Lab Man Week 4
1/93
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
94 Terms
As a lab manager, one needs to have a strong understanding of:
PATIENT and EMPLOYEE SAFETY
Hierarchy of Control
is a traditional method used to prevent workplace hazards.
An Important Infection Control Practice
Hand Hygiene
Chemical Hygiene Plan
Defines the policies and procedures for all chemicals used in the laboratory.
Physical Hazards and other Laboratory Associated Hazards
1.Ergonomics
2.Noise
3.Latex
4.UV light exposure
5.Radiation Safety
6.Radioactive Waste
7.Compressed gasses
8.Centrifuges
9.Dry ice
10.Fire prevention and safety
Who is responsible for regulations relating to general workplace safety and protecting the health of U.S. workers
OSHA
What is PT testing?
CLIA approved Proficiency Testing programs allow laboratories to evaluate their performance on a regular basis; usually 2 to 3 times a year. These programs also allow laboratories to improve the accuracy of the patient results they provide.
If proficiency specimens are not commercially available (most commonly seem in molecular testing)
vLaboratories can exchange blind split samples
vBlinded samples are measured or documented by independent means such as chart review
HEALTH INSURANCE PORTABILITY AND ACCOUNTABILITY ACT OF __
1996
PT is performed usually
two - three times a year
You __ share results with other laboratories
cannot
Requirements for PT
Must fulfill all standards
Keep Results for at least 2 years, signed by person who completed the PT, and lab director
A laboratory is defined as
any facility which performs laboratory testing on specimens derived from humans for the purpose of providing information for the diagnosis, prevention, treatment of disease, or impairment of, or assessment of health.
Laborites that must be CLIA certified includes
cash only models and insurance model laborites
Analytes that do not have a Proficiency Testing program available must be evaluated at least __ a year
twice
What certificate types are available?
◻Certificate of Waiver
◻Provider Performed Microscopy
◻Certificate of Compliance
◻Certificate of Accreditation
Who needs a CLIA certificate?
Any person or facility that performs laboratory tests on human specimens for the purpose of diagnosis and/or treatment is required by federal law to have a CLIA certificate.
Certificate of Waiver
These tests have been approved by the FDA for home use and require very little training to perform.
What are Provider Performed Microscopy tests?
Tests performed by a health care provider such as a doctor, physician's assistant, or nurse practitioner. These tests include: microscopic sediment analysis, wet preps, KOH preps, and other microscopic based procedures.
Is proficiency testing required for Provider Performed Microscopy?
No, proficiency testing is not required for Provider Performed Microscopy. However, the quality of the tests performed must be evaluated at least twice a year.
What types of tests are classified under a Certificate of Compliance?
Moderate or high complexity tests
How often must analytes without a Proficiency Testing program be evaluated under a Certificate of Compliance?
At least twice a year
How frequently are facilities with a Certificate of Compliance inspected?
Every two years
What components must be included in the Quality Assurance program of a facility with a Certificate of Compliance?
Quality control, personnel policies, patient test management, and proficiency testing
What is a Certificate of Accreditation?
These certificates have the same standards as the Certificate of Compliance, but are inspected by a CMS-deemed professional organization, not CMS directly.
Who inspects Certificates of Accreditation?
A CMS-deemed professional organization, not CMS directly.
What are the requirements for testing personnel
For tests classified as waived or moderately complex, testing personnel must have at least a high school diploma or G.E.D. and documentation of training before performing tests.
For tests classified as high complexity, testing personnel must have an associate of science degree or higher and documentation of training before performing tests.
How often must all personel be evaluated
within six months of hire and annually after that.
