NE 101 - Future of Neuroscience
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Lecture 35 and 36
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
Process of Knowledge
Knowledge absorption leads to knowledge generation and application; New discoveries, new treatments, and implementation of treatments
Techniques to study the brain
Include various methods such as neuroimaging, electrophysiology, and behavioral assessments that provide insights into brain function and behavior; Questions we ask are limited by the power of our experimental approach
Observing the Brain in Action
Cellular and Molecular Neuroscience
Systems Neuroscience
Cognitive Neuroscience
EEG (electrodes)
Electrophisiology
Systems Neuroscience
Goal: correlate dynamic neural activity with changes in behavior or stimuli
Ex. Seeing neurons that orientations select for
Challenges for Observing Neural Activity During Behavior
Faithful indicator or readout of neural activity
Ideally voltage; If not voltage, proxy
Resolution
Ideally a single cell or better, fast time resolution
Cell-type identification
Neurons are not all the same; Cell types differ in gene expression, ion channels, etc. which determines their contribution to neural circuit function and behavior
Large scale measurements
Behavior involves coordination of activity across thousands of neurons spread across the brain; whole brain measurements
Electrophysiology
Measures action potentials and local field potentials from a small area around each electrode
Classic methods used single electrodes to record individual neurons
Modern methods use multiple electrodes in lightweight devices which enable recording of more neurons simultaneously
Cell-type Specificity Problem
Electrophysiology faces challenges in accurately identifying and distinguishing between different types of neurons due to their diverse genetic and physiological characteristics, which complicates the interpretation of neural activity data. It does not provide cell-type ID for cells with similar electrical properties.
Fluorescent Proteins
Green Fluorescent Protein (GFP) was discovered in a jellyfish; USed in multiple applications of neuroscience
Fluorescence
Fluorescence results when incoming light energy is absorbed by a molecule in the ‘ground state’, increasing its energy to an ‘excited state’; Molecules in the excited state then emit photons of lower energy as they return to the ‘ground state’ → The emitted photons (light) are of a lower energy and longer wavelength than the excitation light
Ex. GFP absorbs blue light (~480nm) and emits green light (~510nm)
Calcium Indicators
Modifications of GFP can make the fluorescence contingent upon binding certain factors (for example, calcium)
GCaMP is a protein that is comprised of a mutated form of GFP that changes its conformation when it binds calcium
Fluorescence increases when GCaMP is both exposed to blue light (required) AND when it binds calcium. Thus it is a calcium indicator (or sensor) which is a proxy for neural activity
Expressing Fluorescent Sensors
Viruses can be used to deliver payloads of genetic material encoding the sensor (protein) to the brain
Viruses are usually injected directly into the brain because they cannot cross out of the bloodstream and are taken up by neurons which then use their own cellular machinery to transcribe and translate into protein
New variations have been developed that be injected systemically (into the body) so brain injections aren’t needed
These viruses are engineered not to replicate
How can these calcium indicators address the problem of observing specific cell types?
Restrict expression of the sensor gene only to certain cell types!
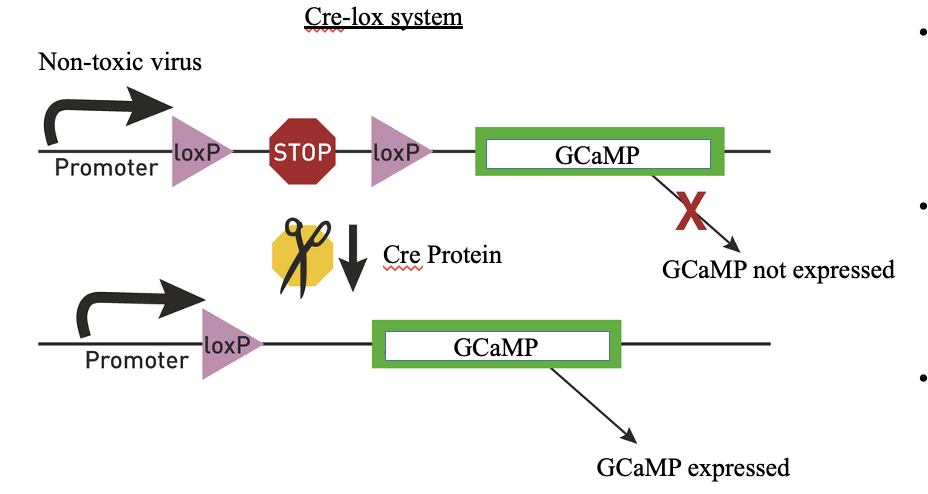
Expression of Genetically Encoded Fluorescent Indicators - Cre-lox system
Non-toxic viruses which contain DNA encoding for GCaMP are injected into the brain and taken up by neurons; GCaMP is not normally transcribed because it is downstream of a ‘STOP’ sequence; When cells express a protein called ‘cre’ the stop sequence is removed and GCaMP can be expressed
Cell-type specific gene expression
A technique to ensure that genes are expressed only in selected types of cells, allowing for targeted observation and analysis of specific neuronal populations.
