3rd year exam prep
1/246
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
247 Terms
What oral diseases are most common in those aged 0-2
Dental caries
What oral diseases are most common in those aged 3-6
Dental caries and tooth wear
What oral diseases are most common in those aged 7-17
Dental caries, gingivitis and toothwear
What oral diseases are most common in those aged 18-65
Dental caries, periodontitis, tooth wear and oral cancer
What oral diseases are most common in those older or vulnerable adults?
Dental caries, periodontitis, tooth wear, oral cancer, dry mouth
What are the major risk factors for those aged 0-2
Diet: sugar containing food/drinks
Lack of fluoride
What are the major risk factors for those aged 3-6?
Diet: sugar containing food/drinks
Lack of fluoride
Poor oral hygiene
What are the major risk factors for those aged 7-17
Diet: sugar containing food/drinks
Low/no of fluoride
Poor oral hygiene
Tobacco commencing
Alcohol commencing
What are the major risk factors for those aged 18-65
Diet: sugar containing food/drinks
Low/no of fluoride
Poor oral hygiene
Tobacco commencing
Alcohol commencing
Polypharmacy
Tooth loss
Dentures
What are the major risk factors for older/vulnerable adults?
Diet: sugar containing food/drinks
Low/no of fluoride
Poor oral hygiene
Tobacco commencing
Alcohol commencing
Polypharmacy
Tooth loss
What to actively promote for everyone in this age group? 0-2
Healthy diet
Parental tooth brushing
Fluoride toothpaste
What to actively promote for everyone in this age group? 3-6
Healthy diet
Parental brushing/assistance
Fluoride toothpaste
Spit don’t rinse after brushing
What to actively promote for everyone in this age group? 7-17
Healthy diet
Good oral hygiene
Fluoride toothpaste
Spit don’t rinse after brushing
Avoid/stop tobacco
Avoid alcohol
What to actively promote for everyone in this age group? 18-65
Healthy diet
Good oral hygiene
Fluoride toothpaste
Spit don’t rinse after brushing
Avoid/stop tobacco
Avoid/minimise alcohol
What to actively promote for everyone in this age group? older/vulnerable adults
Healthy diet
Good oral hygiene(including dentures)
Fluoride toothpaste
Spit don’t rinse after brushing
Avoid/stop tobacco
Avoid alcohol
Dry mouth care
Which group/groups should be recalled every 3-12 months?
0-2, 3-6 and 7-17
Which age group/groups should be recalled every 3-24 months?
18-65 and older/vulnerable adults
Reducing the incidence of disease and health problems within the population, either through universal measures that reduce lifestyle risks and their causes or by targeting high-risk groups
Primary prevention
Detecting the early stages of disease and intervening before full symptoms develop
Secondary prevention
Softening the impact of an ongoing illness or injury that has lasting effects. This is done by helping people manage long-term, often complex health problems.
Tertiary prevention
The GDC is highly confident that desirable consequences outweigh undesirable or undesirable consequences outweigh desirable, typically based on high or moderate certainty evidence
Strong recommendations
The GDC is less confident of the effectiveness of an intervention (low or very low certainty evidence) or the balance between benefits and harms is unclear.
Conditional recommendations
Clinical opinion suggest this advice is well established or supported. No robust underpinning research evidence exists. Good practice points are primarily based on extrapolation from research on related topics and/or clinical consensus, expert opinions and precedent, and not on research appropriate for rating the certainty or quality of evidence.
Good practice
Advice: Use toothpaste containing 1,350 to 1,500 ppm fluoride
Strong recommendation
Advice: For children taking medication frequently or long term, choose or request sugar-free medicines if possible
Good practice
Professional intervention: Apply fluoride varnish (2.26% NaF) to teeth 2 or more times a year
Strong recommendation
Professional intervention: Where the child is prescribed medication frequently or long term, liaise with medical practitioner to request that it is sugar-free
Good practice
Professional intervention: Investigate diet and assist adoption of good dietary practice in line with the Eatwell Guide
Good practice
Professional intervention: Assign a shortened recall interval based on dental caries risk
Conditional
Ask, Advise, Act: at every opportunity, ask patients if they smoke and record smoking status, advise on the most effective way of quitting and act on patient response, such as refer to local stop smoking support.
Strong recommendation
Fluoride content recommended for children below 6
1000 ppm (NaF)
Fluoride content recommended for those above 6 years
1350-1500 ppm (NaF)
Fluoride content recommended for high caries risk above the age of 10
2800ppm (NaF)
Fluroide content recommended for those who have a high caries risk, above the age of 16.
5000 ppm (NaF)
What amount of fluoride is toxic?
5 mg/kg
What is the fluoride content in water
1 ppm
Typical amount of fluoride in FV
22,600ppm
Recommended daily sugar intake for 11+
30g
Recommended daily sugar intake for 7-10
24g
Recommended daily sugar intake for 4-6
19g
Recommended daily sugar intake for under 4
No limit but just avoid
The degree of interproximal bone (use worst site on bone loss due to periodontitis) is classified by…
Staging
The % of bone loss / patient age is classified as
Grading
<15% (or 2mm attachment from the CEJ)
Stage I (early/mild)
Coronal third of root
Stage II (moderate)
Mid third of root
Stage III (severe)
Apical third of root
Stage IV (very severe)
<0.5
Grade A (slow rate of progression)
0.5-1.0
Grade B (moderate rate of progression)
>1.0
Grade C (Rapid rate of progression)
Risk factors for Perio
Smoking, including cigarettes/day
Suboptimally controlled diabetes
BOP <10%
PPD </= 4mm
No BoP at 4mm sites
Currently stable
BoP >/= 10%
PPD </= 4mm
No BoP at 4mm sites
Currently in remission
PPD >/= 5mm or PPD >4/=mm and BoP
Currently Unstable
What is the recommended plaque and bleeding scores to assess engagement?
P-20% B-10%
Which medications cause gingival hypertrophy?
Cyclosporin, Phenytoin and Amlodipine (CCB’s)
What does a BPE code 0 indicate?
Clinical gingival health (Black band is fully visible)
What does a BPE code 1 indicate?
Bleeding on probing and pocket depth >3mm (Black band is fully visible)
What does a BPE code 2 indicate?
Pocket depth >3mm and plaque retentive factors (Black band is fully visible)
What does a BPE code 3 indicate?
Pocket depths of 4-5mm (Black band is partially visible)
What does a BPE code 4 indicate?
Pocket depth of <5mm (Black band is not visible)
What does a BPE code * indicate?
