Marketing
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
125 Terms
1
New cards
What is the role of marketing?
the process that connects customer wants with business products.
* strategic role of marketing goods and services
* interdependence with other key business functions
* production, selling, marketing approaches
* types of markets – resource, industrial, intermediate, consumer, mass, niche
* strategic role of marketing goods and services
* interdependence with other key business functions
* production, selling, marketing approaches
* types of markets – resource, industrial, intermediate, consumer, mass, niche
2
New cards
What is the strategic role of marketing for goods and services?
strategic: long-term, broad aims affecting all key business areas
brings together the products of the business and the customers.
involves:
* customer choice
* standard of living
* brand awareness
* generating employment
* increasing the business's market share
apple:
* ^^Marketing plays a pivotal role for Apple in maximising sales and generating profits. Apple musteffectively communicate these products to their desired market so consumers are aware of new products and services^^
brings together the products of the business and the customers.
involves:
* customer choice
* standard of living
* brand awareness
* generating employment
* increasing the business's market share
apple:
* ^^Marketing plays a pivotal role for Apple in maximising sales and generating profits. Apple musteffectively communicate these products to their desired market so consumers are aware of new products and services^^
3
New cards
Why is choice included in the strategic role of marketing?
businesses compete to attract customers, to do so differentiation from similar products is required (competitive advantage). they can differentiate through price and innovative products etc.
4
New cards
How does marketing contribute to improving the standard of living?
through the products and services provided by businesses, marketing helps improve the standard of living. Research and development play a significant role in providing better products and features that enhance the quality of life.
5
New cards
How is brand awareness achieved?
through strong and effective marketing campaigns that help the product remain in the consumer's mind and influence buying decisions.
6
New cards
What is the significance of employment in marketing?
marketing creates a large amount of employment by providing income for individuals involved in transforming inputs into finished products. This includes activities such as product development, sales, and promotion
7
New cards
How is market share defined?
the percentage of total sales a business has compared with its competitors in a particular market. Increased market share leads to increased sales and profitability.
8
New cards
Interdependance with other key business functions
* **operations:** create product to sell, incorporate needs and wants of consumers. marketing sells product, r&d
* **hr:** employ people with correct skills to promote products. marketing provides job and income
* **finance:** well executed promotion strategies result in profit. efficient allocation of funds towards promoting product
apple:
* ^^Marketing needs finance to fund marketing campaigns^^
* ^^Finance need marketing to generate the income for the firm through effective campaigns^^
* ^^Marketing needs operations to produce products that consumers will be attracted to and purchase^^
* ^^Operations needs marketing to provide information on the requirements for the product including design and features in order to attract the correct market^^
* ^^Marketing needs HR to hire staff with the expertise level and ability to respond to demand through effective marketing campaigns^^
* ^^HR needs marketing to generate sufficient revenue to allow for hiring of quality staff^^
* **hr:** employ people with correct skills to promote products. marketing provides job and income
* **finance:** well executed promotion strategies result in profit. efficient allocation of funds towards promoting product
apple:
* ^^Marketing needs finance to fund marketing campaigns^^
* ^^Finance need marketing to generate the income for the firm through effective campaigns^^
* ^^Marketing needs operations to produce products that consumers will be attracted to and purchase^^
* ^^Operations needs marketing to provide information on the requirements for the product including design and features in order to attract the correct market^^
* ^^Marketing needs HR to hire staff with the expertise level and ability to respond to demand through effective marketing campaigns^^
* ^^HR needs marketing to generate sufficient revenue to allow for hiring of quality staff^^
9
New cards
What are the different approaches to marketing?
* production approach
* selling approach
* marketing approach
apple:
* ^^The innovative design of the IPhone created a selling approach to marketing as the features were beyond consumer expectations^^
* ^^As the market for IPhones had become established, the focus became more persuasive than informative^^
* ^^A highly competitive market has led to the need to effectively market the IPhone^^
* selling approach
* marketing approach
apple:
* ^^The innovative design of the IPhone created a selling approach to marketing as the features were beyond consumer expectations^^
* ^^As the market for IPhones had become established, the focus became more persuasive than informative^^
* ^^A highly competitive market has led to the need to effectively market the IPhone^^
10
New cards
What is the production approach in marketing?
* focuses on attracting customers with existing products.
* involves mass production of standardized products to increase output, reduce production costs, and improve affordability to gain market share.
* involves mass production of standardized products to increase output, reduce production costs, and improve affordability to gain market share.
11
New cards
What is the selling approach in marketing?
* Focus on persuading customer to buy product by emphasising its benefits and features
* Emphasised persuasive sales techniques; door-to-door salesmen
* Emphasised persuasive sales techniques; door-to-door salesmen
12
New cards
What is the marketing approach in marketing?
* focuses on customer needs and wants
* involves conducting market research to understand customer requirements and designing products that meet those needs.
* involves conducting market research to understand customer requirements and designing products that meet those needs.
13
New cards
What are the different types of markets?
* resource
* industrial
* intermediate
* consumer
* mass
* niche
apple
* ^^Apple operate for a mass consumer market^^
* industrial
* intermediate
* consumer
* mass
* niche
apple
* ^^Apple operate for a mass consumer market^^
14
New cards
What is the resource market?
Where production and sale of raw materials occurs; mining, fishing, agriculture
* These resources are then sold to firms producing goods/services for consumers
* E.g. farmer purchases seeds and fertilisers
* These resources are then sold to firms producing goods/services for consumers
* E.g. farmer purchases seeds and fertilisers
15
New cards
What is the industrial market?
Provide both partly made raw materials and finished items to other businesses
* Goods/services that go into the production of other products.
* E.g. coffee beans and cups baristas use to make coffee, car company sourcing parts to complete vehicles
* Goods/services that go into the production of other products.
* E.g. coffee beans and cups baristas use to make coffee, car company sourcing parts to complete vehicles
16
New cards
What is the intermediate market?
Made up of wholesalers and retailers that purchase finished products and sell again to make a profit
* E.g subway buys lettuce to make into sandwiches they sell, car hire company
* E.g subway buys lettuce to make into sandwiches they sell, car hire company
17
New cards
What is the consumer market?
Where businesses sell their products directly to consumers
* Market for goods at their final point of consumption → do not intend to use to make other goods/services
* **Can be divided into niche or mass**
* E.g. department store
* Market for goods at their final point of consumption → do not intend to use to make other goods/services
* **Can be divided into niche or mass**
* E.g. department store
18
New cards
What is a mass market?
Market for goods appealing to the majority of customers
* Aimed at customers regardless of age, gender, residential location, income etc.
* E.g. milk, electricity, bread
* Aimed at customers regardless of age, gender, residential location, income etc.
* E.g. milk, electricity, bread
19
New cards
What is a niche market?
Smaller markets designed to meet the needs of specific customers
* Narrow customer base
* Specific needs and wants
* E.g. gothic clothing, sports wheelchairs
* Narrow customer base
* Specific needs and wants
* E.g. gothic clothing, sports wheelchairs
20
New cards
What are the influences on marketing?
\
* factors influencing customer choice – psychological, sociocultural, economic, government
* consumer laws
* deceptive and misleading advertising
* price discrimination
* implied conditions
* warranties
* ethical – truth, accuracy and good taste in advertising, products that may damage health, engaging in fair competition, sugging
* factors influencing customer choice – psychological, sociocultural, economic, government
* consumer laws
* deceptive and misleading advertising
* price discrimination
* implied conditions
* warranties
* ethical – truth, accuracy and good taste in advertising, products that may damage health, engaging in fair competition, sugging
21
New cards
What are the factors influencing consumer choice?