Animal lines (particularly mouse) can be created which express the cre protein under control of a cell-type specific promoter sequence
Cre will only be expressed in particular cell types, as will the indicator (GCaMP) under Cre control
This system can also be done with viruses alone (so it can be done in humans), but is a more difficult genetic engineering problem…
Visualizing Calcium Signals in the Brain During Behavior
Miniature microscopes can be used to visualize signals from 1000s of neurons expressing GCaMP in freely moving animals
Measuring Neurotransmitter Specific Inputs
Proteins have been engineered which change their fluorescence in the presence of specific neurotransmitters
These proteins can be genetically expressed in specific cell types to measure neurotransmitter specific input signaling
Manipulation of Neural Circuits
Basic research: Are activity patterns or brain regions necessary and/or sufficient to drive behavior (correlation does not always equal causation)?
Clinical applications: Can we manipulate neural circuits precisely enough to treat neural dysfunction without side effects (i.e. therapeutics)?
Sci Fi??: Can we ‘read’ and write’ patterns of neural activity into the brain to alter behavior?
Brain Manipulations
Techniques aimed at altering or influencing neural activity patterns to modify behaviors or treat neurological disorders. These may include electrical stimulation, optogenetics, or pharmacological methods.
Ex. Pharmacology, Deep Brain Stimulation, Surgical Manipulation, ECoG
Classical Methods for Brain Manipulation
Pharmacology, Deep Brain Stimulation, Surgical Removal, and Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS)
Challenges for Brain Manipulations
Electrical stimulation: Region specific, but not cell type specific
Pharmacology: Not region specific, somewhat cell-type specific, SLOW
Circuit Manipulation:
Temporal precision: manipulations would be on the timescale of behavior (100s of ms to seconds)
Spatial specificity: Manipulations restricted only to particular brain areas or sub-circuits
Cell-type or NT specificity
Non-toxic or damage inducing
Achieving Specificity and Precise Timing Control
Strategies aimed at enhancing the accuracy and timing of brain manipulation techniques, ensuring targeted effects on specific neural circuits while minimizing side effects.
Light Sensitive Ion Channel in Green Algae
A light sensitive ion channel called channelrhodopsin was discovered by Peter Hegemann in the 1980’s in green algae
The protein is important for promoting cellular motility and chemotaxis in response to light → gated by presence of light and changes permeability/whether or not the channel opens
Manipulating Neurons with Light Sensitive Ion Channels
Channelrhodopsin can be expressed in neuronal membranes and opened in response to blue light, resulting in inward flow of positive ions and cell depolarization
Another light sensitive channel, halorhodopsin opens in response to yellow light and passes chloride ions which hyperpolarize the neuron
Many other variants of these now exist with different properties for manipulating neurons
Cell-type Specific Expression of Opsins
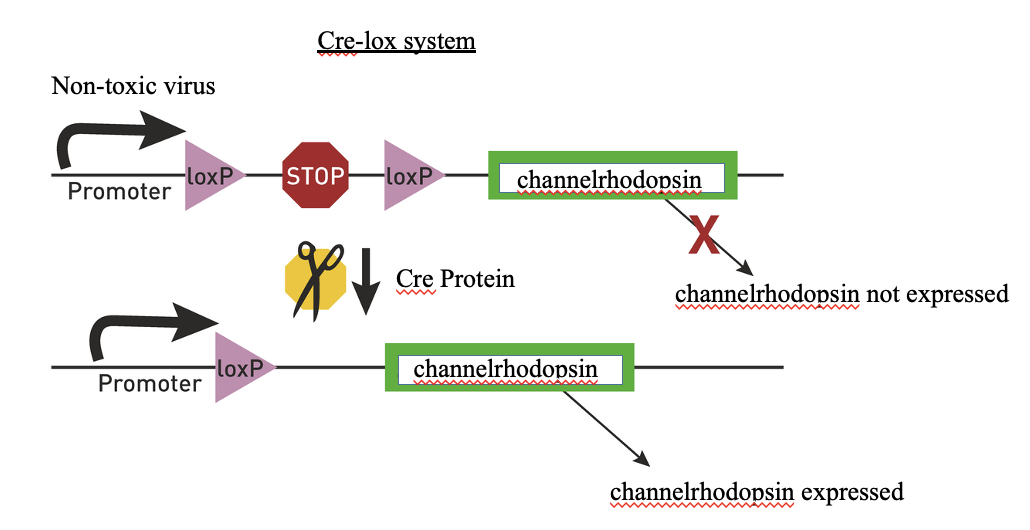
This is the strategy used for experimental mouse models in which a cell-type specific ‘cre’ mouse line is available
In humans and non-human primates, the strategy is to use a cell-type specific ‘promotor’ to get around the cre requirement
Virus encoding construct with a stop codon that are flanked by lox p sites, cre bings to the sites, cuts the out, is recombined, and the gene can be transcribed
Advantages of Opsins over Traditional Approaches
Can be genetically encoded and delivered to specific cell types with viruses and cre/lox recombination, enables spatially restricted manipulations
Manipulations are very fast and can be bi-directional (on and off)
Light Delivery for Neural Manipulations
Light can be delivered through small optical fibers in the brain, activating channel rhodopsin
Light spread can be tightly controlled (typically in the range of <1mm)
Challenges for Translation Into Humans
Human brains are big
Expression of the opsin proteins
Extent of expression
Safety of viruses
Stability of expression
Delivery of light
More volume to cover
Requires invasive surgery if fibers are used
Pharmacogenetics: ‘Targeted Pharmacology’
An area of medicine that studies how individual genetic differences affect responses to drugs, aiming to create personalized medication strategies.
