9618 AS Computer Science
1/282
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
283 Terms
What is Hexadecimal?
Base 16
Usages of Hexadecimal?
In MAC and IP Addresses, Represent Colours in HTML, In error messages and memory dumps
What are the Binary prefixes?
Kibi (Ki) = 1024 bytes, Mebi (Mi) = 1024 KiB, Gibi (Gi) = 1024 MiB, Tebi (Ti) = 1024 GiB
What are the Denary prefixes?
Kilo (k) = 1000 bytes, Mega (M) = 1000 Kb, Giga (G) = 1000 Mb, Tera (T) = 1000 Gb
What is Binary Coded Decimal (BCD)?
Number system that uses 4 bits to represent each denary digit.
Usages of Binary Coded Decimal (BCD)?
Used to represent numbers in calculators and counters, Allows you to accurately measure fractions, Electronically code decimal numbers
Features of ASCII?
American Standard Code for Information Interchange, 128 characters, Only from the English language, 7 bits
Features of Extended ASCII?
256 characters, Most European langauges including English, 8 bits
Features of Unicode?
10,000 characters, variety of languages, current standard, 32 bits
What is a Pixel?
The smallest unit of area in an image representing a single colour
What is a File header
Stores data about the image, Size, Resolution, Colour depth, Number of colours
What is Image resolution?
Number of pixels wide by the number of pixels high
What is Colour depth?
Number of bits used to represent the colours in a pixel
What is Bit depth?
Number of bits used to represent the smallest unit in an image file (or sound file); The larger the bit depth, the better the quality of the sound or colour image.
How do you calculate File size?
File size = (Width x Height x Bit depth (in bytes)) + Header bytes
What are features of Lossy image compression?
Reducing bit depth, fewer bits used to store each pixel in an image, Reducing colour palette, less colours and therefore less bits per pixel, Reduced image resolution, fewer pixels per unit area so less space is needed
How is Lossy image compresion done?
Using Run Length Encoding (RLE), - Looks for a series of consecutive pixels that store the same colour, Indexes the colour and the number of times it occurs.
How Lossless compression is done on sound files?
Reduce amplitude to only the range used, limited amplitudes mean fewer bits per sample, Run-length-encoding, Where consecutive sounds are the same record the binary value of the sound and number of times it repeats, Record the changes instead of the actual sounds
What are Vector images?
Images using 2D points to describe lines and curves and their properties; grouped to form geometric shapes
Features of Vector images?
Can be scaled without losing quality as it gets recalculated., Relatively small file size, stores equations not pixels.
What is Sampling resolution?
The number of bits used to store each sample. Larger values mean more accurate reconstruction of sound but higher file size (more bits used to store the sound)
What is Sampling rate?
The number of samples taken per unit time
How to calculate Sound size?
Sound size = sampling rate x sampling resolution x time
What is Analogue data?
Continous real-world data
What is Digital data?
Discrete electrical data
What is Compression
The reduction of file size
Advantages of Compression
Reduces transfer time, Saves bandwidth, Saves storage space
What are the two methods of Compression?
Lossy and Lossless
What is Lossy compression?
File size compression where original data is lost and cannot be recovered
What is Lossless compression?
File size compression where original data is not lost and can be recovered
Advantages of Lossless compression?
Maintains quality, Useful when all original data needs to be recovered
Pros and cons of Lossy compression?
Pros: Creates a much smaller file size than lossless, Useful when significant size reduction is needed; Cons: Significant loss in quality
What is a Network?
Devices that are inter-connected and communicate between each other.
Features of a Network?
Easily transfer data, like files between devices, Devices can share resources, such as hardware, printers, or same software, Store data in drives connected to the network
What are the two main types of Networks?
Local Are Network (LAN) and Wider Area Network (WAN)
Features of LAN?
Small geographical region, Private ownership, Wi-Fi, Copper, and Coaxial mediums, High speed, Low congestion
Features of WAN?
Large geographical region, Private/Public ownership, PSTN or satellite mediums, Low speed, High congestion
What is a Client server?