Laboratories need to comply with requirements that pertain to their laboratory in order to maintain
licensure and accreditation
Compliance agencies
◦Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS)
◦Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA)
◦Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
◦College of American Pathologists (CAP)
◦Commission on Laboratory Assessment (COLA)
◦American Association of Blood Banks (AABB)
PURPOSE OF ACCREDITATION
To recognize quality
To inform the public that an institution has met minimum standardsTo improve the quality of patient care
Agencies review ____ of the laboratory operation.
all aspects
Identifies deficiencies as phase I or phase II
Two year cycle;
Year 1 self-evaluation
Year 2 on-site inspection
Cycle repeats again
What is a Phase I Deficiency in a CAP Inspection?
Requires a response
What is a Phase II Deficiency in a CAP Inspection?
Requires a response AND documentation that supports that response
AABB
◻Inspection every two years
◻For transfusion services (blood bank) only
◻Inspector is usually a blood banker from another accredited blood service
◻Deficiencies handled the same as CAP
NAACLS (National Accrediting Agency for CLS)
◻It is aaccreditation of educational programs for MLS
◻University/colleges and hospital programs
◻Accreditation can be awarded up to seven years
Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI)
◻CLSI is a World Health Organization Collaborating Center for Clinical Laboratory Standards and Accreditation.
Quality Control (QC)
uis the process by which one monitors analytical procedures in order to ensure the accuracy and precision of test results and thus the validity of patient results prior to their reporting
Quality control is accomplished by
monitoring QC materials such as serum, urine, and CSF alongside with patient samples
Internal QC involves the following:
Monitoring control results over time for changes in precision (random error) or accuracy (systematic error)
External QC involves the following
The comparison of a lab's assay results from unknown test samples with the mean results of those obtained on the same samples by other labs
QC material is prepared by
pooling either human or animal source body fluids.
Lot Switch
uIt is good practice to assay an old lot number of control alongside a new lot number of control when first using it.
Hospitals run levels of controls per ____
shift change, per instrument or batch run
Accuracy
a measure of how closely a test result agrees with the "true" value for that sample
Precision
A measure of how closely repeated measurement of a sample (replicates) agree with each other
Imprecision
Measurements do not closely replicate, and the SD will be larger
Reliability
A measure of both the accuracy and precision of a method
Central Tendency
Represents a large group of data points that are equal to or very nearly the same as one data point (cluster of data points) and are represented by a peak on a frequency diagram
Normal or Gaussian Distribution
Implies that there are approximately the same number and distribution of data points to either side of the peak (bell-shaped curve). Mean, median, and mode are approximately equal values
Mode
the most frequent number or value found in a data set.
Range
the difference between the high and low values of data in a data set.
Variance
A mathematical representation of the dispersion or degree of tightness of data points around the mean or peak in a data set. It is the square of the SD
Variance Formula (population)

Standard Deviation
the mathematical representation of the dispersion or degree of tightness of data points around the mean or peak in a data set. It is easily calculated by taking the square root of the variance
Confidence Interval (CI)
refers to the limits (high and low) between which a specified proportion of the data points in a data set will fall.
68% CI = mean +/- 1 SD
95% CI = mean +/- 2 SD
99% CI = mean +/- 3SD
Coefficient of Variation
the SD divided by the mean and multiplied by 100 to obtain a percentage.
% CV = SD/mean (100)
Levey-Jennings Charts
An approach to monitoring method performance for precision and long term accuracy
Trend
A small but steady and continuous change of the control values on one direction.
Often indicate reagent or calibrator deterioration or gradual instrumental failure
Shift
A change of the mean for the control material.
