A&P I Chapter 6: Skeletal System (Bones and Bone Tissue)
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
162 Terms
lacunae, chondroblasts
Chondrocytes are mature cartilage cells within the ______ and they are derived from the _______
perichondrium, fibroblasts
perichondrium, chondroblasts
lacunae, chondroblasts
lacunae, fibroblasts
fibroblasts, lacunae
living cells (osteocytes) and mineralized matrix
bone is made up of....
organic: collagen fibers
inorganic: hydroxyapatite (Ca plus PO4)
mineralized matrix includes...
rich
bone has a _________ blood supply
reinforced concrete
bone matrix is similar to....
collagen and proteoglycans
bone matrix organic components include.....
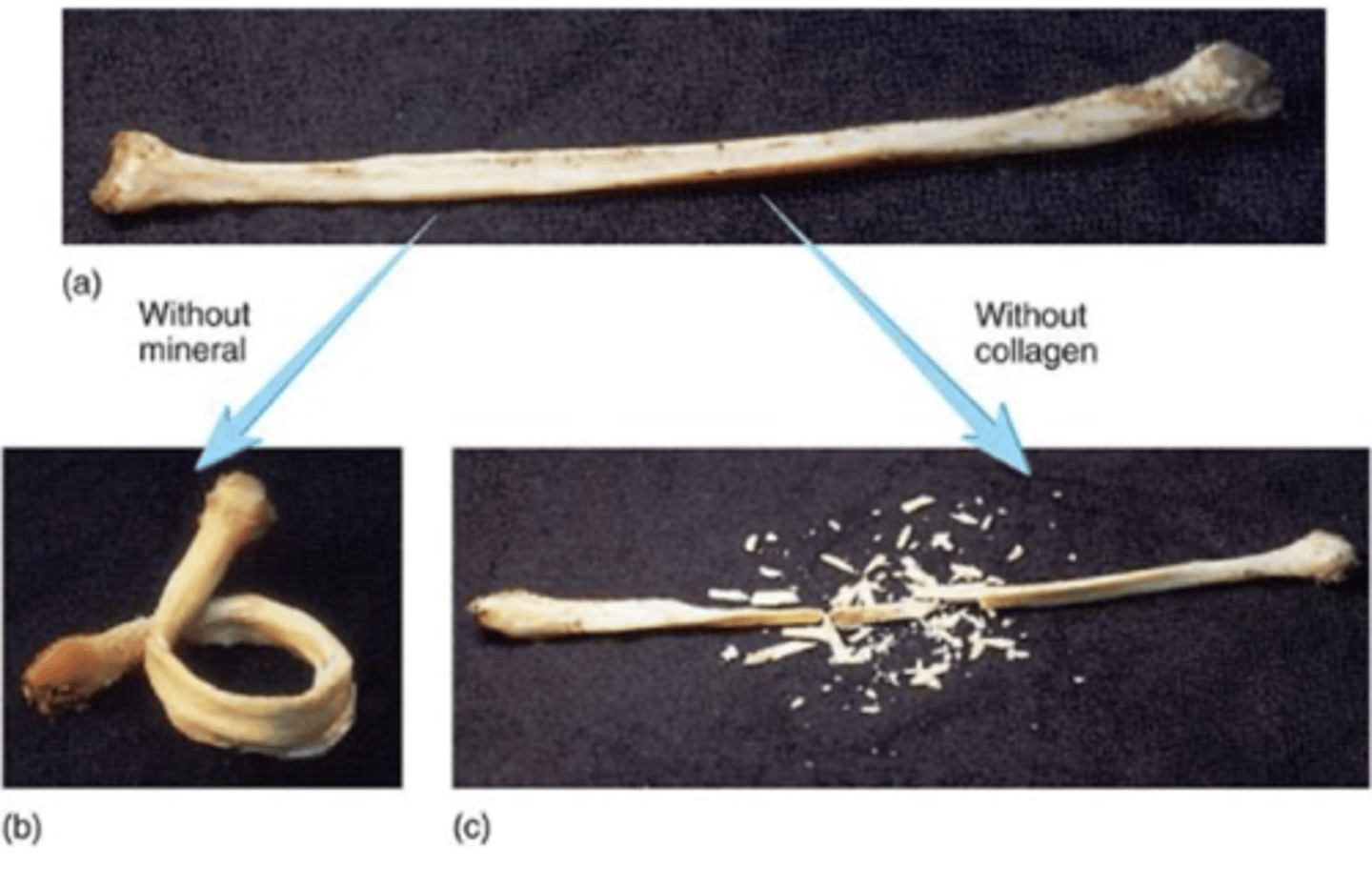
crystallized CaPO4 (hydroxyapatite)
bone matrix inorganic components include.....
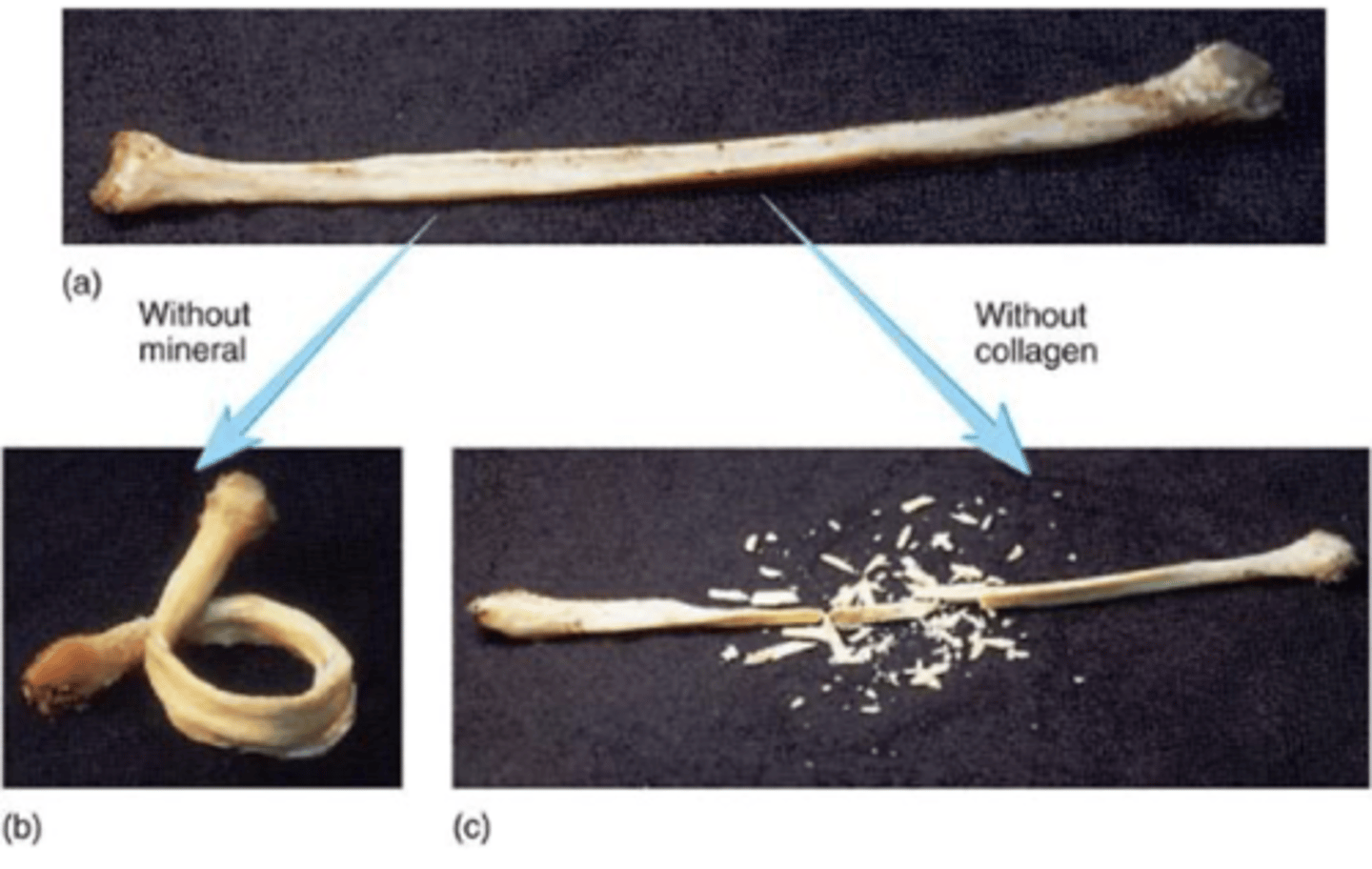
osteoblasts
collagen and proteoglycan produced by the E.R. and packaged by the golgi while precursors of hydroxy apatite stored in vesicles
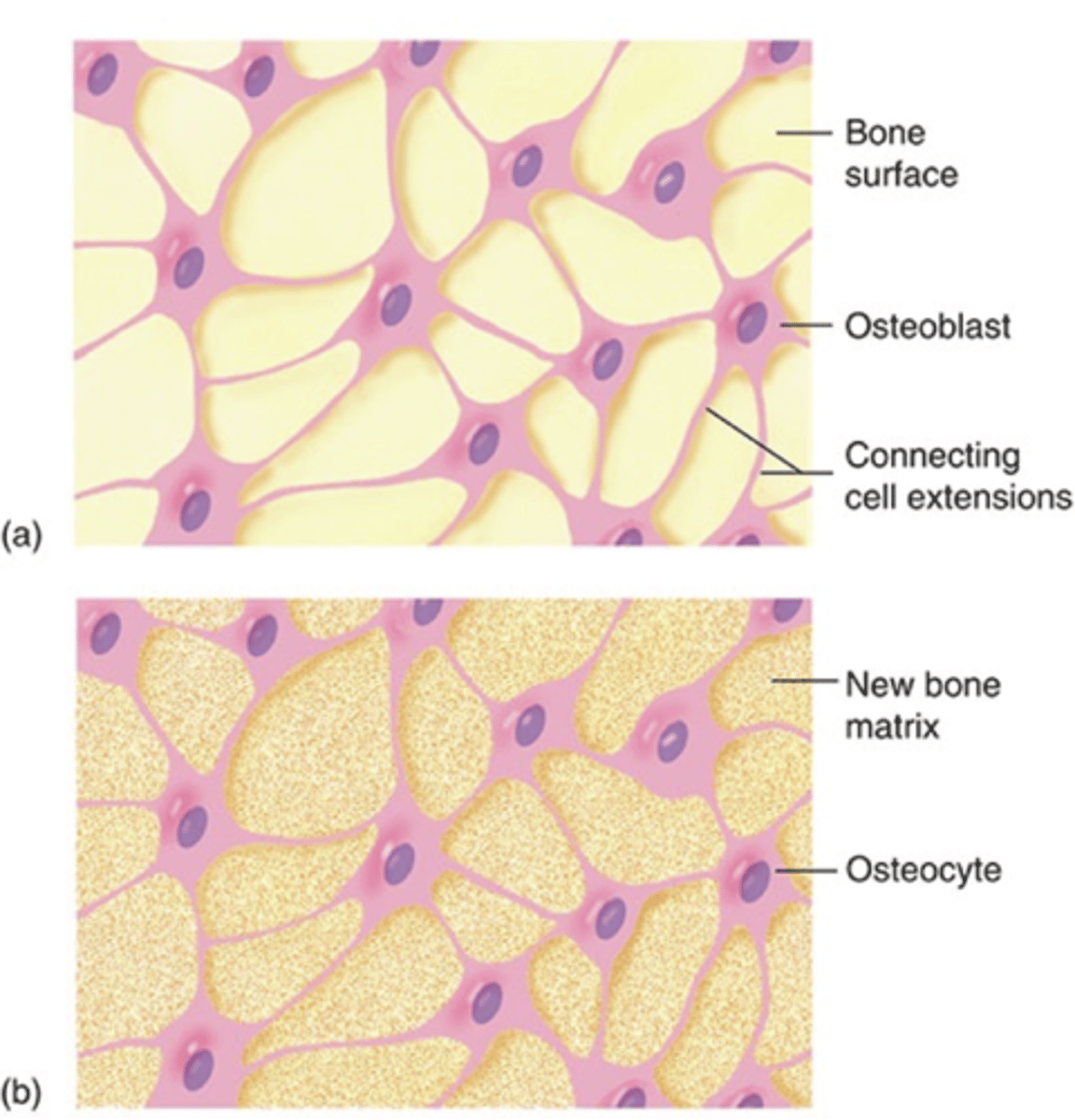
Ossification (osteogenesis)
How are osteoblasts released?