* psychological
* sociocultural
* economic
* government
apple:
* ^^released IPhone 11 in September 2019^^
* ^^released in 6 non-traditional colours^^
* ^^Appealed to those with varying preferences^^
* ^^Directed at consumer personalities^^
* ^^Apple has responded to varying social trends in the design of IPhones– Inclusion of improved camera quality and features and larger screen for social media andgaming^^
* ^^Economic status does not allow for all people to have access to this phone^^
* ^^However, large sociocultural effects tend to ‘force’ people into purchasing the product^^
* sociocultural
* economic
* government
apple:
* ^^released IPhone 11 in September 2019^^
* ^^released in 6 non-traditional colours^^
* ^^Appealed to those with varying preferences^^
* ^^Directed at consumer personalities^^
* ^^Apple has responded to varying social trends in the design of IPhones– Inclusion of improved camera quality and features and larger screen for social media andgaming^^
* ^^Economic status does not allow for all people to have access to this phone^^
* ^^However, large sociocultural effects tend to ‘force’ people into purchasing the product^^
22
New cards
How do psychological factors influence customer choice?
The personal characteristics that influence buying decisions
* A customer’s way of thinking and feeling about a product are affected by their personality, lifestyle, self-concept, motivation and past buying experience
* E.g. iPhone may be bought as they want to be seen as technologically savvy, with the latest phone
* A customer’s way of thinking and feeling about a product are affected by their personality, lifestyle, self-concept, motivation and past buying experience
* E.g. iPhone may be bought as they want to be seen as technologically savvy, with the latest phone
23
New cards
How do sociocultural factors influence customer choice?
Customer’s social grouping influences buying decisions; trust those close to them and value their opinions
* Family (traditions and background), friends, social class, religion, ethnicity, income, education, etc.)
* ^ contribute to customers needs and wants
* Family (traditions and background), friends, social class, religion, ethnicity, income, education, etc.)
* ^ contribute to customers needs and wants
24
New cards
How do economic factors influence customer choice?
Relates to current economic condition and individual income levels
* Price of goods and services may entice or steer customers away
* Economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, boom, recession etc. will affect a customer’s confidence and willingness to purchase products
* Socio-economic status: higher will be able to purchase goods from a wider price range
* Price of goods and services may entice or steer customers away
* Economic conditions such as inflation, interest rates, boom, recession etc. will affect a customer’s confidence and willingness to purchase products
* Socio-economic status: higher will be able to purchase goods from a wider price range
25
New cards
How do government factors influence customer choice?
Influences customer’s decisions through taxes, subsidies and laws as well as their impact on the economy
* Laws like the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 (cwlth) and Fair Trading Act 1987 (NSW) influence marketing decisions
* Social role: age restrictions on the purchasing of alcohol, TV censorship
* Laws like the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 (cwlth) and Fair Trading Act 1987 (NSW) influence marketing decisions
* Social role: age restrictions on the purchasing of alcohol, TV censorship
26
New cards
What are consumer laws?
laws placed to improve the protection and rights of consumers and to clarify the rights and responsibilities of businesses.
* deceptive and misleading advertising
* price discrimination
* implied conditions (statutory warranty)
* warranties
apple:
* ^^The CCA 2010 ensures that Apple’s promotional information does not convey a false impression of the IPhone or suggest certain qualities that it does not have^^
* ^^Apple sells their products at the same price nationwide in Australia^^
* ^^Apple ensures their products comply with the implied conditions and if not, sued/banned etc^^
* deceptive and misleading advertising
* price discrimination
* implied conditions (statutory warranty)
* warranties
apple:
* ^^The CCA 2010 ensures that Apple’s promotional information does not convey a false impression of the IPhone or suggest certain qualities that it does not have^^
* ^^Apple sells their products at the same price nationwide in Australia^^
* ^^Apple ensures their products comply with the implied conditions and if not, sued/banned etc^^
27
New cards
What is the ‘Competition and Consumer Act 2010’?
promote fair and competitive behaviour in the marketplace. Aims to:
* Protect consumers against undesirable practices; deceptive advertising, price discrimination
* Regulate certain trade practices that restrict competition; ensuring a number of businesses are operating at one given time to encourage competition in the market
* Protect consumers against undesirable practices; deceptive advertising, price discrimination
* Regulate certain trade practices that restrict competition; ensuring a number of businesses are operating at one given time to encourage competition in the market
28
New cards
What is the ‘Fair Trading Act’ 1987?
ensures trading is fair for both businesses and their customers
29
New cards
What is the ACCC (Australian Competition and Consumer Commission)?
enforces Competition and Consumer Act and takes action against businesses suspected of breaching these acts.
\
\
30
New cards
What is deceptive and misleading advertising?
refers to advertising that creates a false impression about a product to influence customers to buy it
* occurs when businesses are not truthful with their pricing claims, advertising, and special offers
* examples include overstating benefits, offering discounts that don't exist, and using bait and switch advertising (covered in ‘Competiton and Consumer Act’)
* occurs when businesses are not truthful with their pricing claims, advertising, and special offers
* examples include overstating benefits, offering discounts that don't exist, and using bait and switch advertising (covered in ‘Competiton and Consumer Act’)
31
New cards
What is price discrimination?
refers to charging different prices for an identical product in separate markets.
* include a business favoring some retail stores by offering stock at a lower price, which reduces competition
* Price discrimination is prohibited by the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 and enforced by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC)
* bulk buying for a discount is legal.
* include a business favoring some retail stores by offering stock at a lower price, which reduces competition
* Price discrimination is prohibited by the Competition and Consumer Act 2010 and enforced by the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC)
* bulk buying for a discount is legal.
32
New cards
What are implied conditions?
also known as statutory warranties, are unspoken and oftentimes unwritten terms of a contract
* they guarantee that the product being offered for sale is suitable for its intended use and of reasonable standard.
* merchantable quality (up to the standard for the price charged)
* fit for purpose (suitable for the purpose for which it is being sold).
* they guarantee that the product being offered for sale is suitable for its intended use and of reasonable standard.
* merchantable quality (up to the standard for the price charged)
* fit for purpose (suitable for the purpose for which it is being sold).
33
New cards
What are warranties?
written guarantees that faulty products will be repaired, replaced, or refunded within a set period and under certain conditions of use
* They assure customers that a business has confidence in the quality of its product
* If problems arise with obtaining refunds or other warranty-related issues, consumers can raise the problem with the ACCC.
* They assure customers that a business has confidence in the quality of its product
* If problems arise with obtaining refunds or other warranty-related issues, consumers can raise the problem with the ACCC.
34
New cards
What are the ethical influences on marketing?
where marketing managers understand value systems and morality or what is right or wrong with regard to the marketing of goods or services
includes:
* truth, accuracy and good taste in advertising
* products that may damage health
* engaging in fair competition
* sugging
apple:
* ^^Over-the-top product placement^^
* ^^Encouragement of materialism – aggressively markets the IPhone^^
* ^^Health concerns over radiation and unhealthy habits^^
includes:
* truth, accuracy and good taste in advertising
* products that may damage health
* engaging in fair competition
* sugging
apple:
* ^^Over-the-top product placement^^
* ^^Encouragement of materialism – aggressively markets the IPhone^^
* ^^Health concerns over radiation and unhealthy habits^^
35
New cards
What are some examples of unethical marketing practices?