Furcation involvement
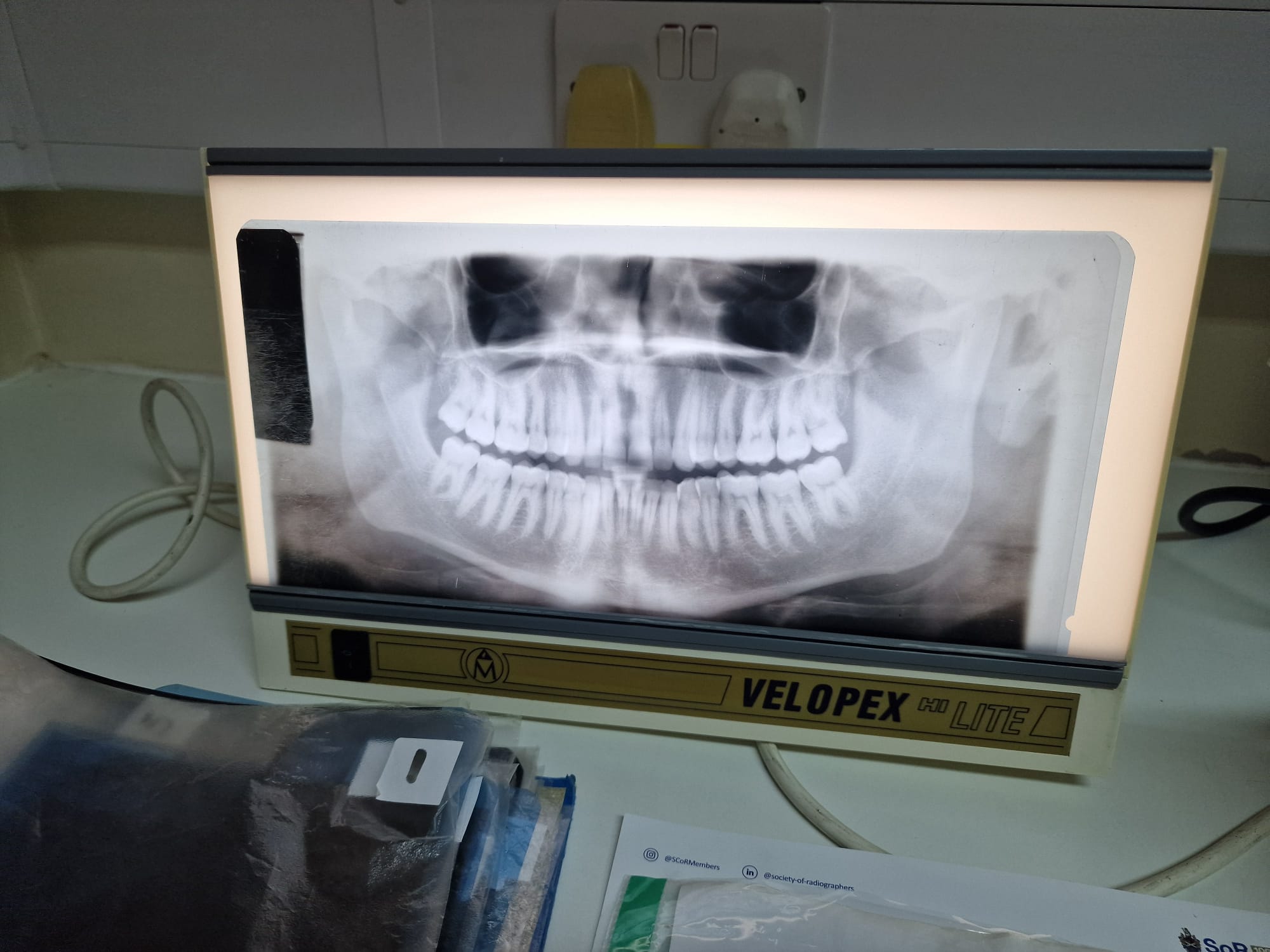
Perfect OPT
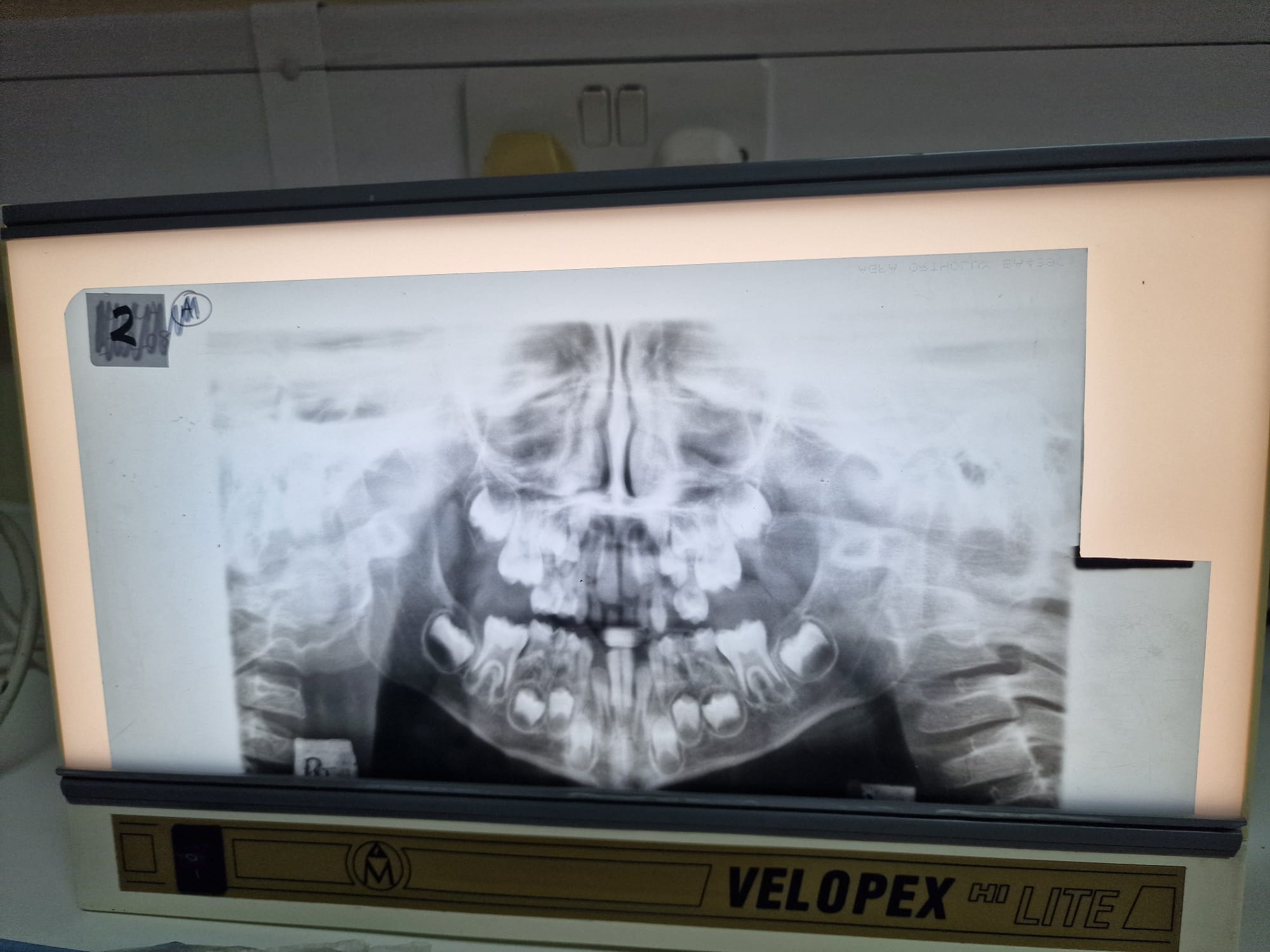
Pt to far in
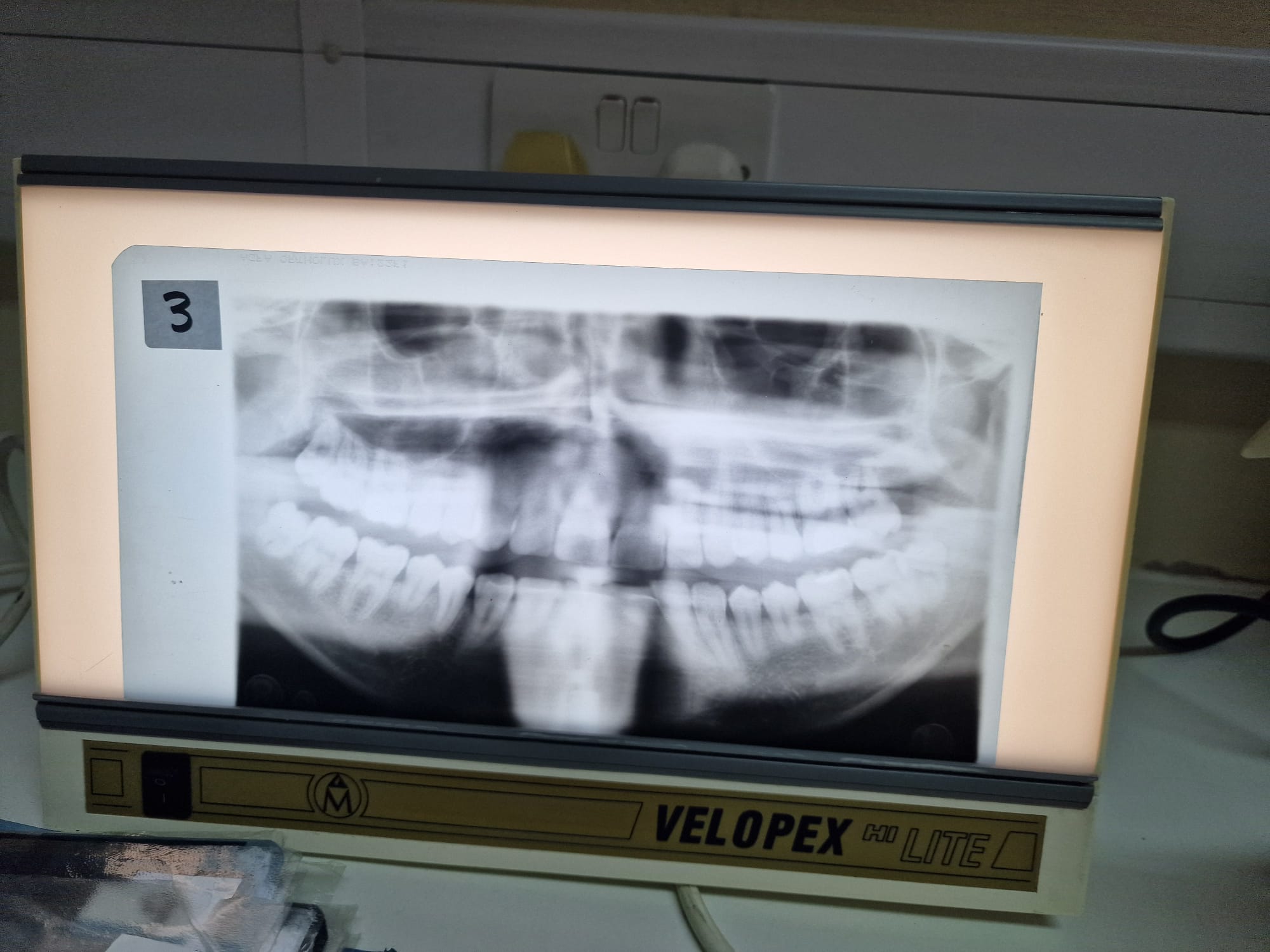
Pt to far out