ossification/osteogenesis
formation of bone by osteoblasts
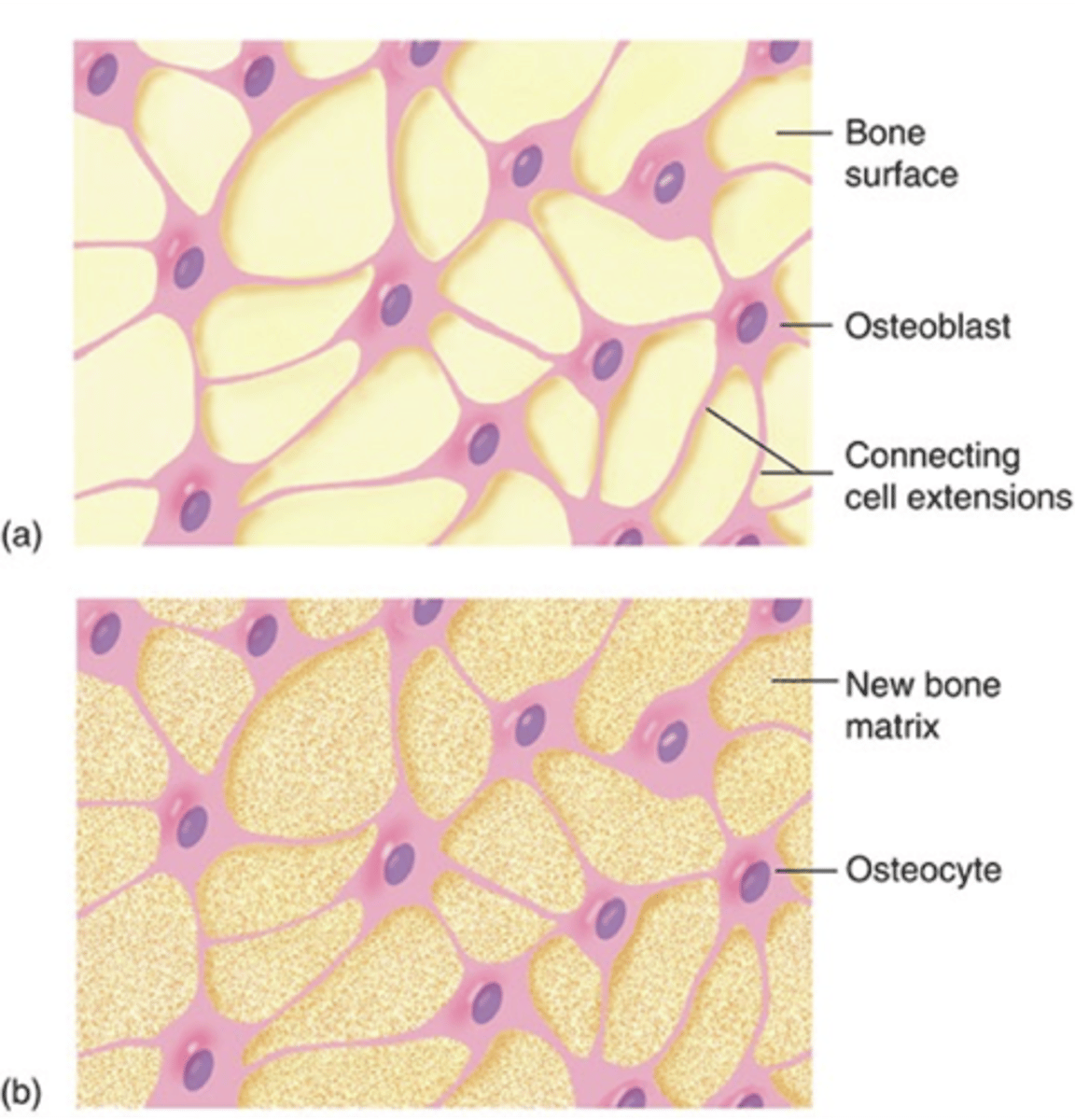
gap junctions
how osteoblasts communicate
matrix
osteoblast cells surround themselves by __________ during ossification
osteocytes
mature bone cells surrounded by matrix
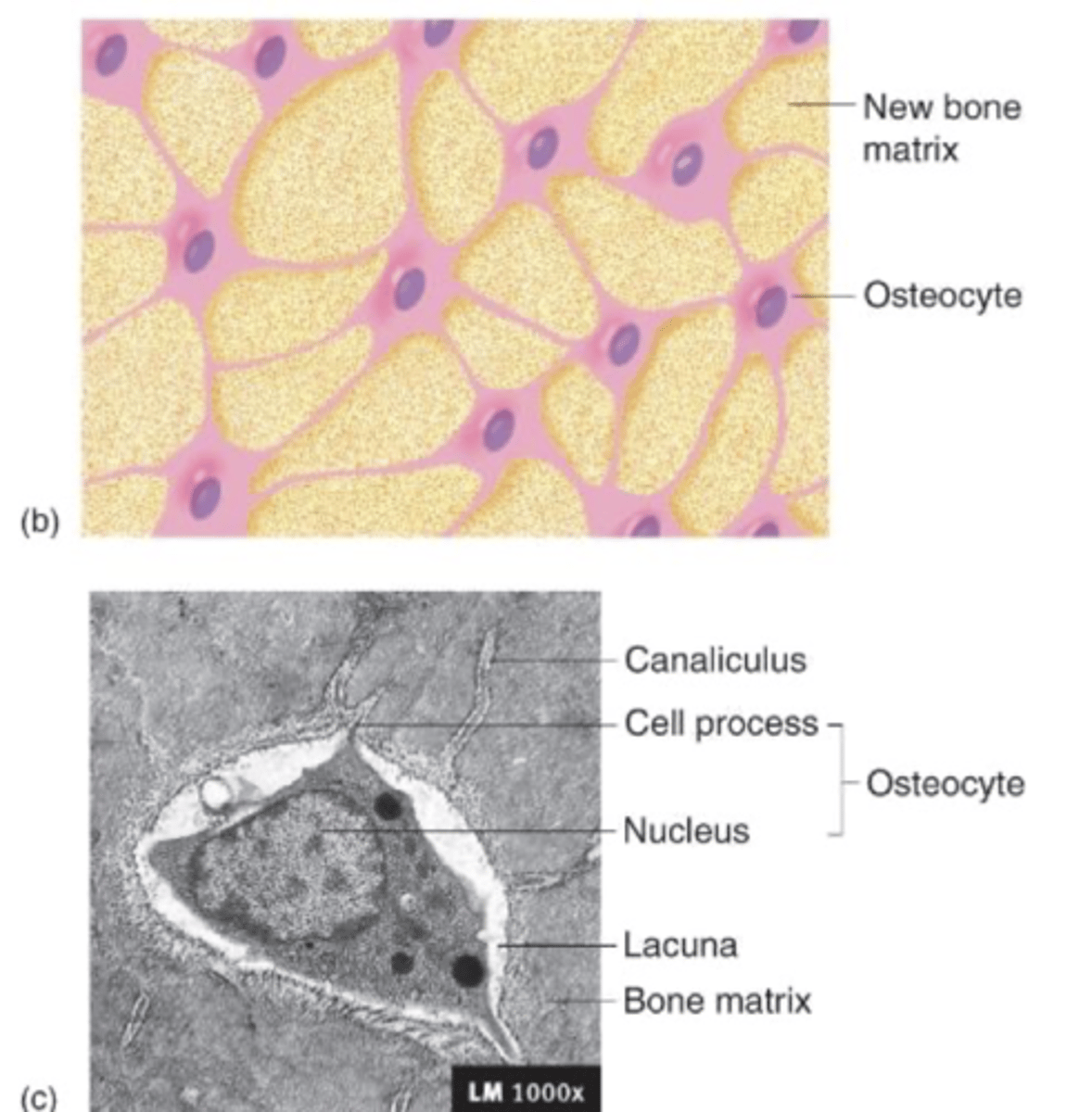
lacunae, with extensions in canaliculi
osteocytes are located at....
direct passage of nutrients between osteocytes
osteocytes facillitate...
