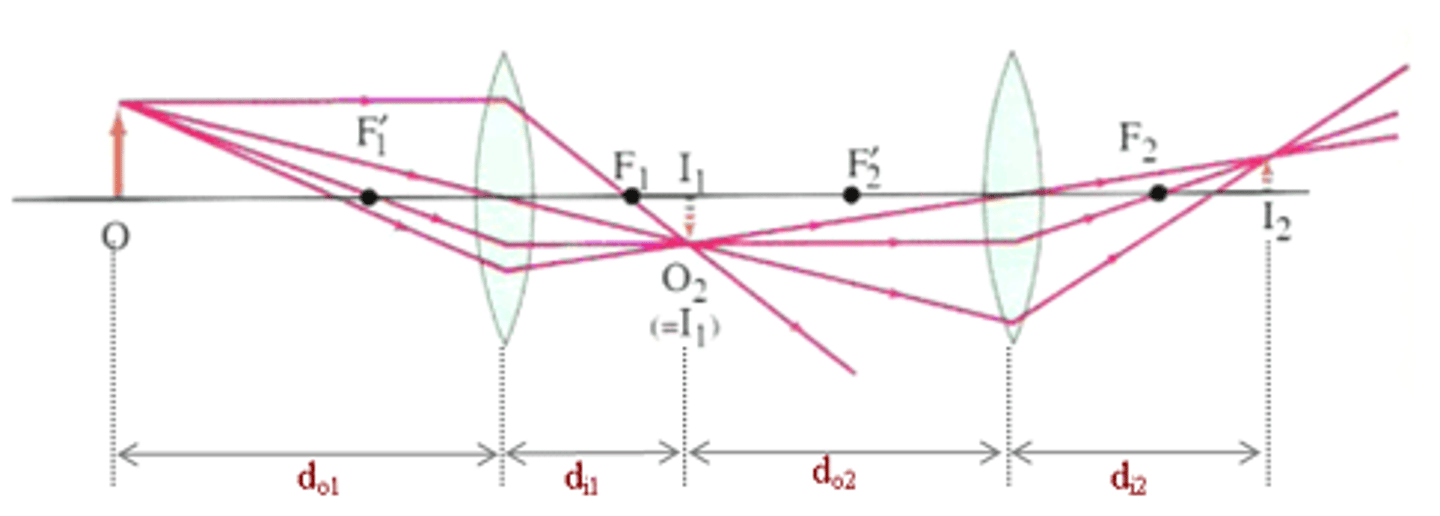
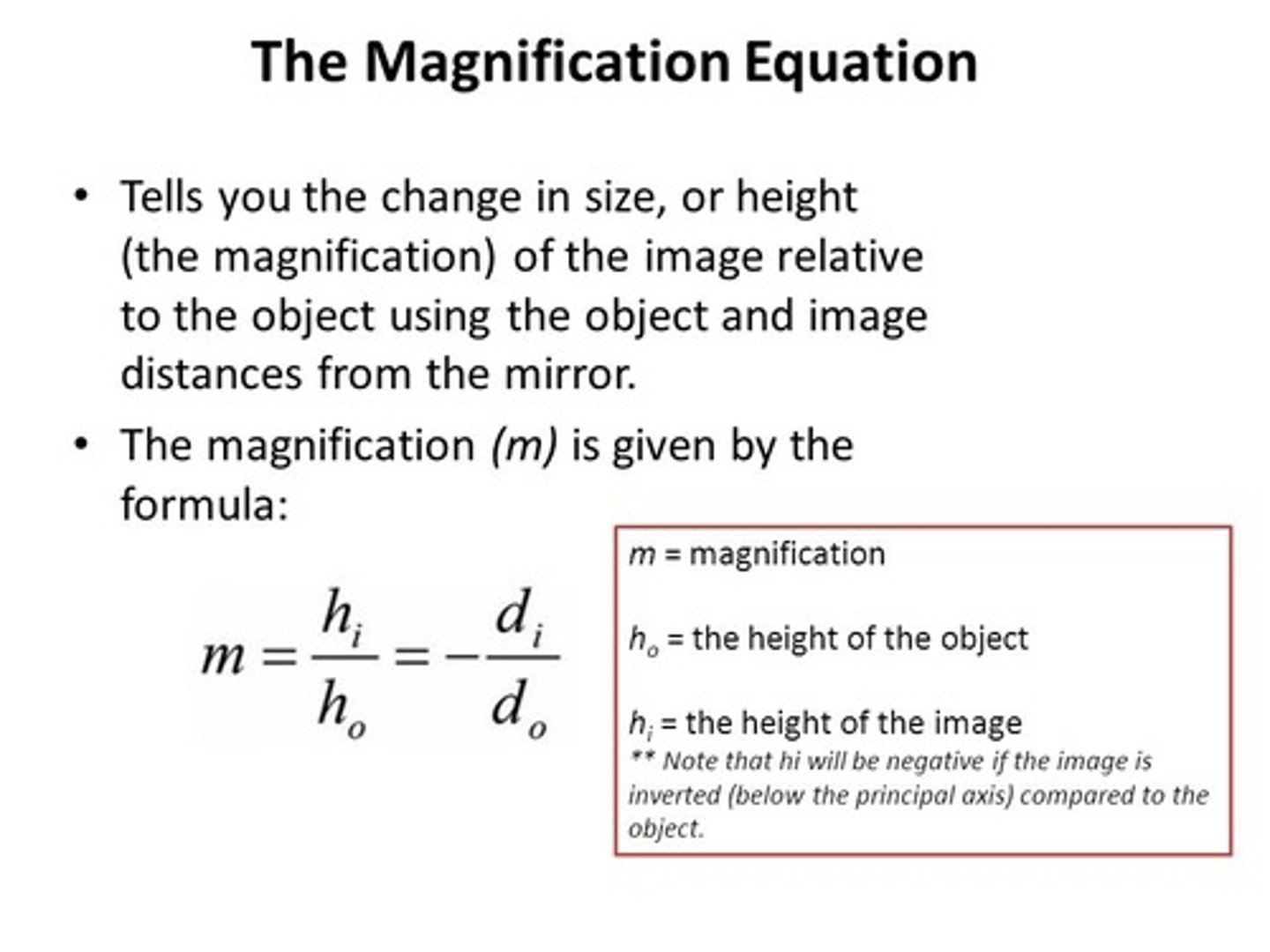
What equation can be used to determine the overall Magnification for a multiple lens system?
Mt = M1 x M2 x M3... x Mn
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
In the lab, your first object is 10 inches high, the first image is 5 inches high, and the second image is 2 inches high. Your lab instructor asks you to calculate the overall Magnification for the two lens set up. What is the answer?
(A) .8
(B) .5
(C) .2
(D) .1
Mt = M1 x M2 x M3... x Mn
Mt = 5/10 x 2/5
Mt = 1/5 or .2
Need help with MCAT math? Become an MCAT math wizard using Andrew's High-speed Math Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-high-speed-math-mastery-course/
What does it mean to say that a lens has a high Power?
To say that a lens has a high Power is to say that the lens is better at bending light.
As focal length increases, what happens to Power?
As focal length increases, Power decreases.
What equation can be used to relate Power and focal length?
P = 1/f
P = Power
f = Focal Length
Struggling to keep your MCAT equations straight? Simply conquer the 100 most important equations using Andrew's 100 Most Essential Equations Mastery Course @ https://mcatselfprep.com/course/andrews-equation-mastery-course/
Describe the phenomenon of Spherical Aberration?
It is the idea that lenses are not perfectly shaped to cause all light to converge at the same exact point. Spherical Aberrations occur, resulting in light rays not converging perfectly.