The server stores all the data and performs the tasks requested by the client
client (sends request) --> server (returns results) --> client (receives results)
e.g:
web pages
emails
company storing files on central server
print/file/email server
Pros and cons of Client-server model
Pros:
- Increases security as only the server has higher privileges
- Increased performance of individuals computers
- Central management of data and software so there is always a backup and each device has consistent software
Cons:
- All operations depend on the main server, if server is down then the others are down too
- Difficult to scale and expensive
- Speed of networks decreases exponentially based on the number of devices connected.
What is a Thin client?
Provides input to the server and receives an output from the server
What is a Thick client?
Carriest out some processing on its own /bbefore\b//rafter\r /bsending\b//rreceiving\r data to the server
What is Peer-to-peer?
All devices on the netwrok are of equal status, each computer has access to all the data and resources of another device, thus each device is responsible for its own safety.
Pros and cons of Peer-to-peer
Pros:
- Setup cost is cheap
- Each device has complete access to any device on t he network
- No central server dependancy
Cons:
- Reduced security, vulnerable to viruses from other devices on the network
- Reduced performance, other devices might also be attempting to access data on a device.
- No central backup of files, if one computer has data and loses it, they all lose access to it.
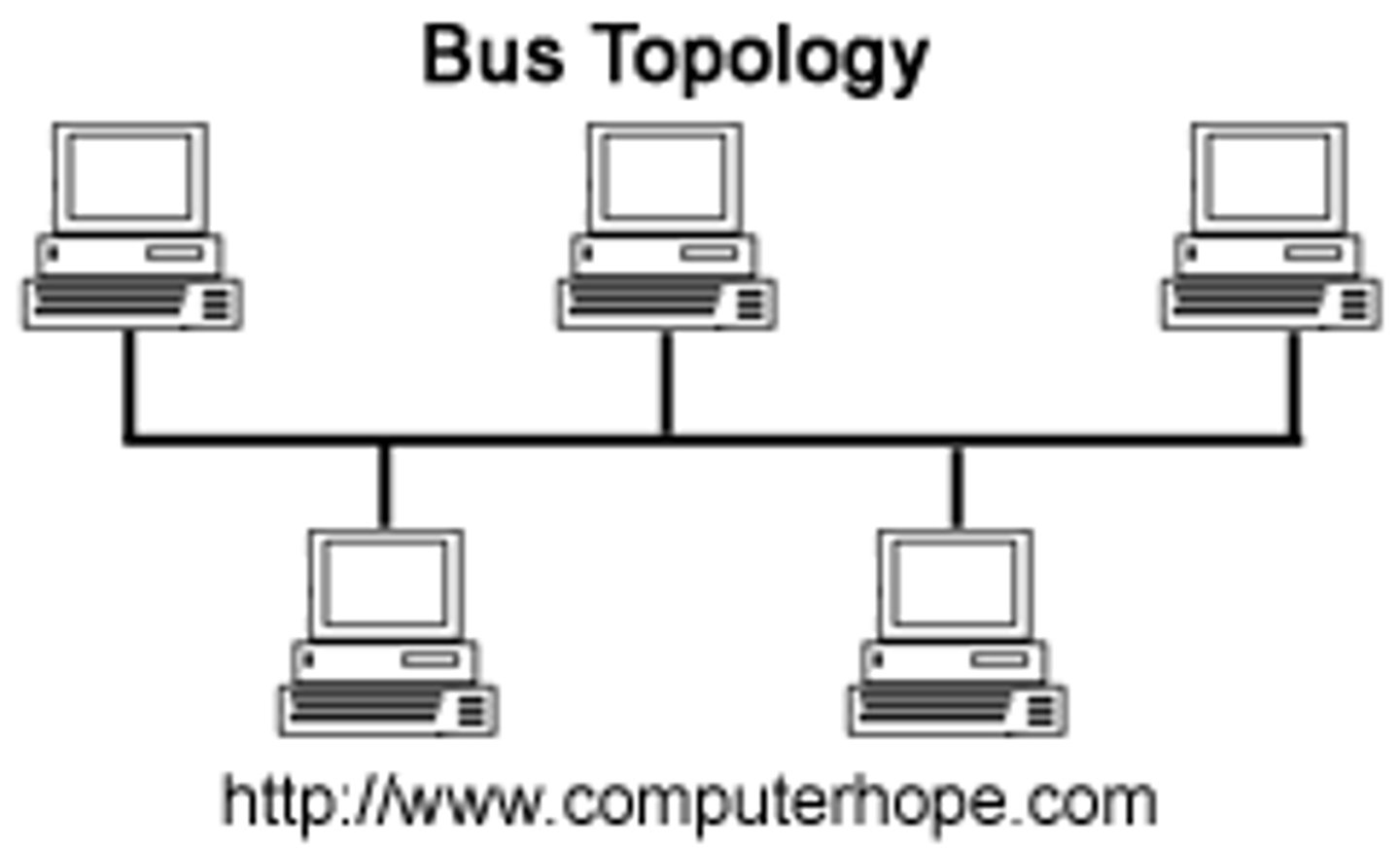
What is a Bus topology?