osteoclast
large, multinucleated cells with a ruffled boder
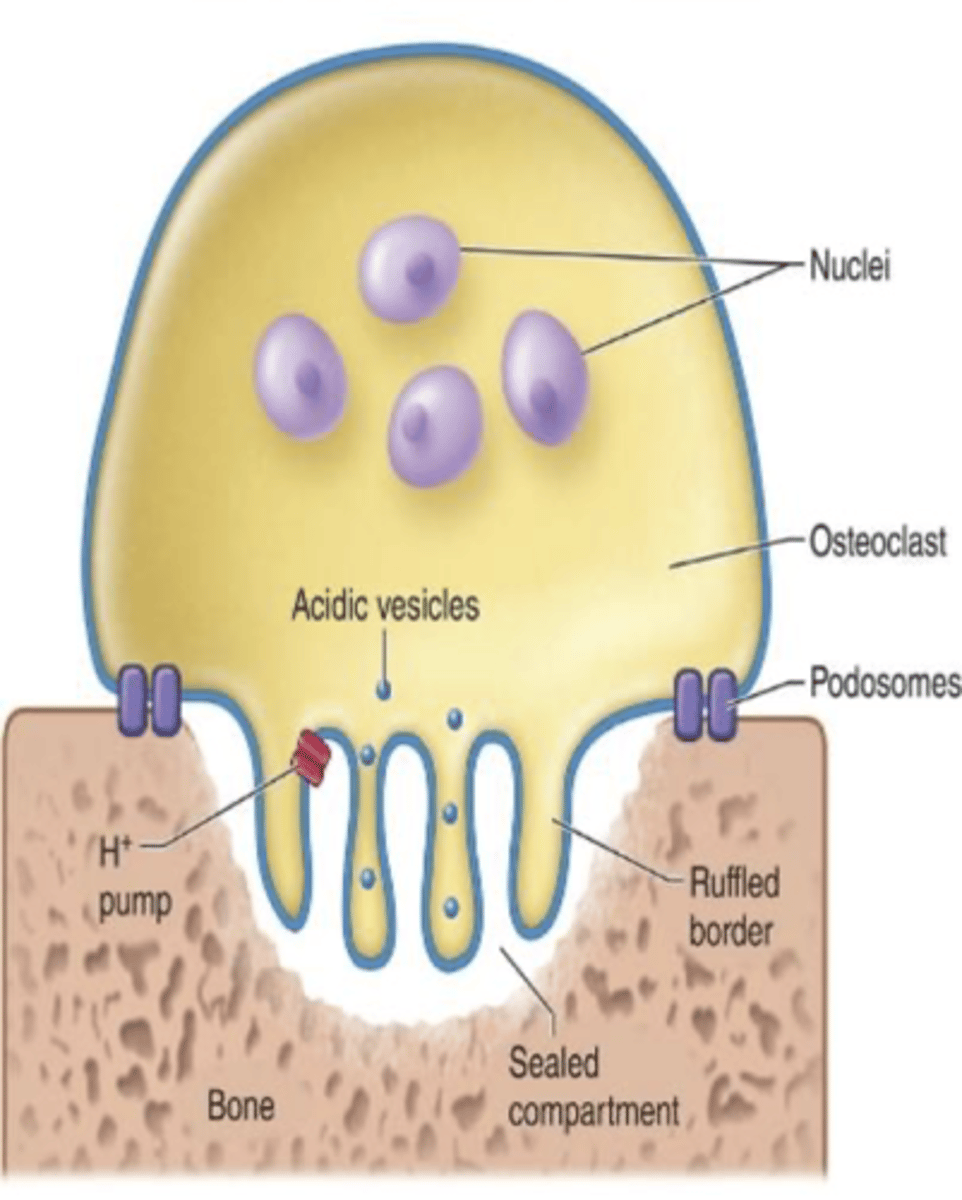
breakdown of bone matrix
reabsorption (osteoclasts)
secrete H+ ions, decalcifies
osteoclasts ___________ in an acidic environment that ____________ matrix
osteocyte secretion
secrete enzymes, digest the protein components of the matrix
collagen
The flexible strength of bone occurs because
hydroxyapatite
collagen
osteoclasts
periosteum
PPI's taken for stomach acid inhibition could also inhibit H+ pumps in osteoclasts. Therefore, they might not be able to create acidic environment to dissolve bone. This would cause a decrease in blood Ca2 levels
Calcium in blood, blood calcium levels going down
Some patients take ATP powered H+ pump inhibitors, also known as proton pump inhibitors (PPI's), to control acid reflux. Predict the effect if any, of long term, high dose of PPI's on blood Ca2+ levels. *
woven bone
collagen fibers are randomly oriented
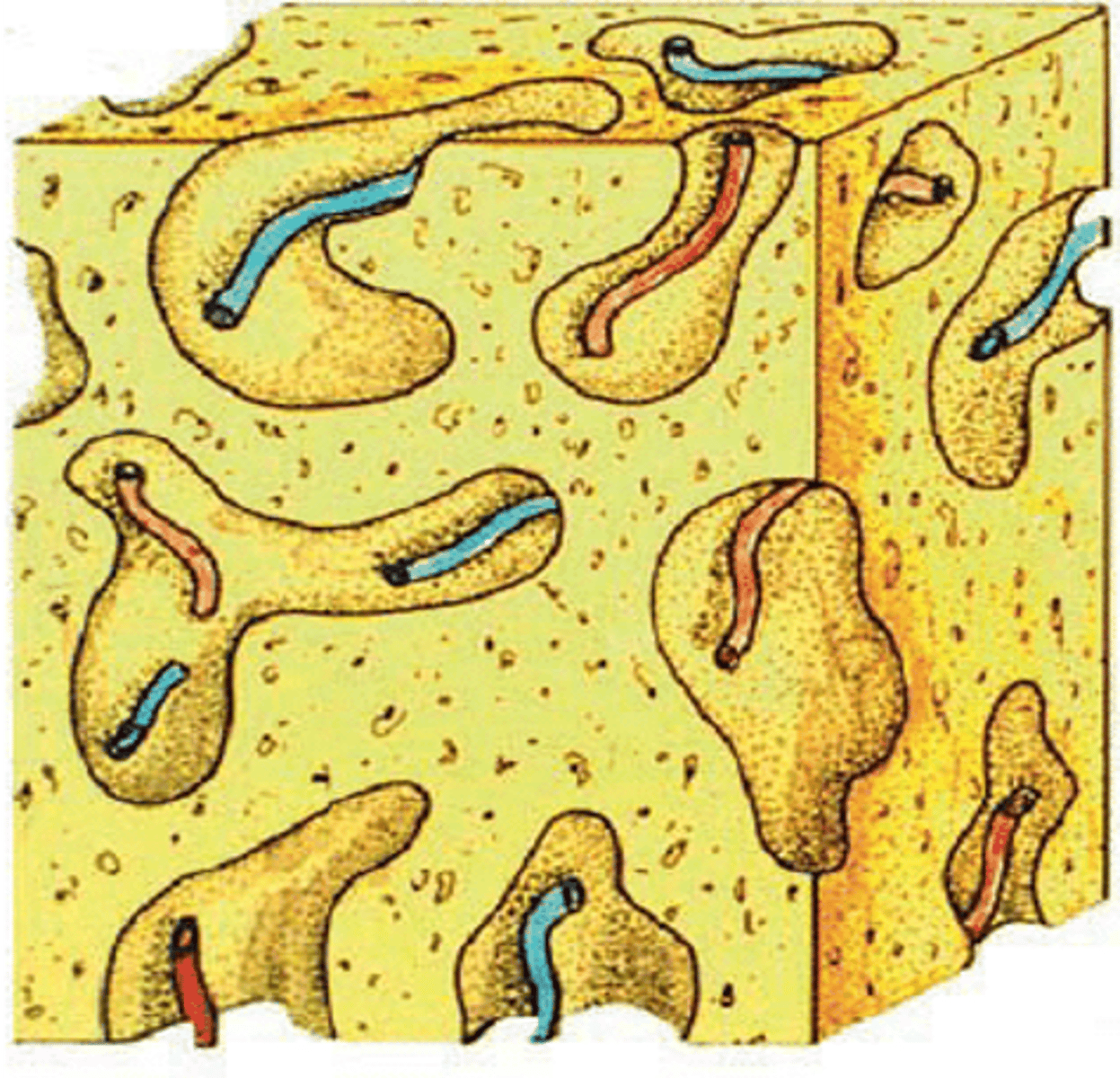
woven bone remodeling
removing old bone and adding new
lamellar bone
woven bone is remodeled into.......
NOT strong at all- weak
how strong is woven bone?
lamellae
Mature lamellar bone is organized into sheets called....
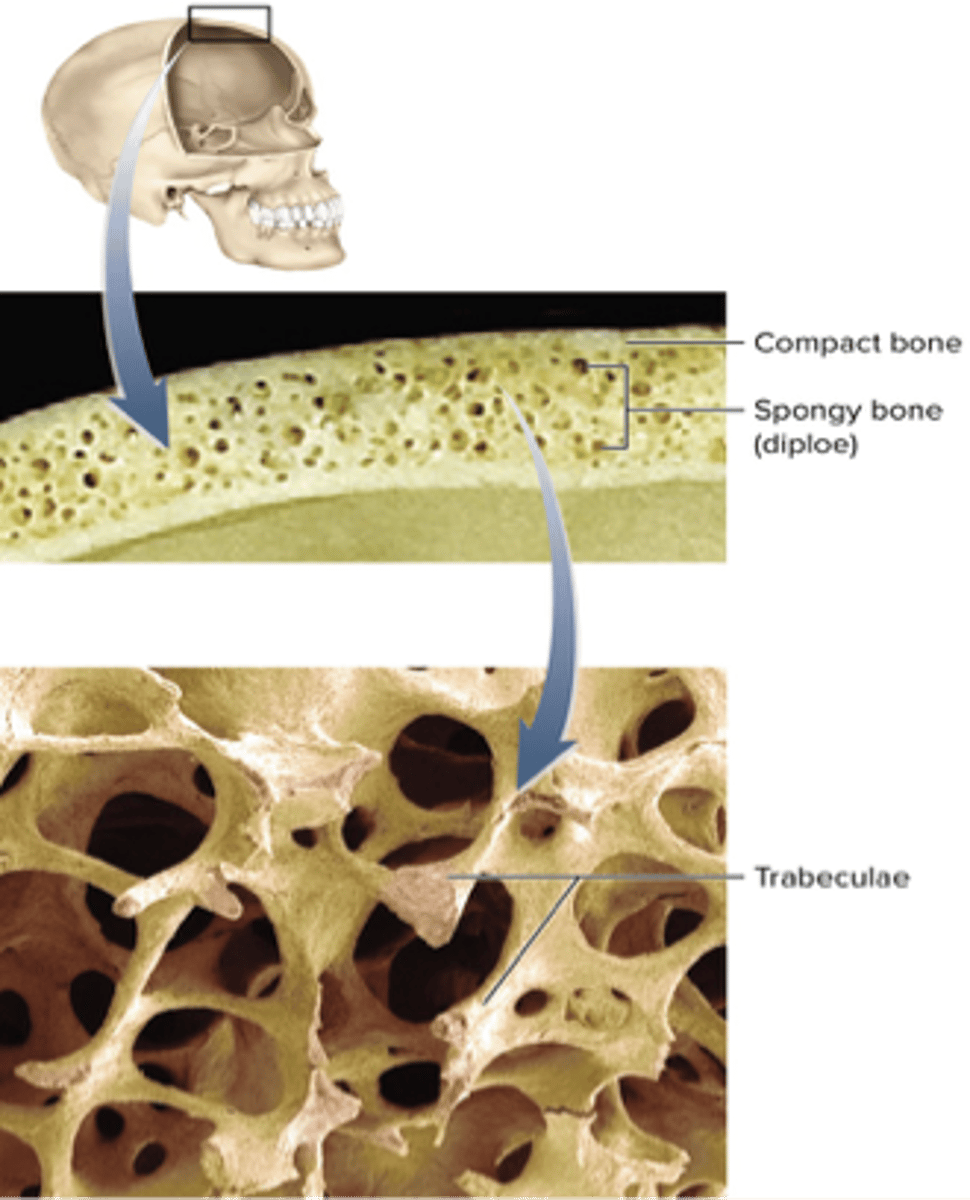
trabeculae
plates of bones with spaces between and looks like a sponge
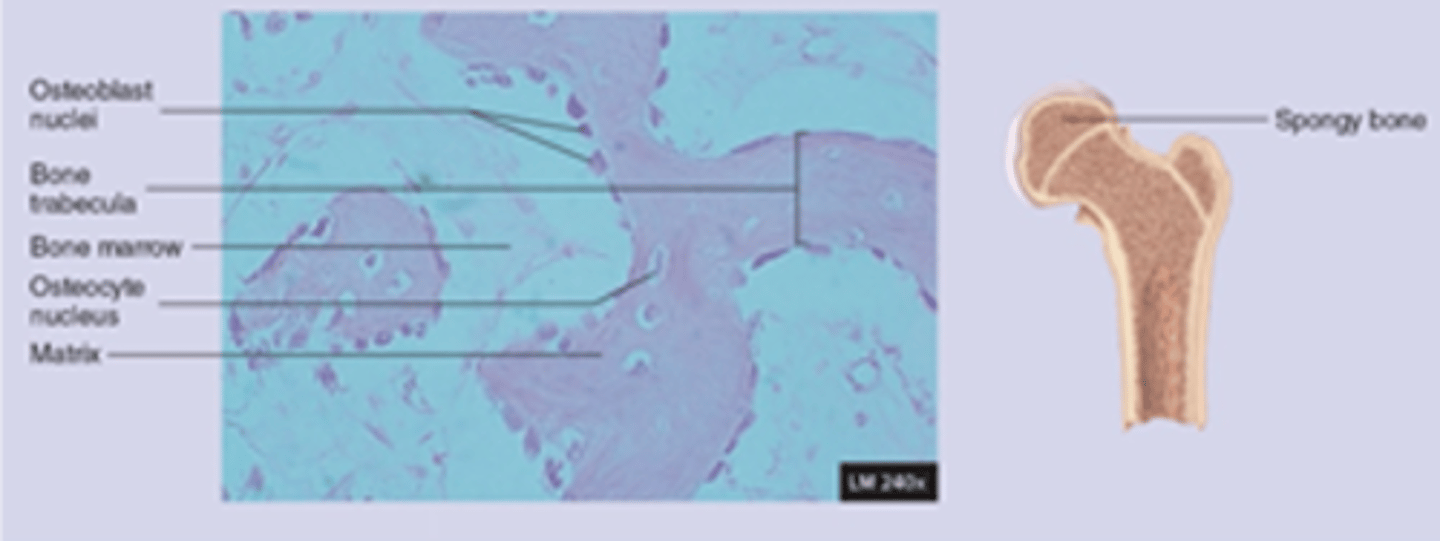
trabeculae location
interior of the skull bones, vertebreae, sternum, pelvis, ends of long bones
trabeculae function
immense strength and support
less matrix and more space
spongy bone has......
