A&P Chapter 1 🧍🏻
1/61
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Anatomy
The study of structure of body parts and their relationships to one another
Physiology
The study of function, the body’s structural machinery
How do physicians study patients?
Inspection: Inspecting the body with the naked eye
Palpation: Touching/feeling different parts of the body
Auscultation: Listening to blockages or fluid in inside the body (lungs, stomach)
Percussion: Tapping part of the body as part of diagnosis
Types of Anatomical Study
Gross or Macroscopic
Cadaver Dissection
Microscopic
Histology
The study of tissues
Cytology
The study of cells
Subdisciplines of Anatomy
Pathological Anatomy: study of structural changes caused by disease
Radiographic Anatomy: Study of internal structures using medical imaging techniques
Molecular Biology: Study of anatomical structures at a subcellular level
What is the relationship between anatomy and physiology?
Structure always reflects function and vice versa
The inductive method
Observational: Making numerous observations until drawing a conclusion
Proof in science: Reliable observations, repeatedly confirmed.
Not falsified by any credible observation
Truth is tentative
Hypothetico-Deductive Method
A hypothesis is formed, consistent with what is already known + can be tested
Falsifiability: Ability to specify what would prove a claim wrong
Experimental Design
Sample size: # of subjects in a study
Controls: Control group does not receive treatment
Psychosomatic effects: effects of subjects state of mind on their biology. Placebo given to control group
Experimenter bias: Double-blind study
Statistical testing: Provided statement that treatment was effective
Necessary life functions
Responsiveness: Ability to sense changes in environment + respond