All devices connected to a central /cable\, has terminators at the end
- Only onecommunication can take place at a time
- Data terminators are needed to prevent a network crash from data collision
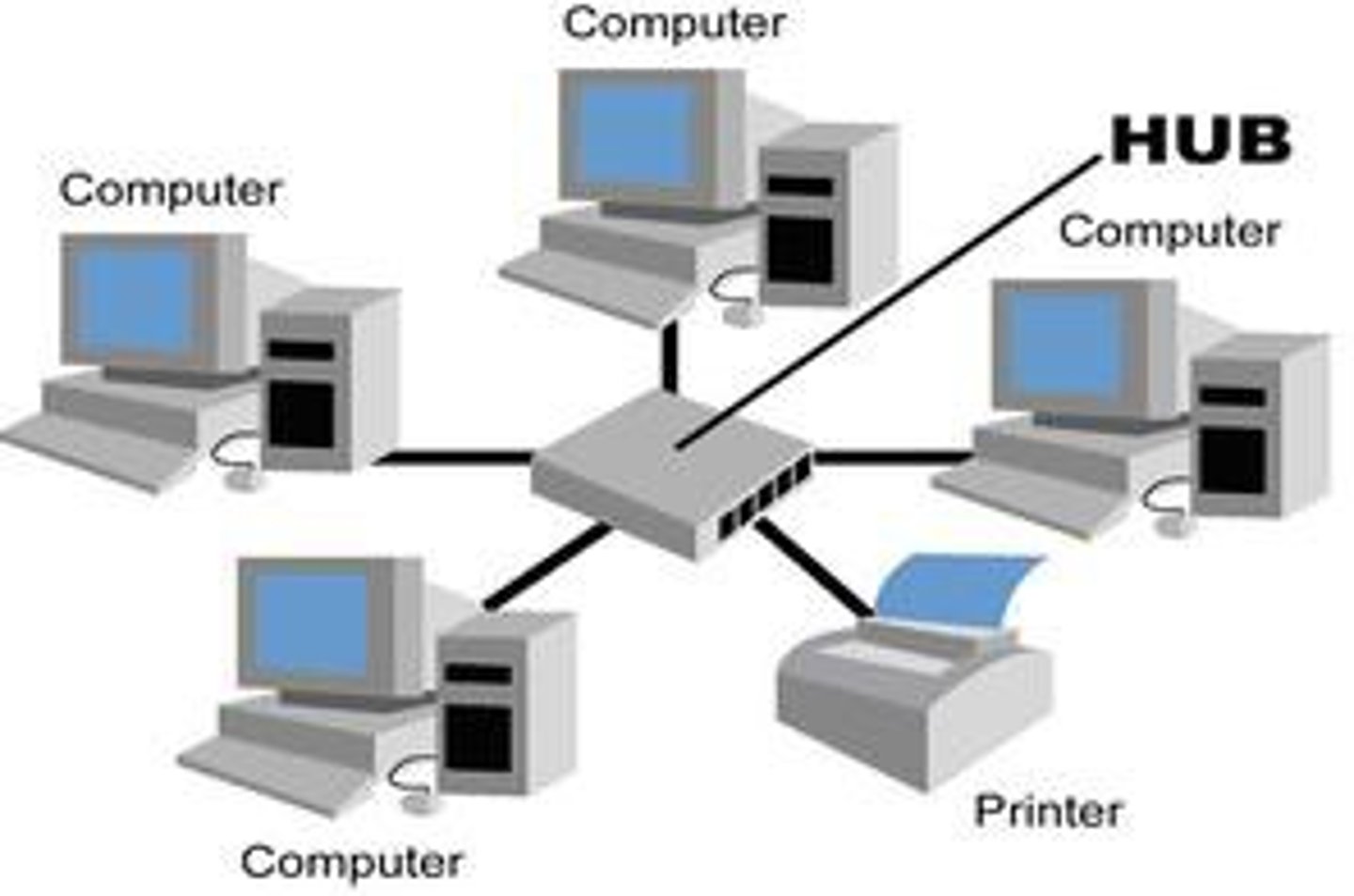
What is a Star topology?
