[DEVC 154] Lesson 3A
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Scholarly communication
Defined as a system through which research and other scholarly writings are: created, evaluated for quality, disseminated to scholarly community, and preserved for future use
Generate
Review
Disseminate
Acquire
Preserve
Discover
Access
Assimilate
What is the scholarly communication lifecycle?
Scholarly Communication
From the Rider University Libraries: It is a process by which academics, students, researchers conduct research; collect information from that research into a publishable format (print or electronic); have their research reviewed; and distributed.
Data Collection, Research, and Analysis
Authoring
Peer Review
Rights Management
Publication Model
Discovery
Collaboration and Discoverability
What is the scholarly communication lifecycle from University of Washington Libraries for Open Access Week (2011) Exhibit?
Scholars/researchers/scientists as authors
Publishers
Libraries
HEIs
Research funding agencies
Who are the major stakeholders of scholarly communication?
Knowledge generation and scientific progress
What are the two main goals of this level?
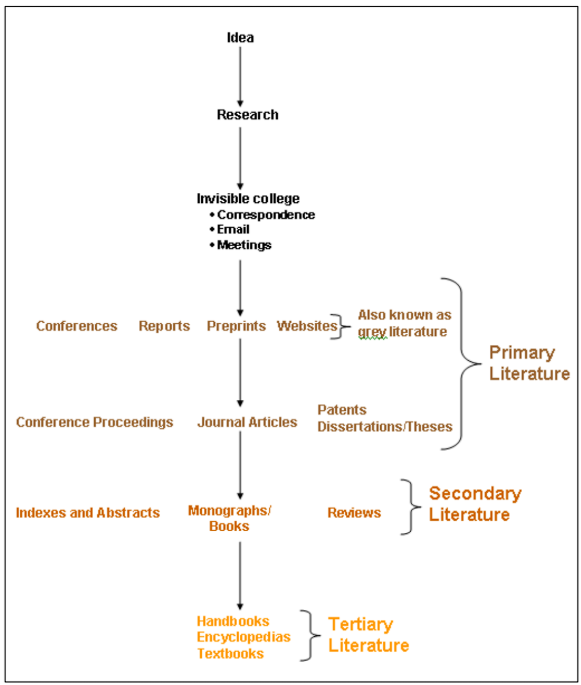
Flow of Scientific Information, Jim Parrott
What is this diagram and who is its proponent?
quantitative
qualitative
pragmatic
advocacy/participatory
What are the four major categories of research?
quantitative
The major category of research where data are collected and converted into numerical form; statistical calculations and variables are involved.
Qualitative
The major category of research where data are recorded and analyzed in an attempt to uncover deeper meaning and significance of human behavior and experience; it does not aim to get information generalizable to larger groups.
Qualitative
The major category of research where researchers tend to adopt an inductive approach, which means they develop a theory or look for a pattern of meaning based on data collected. This involves a move from the specific to the general and is sometimes called a bottom-up approach.
Pragmatic approach
The major category of research where a method best suited to research problem is used; in here, different approaches can be complementary.
Pragmatic approach
The major category of research where researchers have the freedom to use any of the methods, techniques and procedures typically associated with quantitative or qualitative research. They may also use different techniques at the same time or one after the other.
Advocacy/ participatory
The major category of research where research directly or indirectly results in some kind of reform; involves group being studied, preferably at all stages.
Examining a research problem/topic
Identifying a specific research topic
Conceptualizing
Choosing appropriate research methods/tools
Conducting research
Analyzing data
Writing final paper
Publishing
What is the generic model of the research process?