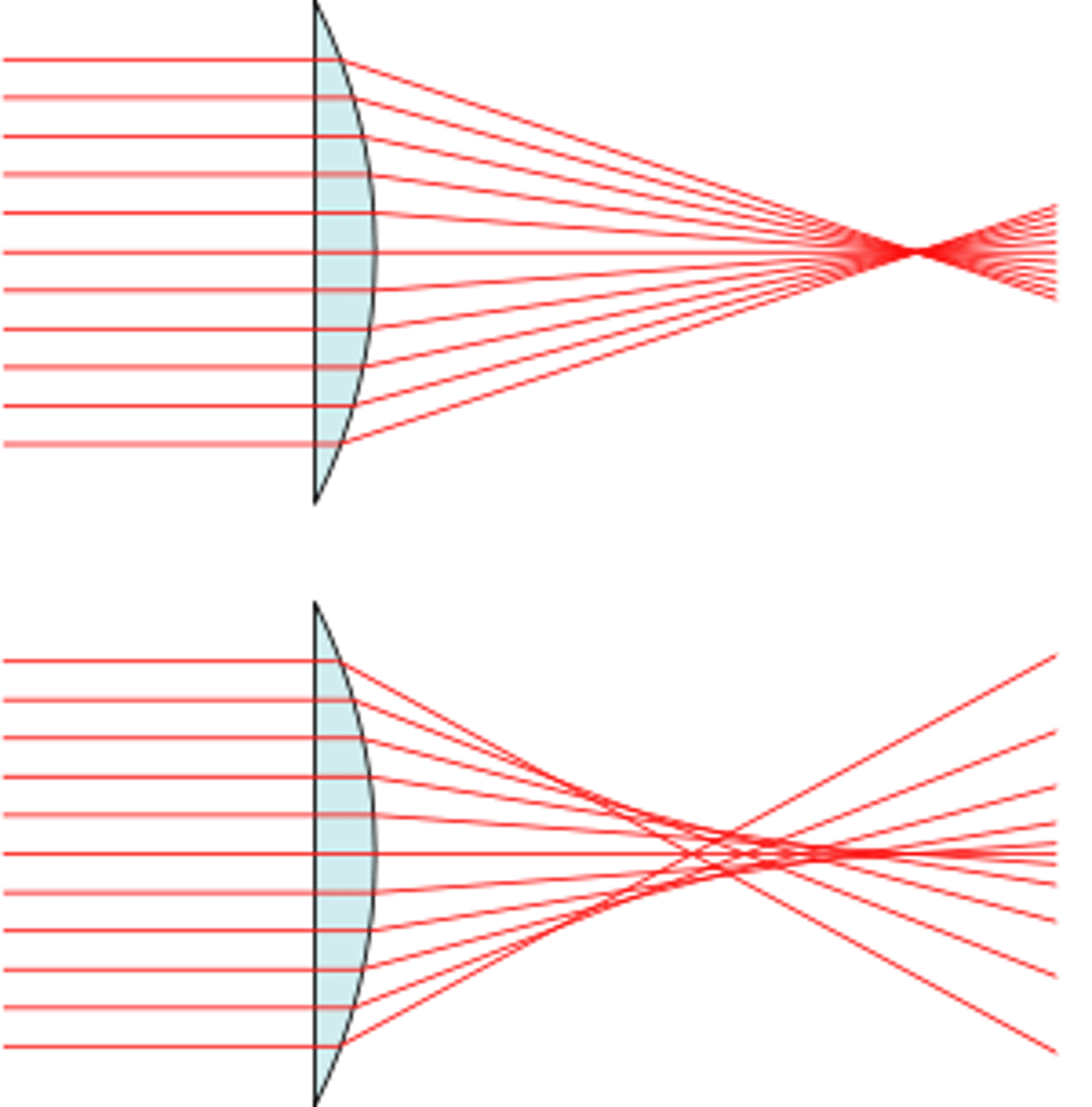
What is the idea of Chromatic Aberration?
Chromatic Aberration refers to the phenomenon in which different colors of light bend to different degrees, which may result in a blurry image.