Digestion: breakdown of ingested food
Metabolism: chemical reactions that occur in the body
Excretion: removal of waste from the body
Reproduction: (Cellular & Organismal)
Growth: Increase in size of body part/organism
Survival Needs
Nutrients: energy + cell repair
Oxygen: metabolic reactions
Water: necessary environment for chemical reactions
Normal BT: for chemical reactions at life sustaining rates
Atmospheric Pressure: proper breathing + gas exchange
Homeostasis
Ability to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes
Homeostatic Control Mechanisms
Variables produce change in the body
Receptor/Senser: Monitors environment + responds to stimuli (changes)
Ex. Thermometer detects drop in temperature
Control center: Determines the set point at which variable is maintained
Ex 2. Thermostat controls heat setting
Effector: provides the means to respond to stimuli
Ex 3. Heater balances temperature
Negative Feedback
Output shuts off original stimulus
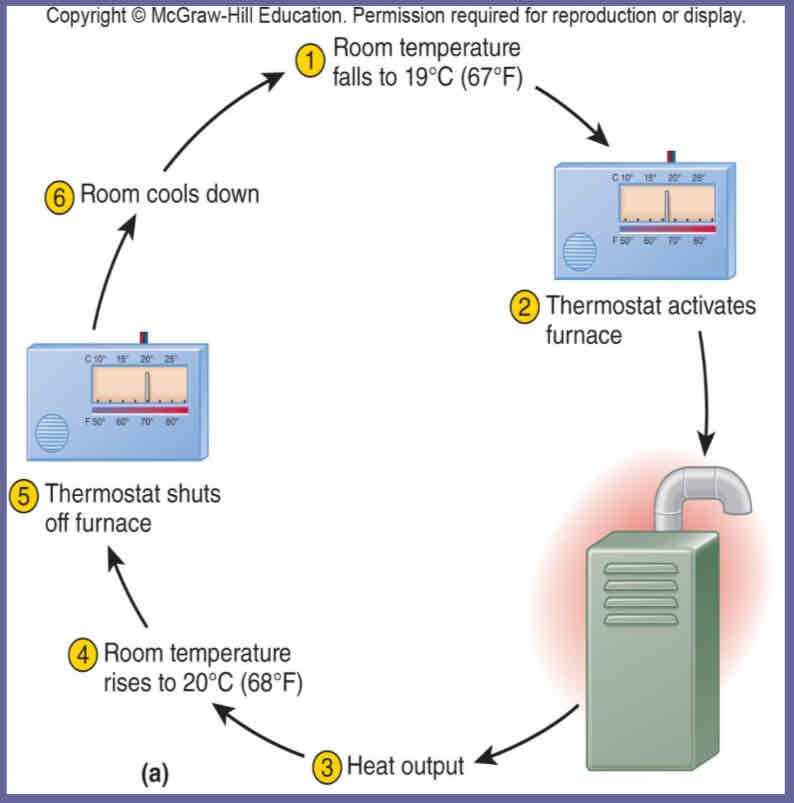
Feedback loop
Feedback mechanisms altering the original changes that triggered them, causing a loop
Homeostasis in body temperature
Too warm: blood vessels dilate; Sweating decreases BT
Too cold: blood vessels constrict; Shivering increases BT
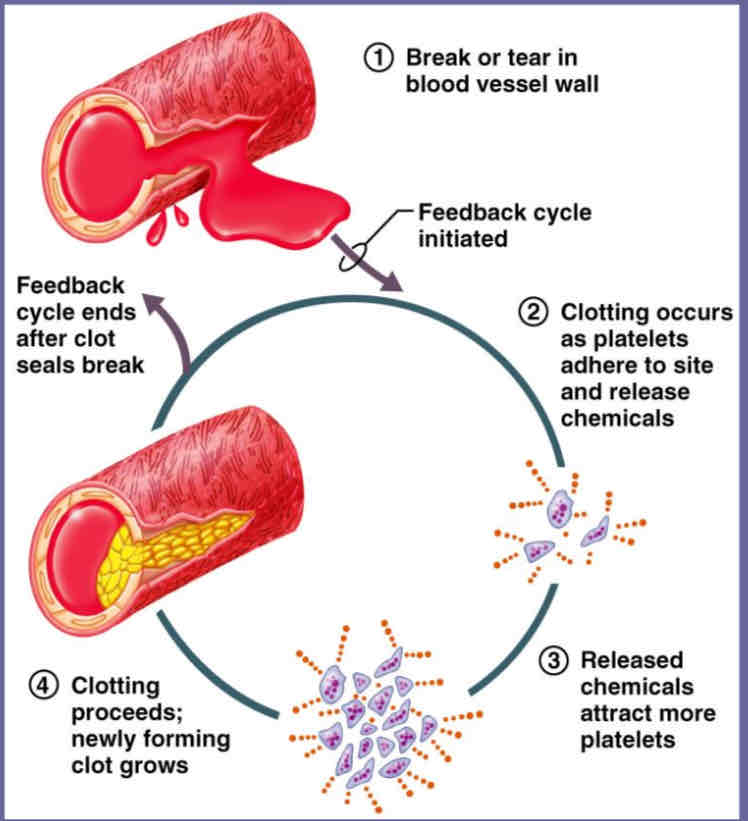
Positive Feedback
Output enhances or exaggerates original stimulus
Hierarchy of Complexity (smallest to largest)
Molecules
Organelles
Cells
Tissues
Organs
Organ Systems
Organisms
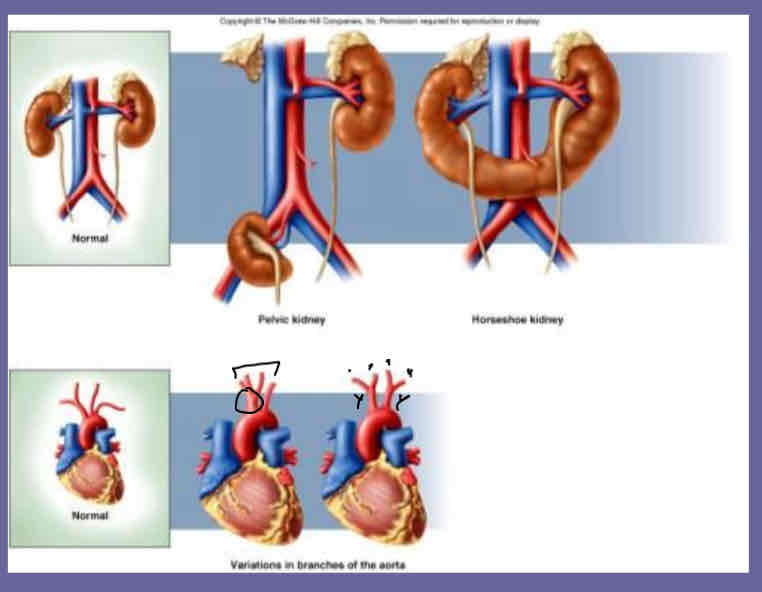
Anatomical Variation
No two humans are exactly alike
Variable # of organs
Variation in organ location
Physiological Variation
Sex, age, diet, weight, physical activity
Female & Male references
22 yrs old
Light physical activity
(F): 128lbs/58kg, 2,000 kcal/day
(M): 154lbs/70kg 2,800 kcal/day