* concealing facts → harm the trust customers have with the business or product
* exaggerating product ability or providing inaccurate information → puffery, mislead customers
* using vague statements → so broad that consumers will assume the intended message
* exaggerating product ability or providing inaccurate information → puffery, mislead customers
* using vague statements → so broad that consumers will assume the intended message
36
New cards
What is truth, accuracy and good taste in advertising?
marketers are expected to engage in fair and honest behaviour when developing marketing campaigns, failure to do so is a breach of the **Competition and Consumer Act 2010**
* honest about product functions, features
* facts and claims about product/service must be true
* good taste in advertising: highly subjective → generally avoid sexualisation, discrimination and lower advantaged social groups.
* honest about product functions, features
* facts and claims about product/service must be true
* good taste in advertising: highly subjective → generally avoid sexualisation, discrimination and lower advantaged social groups.
37
New cards
Products that may damage health
Many believe the marketing of these products/services shouldn’t be promoted
* Health warnings must be displayed on cigarette packs, they cannot be advertised or displayed in stores
* The marketing of products such as junk food, are often criticised because they damage the health of people.
* Health warnings must be displayed on cigarette packs, they cannot be advertised or displayed in stores
* The marketing of products such as junk food, are often criticised because they damage the health of people.
38
New cards
What is engaging in fair competition, and how is it regulated?
Fair competition is when businesses compete legally and ethically to increase sales and profit
* The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) regulates business behavior and enforces the Competition and Consumer Act to ensure fair competition
* The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) regulates business behavior and enforces the Competition and Consumer Act to ensure fair competition
39
New cards
What are some examples of unfair competitive behaviour?
* **Price-fixing:** an agreement among competitors to sell product/service at a fixed price
* **Long-term loss leader:** undercutting smaller competitors and forcing them to engage in price war
* **Misleading advertising regarding the products of a competitor:** making claims about a competitor's product (unfair and potentially illegal)
* **Long-term loss leader:** undercutting smaller competitors and forcing them to engage in price war
* **Misleading advertising regarding the products of a competitor:** making claims about a competitor's product (unfair and potentially illegal)
40
New cards
What is sugging and what ethical issues does it raise?
refers to selling a product under the guise of research
* While not illegal, it raises ethical concerns related to invasion of privacy and deception
* It aims to encourage customers to order products or sign up for services.
* While not illegal, it raises ethical concerns related to invasion of privacy and deception
* It aims to encourage customers to order products or sign up for services.
41
New cards
What are marketing processes?
give purpose and direction for all business activities, elements of marketing plan:
* situational analysis – SWOT, product life cycle
* market research
* establishing market objectives
* identifying target markets
* developing marketing strategies
* implementation, monitoring and controlling – developing a financial forecast; comparing actual and planned results, revising the marketing strategy
* situational analysis – SWOT, product life cycle
* market research
* establishing market objectives
* identifying target markets
* developing marketing strategies
* implementation, monitoring and controlling – developing a financial forecast; comparing actual and planned results, revising the marketing strategy
42
New cards
What does situational analysis involve?
provides a precise understanding of a business's current position and where it is heading. It includes conducting a SWOT analysis and the product life cycle
apple:
* ^^Strengths – strong global brand and customer loyalty, varying products, history as a leading innovator, high profitability, broad range of distribution channels, low costs of production^^
* ^^Weaknesses – high price relative to competitors, incompatibility with different operating systems, high dependence on overseas suppliers and outsources, lack of CSR, high R&D costs, quality concerns with outsourcing^^
* ^^Opportunities – expansion overseas to avoid tax, globalisation, growth of new Asian markets, development of new innovation and technologies^^
* ^^Threats – increased competition, short product life cycles in markets, rising pay levels and regulation of labour, strict intellectual property regulations, and external technical defaults (hacks)^^
apple:
* ^^Strengths – strong global brand and customer loyalty, varying products, history as a leading innovator, high profitability, broad range of distribution channels, low costs of production^^
* ^^Weaknesses – high price relative to competitors, incompatibility with different operating systems, high dependence on overseas suppliers and outsources, lack of CSR, high R&D costs, quality concerns with outsourcing^^
* ^^Opportunities – expansion overseas to avoid tax, globalisation, growth of new Asian markets, development of new innovation and technologies^^
* ^^Threats – increased competition, short product life cycles in markets, rising pay levels and regulation of labour, strict intellectual property regulations, and external technical defaults (hacks)^^
43
New cards
What does SWOT analysis do?
allows a business to evaluate its strategic position.
* Strengths & weakness = **internal** business environment, business has control
* Opportunities & threats = **external** business environment, business has little control
* Strengths & weakness = **internal** business environment, business has control
* Opportunities & threats = **external** business environment, business has little control
44
New cards
What are some examples for a SWOT analysis?
\
**Strengths**
* Loyal and skilled employees
* Good reputation with customers and suppliers
**Weaknesses**
* Dissatisfied and incompetent employees
* Poor reputation
**Opportunities**
* New and fast growing markets
* Changes in consumer taste
**Threats**
* Changes in consumer taste
* Increased competition
\
**Strengths**
* Loyal and skilled employees
* Good reputation with customers and suppliers
**Weaknesses**
* Dissatisfied and incompetent employees
* Poor reputation
**Opportunities**
* New and fast growing markets
* Changes in consumer taste
**Threats**
* Changes in consumer taste
* Increased competition
\
45
New cards
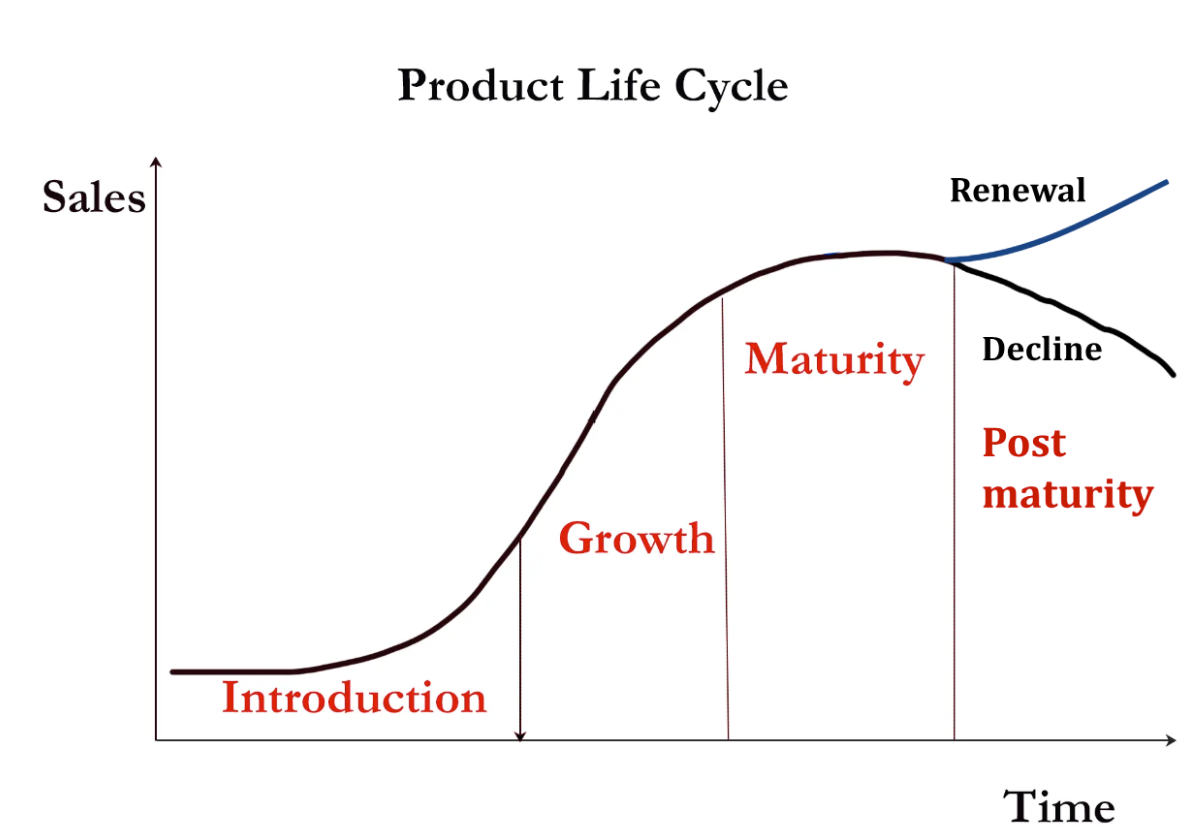
What is the product life cycle?