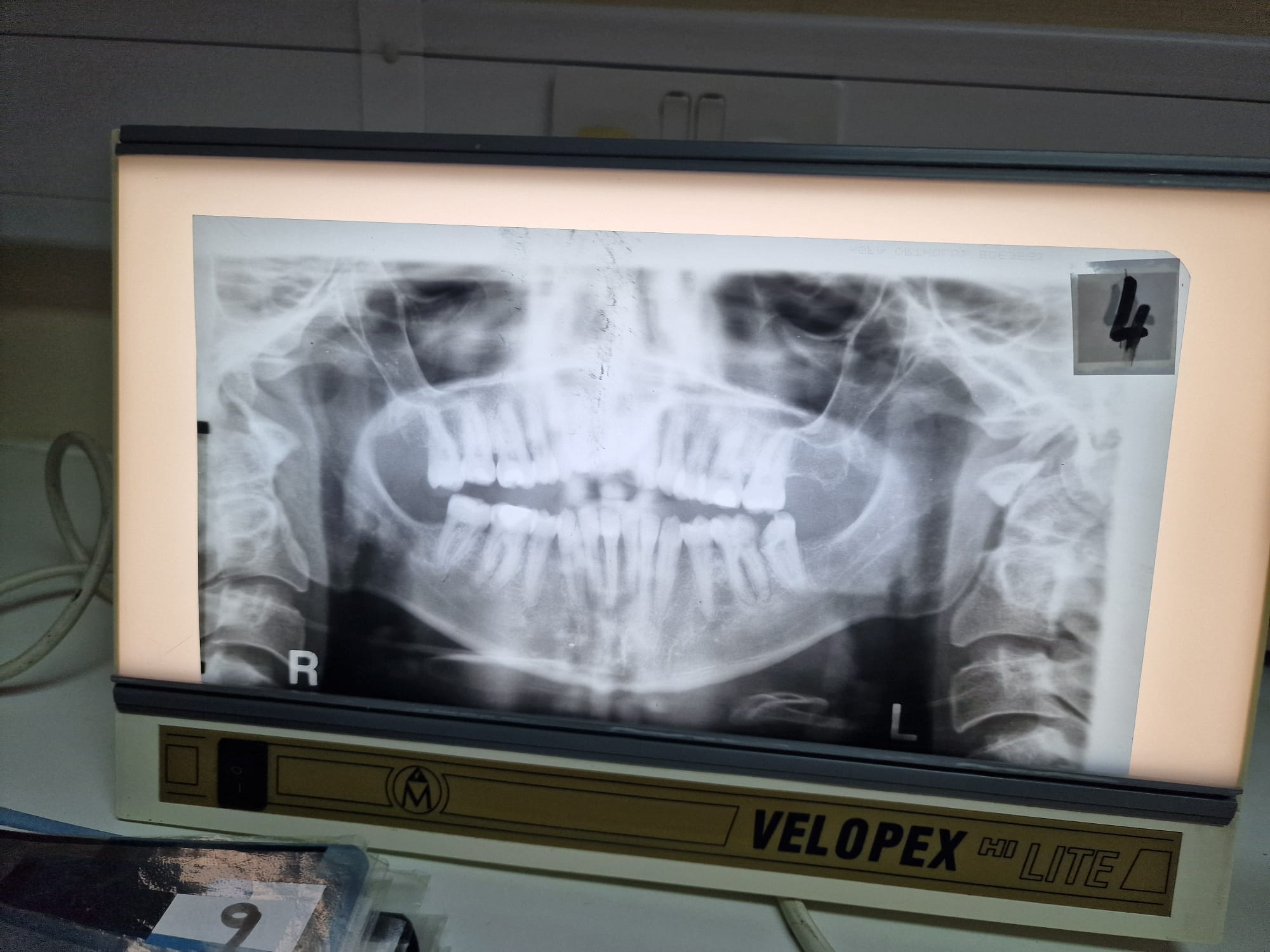
Chin up
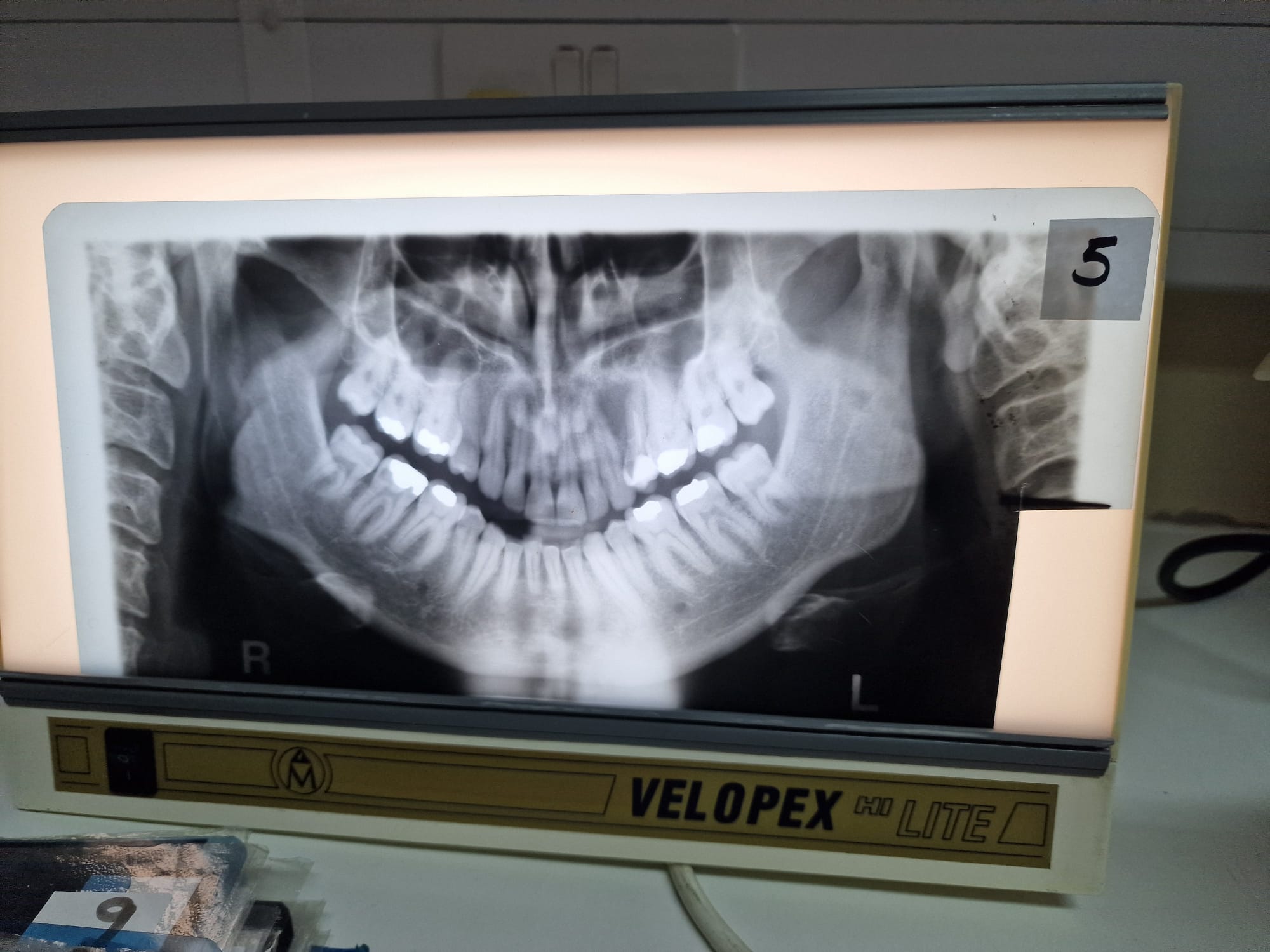
Chin down
Rotated
Head canted
Teeth off centre
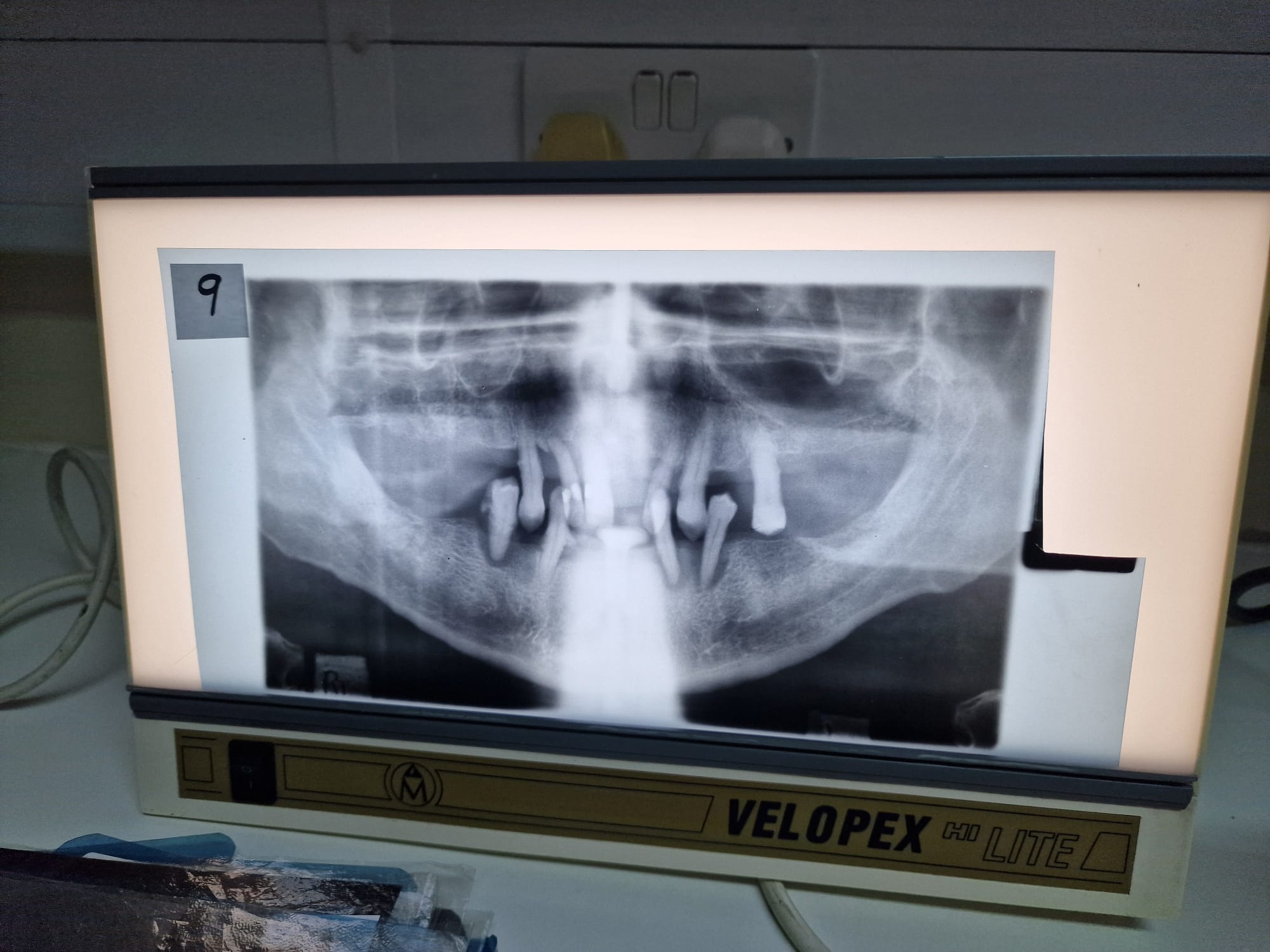