All devices connected to a switch / router independantly
- No collisions can occur and data can be sent out simultaneously
- You can use hub instead of switch but its slower
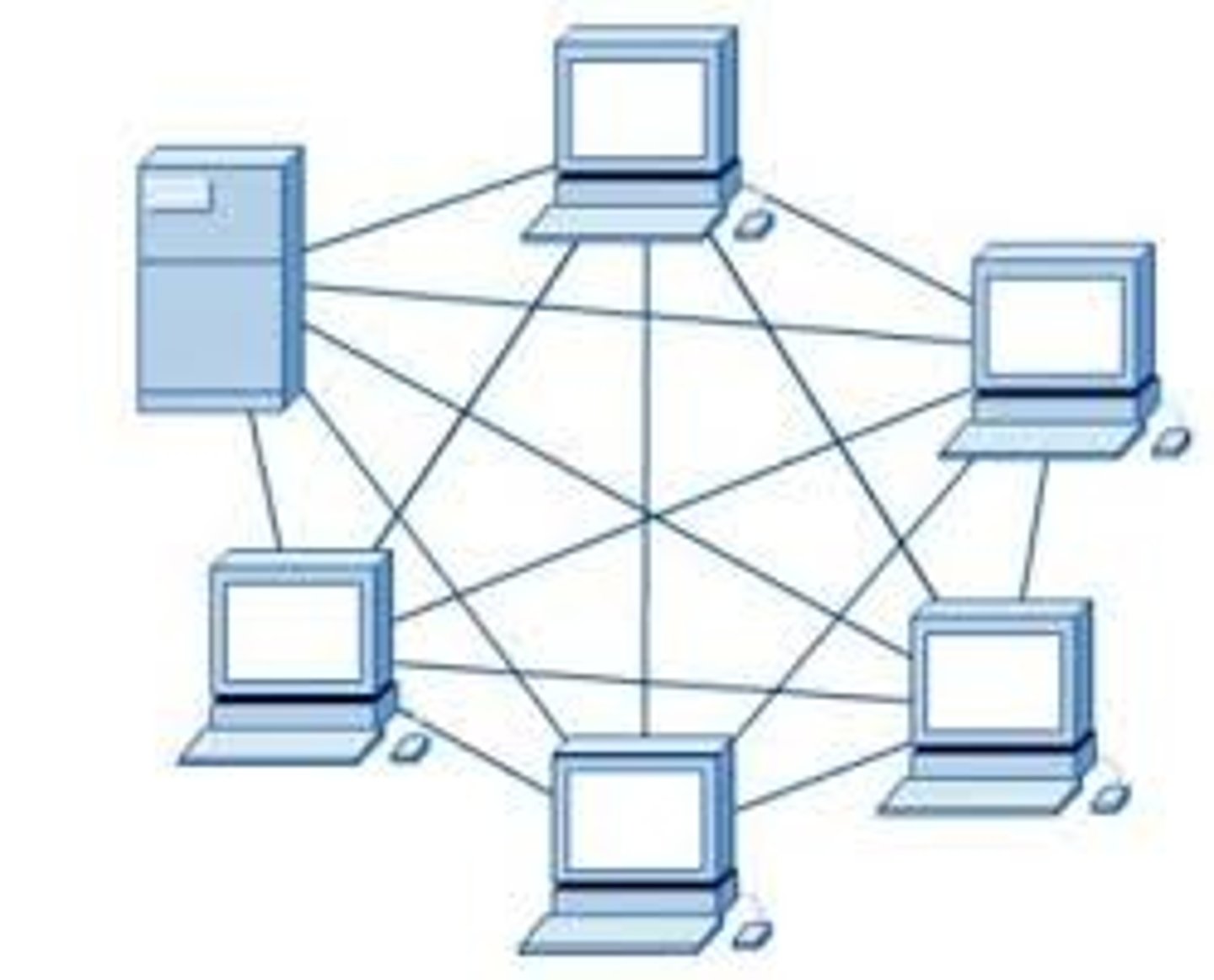
What is a Mesh topology?