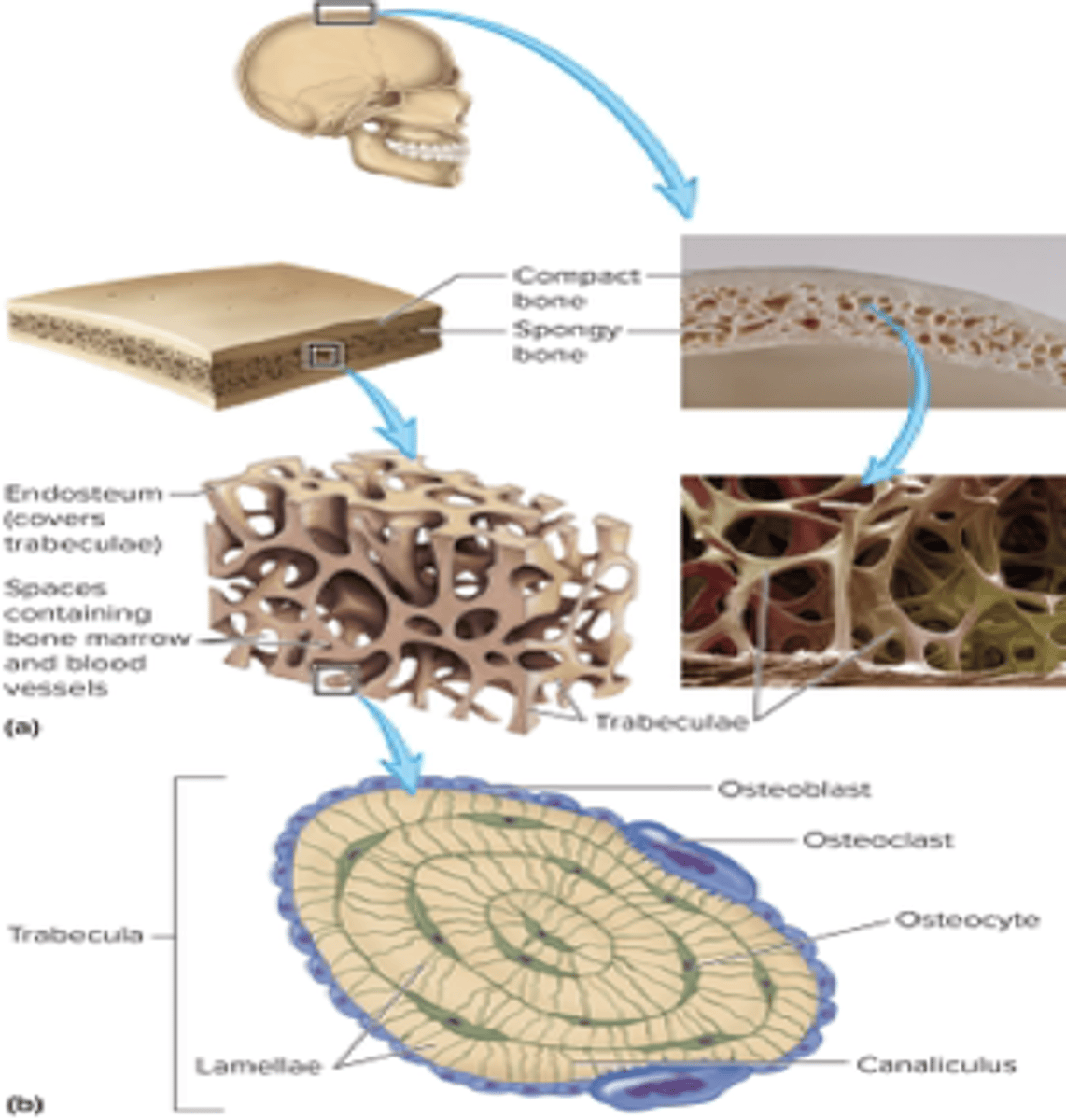
mechanical stress
In spongy bone, interconnecting rods /plates of bone are (trabeculae) oriented alnng the lines of.....
spongy bone appearance
spaces filled with marrow and blood vessels
more matrix with less space
compact bone has.....
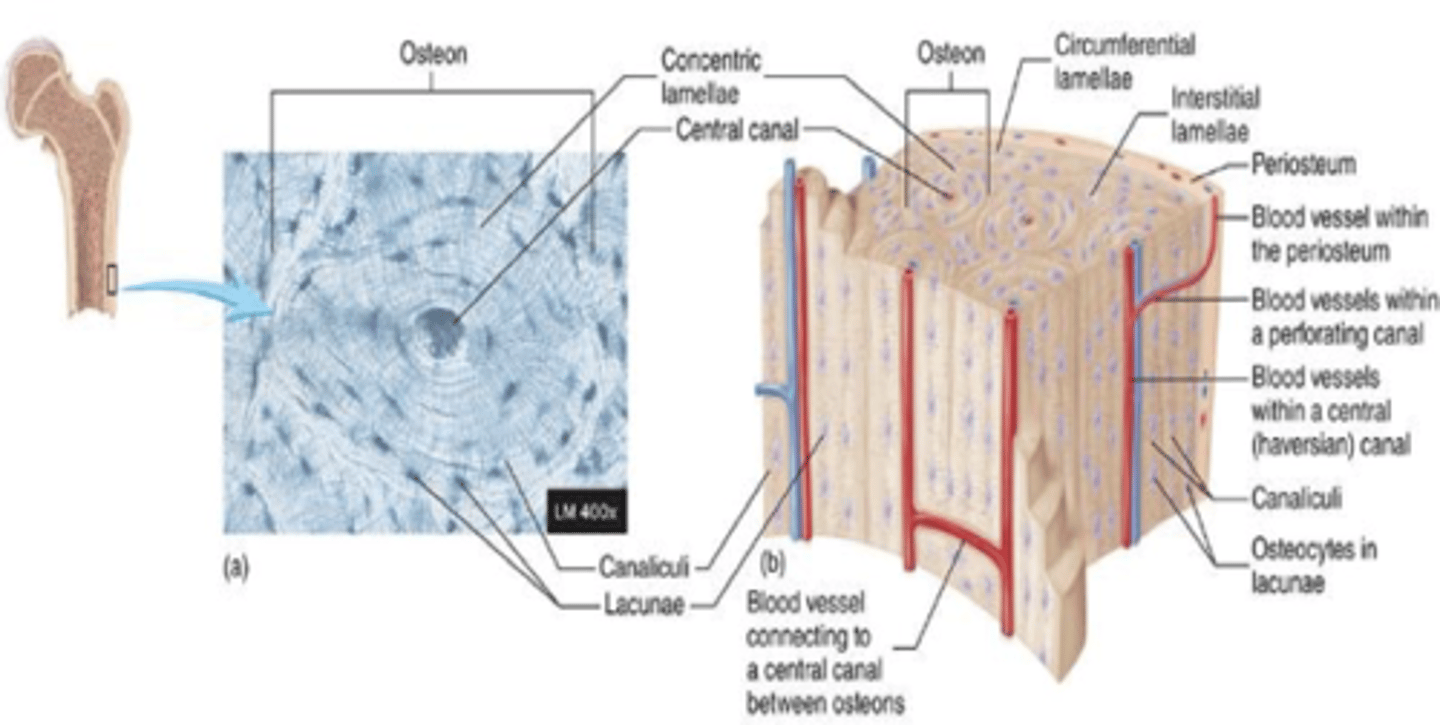
the blood vessels
In compact bone, lamellae is oriented along.........