4 stages a product goes through from its launch on the market to its removal, and its associated levels of sales, volume and market share
* **Establishment/introduction:** new product and little competition, but low sales and difficult to gain market share (requires a high level of promotion to bring awareness)
* **Growth:** sales increase, profits rise, competition grows, high levels of promotion
* **Maturity:** high competition, sales steady, profits may begin to decline
* **Post Maturity:** either decline or renewal
* Decline → sales fall, negative profits, product may stop being made
* Renewal → product is relaunched with increased promotion, increased sales and profits
\
\
* **Establishment/introduction:** new product and little competition, but low sales and difficult to gain market share (requires a high level of promotion to bring awareness)
* **Growth:** sales increase, profits rise, competition grows, high levels of promotion
* **Maturity:** high competition, sales steady, profits may begin to decline
* **Post Maturity:** either decline or renewal
* Decline → sales fall, negative profits, product may stop being made
* Renewal → product is relaunched with increased promotion, increased sales and profits
\
\
46
New cards
What is market research?
the collection and analysis of information to identify customer wants and needs, which helps in making marketing decisions
involves:
* Determining information needs
* Data collection (primary and secondary)
* Data analysis and interpretation
apple:
* ^^Primary research from Apple’s annual reports and internal sources, observation of reviews following release of new products^^
* ^^Secondary research such as sales data and market share data from external sources (stock market, news) provide valuable insight^^
involves:
* Determining information needs
* Data collection (primary and secondary)
* Data analysis and interpretation
apple:
* ^^Primary research from Apple’s annual reports and internal sources, observation of reviews following release of new products^^
* ^^Secondary research such as sales data and market share data from external sources (stock market, news) provide valuable insight^^
47
New cards
How does determining information needs assist in market research?
Businesses need to identify what information is required. The particular info/data to be collected from market research is determined by:
* Identifying market problem → ie how many households in northern NSW would be willing to subscribe to paid television
* Making clear the research purpose
* Planning the research methods and tasks
* Collecting, analysing and interpreting data and reporting findings
* Identifying market problem → ie how many households in northern NSW would be willing to subscribe to paid television
* Making clear the research purpose
* Planning the research methods and tasks
* Collecting, analysing and interpreting data and reporting findings
48
New cards
What are the two types of data used in market research?
primary data and secondary data.
49
New cards
What is primary data?
facts and figures collected from original sources for the purpose of the specific research problem. Methods for collecting primary data include:
* **Observation:** behaviour of customers is watched and analysed
* **Focus groups:** individuals who match the target market are asked specific questions about new or existing products
* **Surveys/questionnaires**: asked a series of questions using methods such as telephone interviews and online surveys
**Experiments:** i.e. market testing → taste testing, researcher compares the results from a test group and a control group
* **Observation:** behaviour of customers is watched and analysed
* **Focus groups:** individuals who match the target market are asked specific questions about new or existing products
* **Surveys/questionnaires**: asked a series of questions using methods such as telephone interviews and online surveys
**Experiments:** i.e. market testing → taste testing, researcher compares the results from a test group and a control group
50
New cards
What is secondary data?
information that already exists, having already been collected for another purpose. Businesses may access secondary data from internal or external sources. May not be as specific to the research purpose as primary data
* **Internal data:** from within the business → financial reports, product performances, budgets, past research
**External data:** from outside of the business, business environment → Australian Bureau of Statistics, specialist research firms, trade associations, consumer databases
* **Internal data:** from within the business → financial reports, product performances, budgets, past research
**External data:** from outside of the business, business environment → Australian Bureau of Statistics, specialist research firms, trade associations, consumer databases
51
New cards
What is the importance of data analysis and interpretation in market research?
final stage of market research, researchers look for relationships between raw data to develop meaning from the facts and figures
* Interpretation: looking at trends/patterns/averages → provides the basis for understanding the data,
* Highlighting relevant information to be used by managers to develop an effective marketing plan and the direction of the business
* Take corrective action/revise marketing strategy when customer wants and satisfaction are not aligned with marketing strategies of the business
* Interpretation: looking at trends/patterns/averages → provides the basis for understanding the data,
* Highlighting relevant information to be used by managers to develop an effective marketing plan and the direction of the business
* Take corrective action/revise marketing strategy when customer wants and satisfaction are not aligned with marketing strategies of the business
52
New cards
What is the SMART approach when establishing market objectives?
Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time.
* It is used to set clear and precise objectives that are measurable, achievable, realistic, and have a specific time frame.
* It is used to set clear and precise objectives that are measurable, achievable, realistic, and have a specific time frame.
53
New cards
What are market objectives?
* increased market share
* expanding product range (mix)
* increased geographical representation
* maximising customer service
* repositioning in the market
apple:
* ^^Increase market share in India by 10% in the next 12 months by securing agreements with Indian government to reduce importing costs^^
* ^^Increase in online sales by 15% through offering discounts^^
* expanding product range (mix)
* increased geographical representation
* maximising customer service
* repositioning in the market
apple:
* ^^Increase market share in India by 10% in the next 12 months by securing agreements with Indian government to reduce importing costs^^
* ^^Increase in online sales by 15% through offering discounts^^
54
New cards
Explain the market objective of increased market share
percentage of total market that the business holds
* Allows business to improve profitability, operate on a greater scale
* Allows business to improve profitability, operate on a greater scale
55
New cards
Explain the market objective of expanding product range (mix)
total range of products offered by the business = product mix
* Product mix depth = similar products
* Product mix width = different products
* Develop a large range of products that satisfy a large range of consumers on the market
\
* Product mix depth = similar products
* Product mix width = different products
* Develop a large range of products that satisfy a large range of consumers on the market
\
56
New cards
Explain the market objective of increased geographical representation
across cities, countries and continents
* Achieved through increasing number of outlets, increasing possibility of access (internet, telephone), expanding overseas, exporting
* Achieved through increasing number of outlets, increasing possibility of access (internet, telephone), expanding overseas, exporting
57
New cards
Explain the market objective of maximising customer service
responding to a customer’s needs, wants and concerns so that they walk away feeling satisfied
* High level of customer service results in improved customer satisfaction → grow customer base and repeat purchases
* High level of customer service results in improved customer satisfaction → grow customer base and repeat purchases
58
New cards
Explain the market objective of maximising customer service
be associated with ‘upper’ or ‘lower’ end of the market
* Jetstar v. qantas
* Jetstar v. qantas
59
New cards
What is a target market and why should a business have one?
specific segment of the total market that the product is aimed at, share similar characteristics; age, income, location etc.