All devices on a network are connected to each other
- The internet itself is an example of mesh topology
What is a Hybrid topology?
A combination of topologies used together
What is Cloud Computing?
Applications and services that deliver over the internet. A third party hosts the data for the user that they can then use. Can exist for public, where it can be used by anyone online, and private use, where it is made specifically for use by a company
Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
Pros:
- Free for small quantities
- Can access data from anywhere if you have internet
- Likely better security and recovery options
Cons:
- Internet access is required to acces it
- Long upload and download time limits access to data
- No control over security and backups
What are the Transmission Mediums of a network?
- Wired
- Twisted pair / Copper cable
- Fiber-optic cable
- Wierless
- Radio waves
- Micro waves
- Satellites
What is a Copper Cable?
Twisted pair of copper wires that carry data as electrical signals
What is a Fiber Optic?
Glass/Plastic cables that rely on total internal reflection to transmit data as light
Features of a Copper Cable?
- Slow
- Travels short distances; needs repeaters
- Higher risk of interference
- Less safe (lower security)
- High durability
- Low price
Features of a Fibre Optic Cable?
- Fast
- Travels long distances
- Low risk of interference
- Safe (better security)
- Low durability
- High price
What are Radio Waves?
An electromagnetic wave that carries data wirelessly; Wi-Fi
What are Micro Waves?
An electromagnetic wave that is used to communicate with satellites
What are Satellites?
A communication device that orbits the Earth and sends / receives data
Features of Radio Waves?
- Cheap
- Other radio waves are its obstacles
- Travels long distances
- Lower size
Features of Micro waves?
- Expensive
- Physical objects are its obstacles
- Travels shorter distances
- High size
Features of Satellites?
- Expensive
- High risk of obstacles
- Travels long distances
- High size
What Hardware is used to Support the LAN System?
- Switch
- Server
- Network Interface Card (NIC)
- Wireless Network Interface Card (WNIC)
- Wireless Access Point (WAP)
- Cables
- Bridge
- Repeater
What is a Switch?
Connects all devices on a network and simultaneously brodcasts information to those devices
What is a Server?
A specialized high-speed computer that handles requests from clients or other computers on the network
What is a Network Interface Card (NIC)?
- A hardware component that provides each device a unique MAC address so that it can be identified on a wrieless network.
- It provides an interface by acting as an antenna to a Wi-Fi network. It receives analogue radio waves that it decodes and converts into digital data, and it sends signal data, that it encrypts and converts into analogue waves, via the antenna.
- It checks incoming transmissions to check if they match the device's IP / MAC address and ignores them if they're not.
What is a Wireless Network Interface Card (WNIC)?
Hardware component that allows a device to connect to a wireless network // Provides a MAC address to the device to identify it on the wireless network
What is a Wireless Acces Point (WAP)?
Hardware component that provides radio communication from the central device to nodes on the network (and vice versa)
Features of Wireless Access Point?
• To receive packets from devices or the Internet
• To forward / route packets to the destination
• To find the destination of the packet
• To assign / allocate private IP addresses to devices on LAN
• To store / update / maintain a routing table
• To find the most efficient path to the destination
• To maintain a table of MAC and IP addresses
What is a Cable?
A wired transmission medium that allows communication in wired networks
What is a Bridge?
A device that interconnects two or more LANs together and forwards data packets
What is a Repeater?
Restores the digital signal so it can be transmitted over greater distances
What is a Router?