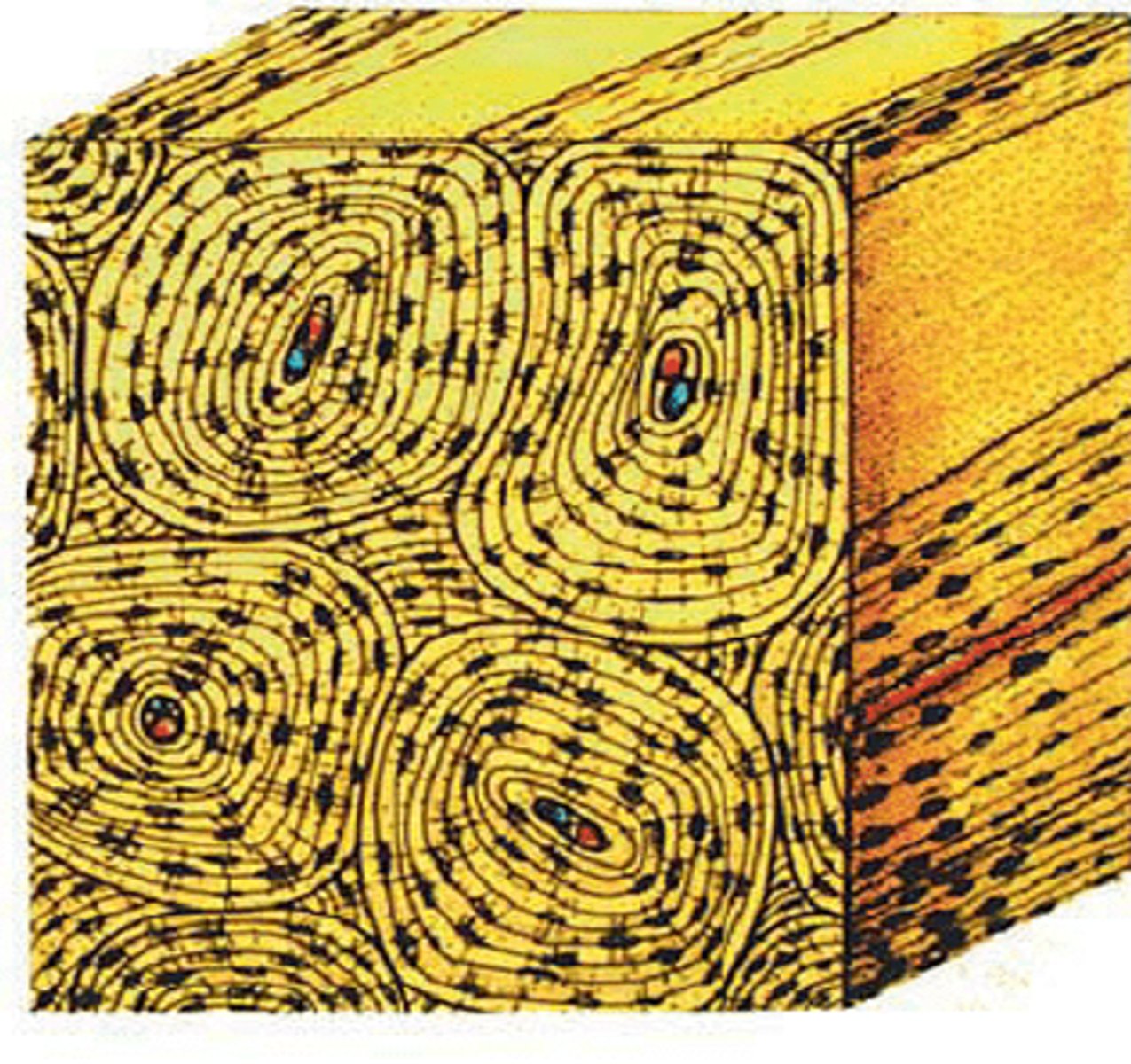
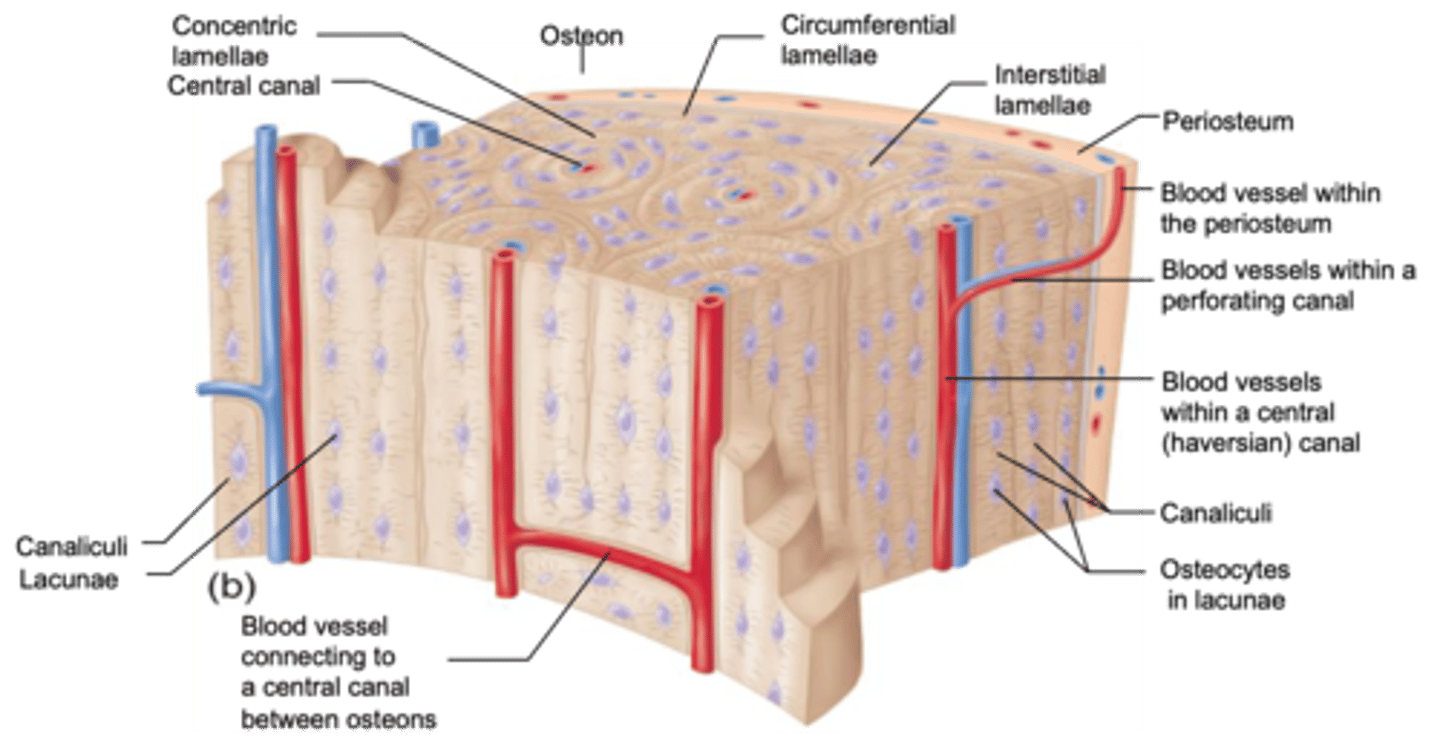
osteons (haversian system)
compact bone is compromised of functional units called.........
haversian system
blood vessel filled central canal
centra canal
In osteons, concentric lamellae of bone surround the......
osteocytes and fluid
In osteons, lacunae and canaliculi contain....
circumferential lamellae
outer surfaces of compact bone are formed by...
interstitial lamellae
What is between the osteons?
remodeling
remnants of osteons are replaced through.......
False
The lamellae found inside osteons are circumferential lamellae.
True
False
volkmann canals
perpendicular canals that deliver blood to central canals of the osteons
long bones
upper and lower limbs
short bones
carpals and tarsals
flat bones
ribs, sternum, skull, scapulae
irregular bones
vertebrae facial
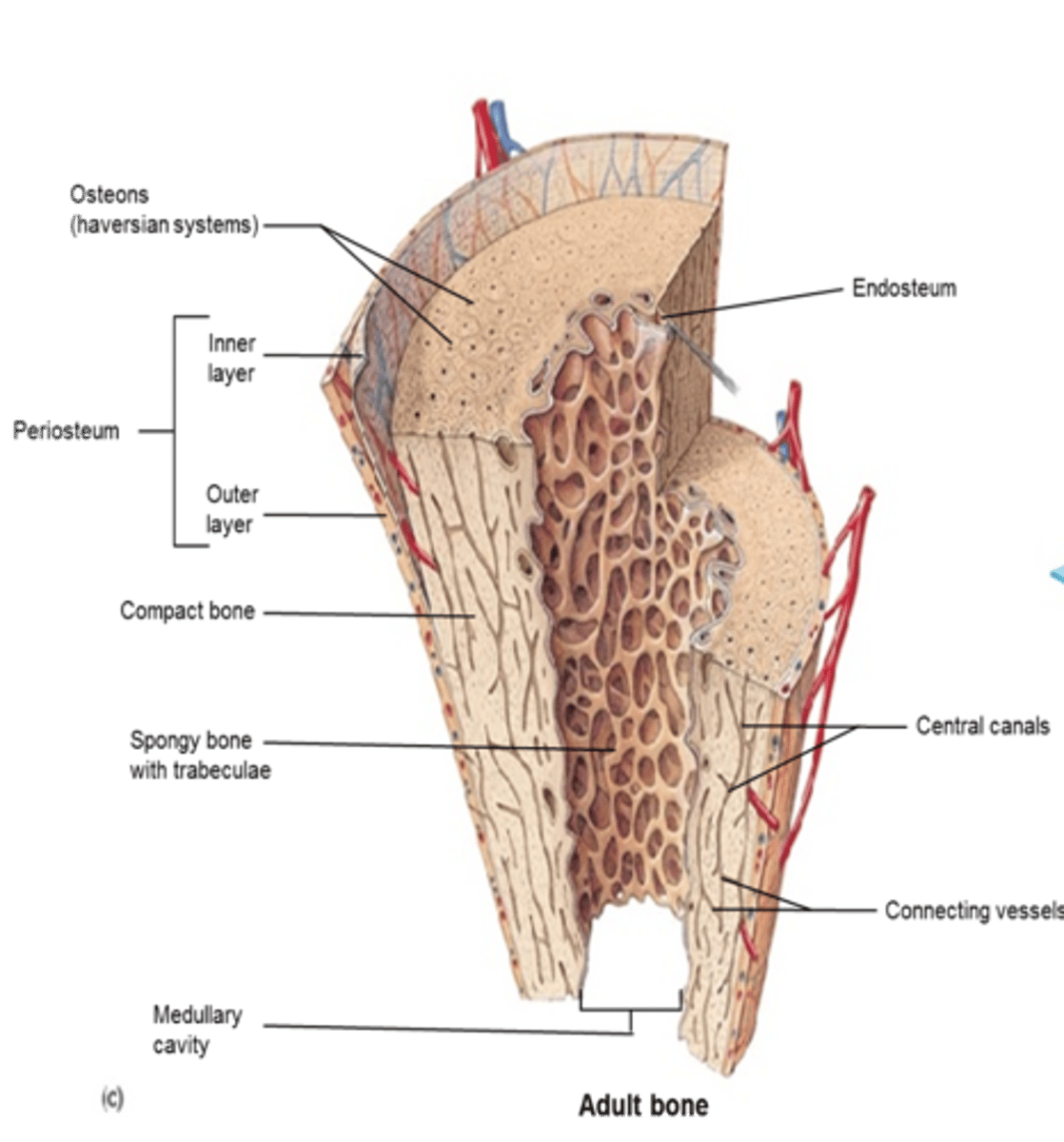
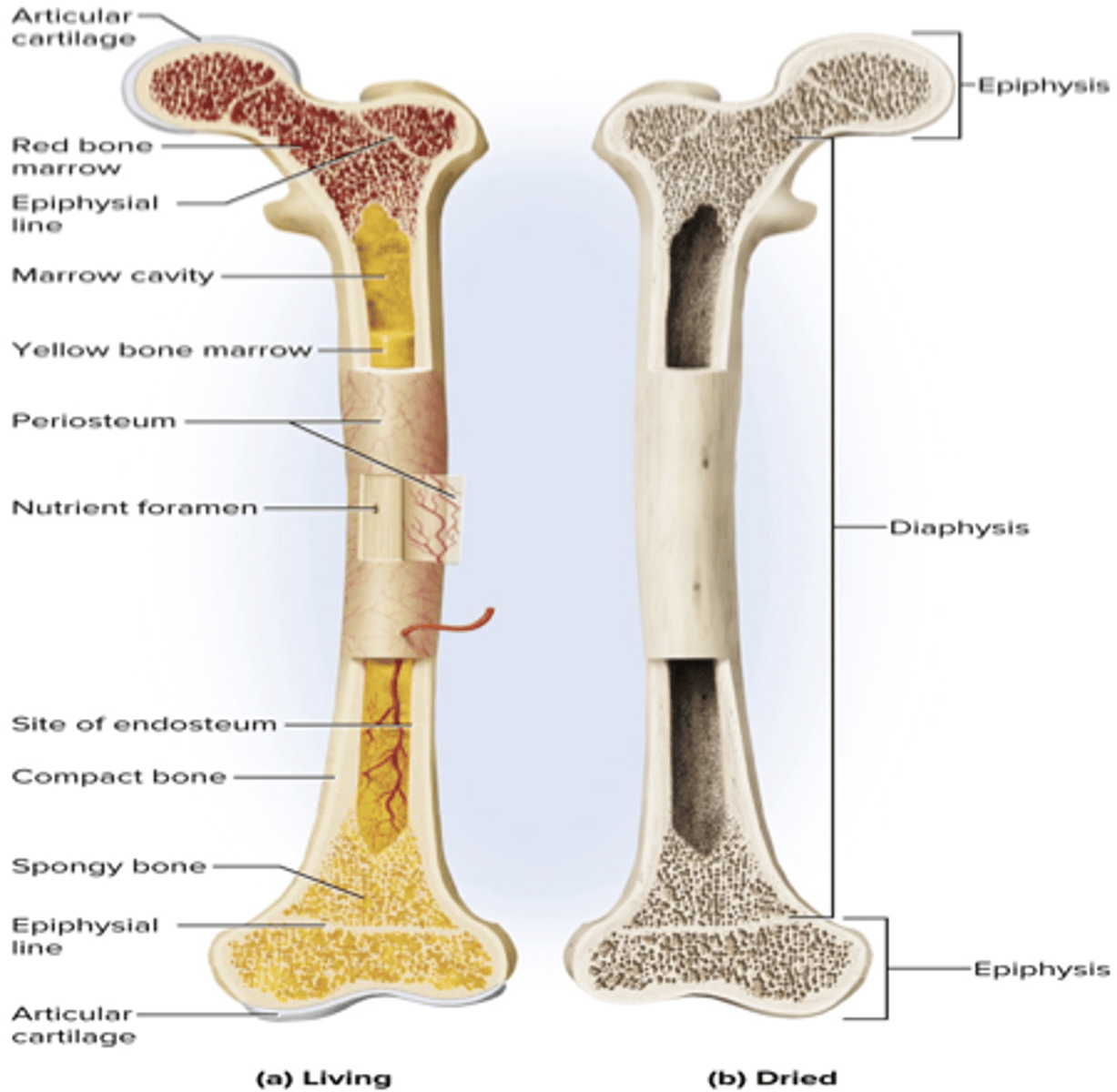
structure of long bone
diaphysis, epiphysis, epiphyseal plate, medullary cavity
diaphysis (shaft)
mostly compact bone, medullary cavity contains marrow
epiphysis (ends of long bone)
mostly spongy bone
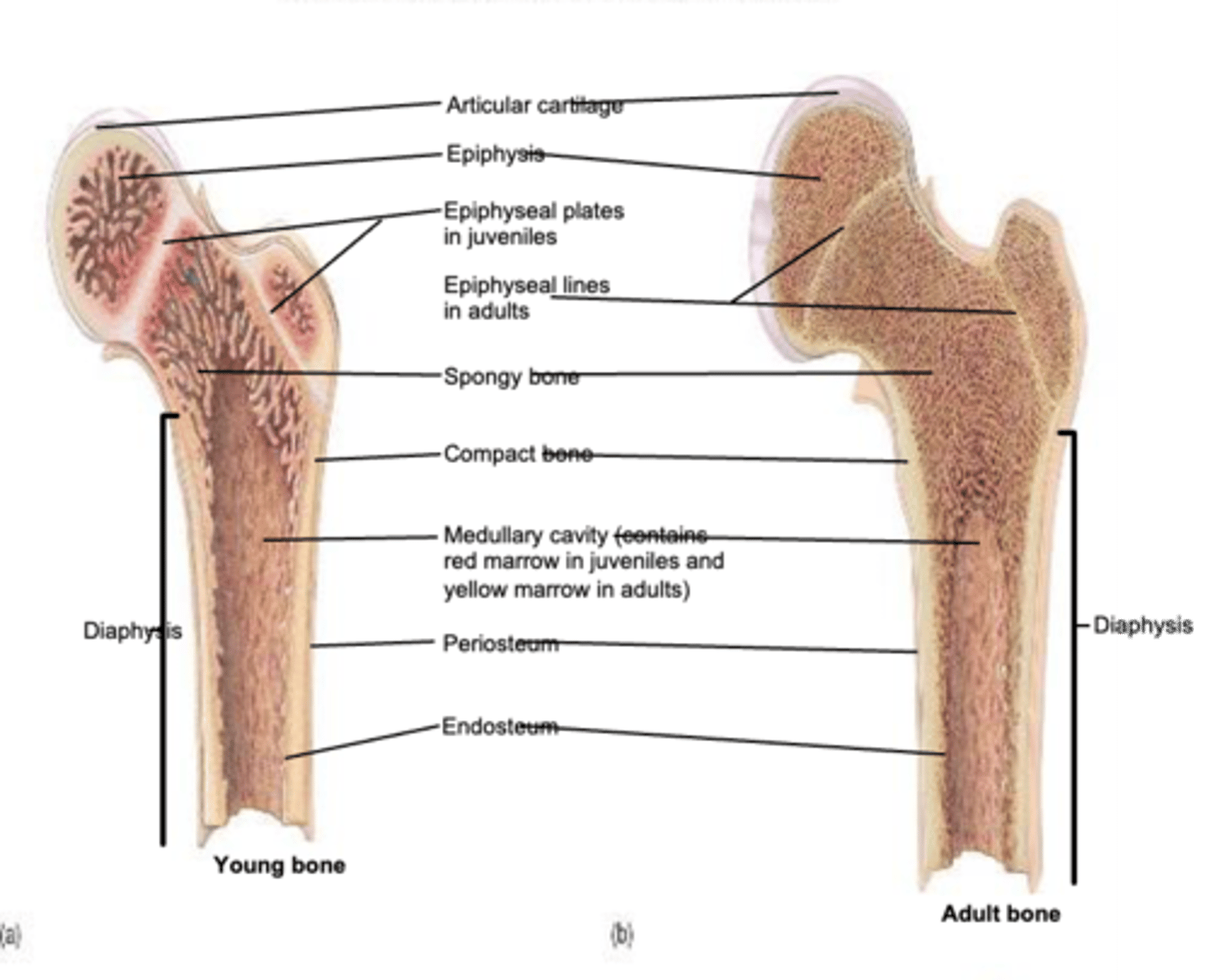
epiphyseal plate (growth plate)
hyaline cartilage; site of bone growth in length until the plate becomes ossified
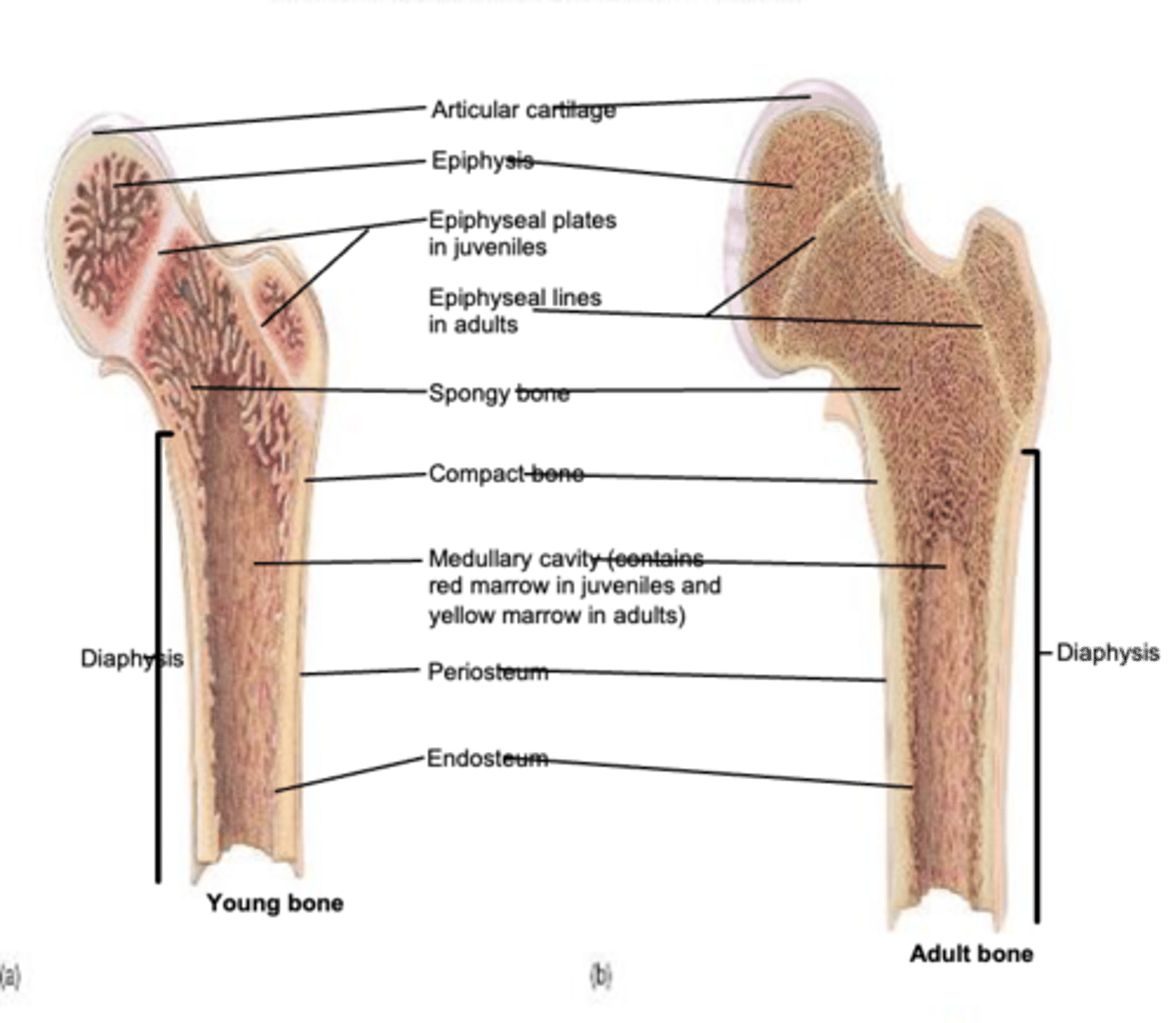
medullary cavity
red marrow-> blood cell production
yellow marrow-> adipose tissue
periosteum
double layered CT on the outer surface
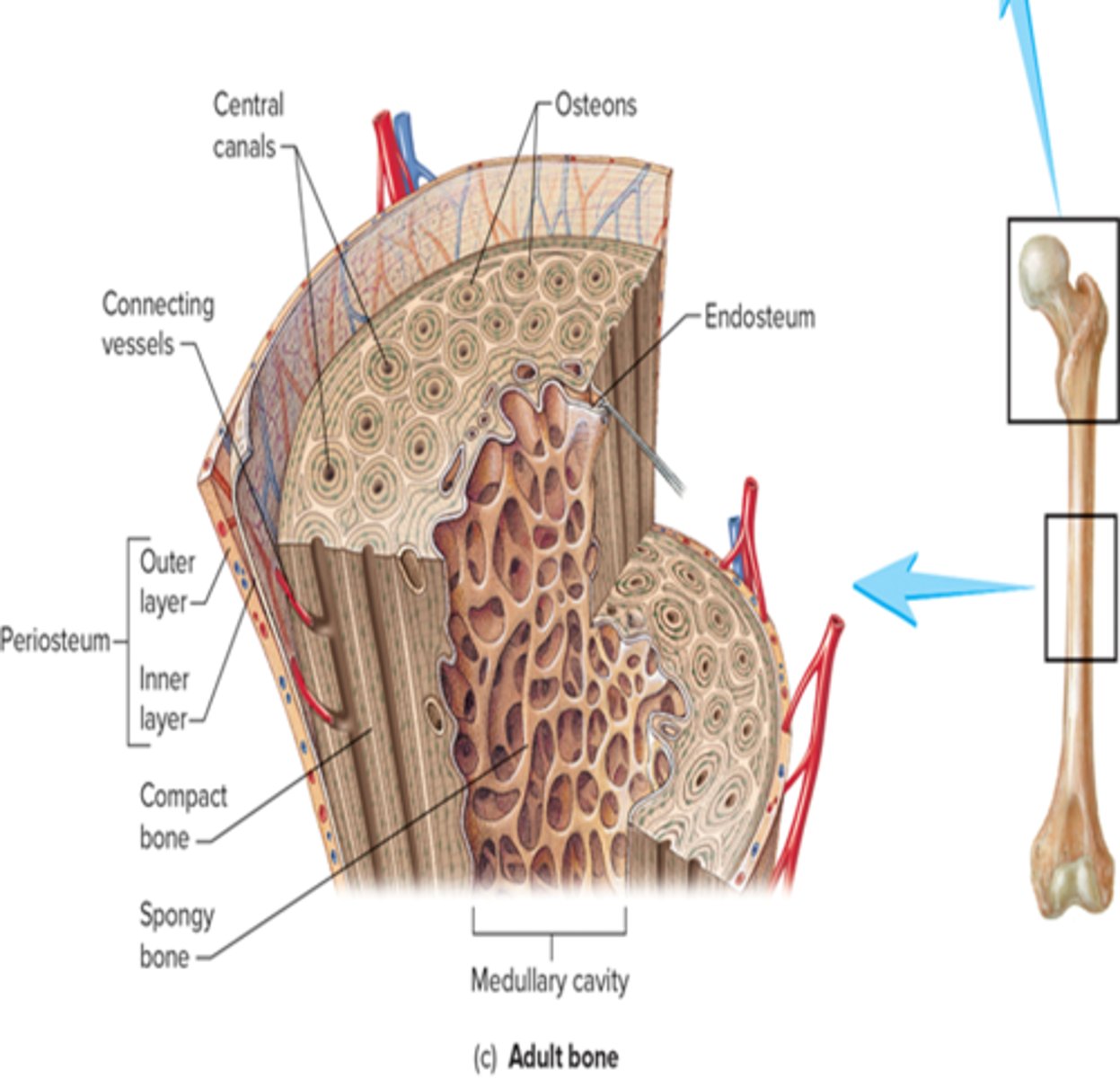
endosteum
single layer of CT that contains bone cells and lines all internal surfaces within bone cavities
diaphysis or epiphysis
flat bones don't have...
compact bone
FLAT bones have sandwich of spongy bones between....
diaphysis and is NOT elongated
short and irregular bone does not have......
short and irregular bone
compact bone that surrounds spongy bone center; similar to structure of epiphysis of long bones
diaphysis
A fracture in the shaft of the bone is where?
epiphysis
articular cartilage
diaphysis
perichondrium
ossification (osteogenesis)
formation of new bone by osteoblatsts is called......