* Marketing resources can be used more effectively → cost-effective and efficient strategies
* Market research data is collected more effectively → business can make comparisons and monitor trends over time
* Better understand consumer buying behaviour
apple:
* ^^Apple uses various strategies to target different segments of the market^^
* ^^Mass market – billboards, websites, social media, TV, ads^^
* ^^Executive – advertisements in business magazines and newspaper^^
* ^^Teens – product placement, social media and celebrity endorsement^^
* Marketing resources can be used more effectively → cost-effective and efficient strategies
* Market research data is collected more effectively → business can make comparisons and monitor trends over time
* Better understand consumer buying behaviour
apple:
* ^^Apple uses various strategies to target different segments of the market^^
* ^^Mass market – billboards, websites, social media, TV, ads^^
* ^^Executive – advertisements in business magazines and newspaper^^
* ^^Teens – product placement, social media and celebrity endorsement^^
60
New cards
What are the three approaches to identifying target markets?
* mass
* large range of customers with common needs/wants
* Mass produce, mass distribute, mass promote
* Bread, milk, eggs
* segment/market segmentation
* total market divided into subgroups, sharing one or more common characteristics
* Demographics: age, gender, job, income, level of education
* Geographics: location (urban, rural, suburbs)
* Sociocultural factors: religion, cultural background
* Psychographics: lifestyle, personality, hobbies
* niche
* narrow target market segment
* unique wants/needs
* large range of customers with common needs/wants
* Mass produce, mass distribute, mass promote
* Bread, milk, eggs
* segment/market segmentation
* total market divided into subgroups, sharing one or more common characteristics
* Demographics: age, gender, job, income, level of education
* Geographics: location (urban, rural, suburbs)
* Sociocultural factors: religion, cultural background
* Psychographics: lifestyle, personality, hobbies
* niche
* narrow target market segment
* unique wants/needs
61
New cards
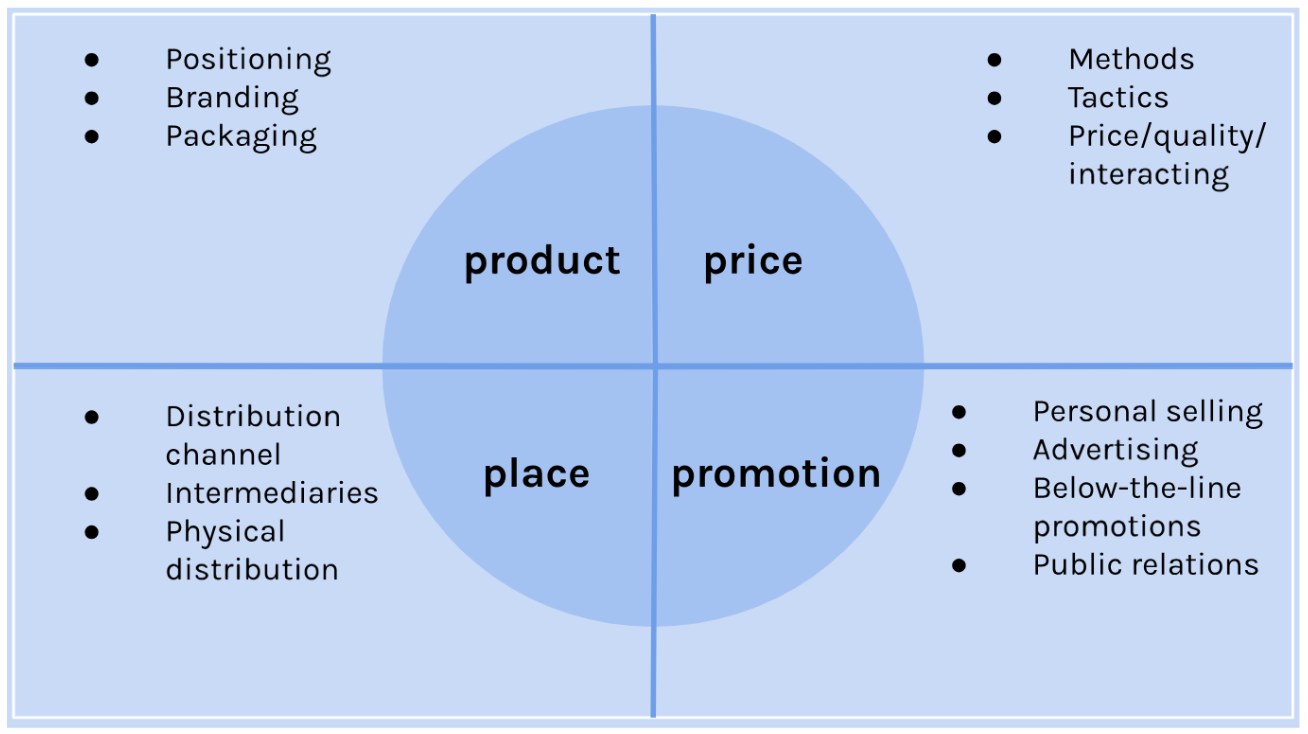
Developing marketing strategies
Marketing strategies are tactics to meet the marketing plan objectives, using the marketing mix (product, place, price, promotion)
* All four elements work together, changing one will alter the others
**product**
Physical good or service → can include packaging, branding, positioning and after-sales service
* Created to satisfy customer needs and wants
**place**
(distribution) how business delivers the product to customers
* Making products available to customers when and where they want them
**price**
Selling price being asked in exchange for a product
* Essential in generating revenue and profit
**promotion**
The strategies used to inform consumers about the product and encourage its purchase
* Generate sales by informing and persuading
apple:
* ^^Large product mix^^
* ^^Variations in price to meet consumer demands^^
* ^^Various promotion strategies for each target market^^
* All four elements work together, changing one will alter the others
**product**
Physical good or service → can include packaging, branding, positioning and after-sales service
* Created to satisfy customer needs and wants
**place**
(distribution) how business delivers the product to customers
* Making products available to customers when and where they want them
**price**
Selling price being asked in exchange for a product
* Essential in generating revenue and profit
**promotion**
The strategies used to inform consumers about the product and encourage its purchase
* Generate sales by informing and persuading
apple:
* ^^Large product mix^^
* ^^Variations in price to meet consumer demands^^
* ^^Various promotion strategies for each target market^^
62
New cards
What is implementing, monitoring and controlling in marketing processes?
