DNA Extraction & Micropippette
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms

model organism
a non-human species that is used in laboratory to help scientists understand biological processes
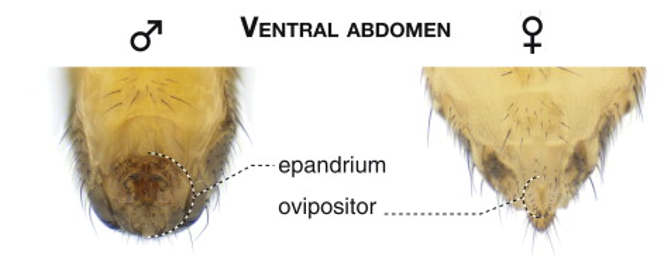
A way to distinguish sex among flies
Presence of epandium (males)
Presence of ovipositor (females)

Micropipettes
dispense small volumes of liquids
What is Micropipette labeled as?
Volumes in uL
usually 1/10th max in volume
Types: P2, P10, P20, P100, P200, P1000
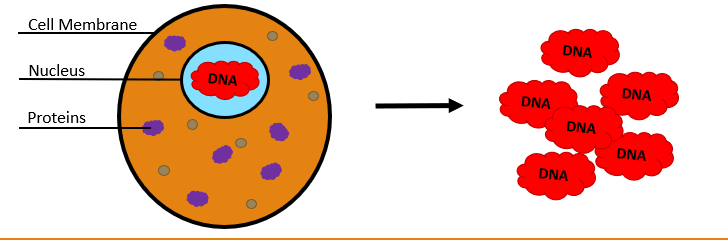
DNA Extraction
A process to isolate DNA from cells and proteins
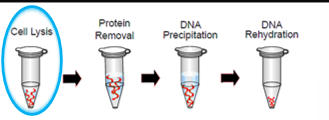
DNA extraction Step 1: Cell Lysis
breaks up the cells in DNA
Components of Lysis Buffer during DNA extraction
SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate)
EDTA (metal chelation)
NaCl+ (positively-charged salt)
Tris-HCl (pH 8.0)
SDS
Detergent. Disrupts the cell membranes & denatures proteins
EDTA (Mg2+)
Inhibits DNA-degrading enzymes such as DNase
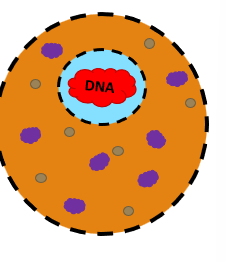
NaCl( positively charged salt)
Creates a protective layer around the negatively charged DNA (blue)
Tris-HCl
a pH buffer to make it pH (8.0)
DNA extraction Step 2: Protein Removal
The bulk of the cell protein needs to be removed
KOAc: concentrated salt solution. K+ binds and precipitates out SDS-bound proteins (Lysis Buffer) and other debris.
Cold temp = reduce solubility = increase cloudiness
ALL PROTEIN will be in the pellet

How is separation achieved?
By Centrifuging
spins samples at 1,000 rpm. Forces the precipitate to form a solid pellet (debris pellet)
TUBES MUST BE EQUALLY SPACED
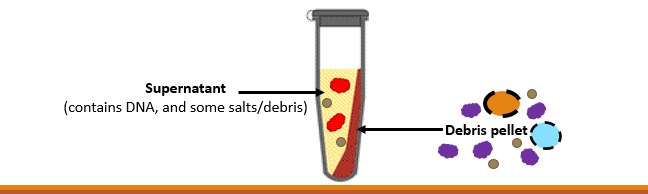
After that, the supernatant (containing the DNA and some salt/debris) must be transferred to a fresh tube

Vortex
mixes small vials of liquids in a rapid motion for 10-15 seconds

Spin (mini centrifuge)
spins down PCR tubes for 10-15 seconds
DNA Extraction Step 3: Alcohol precipitation
Isolate DNA from solution containing salt/debris
Isopropanol: DNA is insoluble in this; it will form a precipitate
Ethanol: salts/organic molecules are soluble in this; cleans up contaminants from precipitate
DNA Extraction Step 4: Rehydrate Pellet
Purified DNA must be rehydrated with a buffered solution
Why? It will be used for PCR and gel electrophoresis
DNA is measured in nanograms (ng)