intramembraneous ossification
preexisting connective tissue membrane
endochondral ossification
preexisting cartilage (e goes with e)
produce woven bone that is then remodeled into lamellar bone
both methods of ossification.....
fifth week of development
embryonic mesenchymal membrane condenses at…….
eighth, 2
ossification begins at ___________ week of development and is complete by ____ years of age
skull bones
mandible
diaphysis of clavicles
MOST of remaining bones of skeletal system
Intramembraneous ossification occurs in which bones?
centers of ossification
locations in membrane where ossification begins
fontanels (soft spots)
large membrane-covered spaces between developing skull bones; unossified
1. Ossification centers appear in the fibrous connective tissue membrane.
2. Osteoid is secreted within the fibrous membrane and calcifies.
3. Woven bone and periosteum form.
4. Lamellar bone replaces woven bone, just deep to the periosteum. Red marrow appears.
the four parts of intramembraneous ossification are.....
1. mesenchymal cells in CT differentiate into OPC's
2. OPC'S differentiate into osteoblasts
3. Osteoblasts produce bone matrix and become osteocytes
4. Trabeculae of woven bone develop
5. Spongy bone forms as more trabeculae join together
6. Cells within spaces form red marrow and cells surrounding bone form perosteum
7. Osteoblasts form periosteum from outer surface compact bone
8. Remodeling converts woven lamellar bone
steps for intramembranous ossification in order are......
example long bone
what should result after endochondral ossification?
*
steps for endochindral ossification
chondroblasts
mesenchymal cells differentiate osteochondral progenitor cells become
where joints will form
these cells in the hyaline cartilage model are surrounded by perichondrium except....
bony collar
the perichondrium becomes the periosteum, and then becomes the...
place in the correct order
perichondrium*
calcified cartliage
internal condrocytes, hypertrophy and cartliage matrix become....
calcified cartliage
a primary ossification center forms once blood vessels and osteoblasts invade the.......