**implementation:** is the process of putting marketing strategies into operation
* Involves daily, weekly and monthly decisions that have to be made to make sure the plan is effective
* Talks about how, when and where plan needs to be done
* developing a financial forecast
**monitoring:** is about observing the actual progress of the marketing plan
* Employees gather information and report any changes, problems or opportunities that may emerge
* comparing actual and planned results
**controlling:** is the comparison of planned performance against actual performance
* Taking corrective action if needed to ensure objectives are achieved
* First step is to establish Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
* revising the marketing strategy
apple:
* ^^Apple closely monitor sales of all devices to identify market saturation^^
* ^^Control may require a new model to be launched, new distribution channels, discounts or a new promotion strategy^^
* Involves daily, weekly and monthly decisions that have to be made to make sure the plan is effective
* Talks about how, when and where plan needs to be done
* developing a financial forecast
**monitoring:** is about observing the actual progress of the marketing plan
* Employees gather information and report any changes, problems or opportunities that may emerge
* comparing actual and planned results
**controlling:** is the comparison of planned performance against actual performance
* Taking corrective action if needed to ensure objectives are achieved
* First step is to establish Key Performance Indicator (KPI)
* revising the marketing strategy
apple:
* ^^Apple closely monitor sales of all devices to identify market saturation^^
* ^^Control may require a new model to be launched, new distribution channels, discounts or a new promotion strategy^^
63
New cards
What is the purpose of developing a financial forecast in a market plan?
**implementation of the market plan**
* forecasting sales and staying within budgeted costs
* a budget of expected revenues and costs over a set period of time. Used to help compare actual and planned results.
* **Cost-benefit analysis:** details costs and revenues for each strategy
* Measures the benefits of strategy against the costs associated → enable managers to best allocate marketing resources and take action
* forecasting sales and staying within budgeted costs
* a budget of expected revenues and costs over a set period of time. Used to help compare actual and planned results.
* **Cost-benefit analysis:** details costs and revenues for each strategy
* Measures the benefits of strategy against the costs associated → enable managers to best allocate marketing resources and take action
64
New cards
What is the purpose of comparing actual and planned results in a market plan?
monitoring of the marketing plan
* monitor the success of the marketing strategy through KPI’s:
* **sales analysis:** compares actual sales against budgeted sales
* Sales figures are usually simple and inexpensive to collect and process
* Sales figures don’t reveal exact profit levels for a strategy → no costs are considered (may limit effectiveness)
* **market share analysis:** compares the business’s portion of total market sales to competitors
* Allows for evaluating marketing strategies used by the business against those of competitors (see how effective strategies are)
* **marketing profitability analysis:** when a business splits up total marketing costs into specific activities (advertising, marketing research) and comparing the costs with results to assess the effectiveness of each activity
* See big picture and different components
\
* monitor the success of the marketing strategy through KPI’s:
* **sales analysis:** compares actual sales against budgeted sales
* Sales figures are usually simple and inexpensive to collect and process
* Sales figures don’t reveal exact profit levels for a strategy → no costs are considered (may limit effectiveness)
* **market share analysis:** compares the business’s portion of total market sales to competitors
* Allows for evaluating marketing strategies used by the business against those of competitors (see how effective strategies are)
* **marketing profitability analysis:** when a business splits up total marketing costs into specific activities (advertising, marketing research) and comparing the costs with results to assess the effectiveness of each activity
* See big picture and different components
\
65
New cards
What is the purpose of revising the marketing strategy in a market plan?
improve its effectiveness and ensure that the marketing objectives are met. It involves making changes to the marketing mix elements and tactics based on the evaluation of actual results.
Changes to the marketing mix will occur over time:
**Product:** upgrade, develop new products, delete older products
**Price:** revised in response to changes in the business environment (inflation, boom, budgets, ect.)
**Place:** as product success increases distribution channels will need to expand. Overseas markets may be developed, old markets may decrease due to demographic changes
**Promotion:** different stages if the product life cycle will create different levels of emphasis on promotion
* When the product first hits the market there may be high levels of advertising and publicity
* Investments in promotion will most likely fall in growth and maturity as customers become more familiar with the business and its products.
Changes to the marketing mix will occur over time:
**Product:** upgrade, develop new products, delete older products
**Price:** revised in response to changes in the business environment (inflation, boom, budgets, ect.)
**Place:** as product success increases distribution channels will need to expand. Overseas markets may be developed, old markets may decrease due to demographic changes
**Promotion:** different stages if the product life cycle will create different levels of emphasis on promotion
* When the product first hits the market there may be high levels of advertising and publicity
* Investments in promotion will most likely fall in growth and maturity as customers become more familiar with the business and its products.
66
New cards
What are marketing strategies and what does it include?
plans to meet marketing plan objectives
* market segmentation, product/service differentiation and positioning
* products – goods and/or services
* branding
* packaging
* price including pricing methods – cost, market, competition-based
* pricing strategies – skimming, penetration, loss leaders, price points
* price and quality interaction
* promotion
* elements of the promotion mix – advertising, personal selling and relationship marketing, sales promotions, publicity and public relations
* the communication process – opinion leaders, word of mouth
* place/distribution
* distribution channels
* channel choice – intensive, selective, exclusive
* physical distribution issues – transport, warehousing, inventory
* people, processes and physical evidence
* e-marketing
* global marketing
* global branding
* standardisation
* customisation
* global pricing
* competitive positioning
\
* market segmentation, product/service differentiation and positioning
* products – goods and/or services
* branding
* packaging
* price including pricing methods – cost, market, competition-based
* pricing strategies – skimming, penetration, loss leaders, price points
* price and quality interaction
* promotion
* elements of the promotion mix – advertising, personal selling and relationship marketing, sales promotions, publicity and public relations
* the communication process – opinion leaders, word of mouth
* place/distribution
* distribution channels
* channel choice – intensive, selective, exclusive
* physical distribution issues – transport, warehousing, inventory
* people, processes and physical evidence
* e-marketing
* global marketing
* global branding
* standardisation
* customisation
* global pricing
* competitive positioning
\
67
New cards
What is market segmentation?
* the process of finding groups of customers, within the total market, who share similar characteristics.
* allows a business to focus its marketing strategies on the most suitable part of the market (target market).
apple:
* ^^There is a high demand for smartphones in Asia, and thus, Apple attempt to appeal to the needs and wants of the Asian market^^
* ^^Psychographic – IPhone users view their phone as a status symbol^^
* ^^Behavioural – many people buy IPhones because of the deals and connections with service carriers^^
* ^^Differentiation has become a major challenge for Apple in the smartphone market^^
* ^^Many of the features in recent IPhones have already been endorsed by competitors^^
* ^^Apple positions their products as superior quality, design and hardware^^
* allows a business to focus its marketing strategies on the most suitable part of the market (target market).
apple:
* ^^There is a high demand for smartphones in Asia, and thus, Apple attempt to appeal to the needs and wants of the Asian market^^
* ^^Psychographic – IPhone users view their phone as a status symbol^^
* ^^Behavioural – many people buy IPhones because of the deals and connections with service carriers^^
* ^^Differentiation has become a major challenge for Apple in the smartphone market^^
* ^^Many of the features in recent IPhones have already been endorsed by competitors^^
* ^^Apple positions their products as superior quality, design and hardware^^
68
New cards
What are the segmentation variables commonly used in market segmentation?
\
* Demographic: age, gender, ethnicity, income, education, religion, etc.
* Geographic: country, region, urban/rural, climatic type, landforms
* Psychographic: personality, lifestyle, motivation, values, interests, self-concept
* Behavioral: knowledge of, attitudes towards, convenience of use, and/or product benefits.
* Demographic: age, gender, ethnicity, income, education, religion, etc.