Teeth not biting edge to edge
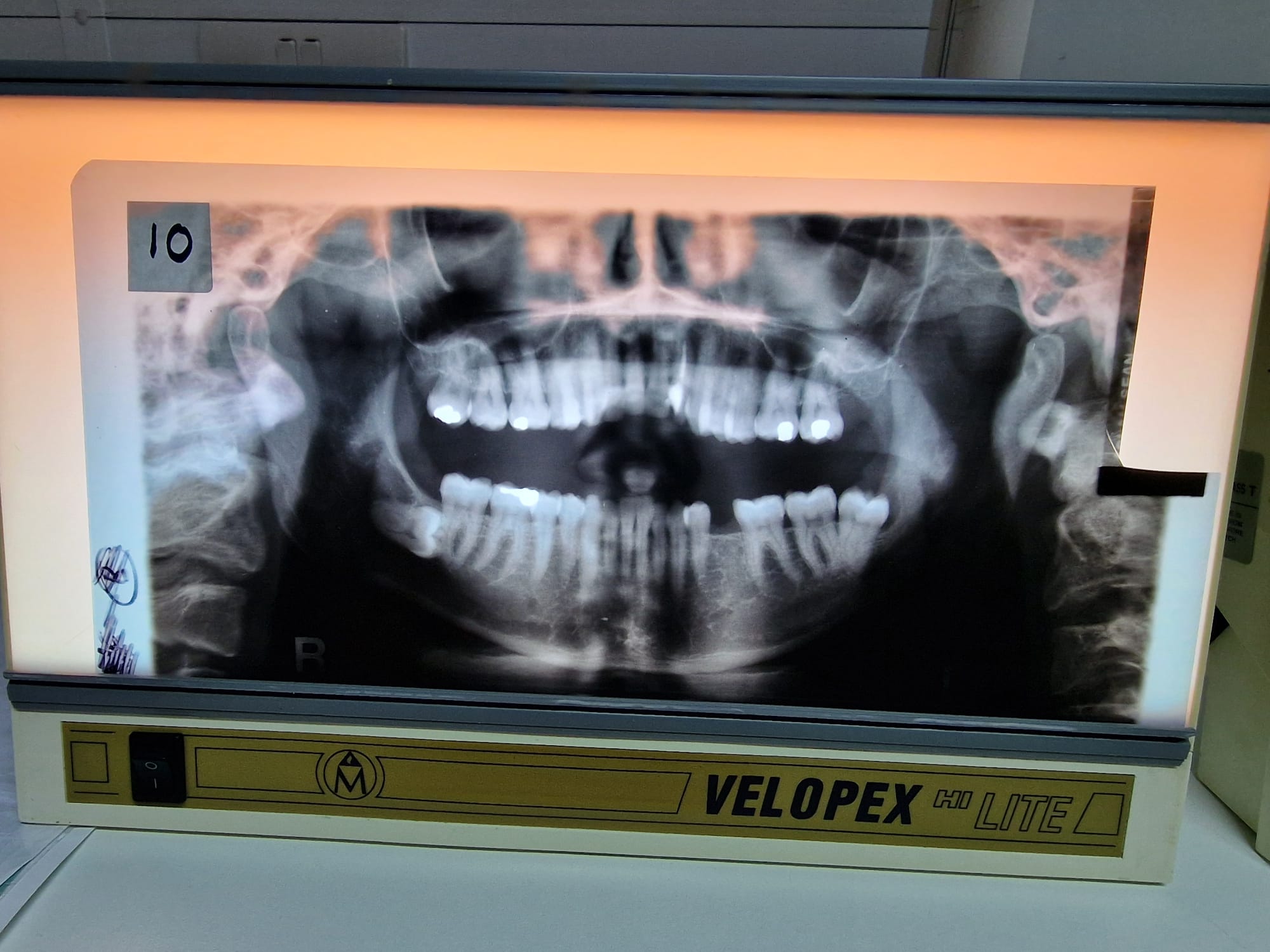
Mouth open
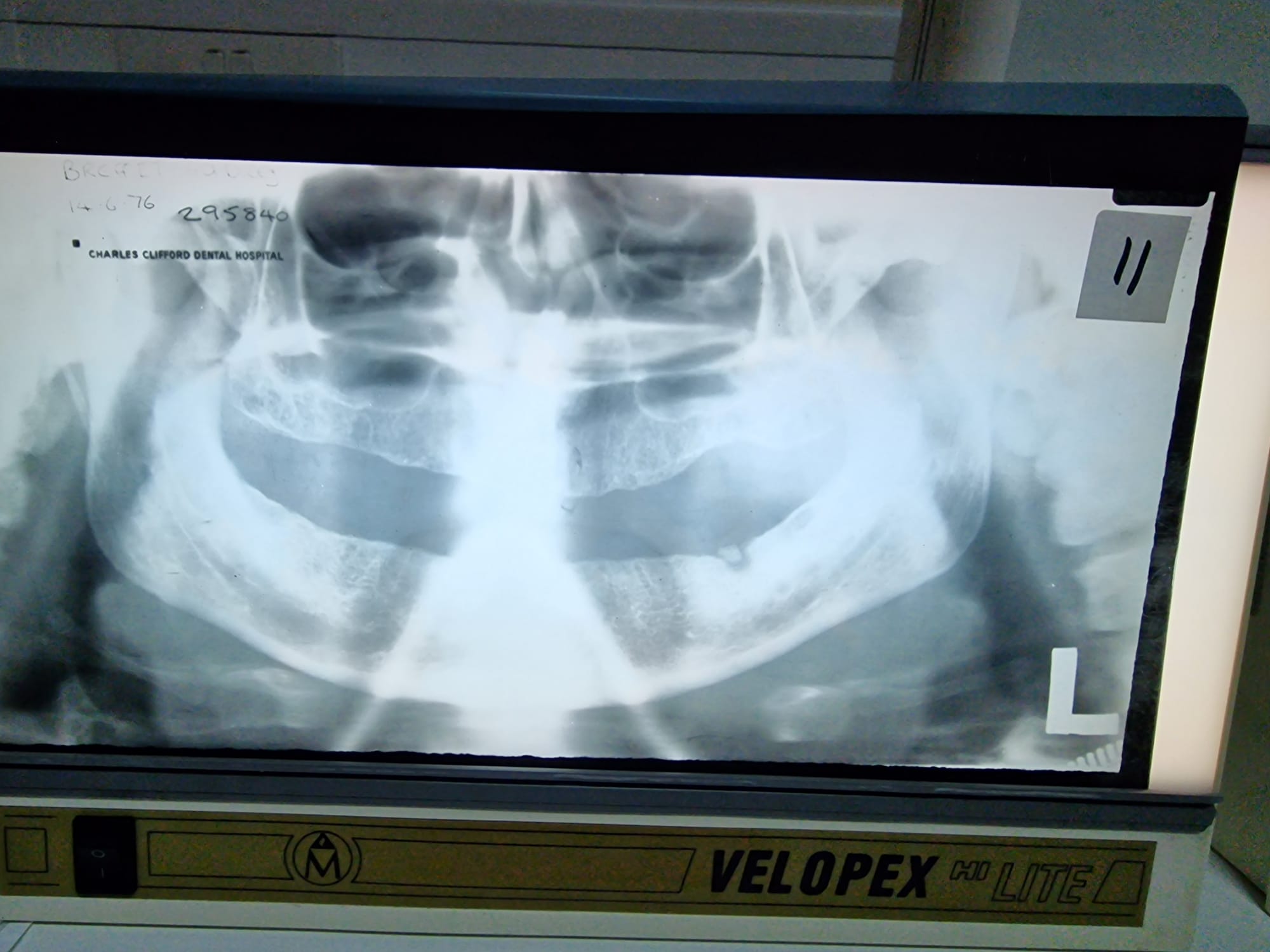
Patient slumped and wearing a necklace