medullary cavity
osteoclasts erode the central portion of diaphysis, which creates the.......
red bone marrow
cells within the cavity specialize and ____________ is created
epiphyses
secondary ossification occurs in.......
medullary cavity
secondary ossification follows the same pattern as primary but without the______
bone
all cartilage is replace with __________ in secondary endochondral ossification
epiphyseal line
the epiphyseal plate ossifies into the........
fully developed
In mature bone, spongy and compact bone are......
3,2,1
Arrange the following events in order.
1. Osteochondral progenitor cells become osteoblast
2. Connective tissue membrane is formed
3. Osteoblasts produce woven bone
3,2,5,1,4
Arrange the following events in order.
1. Chondrocytes die
2. Cartliage matrix calcifies
3. Chrondorcytes hypertrophy
4. Osteoblasts deposit bone
5. Blood vessels grow into lacunae of teh calcified cartilage*
As osteocytes migrate into developing bone and remove cartilage, the cartilage calcifies, diffusion of nutrients ceases, and the chondrocytes die.
Instead, when bone matrix is laid down, osteocytes' cell processes meet forming canaliculi. Thus, these cells receive nutrients through these processes
During endochondral ossification, calcification of cartilage results in the death of chondrocytes. However, ossification of the bone matrix does not result in the death of osteocytes. Explain*
•Cartilage matrix is semisolid (pliable) when compared with bone matrix, which is solid (rigid). The advantage of covering articulations (joints) with cartilage is that it provides a flexible, smooth surface for bone movement.
A major impetus for many joint replacement surgeries is degeneration of the articular cartilage, as movement of a joint without articular cartilage is quite painful.
Explain why it is advantageous for the articular cartilage to never become ossified.
bone length and bone width
unlike cartilage, bone only show appositional growth in......
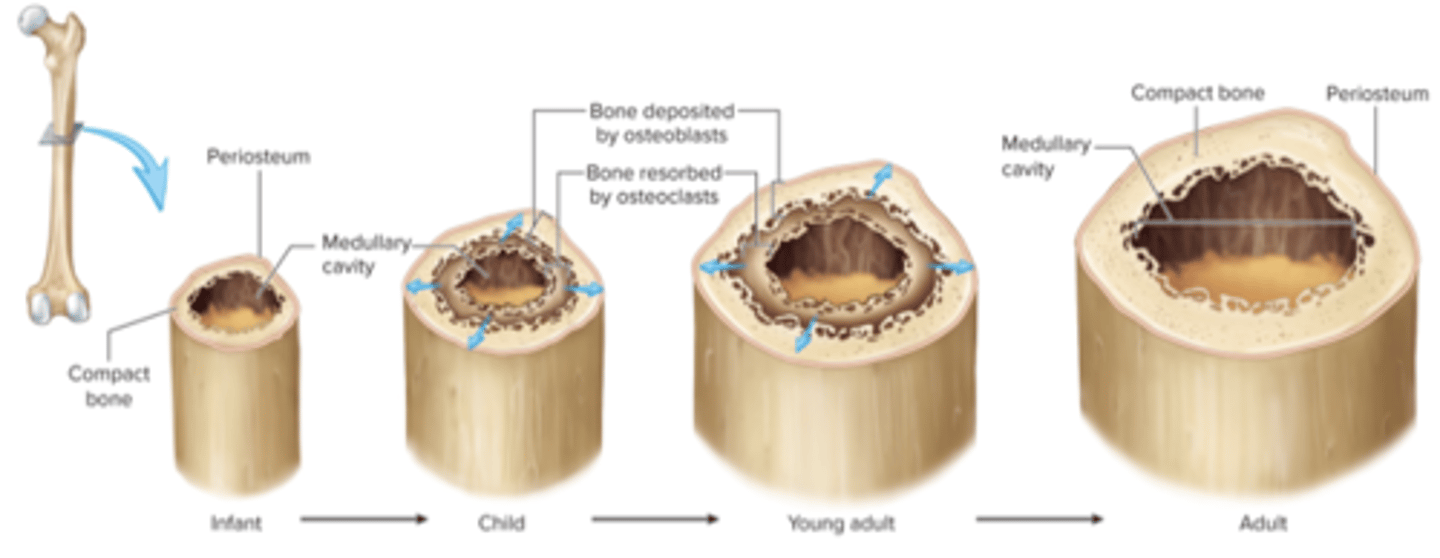
epiphyseal plate
growth in bone length occurs at the......