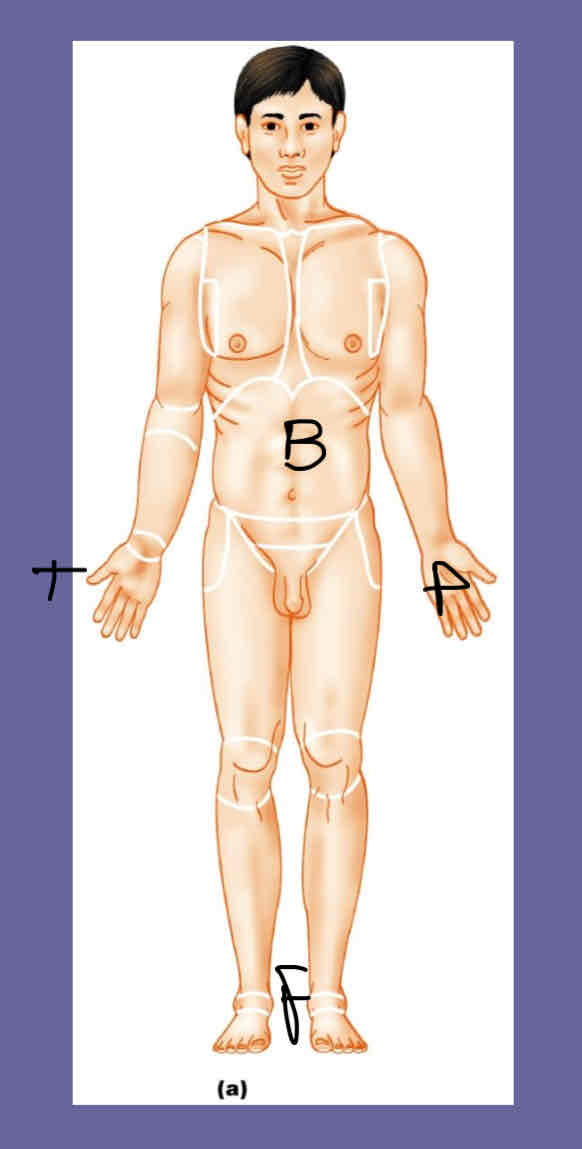
Anatomical Position
Body erect
Feet slightly apart
Palms facing forward
Thumbs pointing away from body
Superior
Toward the head or upper part of of a structure or the body; above
Ex. The head is [________] to the abdomen
Inferior
Away from the head end or toward the lower part of the structure or the body; below
Ex. The navel is [________] to the chin
Anterior/Ventral
Toward or in front of the body; in front of
Ex. The breastbone is [________] to the spine
Posterior/Dorsal
Toward or at the back of the body; behind
Ex. The heart is [________] to the breastbone
Medial
Towards the midline of the body
Ex. The heart is [________] to the arms
Lateral
Away from the midline of the body
Ex. The arms are [________] to the chest
Intermediate
Between a more medial and a more lateral structure; in between
Ex. The collarbone is [________] between the breastbone and shoulder