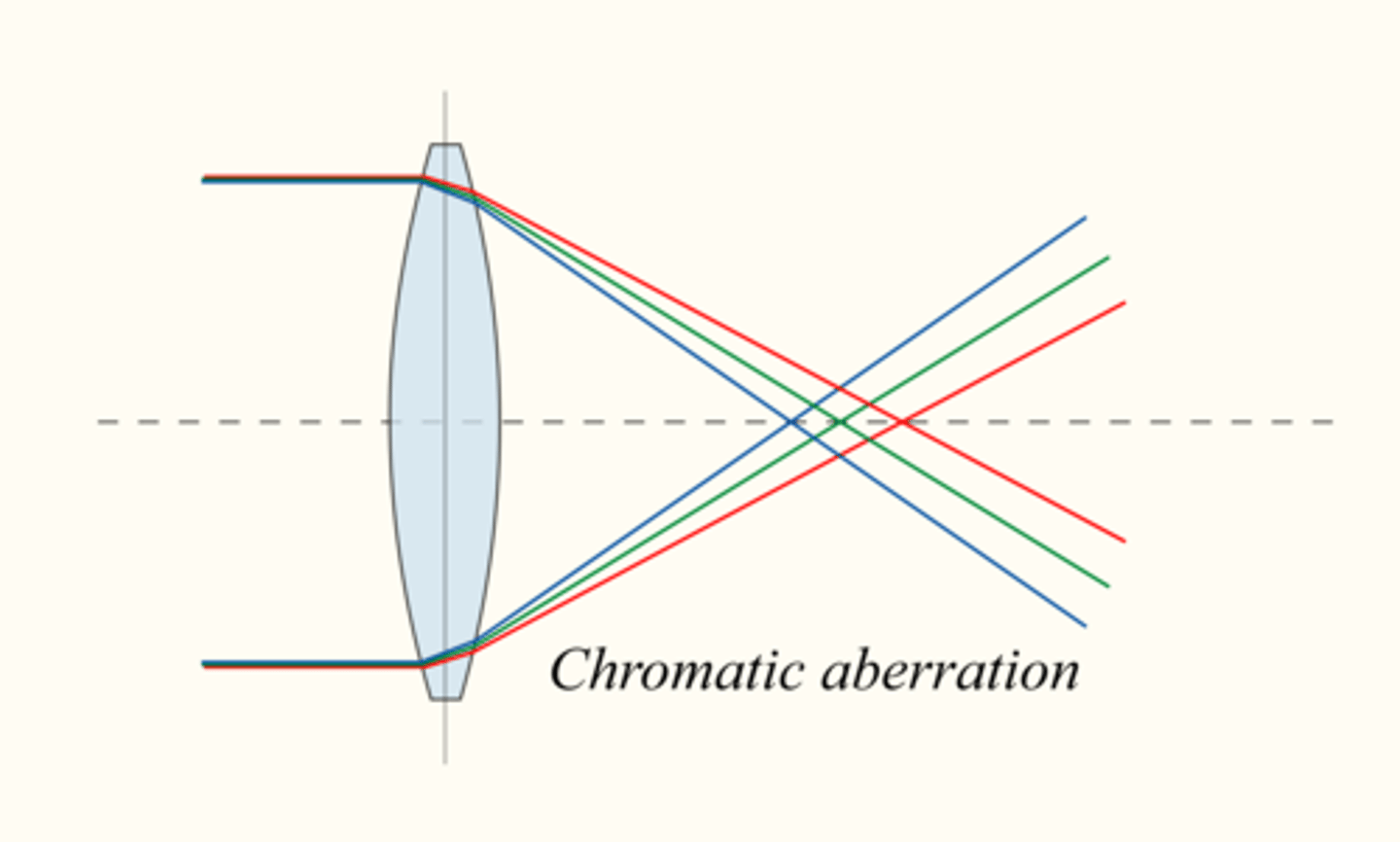
CRB True or false? Chromatic Aberration is usually seen in Spherical lenses.
True. Chromatic Aberration is usually seen in Spherical lenses.
The image that hits your retina is upright or inverted?
The image that hits your retina will be inverted.
CRB Which of the following structures acts as the primary source of refractive power in the human eye, and why?
(A) The Vitreous Humor, because the change in the refractive index from air is so large.
(B) The Vitreous Humor, because it has the largest volume inside the eye.
(C) The Cornea, because the change in the refractive index from air is so large.
(D) The Cornea, because it has the largest volume inside the eye.
(C) The Cornea, because the change in the refractive index from air is so large.
CRB Which of the following is the correct (simplified) Pathway of how light enters the eye, from beginning to end?