Receives and sends data between two networks operating on the same protocol
- Can be used to segment a network
Functions of a Router?
- Maintain a table of MAC and IP addresses
- Assign private IPs to a device on a network
- Routes packets to their destination but doesn not direct packets to each device attached to it
- To receive packets from devices or the Internet
What is an Ethernet?
The most common form of wired connection used in LAN and WAN that is based on Bus topology.
- Due to this it is possible for data collisions to occur, hence a Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection (CSMA/CD) is used.
What is Carrier Sense Multiple Access / Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)?
-A workstation listens to the communication channel, when it receives a request first it will check if the line is empty, if empty sends data.
-- If a collision occurs because both devices checked if the line was empty at the same time, then the workstation will send an abort signal and the data will be sent back.
--- And a random wait time is assigned to each device before resending
Features of Wired Internet?
- Faster
- More stable
- More secure
- Restricted movement
- High cabling
- Difficult to expand
Features of Wireless Internet?
- Slower
- Less stable
- Less secure
- Free movement
- Less cabling
- Easy to expand
Internet Hardware?
- Modem
- Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN)
- Dedicated lines
- Cell phone network
What is a Modem?
A device that allows users to connect to the internet via telephone line; converts analogue signals into digital signals.
What is a Public Switch Telephone Network (PSTN)?
Full duplex form of communication over wire via circuit swtiching that remains active during power outages
What is a Dedicated Line?
A permanent connection for communication that is expensive but faster and more secure/consistent
What is a Cell Phone Network?
A wireless connection that relies on mobile connection and cell towers that use radio waves
What is Bit Streaming?
- A video is compressed and is then sent as a continuous stream of bits. When it is downloaded the server sends the data to the buffer which then sends a continuous stream of data to the user
- Higher bit-rate speed and broadband speed means users can stream the video faster and with less buffering
Methods of Bit Streaming?
- Real time
- On demand
What is Real-Time Bit Streaming?
Used when watching a live stream of events that are currently taking place. The event is captured live with a video camera connected to a computer, and it cannot be paused or rewound.
What is On-Demand Bit Streaming?
Used when watching an event that has taken place in the past. Existing media are encoded to bit streaming format and uploaded to a server. It can be paused and rewound.
Types of Video Redundancies?
• Temporal - Sequence of consecutive pixels have the same value on a frame
• Spatial - Sequence of consecutive pixels between frames have the same value
What is the World Wide Web (WWW)?
A collection of websites that are available on the internet. When you access a website, you are using both the internet and the world wide web because the website is stored on WWW but the internet provides the necessary infrastructure.
What is an IP Address?
- The unique address that identifies a device a network and to allow router to send data from the internet to the device.
Features of IPv4?
- 4 groups
- Group range: 0-255
- Separator = .
- Size is 32 bits
- Example : 192.168. 1.1
Features of IPv6?
- 8 groups
- Group range = 0-65535
- Separator = :
- Size is 64 bits
- Example : fe80:d4a8:6435:d2d8:d9f3b11
What are the types of IP addresses?
- Public
- Private
- Static
- Dynamic
What is a Public address?
Assigned by the IP visible on the internet, must be unique on the internet.
Only the router has a public IP address, devices on the netwrok do not as all data passes through the router, which also protects the device from external threats.
What is a Private address?
Assigned by the router that is visible to devices on the network, must be unique on that specific network.
What is a Static address?
Remains constant, whenever a device connects to the internet. Webpages need Satatic IP addresses so the DNS does not need to be updated everytime which can cause delays and errors.
What is a Dynamic address?
A new IP address is allocated every time a device connects to the internet.
What is Subnetting?
Dividing a network into smaller groups
Advantages of Subnetting?
- Reduces traffic
- More secure
What is a URL?
Uniform Resource Locator, easier way to remember IP addresses for websites.
- e.g, Duck.com = 52.250.42.157, Google.com = 2a00:1450:4019:80c
What is a DNS?
Domain Name Server, the DNS looks up the URL within a table, if it finds the corresponding IP address, it's then returned to the client. If it's unable to find it, the request is forwarded to a higher DNS.
What is Primary storage?
Main memory storing critical program instructions and data.