Proximal
Closer to the body trunk
Ex. The shoulder is [________] to the wrist
Distal
Farther from the body trunk
Ex. The knee is [________] to the thigh
Superficial/External
Toward or at the body surface
Ex. The skin is [________] to the muscles
Deep/Internal
Away from the body surface; more internal
Ex. The lungs are [________] to the skin
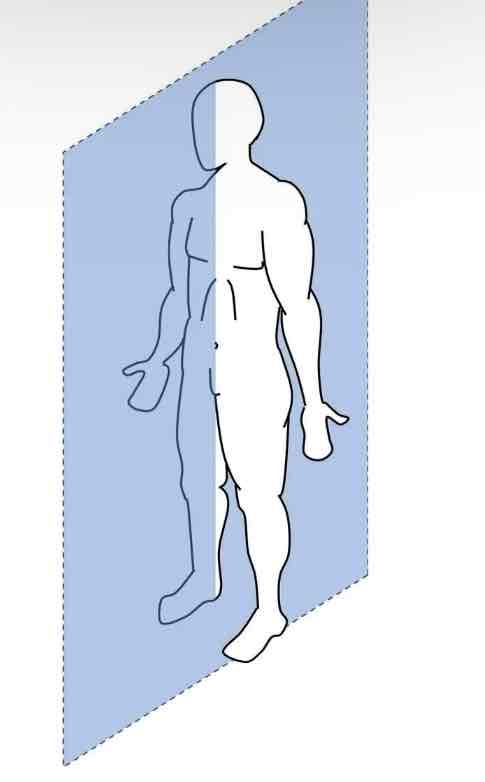
Sagittal
Plane that divided the body into RIGHT and LEFT parts
Midsagittal/Medial
Sagittal plane that lies on the midline
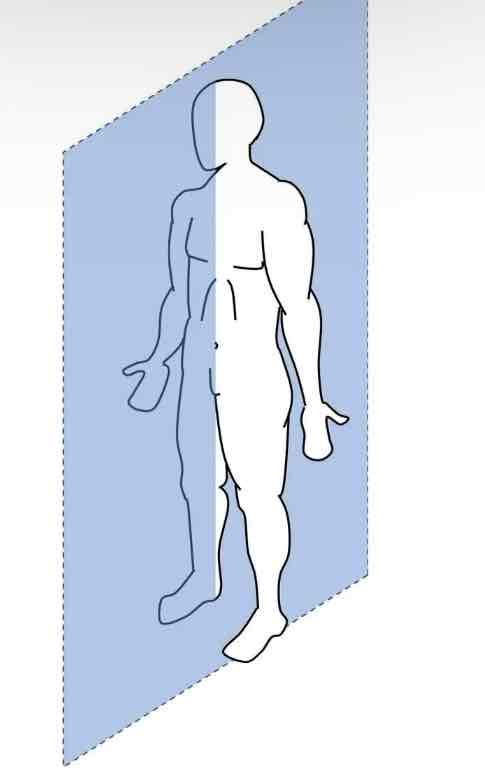
Frontal/Coronal
Divides the body into ANTERIOR and POSTERIOR parts
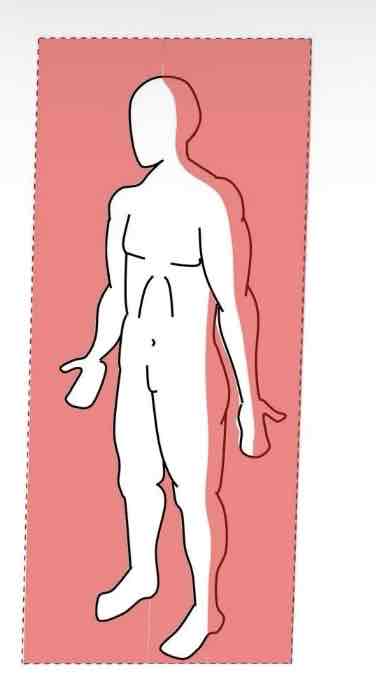
Transverse/Horizontal
Divides the body into SUPERIOR and INFERIOR parts
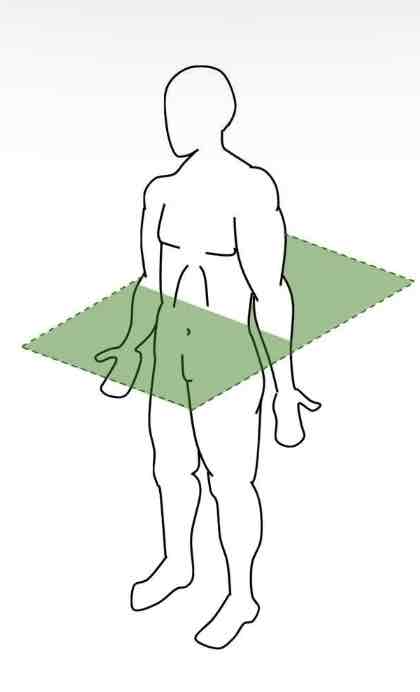
Oblique Section
Cuts made diagonally /
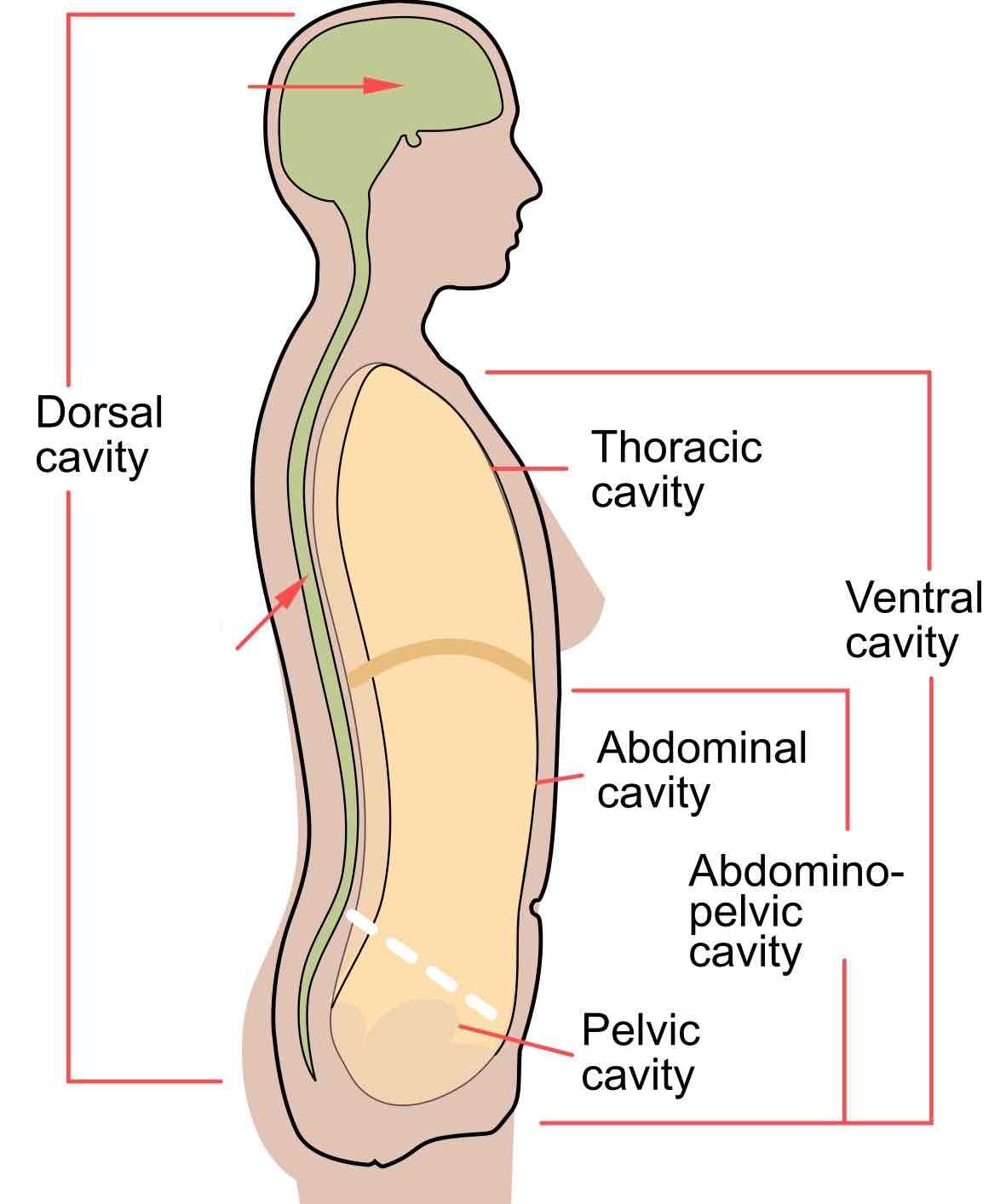
Dorsal Cavity
Cranial cavity: within the skull, encases the brain