DREADDs: Synthetic G-protein coupled channels which are inhibitory or excitatory and can be virally delivered to specific cell types in the brain
CNO: Crosses the blood-brain barrier so it can just be injected into the body like a normal drug (no surgery needed)
Implanting Neural Activity in the Brain
The process of inserting electrodes or devices into brain tissue to monitor or stimulate neural activity, often used in research and therapeutic contexts.
Implanting/taking away memories
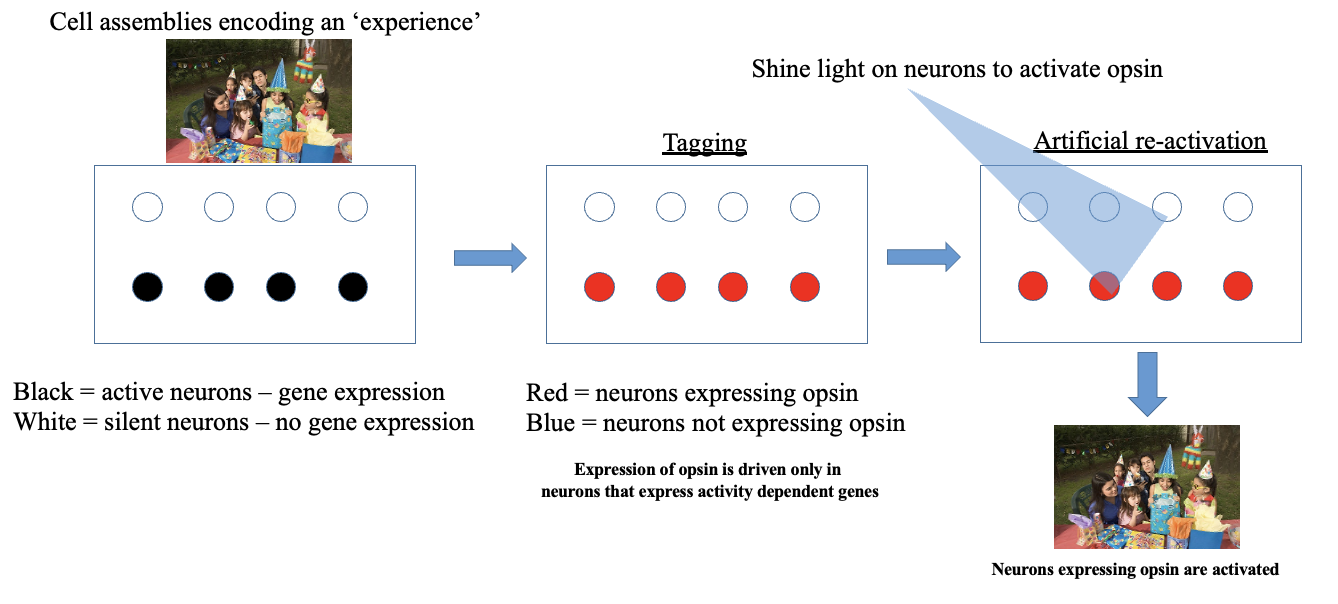
Manipulating Memories
Cell assemblies represent different components (of the party) and the strengthened connections is the ENGRAM for the memory; Memories - activation of different cell assemblies that encompass cell systems and parts of the brain, plasticity is triggered
Targeting Cell Assemblies - Activity Dependent Gene Expression
Neural activity (action potentials) results in calcium entry into neurons
Calcium entry (and other factors) can trigger expression of certain genes (called immediate early genes)
Targeting Active Cell Assemblies
A technique that focuses on the neural pathways that are activated during specific activities, leading to gene expression changes that can affect behavior and memory. This method utilizes neural activity to enhance understanding of how memories are formed and recalled. Target cells → part of cell assembly