New mean is continuous but different from the original mean
Can be caused by resetting an instrument, a small but consistent flaw in the instrument, or a change of lot number of control
95% rule
Rule of thumb; the control value should fall within +/- 2 SD (95%) of the mean
Imprecision
large amount of scatter about the mean. Usually caused by errors in technique
Inaccuracy
may see as a trend or a shift, usually caused by change in the testing process
Random error
= no pattern. Usually poor technique, malfunctioning equipment
Westgard rules
"Multirule Quality Control"
Uses a combination of decision criteria or control rules
Allows determination of whether an analytical run is "in-control" or "out-of-control"
4 different areas that the LIS communicates between
–Laboratory LIS TEAM (all depts)
–Pharmacy
–Doctors Notes
–Nurse Notes
LABORATORY LIS requirements
Needs to be user friendly
Customizable
Secure of patient records
Cost-Effective
Bi-directional
Test Menu
Sample Requirements
Two different access codes or passwords per user for access to system
–User ID
–Unique password
–HIPAA mandated
Assign a ___ accession number to each patient sample received and/or each test ordered
unique
Provide a clear result screen page for each lab result that includes __/__ranges and flagging of critical values
normal/therapeutic
Provide a unique file for each assay that provides information about the assay
–Sample type, volume required, ranges, reference lab sent
(1/3) additional minimum requirements for LIS
Two different access codes or passwords per user for access to system
–User ID
– Unique password
–HIPAA mandated
Assign a unique accession number to each patient sample received and/or each test ordered
–M12345
Provide a clear result screen page for each lab result that includes normal/therapeutic ranges and flagging of critical values
Provide a unique file for each assay that provides information about the assay
–Sample type, volume required, ranges, reference lab sent
(2/3) additional minimum requirements for LIS
Record for each test such as time collected, rec’d, and initials or unique identifier of who received it, and who released results
Allow techs to create worksheets for testing
Create lists of pending logs and overdue tests
Print bar-code labels
Interface with major instruments so that demographics and tests ordered may be downloaded
(3/3) additional requirements for LIS
Allow for reports to be pulled
–Tests per month
–Workload units
–TAT (turn-around-times)
Allow for additional tests to be added to an existing order
Allow access to past laboratory tests
Allow for comments to be entered in the test results field
–Verified K level; Called to Dr. Robert Benson at 0100
Back up files daily
System components of LIS
Computer: hardware software date entry tools
Servers
Interface software
Electronic medical record contains
all patient information
Electronic LIs systems help with disease __
surveillance
LIS systems improve ___ ___
lab efficiency
new LIS system take how long to complete?
months to years
STEPS in LIS Acquisition
Define system Requirements
Request Bids
Request Demonstrations
Assign Staffing Roles
Implementation
Standard Operating Procedures
Data Security
Data Retention
Define System Requirements
Construct a workflow diagram and consider the data management requirements
Create a team of lead technologists who can provide insight on each lab section for reports
The __ is ultimately responsible for safe-guarding the health of its employees.
EMPLOYER
How long should a safety/incident report be maintained
30 years
R.A.C.E
Rescue, Alert/Alarm, Confine, Extinguish/Evacuate
P.A.S.S
Pull, Aim, Squeeze, and Sweep when using a fire extinguisher.
Safety Data Sheets (SDS),
previously called Material Safety Data Sheets must be provided to the laboratory for all chemicals received. Employers must provide the SDS to their employees.