* Geographic: country, region, urban/rural, climatic type, landforms
* Psychographic: personality, lifestyle, motivation, values, interests, self-concept
* Behavioral: knowledge of, attitudes towards, convenience of use, and/or product benefits.
69
New cards
What is product/service differentiation?
* refers to the perception of a difference in a product or service compared to its competitors, making it stand out.
* businesses can implement marketing strategies such as increased price because they are offering something unique.
* businesses can implement marketing strategies such as increased price because they are offering something unique.
70
New cards
What are some ways a business can differentiate its product?
product differentiation features can include quality, packaging, customer service, distribution, and value for money.
71
New cards
What is product positioning?
* developing an image or identity for a product or brand that distinguishes it from its competitors
* how the target market views the business and its products
* factors that can influence positioning include price, quality, luxury, and safety.
* how the target market views the business and its products
* factors that can influence positioning include price, quality, luxury, and safety.
72
New cards
marketing strategies 4P’s graphic
73
New cards
Marketing strategies: Product
good or service with the aim of satisfying a customer’s need or want.
* **Tangible:** physical objects (goods)
* **Intangible:** can’t be touched (service)
Most products are made up of both tangible and intangible benefits → tangible: product itself, intangible: friendly service
\
involves
* branding
* packaging
apple:
* ^^Focus on quality, design and appearance^^
* ^^Unique operating system^^
* ^^A plethora of apps available for purchase/download^^
* ^^Location and voice recognition^^
* ^^Strong brand image and highly recognisable logo^^
* ^^Package suggestive of quality^^
* **Tangible:** physical objects (goods)
* **Intangible:** can’t be touched (service)
Most products are made up of both tangible and intangible benefits → tangible: product itself, intangible: friendly service
\
involves
* branding
* packaging
apple:
* ^^Focus on quality, design and appearance^^
* ^^Unique operating system^^
* ^^A plethora of apps available for purchase/download^^
* ^^Location and voice recognition^^
* ^^Strong brand image and highly recognisable logo^^
* ^^Package suggestive of quality^^
74
New cards
What is branding?
the name or reputation a product/service acquires over time, distinguishing it from competitors and creating recognition and loyalty among customers.
75
New cards
How does branding help customers?
\
* Identifying products they like so they can continue to purchase
* Evaluate quality → purchasing from well-known, trusted brands
* Reduced level of perceived risk (same as above)
* Psychological reward → purchasing prestige brands
* Identifying products they like so they can continue to purchase
* Evaluate quality → purchasing from well-known, trusted brands
* Reduced level of perceived risk (same as above)
* Psychological reward → purchasing prestige brands
76
New cards
How does branding help businesses?
* Familiarity → repeat sales, easily introduce new products due to existing customer base
* Differentiation
* Brand loyalty
* Differentiation
* Brand loyalty
77
New cards
What is packaging and its function?
involves the development of a container and the graphic design of a product. Well-designed packaging can give a positive impression and encourage first-time buyers
* Protection
* Attracts customer attention → bright colours, slogan
* Convenience → transportation, storage and use (juice poppers come with straws)
* Protection
* Attracts customer attention → bright colours, slogan
* Convenience → transportation, storage and use (juice poppers come with straws)
78
New cards
What is labelling?
the part of the product/its package that provides important information
**Includes:**
* Ingredients
* Use-by date
* Country of origin
* Package size
* Nutritional info
They can encourage proper use of the product, and promote other products
\
**Includes:**
* Ingredients
* Use-by date
* Country of origin
* Package size
* Nutritional info
They can encourage proper use of the product, and promote other products
\
79
New cards
Marketing strategies: Price
* amount of money a business charges for a product, amount consumers are willing to pay
* generally reflects the costs of production, for services reflects level of knowledge/expertise
* has the ability to be adjusted quickly in response to competitor actions/changes in the market
\
involves:
* pricing methods
* pricing strategies
* price and quality interaction
apple:
* ^^Extensive use of price skimming strategy^^
* ^^When a model is upgraded, the older model price is reduced to be more competitive (competition based pricing)^^
* ^^Premium pricing is linked with all Apple products^^
* ^^Large focus on research and development^^
* generally reflects the costs of production, for services reflects level of knowledge/expertise
* has the ability to be adjusted quickly in response to competitor actions/changes in the market
\
involves:
* pricing methods
* pricing strategies
* price and quality interaction
apple:
* ^^Extensive use of price skimming strategy^^
* ^^When a model is upgraded, the older model price is reduced to be more competitive (competition based pricing)^^
* ^^Premium pricing is linked with all Apple products^^
* ^^Large focus on research and development^^
80
New cards
What are the three pricing methods?
* cost-based
* price = cost + markup
* determine cost of production, add markup for profit
* market-based
* set following level of supply and demand
* demand greater than supply → price increases
* supply greater than demand → price falls
* competition-based
* set based on competitors prices
* below → break into new markets
* equal → avoids risk of price competition, compete on features e.g. quality
* above → superior image, status conscious consumers
* price = cost + markup
* determine cost of production, add markup for profit
* market-based
* set following level of supply and demand
* demand greater than supply → price increases
* supply greater than demand → price falls
* competition-based
* set based on competitors prices
* below → break into new markets
* equal → avoids risk of price competition, compete on features e.g. quality
* above → superior image, status conscious consumers
81
New cards
What are the pricing strategies?
used once base price is set
* skimming
* penetration
* loss leaders
* price points
* skimming
* penetration
* loss leaders
* price points
82
New cards
What is price skimming?
charge high price for product during the introduction stage of its lifecycle
* Likely to be used if product is unique/new product with unknown demand
* Customers willing to pay any price to purchase
\
\+ gain market share, recover costs quickly
\- may backfire, if price lowered customers may be angry
* Likely to be used if product is unique/new product with unknown demand
* Customers willing to pay any price to purchase
\
\+ gain market share, recover costs quickly
\- may backfire, if price lowered customers may be angry
83
New cards
What is price penetration?
business charges lowest price possible when product first hits the market
* Used to penetrate market and gain market share quickly
\
\+ discourage competitors, can increase price once established
\- if too low harder to cover costs and make a profit
* Used to penetrate market and gain market share quickly
\
\+ discourage competitors, can increase price once established
\- if too low harder to cover costs and make a profit
84
New cards
What is loss leaders?
business sells their product at, or below their cost price
* Attracts customers to the business to entice them to purchase other goods/services
* Business makes up for loss by selling its other higher-priced items
\
\+ positioned as high value, can be used for overstock
\- if done incorrectly can lose money
* Attracts customers to the business to entice them to purchase other goods/services
* Business makes up for loss by selling its other higher-priced items
\
\+ positioned as high value, can be used for overstock
\- if done incorrectly can lose money
85
New cards
What are price points?
products are sold at predetermined prices
* Different product lines with different prices
* Psychological: based on customer’s perception of value for their money (e.g. paperback costs $15 and hardback costs $25)
\
\+ customers encouraged to trade up to next price point
\- may restrict flexibility of pricing
* Different product lines with different prices
* Psychological: based on customer’s perception of value for their money (e.g. paperback costs $15 and hardback costs $25)
\
\+ customers encouraged to trade up to next price point
\- may restrict flexibility of pricing
86
New cards
How do price and quality interact?