Vertebral cavity: runs within the vertebral column, encases the spinal cord
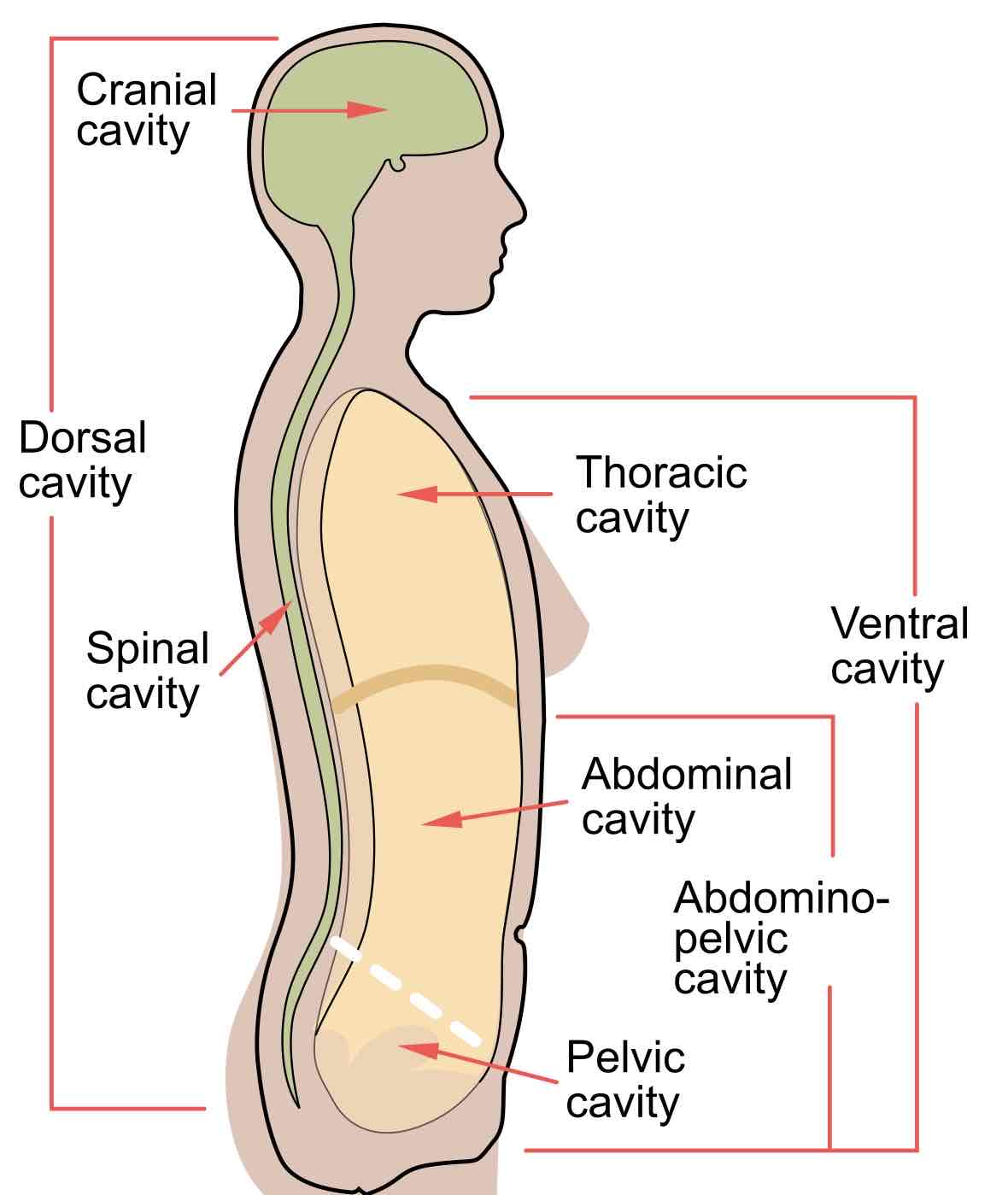
Ventral Cavity
Thoracic cavity: Contains heart and lungs
Abdominopelvic cavity:
(Abdominal cavity) contains digestive viscera,
(Pelvic cavity) contains bladder, reproductive organs, and rectum
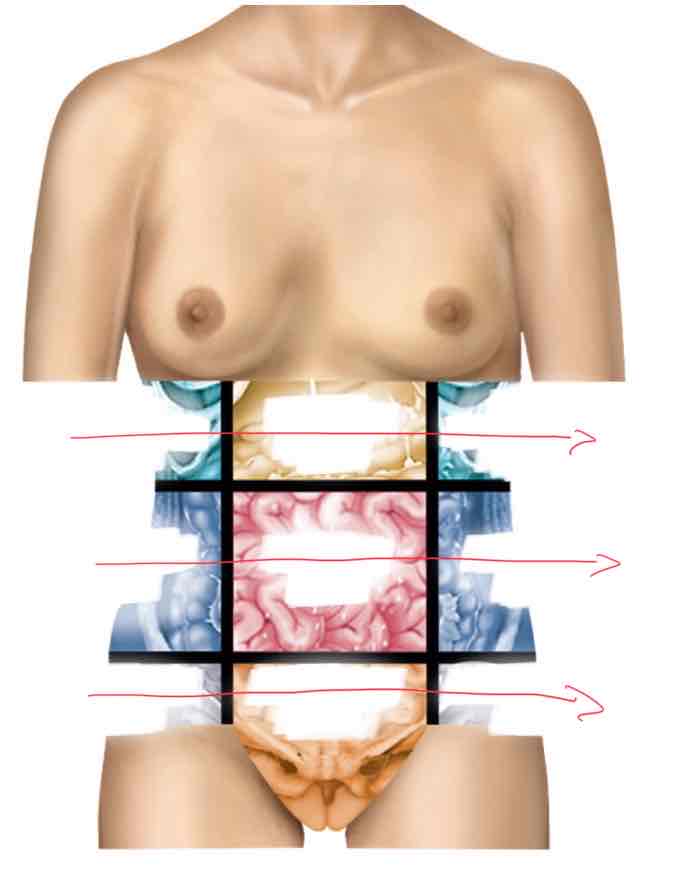
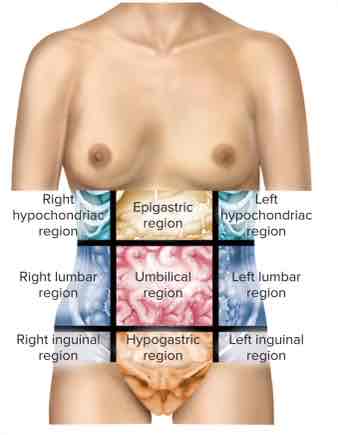
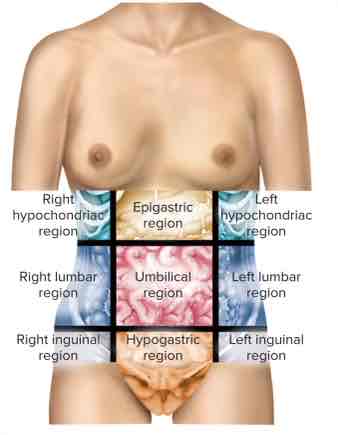
Abdominopelvic Regions (from front view, right to left)
Right hypochondriac region
Epigastric region
Left hypochondriac region
Right lumbar region
Umbilical region (bellybutton)
Left lumbar region
Right inguinal region
Hypogastric region
Left inguinal region
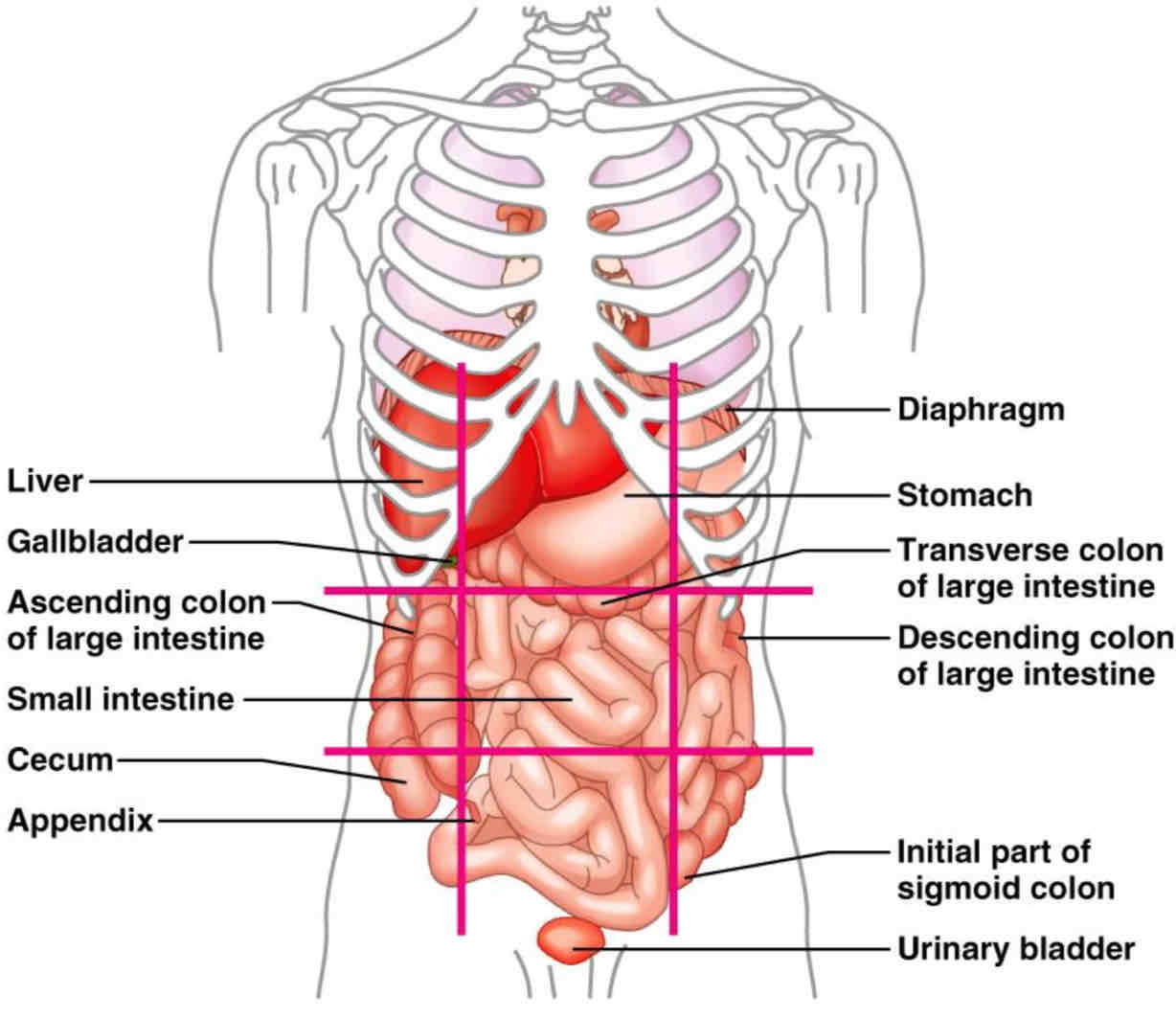
Organs of the abdominopelvic region
Right hypochondriac region: liver, gallbladder
Epigastric region: stomach
Left hypochondriac region: diaphragm (?)