Know the colors of the safety diamons
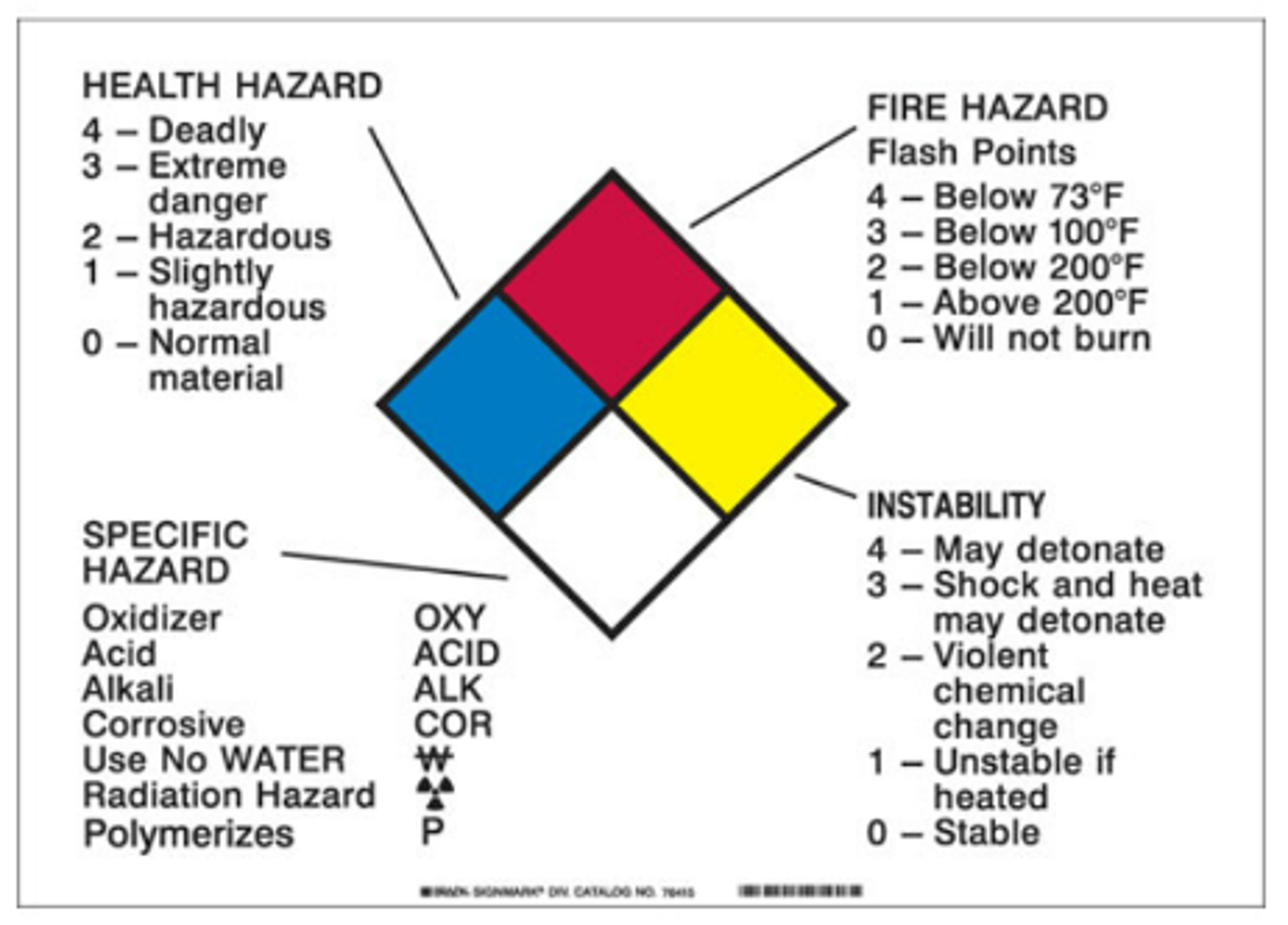
What are the types of fir extinguishers? class ABCD
Class A (water base) - for paper and wood
Class B (foam or dry chemical) – flammable liquid or gases
Class C (foam or dry chemical) – for electrical
Class D (graphite or dry chemical) – metal fires
Safety training and review records must be maintained during employee’s tenure and for ___ after the employee has left employment
3 years
Biosafety
addresses the safe handling and containment of infectious microorganisms, genetic material, and hazardous biological materials in order to protect employees and the general public.
Biosecurity
addresses the protection of infectious microorganisms, genetic material, and hazardous biological materials from intentional misuse, for example bioterrorism.
Infectious Disease Classifications
Cat. A: Infectious substance affecting humans. UN2814
Cat. A: Infectious substance affecting animals. UN2900
Cat. B: Infectious substance-biological substance. UN3373
Risk Assessment Cycle
1.Identify hazards
2.Evaluate associated risks
3.Determine controls to mitigate risks
4.Implement controls
5.Assess effectiveness of risk assessment