Biology A-Level (Edexcel A) T2.7.19 - Genetic Screening and CF
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
what causes CF
mutation in the gene coding for CFTR protein . if CFTR protein is malfunctioning or absent chloride ions can’t diffuse out of the cell and into the mucas and water moves in to the cell by osmosis therefore making muscas thicker
CF on gas exchange
cillia can’t move thicker mucus which means the mucus blocks the trachea meaning the diameter of the lumen of the trachea reduces which means ventilation is reduced and less oxygen enters the lungs.the O2 conc gradient between alveoli and capillaries reduces and according to ficks law of diffusion O2 diffuses from alveoli to blood at slower rate, therefore less o2 for aerobic respiration
CF on lung infections
thicker mucus can’t be moved by cilia so bacteria gets trapped inside and it starts to reproduce due to the ideal conditions of the mucus and cause infections
CF on digestion
due to thicker build up of mucus the pancreatic duct becomes blocked therefore less enzymes are relased into the small intestines therefore less enzyme substrate complexes are formed and large molecules like lipid and starch are not broken down to small molecules
CF on reproduction
if the sperm ducts become blocked less sperm is released for ejaculation. Eventually the sperm ducts may disappear resulting in infertility. In females the thick mucus plugs the cervix which stp the sperm from reaching the ovum in the oviduct. Therefore less chance of fertilisation
DEFINE: prenatal
prenatal means before birth
EXPLAIN: the importance of prenatal and genetic screening
prenatal screening allows parents to prepare for a child with the disease or decide to have an abortion
(theses tests cannot cure genetic diseases)
genetic screening can also help identify carriers of the disease
DEFINE: false positive
a false positive occurs when a genetic test has wrongly detetcted a faulty allele/chromosome
DEFINE: false negative
a false negative occurs when a genetic test has failed to detect a faulty allele/chromosome
LIST: the 4 main methods of genetic screening
1) Amniocentesis
2) Chronic Villus Sampling (CVS)
3) Non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
4) Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
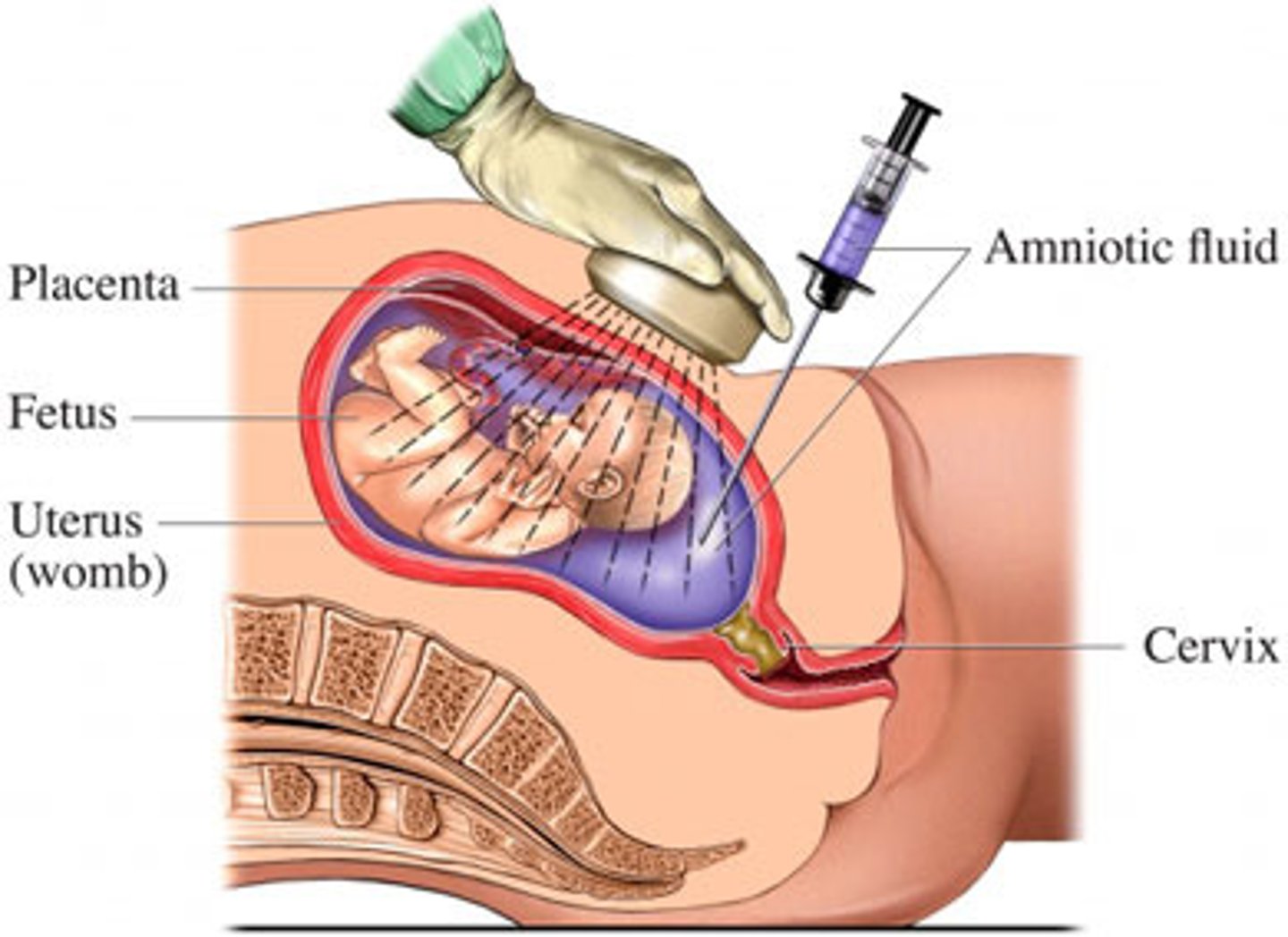
EXPLAIN: how amniocentesis works
A needle is inserted into amniotic fluid to collect foetal cells. (This occurs between 15-17 weeks of pregnancy)