Right lumbar region: Ascending colon of large intestine
Umbilical region (bellybutton): small intestine
Left lumbar region: Descending colon of large intestine
Right inguinal region: Cecum
Hypogastric region: appendix, urinary bladder
Left inguinal region: initial part of sigmoid colon
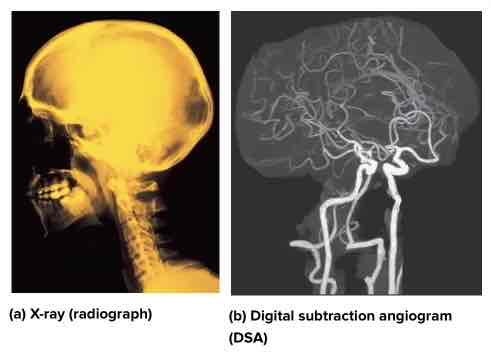
Radiography (X-rays)
Penetrate soft tissues
Dense tissues remain white
Can see hollow structures (intestinal tract, DSA blood vessels)
Radiopaque substances are injected or swallowed
Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
low-intensity x-rays and computer analysis
Increased sharpness
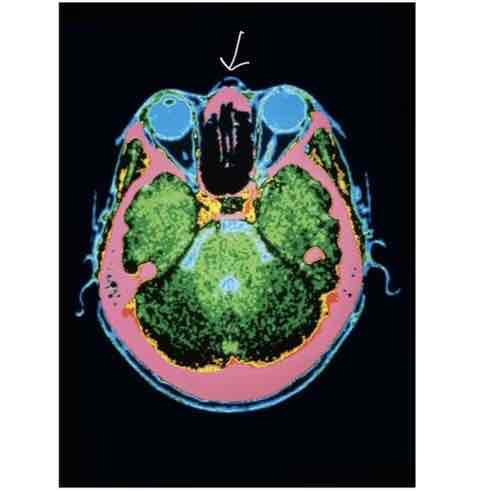
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Best for soft tissue
Can see through the skull & spine
Mechanics for MRI:
Magnetic field aligns atoms
Radio waves REALIGN atoms
Radio turned off
Atoms realign to MAGNETIC FIELD
Energy given off depending on tissue type
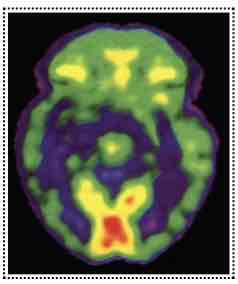
Positron Emission Tomography (PET Scan)
Assesses metabolic state
Mechanics of PET:
Inject labeled glucose (goes to all cells that use energy)
Positrons & electrons collide, gamma rays given off
Analyzed by computer
Image of glucose (energy) usage
Sonography
Second oldest + second most widely used
Mechanics of sonography:
High frequency sound waves echo back from internal organs
Avoids harmful x-rays
(Obstetrics/Sonograms)
Image not very sharp
Integumentary System
Forms external covering of the body
Composed of skin, hair, nails, sweat glands & oil glands
Protects deep tissue from injury + synthesizes vitamin D
Skeletal System
Composed of bone, cartilage & ligaments
Protects & supports body organs
Provides framework for muscles
Sit of blood cell formation
Stores minerals
Muscular System
Composed of muscles & tendons
Allows manipulation of environment, locomotion (movement), & facial expression
Maintains posture
Produces heat
Nervous System
Composed of the brain, spinal column, & nerves
Is the fast-acting control system of the body
Responds to stimuli by activating muscles & glands
Cardiovascular System
Composed of the heart & blood vessels
The heart pumps blood
Blood vessels transport blood throughout the body
Distributes oxygen
Lymphatic System
Composed of red bone marrow, thymus, spleen, lymph nodes, & lymphatic vessels
Picks up fluid leaked from blood vessels & returns it to blood
Disposes of debris in the lymphatic system
Houses white blood cells
Respiratory System
Composed of the nasal cavity, pharynx, trachea, bronchi, & lungs
Keeps blood supplied with oxygen
Removes carbon dioxide
Digestive System
Composed of oral cavity, esophagus, stomach, liver, small intestine, large intestine, rectum & anus
Breaks down food into absorbable units that enter blood
Eliminates indigestible foodstuffs
Urinary System
Composed of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, & urethra
Eliminates nitrogenous waste
Regulates water, electrolyte, & pH balance of the blood
Endocrine System
Composed of hypothalamus, pituitary gland, pineal gland, thyroid gland, adrenal glands, pancreas, gonads
Produces hormones to coordinate metabolic processes; growth, metabolism, reproduction
Male Reproductive System
Composed of prostate gland, penis, testes, scrotum, & ductus deferens
Main function: production of offspring
Testes produce sperm + make sex hormones
Ducts & glands deliver sperm to the female reproductive tract
Female Reproductive System
Composed of mammary glands, ovaries, uterine tubes, uterus, & vagina
Ovaries produce eggs + female sex hormones
Remaining structures serve as sites for fertilization & fetus development
Mammary glands produce milk to nourish newborn
How are organ systems interrelated?
Nutrients & oxygen are distributed by the blood
Metabolic wastes are eliminated by the urinary & respiratory systems