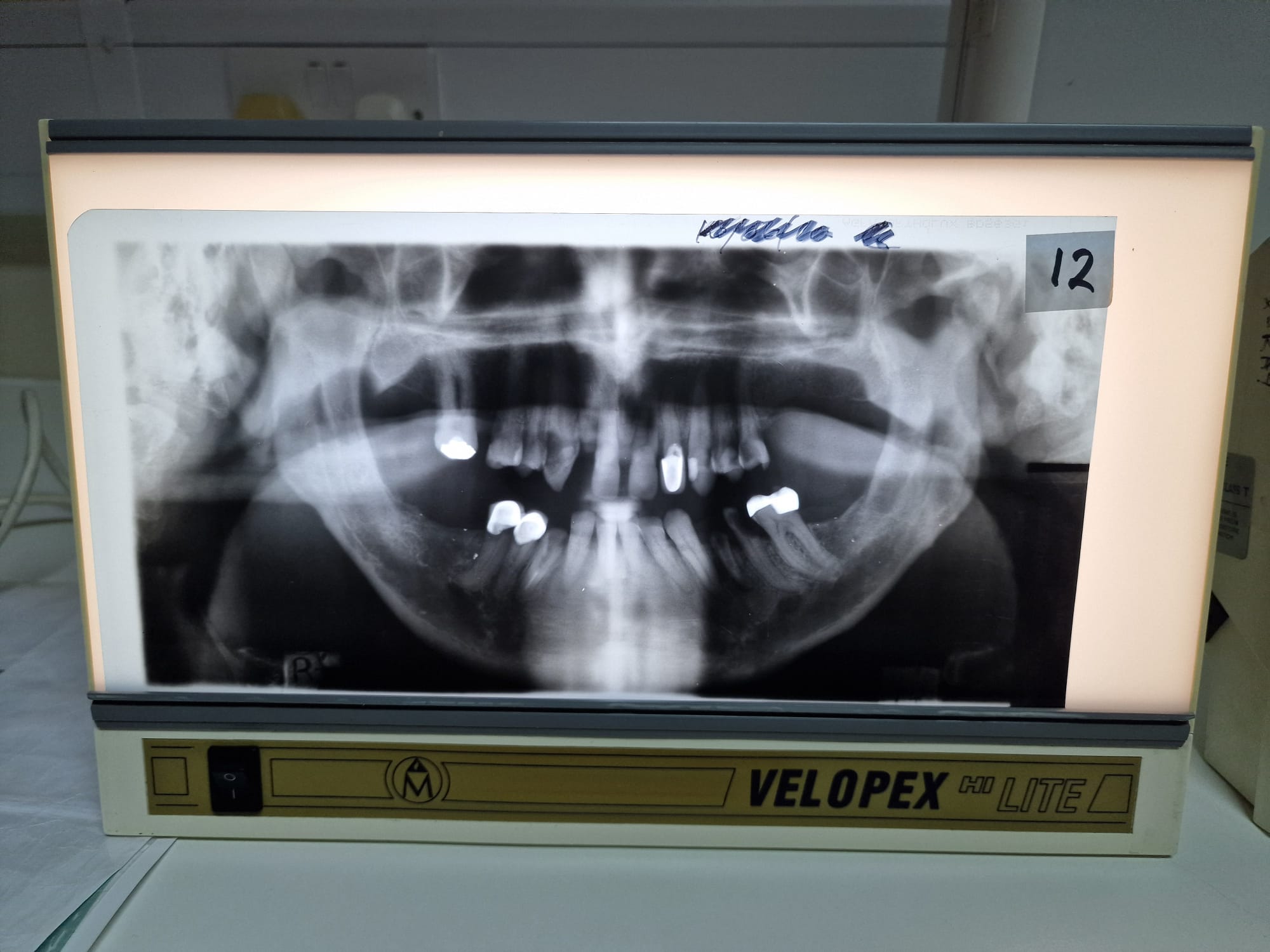
Patient not swallowed
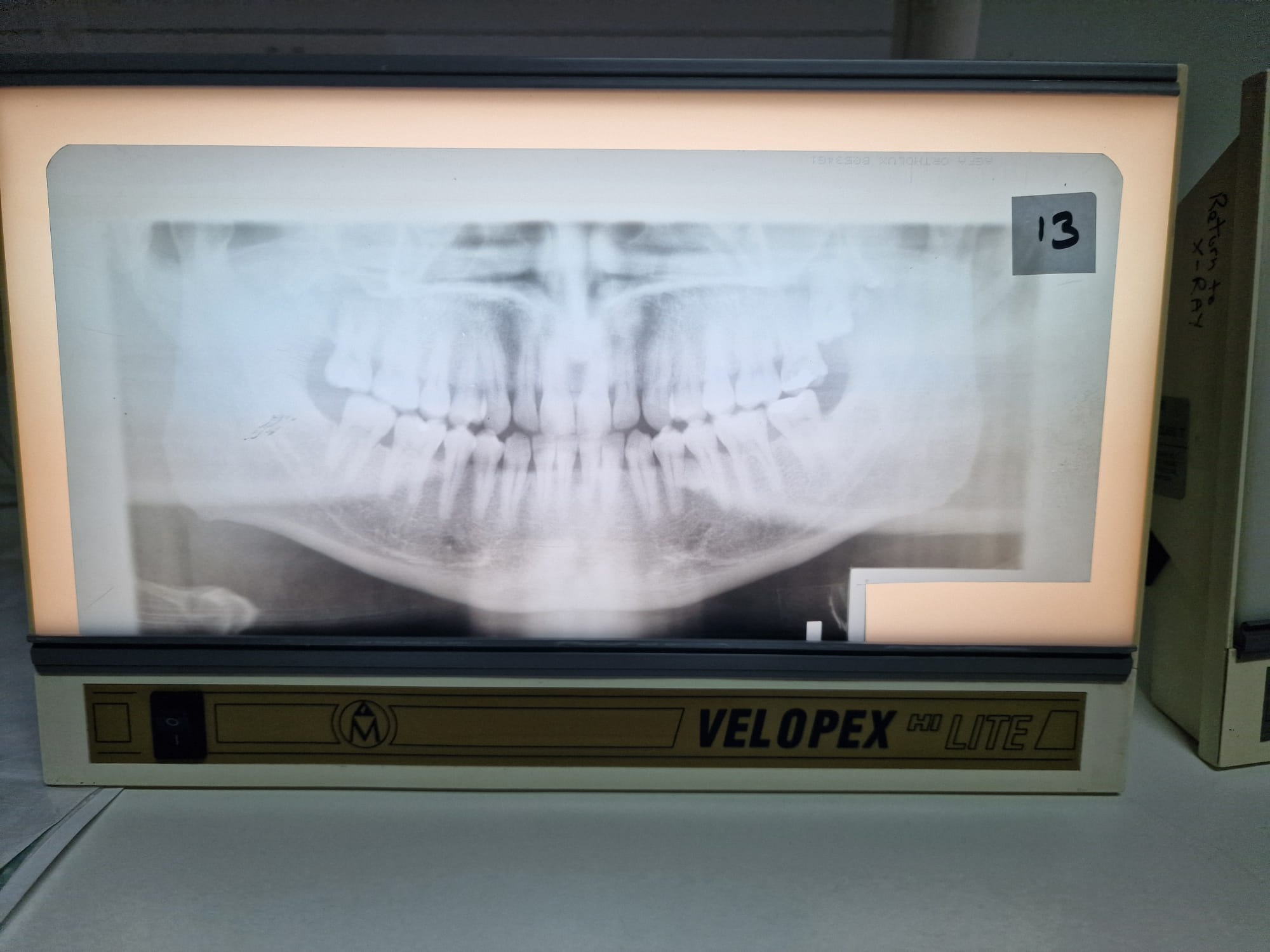
Over exposed
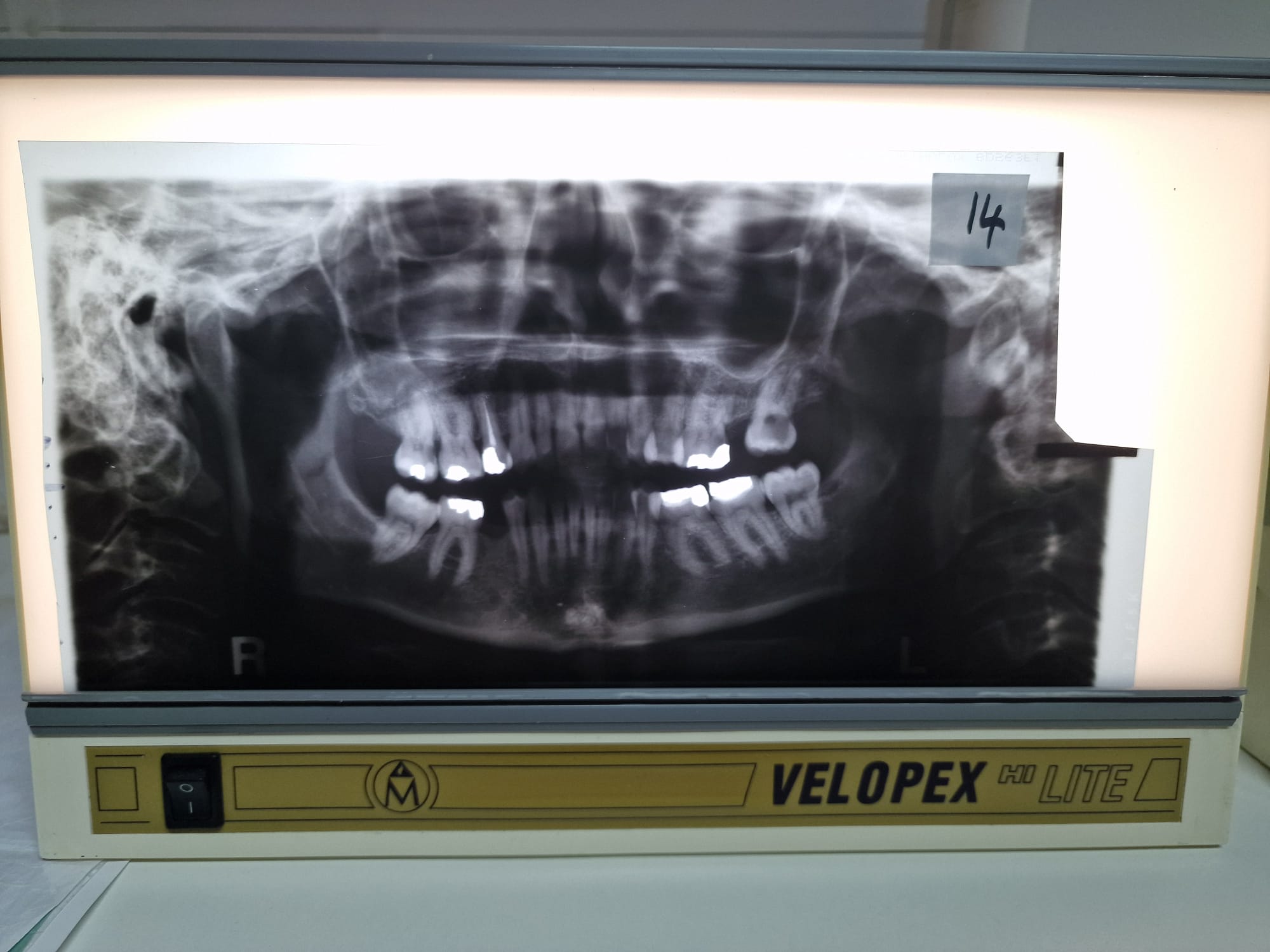
Under exposed
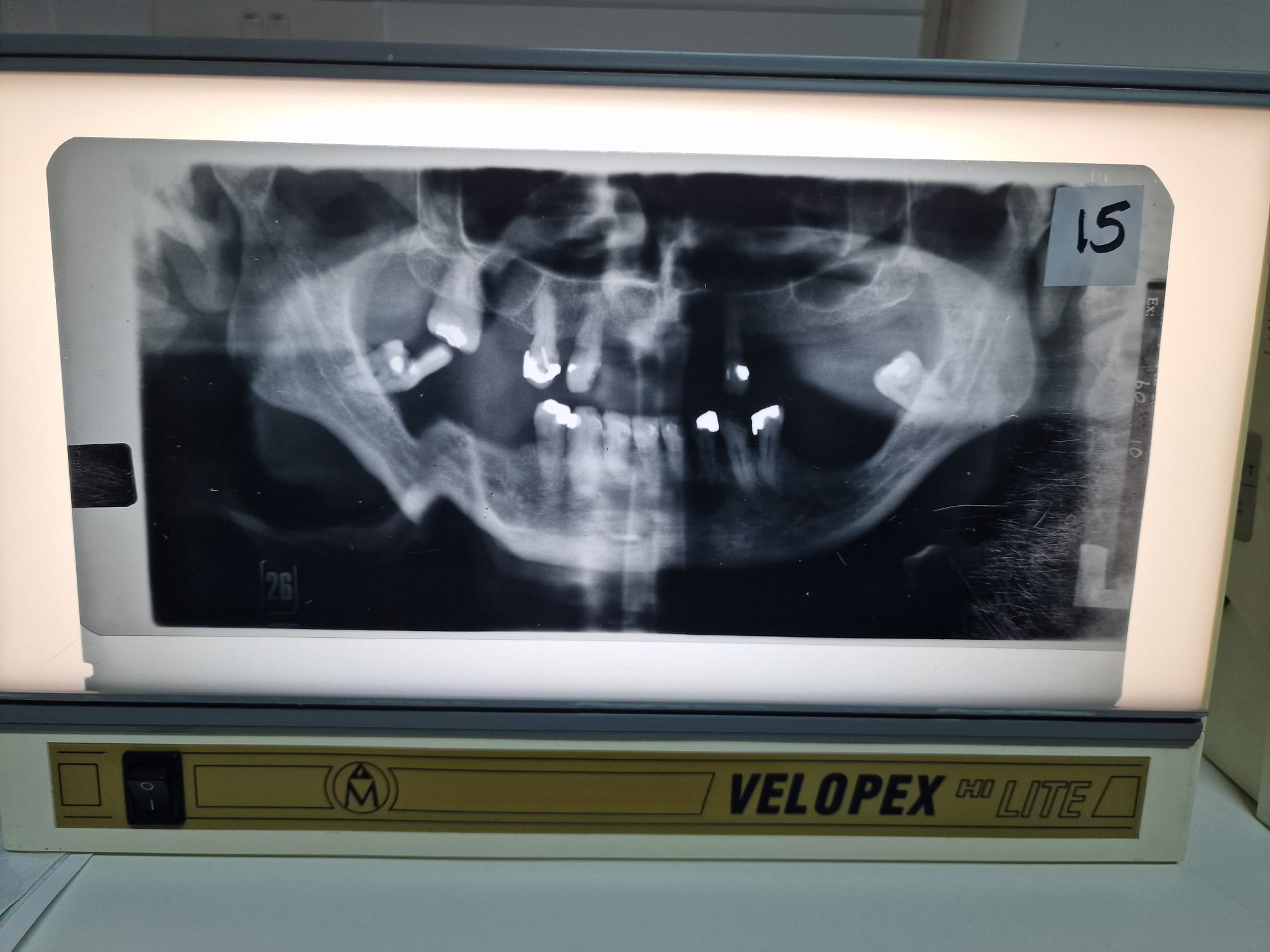
Patient moved
A 25-year-old man attends for review. He has clinical signs of Treacher-Collins syndrome, and the consultant is discussing the first and second pharyngeal arch syndromes. A junior dental student asks which cranial nerve develops with, and goes on to innervate the second pharyngeal arch. Which is the single most appropriate response?
