CSD 557 Quiz 1 - SLPs and Audiology
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
ASHA defined the practices of the audiologist and the SLP by quoting the United States Department of Labor’s Dictionary of Occupational Titles – 1977:
True
In November, 1989, the ASHA Legislative Council adopted its first official scope of practice statement:
True
What are audiology-based duties that SLPs can perform?
a. | Provide aural rehabilitation and related counseling services to individuals with hearing loss and to their families | |
b. | Collaborate in the assessment of central auditory processing disorders in cases in which there is evidence of speech, language, and/or other cognitive-communication disorders | |
c. | Conduct pure-tone air conduction hearing screening and screening tympanometry | |
d. | All of the above |
What are the main differences between the 2001 Scope of Practice and the 2007 scope of practice?
The 2007 scope of practice includes screening using otoacoustic emissions as a method that can be employed by SLPs and the 2001 document does not
Because the SLP can provide such a wide variety of services within the audiology arena, educational modules targeting each of these areas need to be present in the university training programs and in continuing educational programs for SLPs:
True
One-third of persons 65+ are affected by disabling hearing loss
True
In 2018, how many people had disabling hearing loss worldwide?
466 million
What are some roles in audiological rehabilitation?
all of the above
In the realm of Aural Rehabilitation and Audiologic Rehabilitation, Speech-language pathologists perform ________________ with children who have auditory problems.
Aural Rehabilitation
What are some characteristics of hearing loss?
Degree and Configuration
threshold - softest sound that can be detected 60% of the time:
False
An audiogram plots the intensity (loudness) that a sound must be in order for the person to detect the sound:
True
What is the highest frequency most commonly tested and plotted on the audiogram?
8000 Hz
How do you read an audiogram?
left to right
What is considered to be the range of "normalcy" for a child?
-10 to 15
What are some common configurations of an audiogram?
a. | Flat – hearing is relatively the same | |
b. | Sloping –hearing is better in the low frequencies and worse in the high frequencies | |
c. | Notch – Sharply poorer at one frequency with recovery at adjacent frequencies | |
d. | all of the above |
A person with a high frequency hearing loss may miss which word?
Sis
The “S” on the phonetic audiogram is falls around the 6000 Hz range:
True
/m/, /b/, and /d/ are all mid-to-high frequency sounds:
False
Vowels are higher in intensity (louder) and consonants are softer in intensity
True
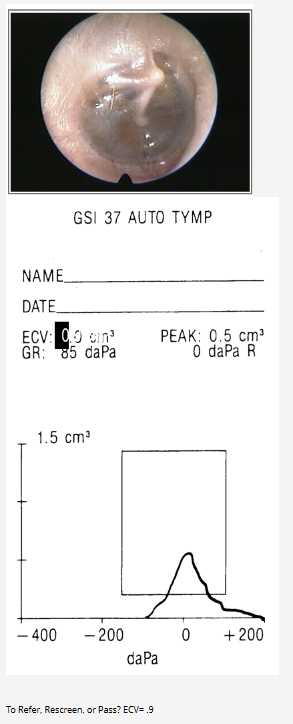
Pass
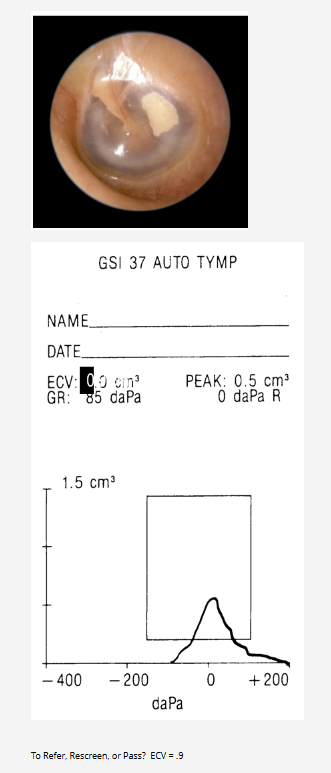
Pass
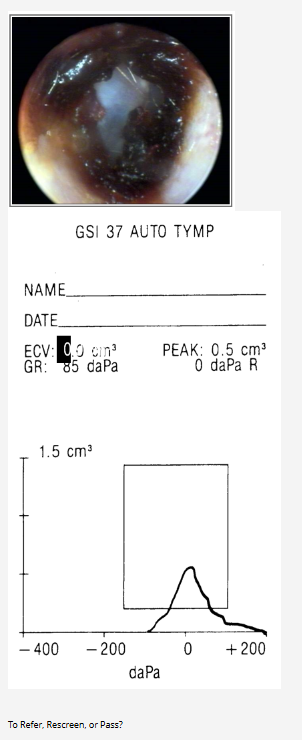
Pass
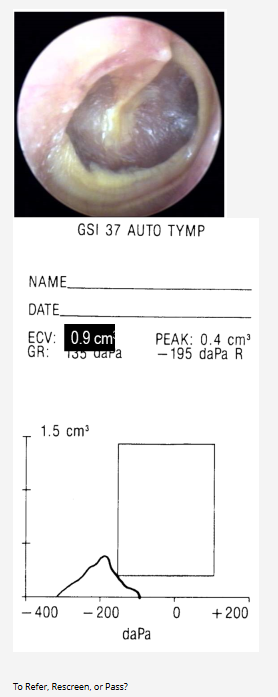
Pass
Pass

Rescreen
Refer

Refer

Reinstruct, reposition, rescreen

Refer to audiologist
Adjusting to hearing loss and receiving recommendations regarding aural rehab can be difficulty for many patients and their families:
True
More than 32 million individuals in the U.S. have some degree of hearing loss:
True
Even a mild degree of hearing loss can adversely affect vocabulary development and the subtle intricacies of language use
True
Who may be less likely to hold negative preconceived notions about hearing loss?
Preschoolers
It seems that most parents experience emotional reactions consistent with the stages of the “grief cycle” which include:
Shock
Denial
Depression
Sometimes adults can also acquire a hearing loss from: a side effect of some medication, a result of head injury, or noise exposure:
True
What are some characteristics of the Biopsychosocial Model?
Horizontal Communication
Person Focused
Interactive, facilitative
The traditional Biomedical Model does what?
Assumes a detached perspective
Finds the impaired part
Fixes the impairment
Patient centered communication is believed to lead to patient satisfaction:
True
Being truly person-centered entails identifiying the best approach to work with each individual.
True
An SLP can recommend and fit the best FM system for a school-aged child in the classroom:
False
What are some myths about hearing aids?
A. Hearing aids are the solution | |
B. Hearing aids restore perfect hearing | |
C. Once the child recieves hearing aids, they can hear like their peers | |
D. All of the above |
Auditory age/hearing age are terms used to put the language development of a child in
perspective:
True
92-95% of those who are “deaf” have SOME hearing. This is called residual hearing:
True
An SLP can provide education and training about noise-induced hearing loss to the high school
rifle team:
True
Adjusting to hearing loss and receiving recommendations regarding aural rehab can be is a
relatively quick and easy process for people with hearing loss:
False
More than 32 million individuals in the U.S. have some degree of hearing loss:
True
Even a mild degree of hearing loss can adversely affect vocabulary development and the subtle
intricacies of language use that SLPs need to be aware of.
True
Who may be less likely to hold negative preconceived notions about hearing loss?
Preschoolers
IT seems that many parents of children with hearing loss experience emotional reactions consistent with the stages of the “grief cycle” which include:
A. Shock | |
B. Denial | |
C. Depression | |
D. All of the above |
Sometimes adults can also acquire a hearing loss from: a side effect of some medication, a result of head injury, or noise exposure:
True
Threshold - softest sound that can be detected 50% of the time:
True
What are audiology-based duties that SLPs can perform?
A. Provide aural rehabilitation and related counseling services to individuals with hearing | |
B. Collaborate in the assessment of central auditory processing disorders in cases in which there is evidence of speech, language, and/or other cognitive-communication disorders | |
C. Conduct pure-tone air conduction hearing screening and screening tympanometry as | |
D. All of the above |
What are the main differences between the 2001 Scope of Practice and the 2007 scope of
practice?
the 2007 scope of practice includes screening using otoacoustic emissions as a
method that can be employed by SLPs and the 2001 document does not
Since SLP cannot provide many services within the audiology arena, educational modules
targeting each of these areas are not necessary in the university training programs and in
continuing educational programs for SLPs:
False
One-third of persons 65+ are affected by disabling hearing loss
True
Auditory Training begins with the accurate assessment of auditory skills.
True
The 4 basic listening levels include all but:
Sound intensity judgment
A 12-month old recently fit with cochlear implants will begin the auditory training process at
which listening level?
Sound awareness
All of the following are speech recognition tests for adults except:
Nonsense syllable test
Which of the following is a speech recognition (speech perception) test for children?
