ACC 111
0.0(0)Studied by 4 people
Card Sorting
1/172
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 3:12 AM on 9/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
173 Terms
1
New cards
2
New cards
Finance
the system that includes:
* the circulation of money
* the granting of credit
* the making of investments, and
* the provision of banking facilities
\
3
New cards
Finance
management of money
4
New cards
Financial Management
also known as **Corporate Finance**
5
New cards
Financial Management
3 Functions:
* Investing
* Financing
* Dividend Policy Making
* Investing
* Financing
* Dividend Policy Making
6
New cards
Financial Management
focuses on decisions relating to how much and what types of assets, how to raise the capital needed to purchase assets, and how to run the firm so as to maximize its value.
7
New cards
Money Market
**short-term** capital market
8
New cards
Money Market
examples: treasury bills, time deposits, foreign exchange, overnight markets/borrowings
9
New cards
Treasury Bills
issued by the government **to raise money** to support the operations of the government
10
New cards
Reserve Requirement
the portion of the deposit kept by the BSP
11
New cards
Capital/Financial Market
**long-term** capital market
12
New cards
Primary Market
stocks or bonds **issued for the** __**first time**__
13
New cards
Secondary Market
stocks or bonds **sold by the** __**investors of the primary market**__
14
New cards
Investments
it concerns **decisions about stocks and bonds** and includes a number of activities.
15
New cards
Security Analysis
through the use of fundamental analysis and technical analysis in **finding the true values of the security**
16
New cards
Fundamental Analysis
looking at the **Financial Statements and the Financial Ratio**s
17
New cards
Technical Analysis
looking at the **trend or pattern** of the investment
18
New cards
Chartist
they look at the trend, pattern, and movement of the stock
19
New cards
Portfolio Theory
deals with the best structure or combination of stocks and bonds with the lowest risk;
20
New cards
Portfolio Theory
to get the best combination of the capital structure to maximize the price of the stock of the company (which maximizes profits)

21
New cards
Market Analysis
that deals with the issues of stocks and bonds are overvalued or undervalued at any given time.
22
New cards
Cost of Capital
minimum required rate of return by the company
23
New cards
overvalued stock
when the actual market price is higher than the intrinsic value. You don’t buy but you sell if you have stocks
24
New cards
undervalued stock
when the actual market price is below the intrinsic value, you buy stocks
25
New cards
Behavioral Finance
the psychology of investing is being examined as the behavior of the investors, when it comes to buying and selling, have impact on the financial instrument
26
New cards
Firm’s Goal
To maximize a stockholder's wealth is through the value of their ordinary share. We want to maximize the price of the stock of the company
27
New cards
Intrinsic Value
the true value of the stock
28
New cards
\\Market Price
prevailing price of the stock in the market
29
New cards
Market Equilibrium
intrinsic value = market price
30
New cards
Investments
the **most important function** of the finance manager in the corporation
31
New cards
Investments
it entails an outflow of resources with the expectations of a benefit in the form of cash inflows in the near future.
32
New cards
Investment Decision
the most important of the three distinct types of decisions when it comes to value creation.
33
New cards
Investments
the firm’s life support in continuing its existence.
34
New cards
Financing Decision
It considers the best possible financing mix or capital structure of the company.
35
New cards
Financing Decision
to look for resources that will give the company the lowest weighted average cost of capital (WACC)
36
New cards
Financing
the one that supports the investing activities
37
New cards
Dividends
the retained earnings distributed to stockholders.
38
New cards
Vice President - Finance
also known as the Chief Finance Officer (CFO)
39
New cards
Treasurer
the true function of the financial management
40
New cards
Controller
the true work of the accounting
41
New cards
Risk Return Trade-Off
an increase in return is coupled by a corresponding increase of risk.
42
New cards
Risk Return Trade-Off
the higher the risk the higher the return
43
New cards
Sole Proprietorship
among the three forms of business organizations, this is the easiest to organize
44
New cards
Partnership
the partners contributed something to the partnership in return for the profits to be divided among the partners
45
New cards
Limited Liability Company
It is a hybrid between a partnership and a corporation.
46
New cards
Limited Liability Company
A form of business organization with the liability-shield advantages of a corporation and the flexibility and tax pass-through advantages of a partnership.
47
New cards
General Partnership
subject to tax similar to a corporation
48
New cards
General Professional Partnership (GPP)
a type of partnership which is not subject to tax
49
New cards
Limited Liability Partnership
It is used for professional firms in the fields of accounting, law, engineering, architecture, and others.
50
New cards
Corporation
It is an artificial being created by operation of law having the right of succession and the powers, attributes and properties expressly authorized by law or incident to its existence.
51
New cards
Agency Theory
it poses a potential conflict of interest between the stockholders and managers.
52
New cards
Managers
naturally inclined to act in their own best interests (which are not always the same as the interest of stockholders)
53
New cards
Stockholders
more likely to prefer riskier projects, because they receive more of the upside if the project succeeds.
54
New cards
Bondholders
receive fixed payments and are more interested in limiting risk. They are particularly concerned about the use of additional debt.
55
New cards
Creditors
does not want stockholders (corporation) to owe more debt as there are more chances that the first creditors would not be paid
56
New cards
Financial Statements
provides the financial position and financial performance of a company as of a particular period of time so that it would help the firm and the stakeholders to make decisions
57
New cards
Financial Statements Analysis
the process of analyzing the financial statements for the purpose of making business decision.
58
New cards
Financial Statements Analysis
an evaluation of the past and current performance of the firm and its perception in the future.
59
New cards
Predictive Value
based on the record you can predict what is most likely to happen in the future
60
New cards
Horizontal Analysis
used to evaluate the trend in the accounts over the years. It is usually shown in comparative financial statements.
61
New cards
Comparative Statements
Compares two comparative years and show the increases or decreases in the account balances with their corresponding percentages.
62
New cards
Comparative Statements
Formula:
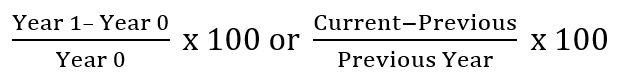
63
New cards
Trend Ratio
A firm’s present ratio is compared with its past and expected future ratios to determine whether the company’s financial condition is improving or deteriorating over time.
64
New cards
Trend Ratio
If we want to see the more essential analysis
65
New cards
Trend Ratio
Formula:
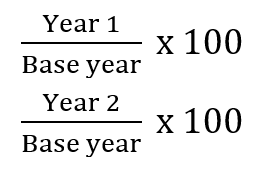
66
New cards
Base Year
the farthest year used to compare the present ratio, it is to determine the increase or decrease
67
New cards
Common Size Statement
A significant item in a financial statement is used as a base value.
68
New cards
Base Values
* Statement of Financial Position
* Total Assets
* Liabilities + Equity
* Comprehensive Income Statement
* Net Sales
* Total Assets
* Liabilities + Equity
* Comprehensive Income Statement
* Net Sales
69
New cards
Financial Ratios
analysis from one statement to another statement or the same statement
70
New cards
Combination of Accounts
a kind of Financial Ratio where one account is coming from one statement and the other is coming from another. The denominator is always average.
71
New cards
Industry Comparison
financial ratios are computed and compared with the industry average.
72
New cards
Trend Analysis
the firm’s financial ratios are computed and compared with their past performance.
73
New cards
Liquidity Ratio
A financial ratio where it is the **company’s ability to meet its maturing short-term obligations**.
74
New cards
Current Ratio
A __liquidity ratio__ where it is used **to measure the ability of the firm to meet its current liabilities** as paid by its current assets.
75
New cards
Current Ratio
Formula:
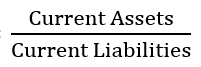
76
New cards
Acid-test Ratio / Quick Ratio
A stringent test of a firm’s liquidity; test of **ability to meet current liabilities from a more liquid assets**.
77
New cards
Acid-test Ratio / Quick Ratio
Formula:
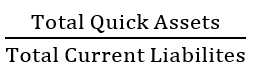
78
New cards
Cash Position Ratio
It determines how much **cash and marketable securities** can pay for every peso of current liabilities.
79
New cards
Cash Position Ratio
Formula:
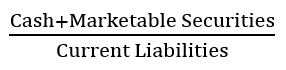
80
New cards
Working Capital
It shows what absolute amount is **the excess or shortage of current assets** to pay-off current liabilities.
81
New cards
Working Capital
Formula: current assets – current liabilities
82
New cards
Working Capital to Total Assets
It shows how much portion of the total assets are invested in the working capital.
83
New cards
Working Capital to Total Assets
Formula:

84
New cards
Cash Flow Liquidity Ratio
This measures short-term liquidity by adding cash, marketable securities, cash flow from operating activities.
85
New cards
Cash Flow Liquidity Ratio
Formula:

86
New cards
Activity or Asset Utilization Ratio
A financial ratio where it is used to determine how quick various accounts are converted into sales or cash.
87
New cards
Operating Cycle
It measures the length of time required to convert cash to finished goods to sales to receivable and then back to cash.
88
New cards
Operating Cycle
Formula: Ave. Collection period + Ave. Age of Inventory
89
New cards
Cash Conversion Cycle
It measures the length of time required to convert cash to finished goods to sales to receivable, back to cash to payables.
90
New cards
Cash Conversion Cycle
Formula: age of receivables + age of inventory – age of payables
91
New cards
Merchandise Inventory Turnover
It determines efficiency of the firm in managing and selling inventories. Only for **merchandising** company.
92
New cards
Merchandise Inventory Turnover
Formula:
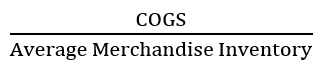
93
New cards
Finished Goods Inventory
It determines efficiency of the firm in managing and selling inventories. Only for **manufacturing** company.
94
New cards
Finished Goods Inventory
Formula:
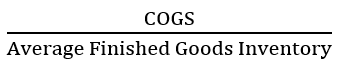
95
New cards
Average Age of Inventory
It determines the average number of days to **sell or consume the average inventory**.
96
New cards
Average Age of Inventory
Formula:
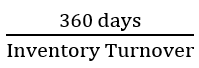
97
New cards
Accounts Payable Turnover
It measures the efficiency of the company in **meeting trade payable.**
98
New cards
Accounts Payable Turnover
Formula:
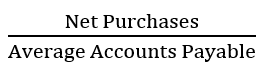
99
New cards
Average Age of Payable
Formula:
100
New cards
Working Capital Turnover
It determines the **adequacy & activity of working capital**.