one of the biggest factors influencing price is quality. Products higher in quality are normally sold for higher prices and vice versa as higher quality products usually require higher costs
* Low priced products may be perceived as cheap
* High priced products may be perceived as prestigious and high quality (prestige pricing)
* Low priced products may be perceived as cheap
* High priced products may be perceived as prestigious and high quality (prestige pricing)
87
New cards
Marketing Strategies: Promotion
involves the activities used to inform, persuade and remind current and potential customers about its products
\
includes:
* elements of the promotion mix
* the communications process
apple:
* ^^media is used to highly publicise the release of a new product^^
* ^^Promotion has traditionally focused on innovation, quality and design of Apple products^^
* ^^Shot on IPhone campaign^^
* ^^Extensive use of social media advertising^^
* ^^Celebrity endorsement (U2)^^
* ^^High care to ensure positive public relations and publicity remain in place^^
\
includes:
* elements of the promotion mix
* the communications process
apple:
* ^^media is used to highly publicise the release of a new product^^
* ^^Promotion has traditionally focused on innovation, quality and design of Apple products^^
* ^^Shot on IPhone campaign^^
* ^^Extensive use of social media advertising^^
* ^^Celebrity endorsement (U2)^^
* ^^High care to ensure positive public relations and publicity remain in place^^
88
New cards
What are the reasons for promotion?
\
* Informing customers
* Develop a products image
* Persuade customers
* Increase sales
* Informing customers
* Develop a products image
* Persuade customers
* Increase sales
89
New cards
What are the elements of the promotion mix?
* advertising
* personal selling
* relationship marketing
* sales promotions
* publicity and public relations
* personal selling
* relationship marketing
* sales promotions
* publicity and public relations
90
New cards
What is advertising?
paid, non-personal message that’s communicated to mass audience through a mass medium:
* Mass marketing: television, radio, newspapers
* Direct marketing: catalogue mailed to individual homes
* Telemarketing: using phone to personally contact the customer
* E-marketing: using internet to deliver advertising messages
* Social media advertising: simply using social media to advertise
* Billboards: large signs placed in strategic locations, usually high traffic
\
dependant on variables such as: type of product and positioning, size of target markets, marketing budget, cost of advertising, products position in the life cycle.
* Pros: flexible
* Cons: expensive
* Mass marketing: television, radio, newspapers
* Direct marketing: catalogue mailed to individual homes
* Telemarketing: using phone to personally contact the customer
* E-marketing: using internet to deliver advertising messages
* Social media advertising: simply using social media to advertise
* Billboards: large signs placed in strategic locations, usually high traffic
\
dependant on variables such as: type of product and positioning, size of target markets, marketing budget, cost of advertising, products position in the life cycle.
* Pros: flexible
* Cons: expensive
91
New cards
What is personal selling?
aka face-to-face selling, involves the activities of a sales consultant directed to a customer in an attempt to make a sale
**advantages:**
* Messages can be modified to suit individual customers
* Individualised assistance to customers → create long-term relationship and repeat sales
* Sales consultants can provide after sales service to product features, installations etc.
**disadvantages:**
* Expensive as it requires more employees
* Employees need the skills to interact and connect with customers
* Face-to-face communication is difficult with customers who live further away
**advantages:**
* Messages can be modified to suit individual customers
* Individualised assistance to customers → create long-term relationship and repeat sales
* Sales consultants can provide after sales service to product features, installations etc.
**disadvantages:**
* Expensive as it requires more employees
* Employees need the skills to interact and connect with customers
* Face-to-face communication is difficult with customers who live further away
92
New cards
What is relationship marketing?
involves building strong relationships with individual customers that are long term and cost effective → rewarding customers who make frequent purchases so they keep coming back. E.g. loyalty cards and reward programs
* Pros: by knowing customers → meet their individual needs and wants, this gains competitive advantage and brand loyalty
* Cons: time-consuming, requires ongoing effort
* Pros: by knowing customers → meet their individual needs and wants, this gains competitive advantage and brand loyalty
* Cons: time-consuming, requires ongoing effort
93
New cards
What are sales promotions?
Short term attempt to get customers to buy more of a product e.g. competitions, samples, BOGOF etc.
* Pros: attracts new customers, boosts sales in short-term → can lead to repeat purchases if customer likes product
* Cons: doesn’t work for every product (luxury items), if overused → customers get used to reduced price and may be hesitant to purchase at full price
* Pros: attracts new customers, boosts sales in short-term → can lead to repeat purchases if customer likes product
* Cons: doesn’t work for every product (luxury items), if overused → customers get used to reduced price and may be hesitant to purchase at full price
94
New cards
What is publicity and public relations?
**publicity:** any free news coverage about a business or its products → boost business profile without spending any money. __Unplanned__
**Public Relations (PR)**: activities aimed at creating and maintaining relations with a business and its customers. Planned
**Public Relations (PR)**: activities aimed at creating and maintaining relations with a business and its customers. Planned
95
New cards
What is the communication process?
The way marketing managers make connections and express messages to their customers. Often customers are more willing to buy a product/service if the message is communicated via a respected and trusted channel such as:
* opinion leaders
* word of mouth
* opinion leaders
* word of mouth
96
New cards
What are opinion leaders?
a person with the ability to influence others
* Their opinions and advice are highly respected and can make customers more motivated to make certain purchases.
* Celebrities are often used as opinion leaders to endorse products
* Their opinions and advice are highly respected and can make customers more motivated to make certain purchases.
* Celebrities are often used as opinion leaders to endorse products
97
New cards
What is word of mouth?
when people influence each other through conversations
* Advice and recommendations from friends and family are highly valued and important when choosing between competing products.
* Social media is an increasingly common way to spread word of mouth
* Cannot be controlled directly by business
Buzz marketing: attempt by business to control the communication process → people are paid to recommend products in an unassuming way; recommend product loud enough for potential customers to overhear
\
* Advice and recommendations from friends and family are highly valued and important when choosing between competing products.
* Social media is an increasingly common way to spread word of mouth
* Cannot be controlled directly by business
Buzz marketing: attempt by business to control the communication process → people are paid to recommend products in an unassuming way; recommend product loud enough for potential customers to overhear
\
98
New cards
Marketing Strategies: Place
product available to customers at the time and location they want to purchase them → geographic representation and process of getting product to target market
includes:
* distribution channels
* channel choice
* physical distribution issues
apple:
* ^^Distribution through online sales, Apple stores, mobile carriers and retail mobile stores^^
* ^^2017 – 498 retail stores in 22 countries^^
* ^^30% of sales made though indirect channels (retailers)^^
* ^^sales to educational institutions and government is made through direct selling^^
* ^^Selective distribution^^
* ^^Producer to retailer to consumer (channel choice)^^
includes:
* distribution channels
* channel choice
* physical distribution issues
apple:
* ^^Distribution through online sales, Apple stores, mobile carriers and retail mobile stores^^
* ^^2017 – 498 retail stores in 22 countries^^
* ^^30% of sales made though indirect channels (retailers)^^
* ^^sales to educational institutions and government is made through direct selling^^
* ^^Selective distribution^^
* ^^Producer to retailer to consumer (channel choice)^^
99
New cards
What are distribution channels?
path product takes in order to reach the market → usually involves a number of intermediaries: wholesaler, broker, agent or retailers
100
New cards
What are the three distribution channels?
* producer to consumer
* producer to retailer to consumer
* producer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer
* producer to retailer to consumer
* producer to wholesaler to retailer to consumer