Early Speech Perception Test
Which of the following is a speech recognition test for children?
Early Speech Perception Test
Visual info is transmitted by means of a manual or oral communication system.
True
Oral communication consists of watching the speaker’s mouth, face, hands, and body for
information
True
Basic monitoring of a CI may include:
A. Checking battery function | |
B. Checking battery function | |
C. Use of signal check device to monitor if signal is being transmitted | |
D. All of the above | |
Katz, Stecker & Henderson (1992) described central auditory processing as "what we do with what we hear”
True
Sound localization and lateralization:
Where the sound is located
Prevalence of HL increases with age
True
Physical conditions that affect the elderly client include:
A. Loss of youth | |
B. Changes in physiological and biological aspects of the body cause poor health and its | |
C. Many older people retire | |
D. None of the above |
Patient-centered practice follows a bio-medical model.
False
Hearing loss is associated with:
A. Poorer sleep | |
B. Long-term illness | |
C. poorer self-rated health | |
D. All of the above |
Which of the following is an ecological factor to consider when creating the plan for AR?
A. Communication demands at home | |
B. Communication demands in the workplace | |
C. Communication demands in social situations | |
D. All of the above |
Good patient education leads to improved success with amplification.
True
For most people who have hearing loss, communication is their primary problem
True
Listener (PHL) Factors that Contribute to Communication Problems include:
A. Talks too rapidly or too slowly | |
B. Talks to loudly or too softly | |
C. Does not project voice | |
D. None of the above |
Speaker (CP) Factors That Contribute to Communication Problems include:
A. Does not speak clearly | |
B. Has foreign accent or regional dialect | |
C. Has distracting mannerisms | |
D. All of the above |
A person with a high frequency hearing loss may miss which word?
Sis
The “S” on the phonetic audiogram is falls around the 6000 Hz range:
True
Vowel sounds are ____________ in intensity than consonant sounds.
Louder
What do the 5 softest sounds have in common?
They are all fricatives
Bailey is 12-month old infant just fit with cochlear implants who just joined your caseload. In
setting your goals for this baby, what listening level will you start with?
Sound awareness/detection
What are some of the first sounds that you will start working with in teaching Bailey
listening and spoken language?
The Ling sounds
Which of the following are within your scope of practice for Bailey?
A. Teaching Bailey’s parents how to troubleshoot basic issues with her implant | |
B. Teaching Bailey’s parents about the most appropriate programming techniques for | |
C. Teaching Bailey’s parents how to direct Bailey’s attention to novel sounds in her | |
D. Teaching Bailey’s parents about the best remote microphone systems that Bailey can | |
E. A and C | |
F. C and D |
Which goal below would be most appropriate in beginning to work with LING sounds with
Bailey?
Start with “AHHH” because it is a Ling sound that is loudest and easiest to perceive
What might be some emotions that Bailey’s parents may be experiencing as you begin
therapy?
A. Feelings of being overwhelmed with all they have to learn | |
B. Depression and stages of the grief cyle | |
C. Confusion as to what the future may “look like” now | |
D. All of the above | |
E. None of the above |
Bob is an 86 year old with hearing loss who is in the hospital. You are his speech therapist
working on swallowing problems secondary to a recent stroke. Though his chart says he wears
hearing aids, his family did not want them brought to the hospital. Which of the following are
true for Bob?
A. | Your swallowing therapy may very well depend upon how well Bob can understand | |
B. | Since Bob’s family is not xconcerned with Bob hearing while he is in the hospital, | |
C. | A “pocket talker” may be valuable in helping Bob hear you. | |
D. | A and C | |
E. | None of the above |
In working with Bob, which of the following may be true:
You can use the pocket talker that the audiologist on staff has recommended that
SLPs have accessible in case they have a patient with hearing loss who did not have access to their aids.
In speaking with Bob, you must keep in mind to use:
A. Clear speech which over articulates every phoneme | |
B. Clear speech which is naturally slower because every phoneme is articulated | |
C. Clear speech which is naturally louder as the phonemes are articulated with | |
D. B and C | |
E. A and B |
You have Billy, a 12 year old with a moderate hearing loss in public school, who is
embarrassed to wear his FM/DM remote microphone system in class. He is also in literacy
therapy with you to assist with his reading. Which statement is true:
It is within your scope of practice to counsel Billy to assist him in addressing his
reluctance in wearing his FM/DM in class
Billy’s literacy issues can may also be linked to his hearing loss.
True