EXPLAIN: how chorionic villus sampling (CVS) works
A small smaple of placental tissue (includes cells of embryo/foetus) is removed from the abdomen or the vagina
(this occurs between 8-12 weeks)
EXPLAIN: how non-invasive prenatal diagnosis works
DNA fragments in the mother's blood plasma during pregnancy is analysed
Most cell free DNA comes from the mother but a small amount (10%-20%) of cell free DNA comes from the embryo
cell free foetal DNA becomes detetctable between 4-5 weeks of pregnancy; however, levels are too low to be analysed so smaples are collected 7-9 weeks of pregnancy
EXPLAIN: how preimplantation genetic diagnosis works
couples must undergo IVF in order to create embryos that can be tested (before transfer to the uterus)
when early embryos grow in culture (and has roughly 8 cells) a cell is removed for genetic testing. The DNA can be analysed and the results oft he genetic testing are used to decide whether to place the embryo back into the uterus
only healthy embryos are placed back inside the mother
DESCRIBE: advantages and disadvantages of amniocentesis works
ADVANTAGES:
cheap
low risk of miscarriage
DISADVANTAGES:
still a risk of miscarriage
time consuming
5% risk of false positive
happens later in pregnancy so abortion may be difficult
DESCRIBE: advantages and disadvantages of CVS
ADVANTAGES:
happens early
no need to wait for amniotic fluid to develop
DISADVANTAGES
higher risk of miscarriage than amniocentesis
limited research on risks
DESCRIBE: advantages and disadvantages of non-invasive prenatal diagnosis
ADVANTAGES:
used for multiple diagnostic tests
no risk of miscarriage
only requires a blood sample
DISADVANTAGES:
can only be used to diagnose a limited number of single gene disorders
DESCRIBE: advantages and disadvantages of preimplantation genetic diagnosis
ADVANTAGES:
avoids need for possible abortion
only healthy embryos are placed back inside the mother
DISADVANTAGES
IVF is expensive and stressful
low sucess rates
LIST: factors to be considered when deciding whether to go ahead with prenatal screening (7 factors)
1) risk of miscarriage/ harm to foetus from testing
2) religious beleifs - right to life of the foetus
3) potential abortion if diagnosis is positive
4) cost of raising a baby with genetic diseases
( 5) mental/emotional issues surrounding birth of disable baby
6) choosing to not become a parent
7) dealing with risk/ consequqnces of false negatives and false positives )