I. Retina
II. Vitreous Humor
III. Cornea
IV. Adaptive Lens
(A) I > II > III > IV
(B) IV > III > II > I
(C) III > IV > II > I
(D) II > IV > III > I
(C) III > IV > II > I
The correct order of how light enters the eye is as follows:
1st. Cornea
2nd. Adaptive Lens
3rd. Vitreous Humor
4th. Retina
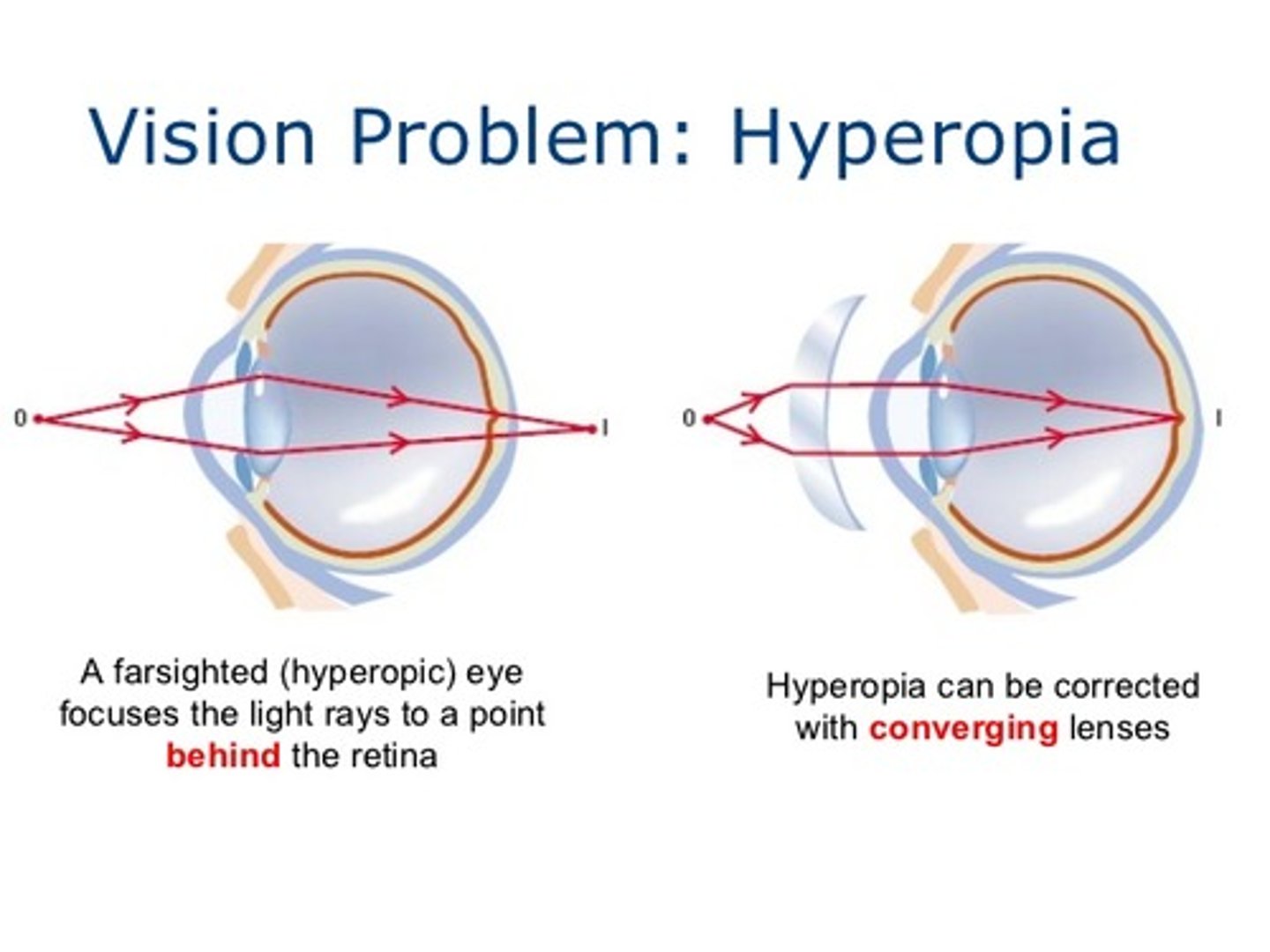
A person who is farsighted will form the image __________ their retina and should be prescribed a __________ lens.
(A) behind, concave
(B) behind, convex
(C) in front of, concave
(D) in front of, convex
(B) behind, convex
A person who is farsighted will form the image behind their retina and should be prescribed a convex lens.
CRB There will always be scenarios where the eye must adjust to focus on nearby objects. Which of the following statements about this process are true?