appositional, existing
new cartilage by interstitial growth is followed by ____________ bone growth on the surface of ______________ cartilage
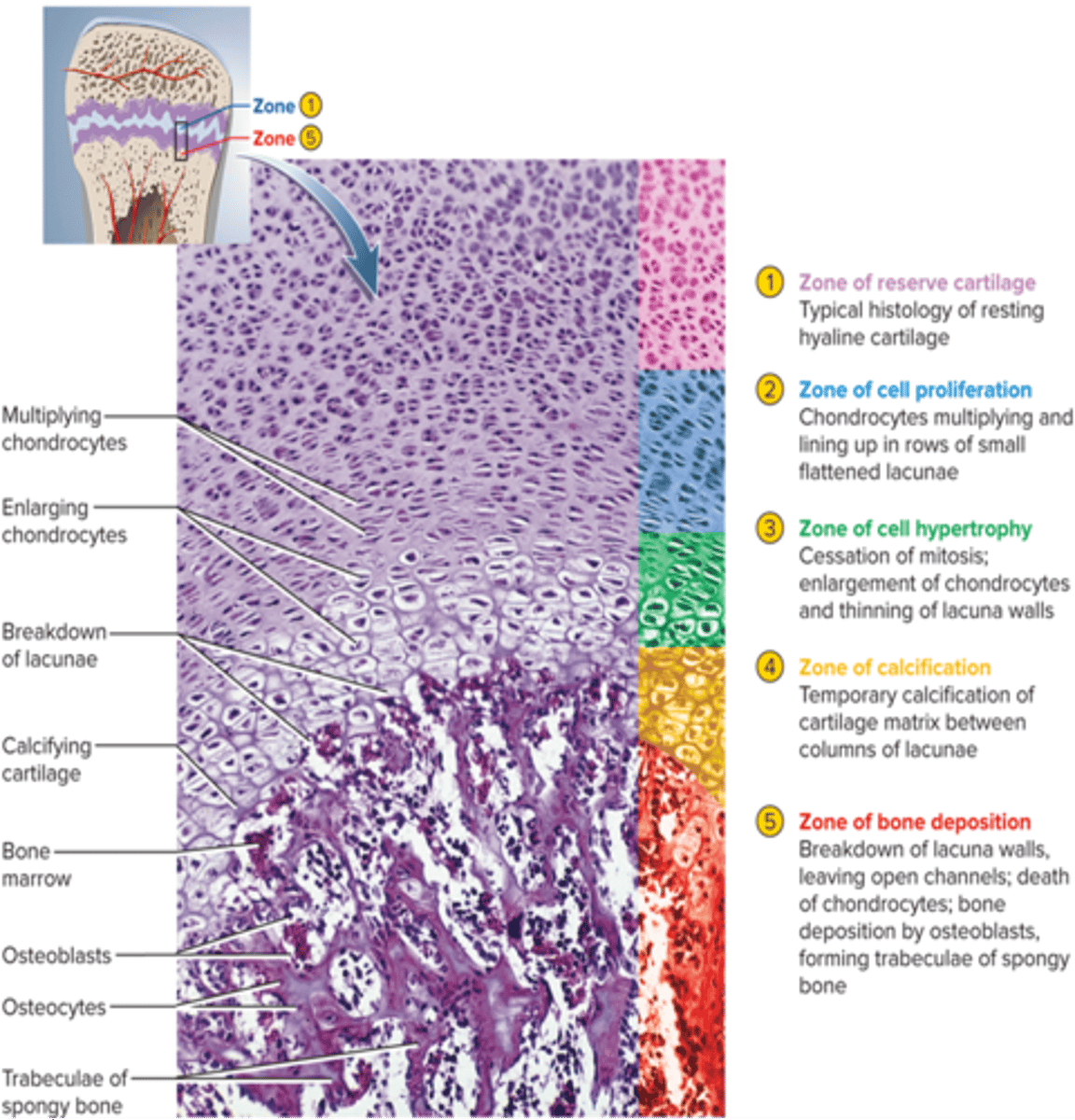
zone of resting cartliage
nearest to epiphysis, slowly dividing chondrocytes
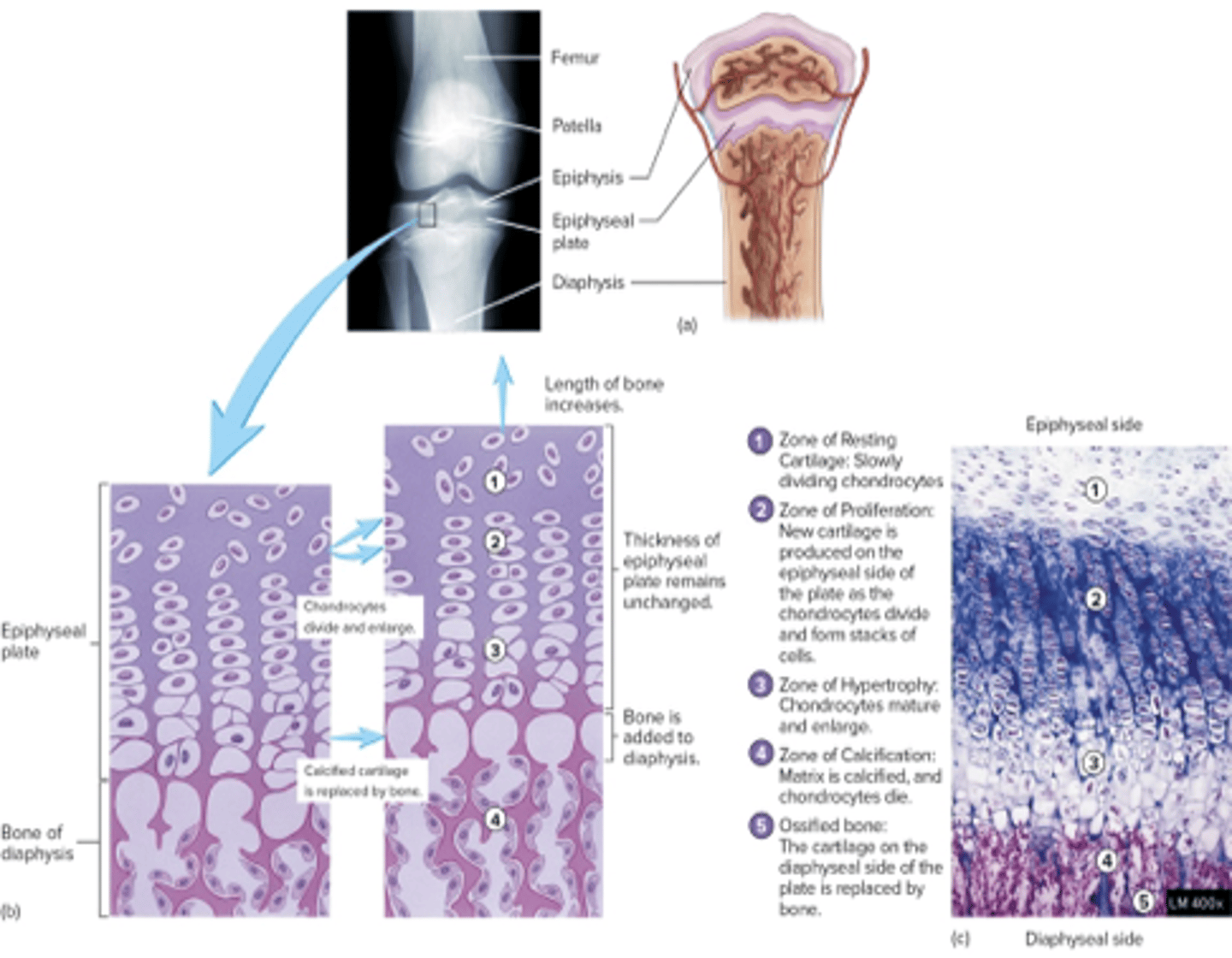
zone of proliferation
rapidly dividing chondrocyte columns -> new cartilage (interstitial growth)
zone of hypertrophy
chondrocytes mature and enlarge closer to diaphysis
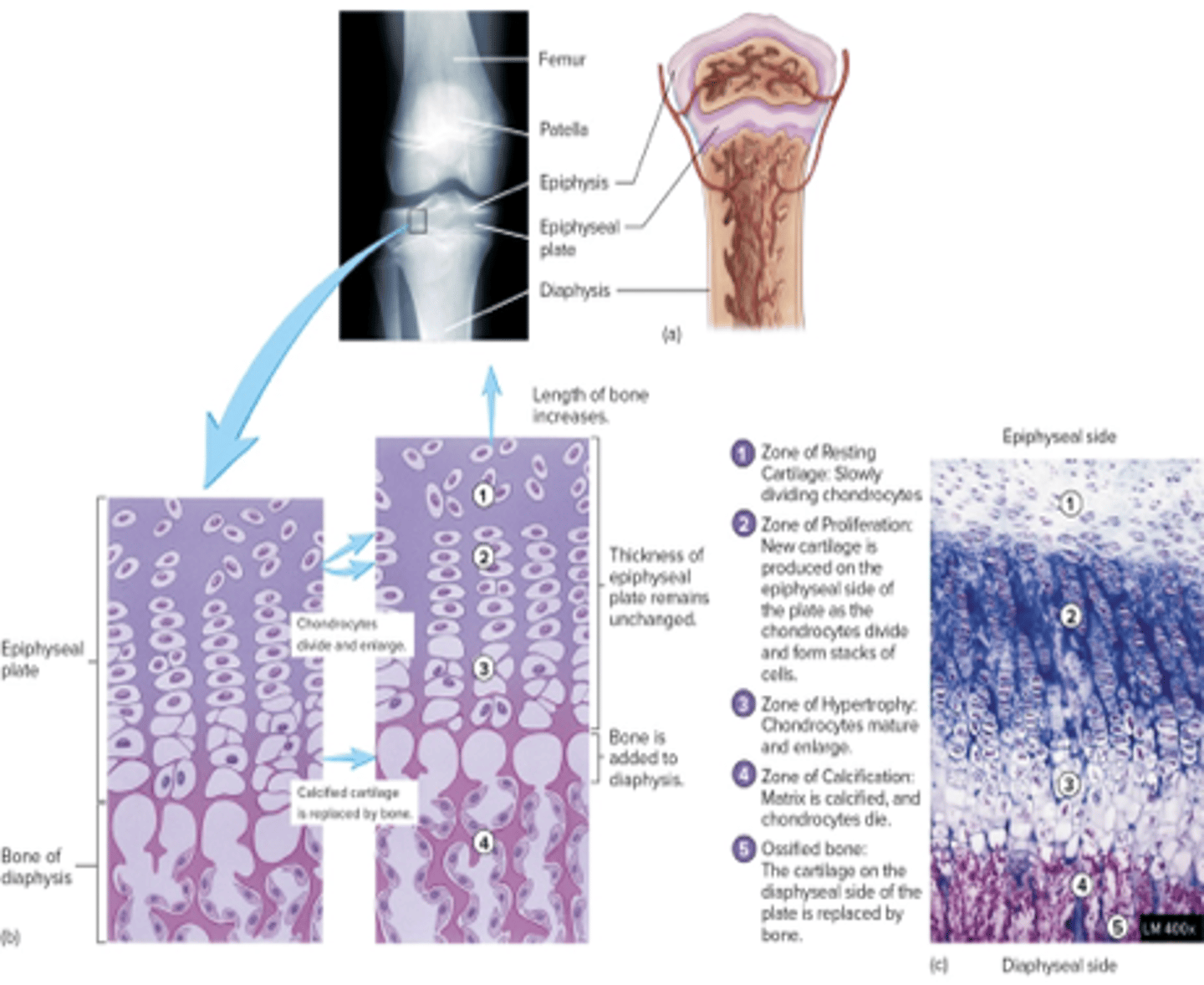
zone of calcification
dead hypertrophied chondrocytes within calcified cartilage matrix
zone of ossified bone
osteoblasts lay down new bone by appositional growth on the cartilage surface
the epiphyseal plate
The spurt growth in puberty results from cell proliferation and hypertrophy in...
the epiphysis
compact bone
the epiphyseal plate
epiphyseal line
spongy bone
periosteum, medullary
osteoblasts from the _______________ lay down bone under the periosteum which gradually increases the amount the bone surrounding the ________________ cavity