Global Health Issues: Week 3
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
What are two reasons why the term “two-thirds world“ is sometimes used instead of third world?
To show that 2/3 of the world live in extreme poverty and can be considered third world or worse
Third world has become stigmatized
Determinants of Health
Range of personal, social, economic, and environmental factors that determine the health status of individuals or populations.
Social Determinants of Health
Specific group of social and economic factors within the broader determinants of health. These relate to an individual's place in society, such as income, education or employment. Experiences of discrimination, racism and historical trauma are important social determinants of health for certain groups such as Indigenous Peoples, LGBTQ and Black Canadians
When the determinants of health and social determinants of health overlap, what is it called?
Intersectionality
The Social Gradient
the phenomenon whereby people who are less advantaged in terms of socioeconomic position have worse health (and shorter lives) than those who are more advantaged
How many DOHs does Canada have?
12.
Name 5 of Canada’s DOHs
Income and Social Status
Employment and working conditions
Education and Literacy
Childhood experiences
Physical environments
Social supports and coping skills
Healthy behaviours
Access to health services
Biology and genetic endowment
Gender
Culture
Race/Racism
What is HALE and how is it calculated?
Health-Adjusted Life Expectancy
Calculated by weighting the number of years of ill health according to severity, subtracted from the overall life expectancy. HALE = Life expectancy - years lived with disability.
Not a health gap measure.
What is DALY and how is it calculated?
Disability-Adjusted Life Year. Used to quantify disease burden. 1 DALY = 1 lost year of healthy life.
Calculated by subtracting the age at which one dies and one’s life expectancy at that age. or,
Years of life lost + years lived with disability.
Health gap measure.
What are the 3 groups of burden of disease by cause of death and DALYs?
Communicable, maternal, perinatal conditions, nutritional disorders (SSA mainly)
Non-communicable (higher income)
Injuries (higher income)
*Ischemic heart disease THE BIGGEST problem everywhere
Low-income leading cause of death: Under-5
Malaria
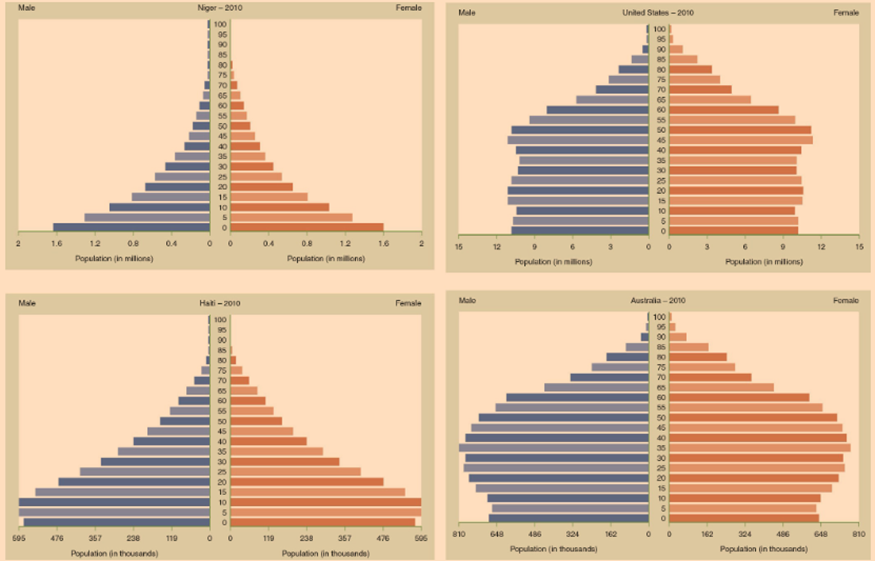
According to the demographic divide, higher income countries have ___ fertility, ___ populations, and ___ aging populations.
low, declining, aging
According to the demographic divide, lower income countries have ____ fertility.
High fertility
The demographic transition (gradient) describes…
the nature in which first world countries have LOW fertility and mortality, while third world countries have HIGH fertility and mortality. Improved hygiene and nutrition create decrease in mortality and in fertility.
The epidemiologic transition describes…
How countries shift from high to low mortality:
-Starts high and fluctuating,
-then progressive decline as epidemics become less frequent,
-finally increase in life expectancy and predominance of non-communicable diseases.
Diarrhea to Alzheimer’s.
Some factors of burden of disease, along with the DOHs:
economic development, scientific and tech change, climate change, political stability, emerging and re-emerging infectious disease.
Risk factors for deaths and DALYs in high income countries is largely…
behavioural
Risk factors for deaths and DALYs in low income countries is largely…
nutritional issues, water sanitation, pollution, tobacco
What are some components of Health Systems
· Agencies that plan, fund, and regulate health care
· The money that finances health care
· Those who provide preventive health services
· Those who provide clinical services
· Those who provide specialized inputs into health care, such as the education of healthcare professionals and the production of drugs and medical devices (pacemaker)
3 goals of health systems
1. Good health
2. Responsiveness to the expectations of the population
3. Fairness of financial contribution
4 functions of health systems
1. Provide health services
2. Raise money that can be spent on health, referred to as “resource generation”. Places like CHEO that do fundraising because govt funding isn’t enough.
3. Pay for health services, referred to as “financing”
4. Govern and regulate the health system, referred to as “stewardship”
3 categories of health services and some example countries
National Health Service: UK, Cuba
National Health Insurance: Canada, France
Pluralistic: USA, India
Three levels of care and examples
Primary: Family doc
Secondary: General surgeon
Tertiary: CHEO, specialized hospitals (rare in rural)
Public sector roles
· Stewardship of the system
· Raising the funds for the health system
· Making decisions about allocating those funds
Establishing approaches to health insurance
Private (for-profit) sector roles
· Involved in the provision of services including non-licensed “medical practitioners”
· Involved in the operation of health clinics, hospitals, services, and laboratories
· Can partner with the public sector or work under contract to the public sector
· Is involved in all countries
NGO roles
· mission-driven advocacy or service orgs in the nonprofit sector.
community-based efforts to promote better health through education, improved water, and sanitation
7 issues in the health sector
1. Demographic and Epidemiologic Change
2. Stewardship
3. Human Resource Issues
4. Quality of Care
5. Financing of Health Systems
6. Financial Protection and Provision of Universal Coverage
7. Access and Equity
Universal health care in Canada in…
1984
The 5 criteria and 2 conditions in the Canada Health Act
Criteria:
Public administration
Comprehensiveness
Universality
Portability
Accessibility
Conditions:
Information from gov to min of health
Recognition by gov of fed financial contributions