I. It is called Accommodation
II. It is mediated by the ciliary muscles adjusting the curvature of the lens.
III. Squeezing the lens would increase the curvature and the focal length.
(A) I only
(B) I and II only
(C) II and III only
(D) I, II and III
(B) I and II only
Each of the following statements are true:
I. It is called Accommodation
II. It is mediated by the ciliary muscles adjusting the curvature of the lens.
III. Squeezing the lens would increase the curvature and decrease the focal length.
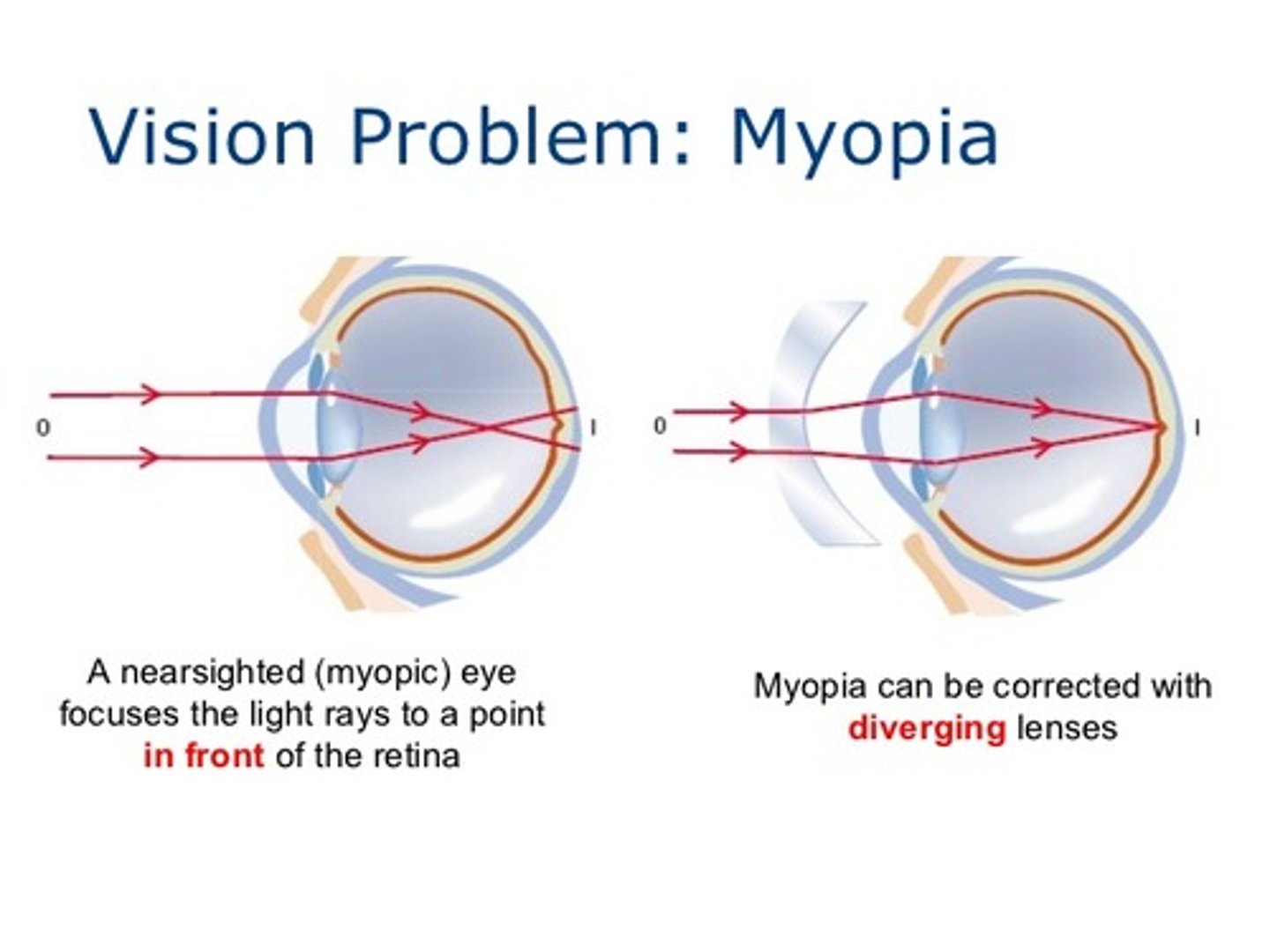
A person who is nearsighted will form the image __________ their retina and should be prescribed a __________ lens.
(A) behind, concave
(B) behind, convex
(C) in front of, concave
(D) in front of, convex
(C) in front of, concave
A person who is nearsighted will form the image in front of their retina and should be prescribed a concave lens.
CRB True or false? The image of a distant object will appear at a focal point for both convex and concave lenses.
True. The image of a distant object will appear at a focal point for both convex and concave lenses.