The facial nerve (CN VII)
A 23-year-old woman returns to the surgery 5 days after surgical extraction of her lower right third molar. She reports loss of sensation from the floor of the mouth on the right-hand side. Which single nerve is most likely to have been damaged during her extraction?
The lingual nerve (a branch of CN V3)
A 45-year-old man is receiving an inferior alveolar nerve block for the restoration of a lower right first molar from a dental student, who is administering the injection for the first time. They are using a direct technique (over the contralateral premolar teeth), and their supervisor asks them which single muscle will the needle pass through?
Buccinator
A 18-year old mn is having a cranial nerve assessment performed after a traumatic incident. Upon protrusion of his tongue, the tongue deviates to the left-hand side. Which single nerve has been affected?
Hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
A 33-year-old woman attends for extraction of the upper left second premolar. The clinical tutor asks the student to anaesthetize the patient using infiltrations prior to the procedure. Which nerves require anaesthetizing?
Middle superior alveolar nerve + greater palatine nerve
A 34-year-old woman requires root canal treatment on an asymptomatic lower left first permanent incisor (LL1), which has two canals. Having been given two buccal infiltrations for anaesthesia, she can still feel pain. Which single nerve is most likely to be providing accessory innervation to the tooth?
Right inferior alveolar
A 15-year-old boy attends your surgery for a routine examination. His upper right permanent canine is yet to erupt. His upper left permanent canine erupted at the appropriate age. At approximately what age would you expect this tooth to have erupted?
10-11
A 14-month-old girl is brought to the surgery y her mother. She is concerned that a gap is present between some of her child’s developing upper teeth. Which teeth would you expect to have erupted in the maxillary arch of this child?
A’s, B’s and D’s
The babysitter of a 4-year-old boy telephones the practice, as the child fell down a staircase and has knocked out his upper right deciduous central incisor. The boy was momentarily unconscious but appears normal now. which is the single most appropriate advice to give to the babysitter over the phone?
Do not re-implant and take the child to the ER
A 3-year-old girl attends, following a recent fall. The crown of the ULA is significantly displaced labially. The tooth is non-mobile. A radiograph confirms the clinical diagnosis of lateral luxation. Which is the single most appropriate treatment
Extract ULA
A 9-year-old girl attends for a single routine restoration with her father. When asked, the father says that he was not married to the child’s mother at birth, but that they subsequently married and that he is named on the birth certificate. Which single most appropriate option for obtaining consent for this procedure
Father only
A 13-year-old girl attends for a routine dental examination, and multiple white spot lesions are noted around the cervical region of the upper and lower incisors. She reports frequent intake of sugary carbonated beverages (2L/day). In this scenario the single most appropriate management to reduce her caries risk
Reducing the frequency of sugar attacks
A 10-year-old girl has marked plaque-induced gingivitis. A ‘simplified BPE’ is performed. This procedure involves assessment of selective teeth termed ‘index teeth’. These teeth include all permanent first molars. Which other teeth are included?
Upper right and lower left permanent central incisors
A subdued 5-year-old boy is seen in the practice. He has multiple injuries on his hands, knees, chin and back of the neck. The parents report that the patient recently feel in the park. Injury to which single region would raise the most suspicion of a non-accidental injury?
Behind the ears
A 7-year-old girl has has a pulpotomy performed on her lower right second primary molar. Which single coronal restoration is considered the most appropriate
PMC
A 7-year-old girl has been referred for extraction of all of her carious primary molars under GA. Extensive OHI and prevention were given to the child and her parents prior to the GA appointment. Which is the single most appropriate future management for this child
3/12 recall with FV and fissure sealants
A 8-year-old boy has occlusal caries in his lower right first permanent molar. He is an irregular attender. Clinically the caries is minimal and confined to the distal section of the fissure system. A bitewing shows the caries extends into the outer third of the dentine. Which is the single most appropriate restorative management strategy for this tooth
PRR
An 8-year-old boy has a routine examination, an the patient’s mother has brought a 3-year-old sibling with no dental experience to observe their first examination. Which is the single most appropriate definition of this non-pharmacological behaviour management strategy.
Live modelling
A 45-year-old man is being reviews, following a course of non-surgical periodontal therapy. His current full mouth plaque score is 15% and he has had a good response to the treatment. Following repeat periodontal indices, he still has a number of isolated probing depths of 5mm, which have reduced from 8mm. Additional recession is present in these areas, varying from 1-2mm. Which single clinical indicator would suggest these sites are stable.
Absence of bleeding on probing
What is the optimum angle for a graceys curette
70 degrees
A 28-year-old man present for a routine examination. He is a smoker but otherwise fit and well. His previous clinical notes report diagnosis of plaque-induced gingivitis. However, following clinical examination today, his diagnosis has changed to generalised stage I grade B periodontitis. Which clinical finding is fundamental in differentiating between these two diagnoses?
Loss of attachment
A 78-year-old man complains of loose teeth. he has not attended the dentist in many years, and a detailed examination reveals:
- Poor plaque control
- Widespread periodontal probing depths of >8mm
- Furcation involvement of a number of teeth
- Generalized horizontal bone loss of up to 70%
He is a smoker of 5/day for 15 years.
What is the most appropriate diagnosis?
Generalised stage IV grade B
A basic examination is performed on a 42-year-old woman. Her oral hygiene is generally good, but generalized recession of 2-3mm is noted. In the upper right posterior sextant, a 2* is recorded. What single meaning does * indicated in the context?
Furcation involvement