Food Science 9/30/2025
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Atoms
Basic building blocks of matter. Individual elements
Molecule
A unit composed of 2 or more atoms, held together by chemical bonds
Compound
Substance whose molecules consist of unlike atoms
Ionic Bonds
A metal loses an electron to a non metal atom
Sodium loses an electron to oxygen or chlorine
Oxygen or chlorine are negative
Sodium is positive
Sodium hangs around the atom that took its electron (opposites attract)
What are characteristics of Ionic bonds?
Characteristics
Dissolve easily in water
Form crystals at high temperatures
Conduct electricity in solution
Examples
Table salt (NaCl)
Salt substitute (KCl)
Covalent bonds
Electrons shared between two non metal atoms
Energy is released and system becomes more stable
Atoms make as many bonds as possible
Stay stuck together until energy is added to pull them apart
Hydrogen bonds
Some atoms (Flourine, oxygen nitrogen) have strong affinities for electrons, when covalently bonded to hydrogen, the electrons hang out closer to the heavier atom than near the hydrogen
Polar molecules
One end sl + and the other sl -
Electrostatic attractions
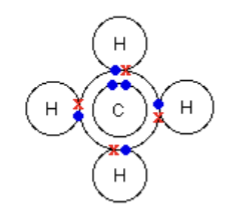
Methane
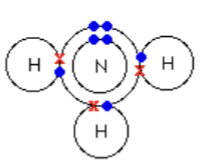
Ammonia
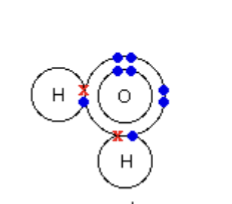
Water
What is a polar molecule?
One end sl + and the other sl -
Oxygen Atom
Larger, red ball
Slightly negative charge
Hydrogen atom
Smaller, white ball
Slightly positive charge
Hydrogen bond
Dotted line is an attraction
Dotted line with arrows is a repulsion
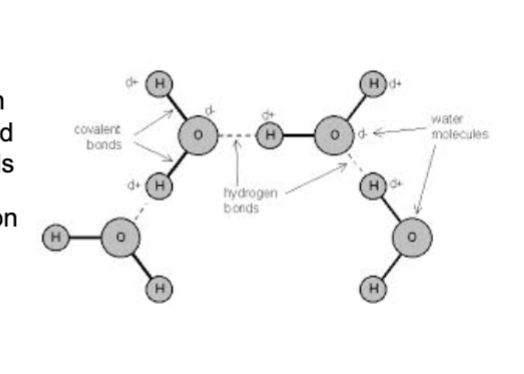
The H atoms and O atom within a molecule are held by covalent bonds
The electrostatic attraction between molecules are hydrogen bonds
Nutrients
Food components that nourish the body to provide growth, maintenance and repair
Macro nutrients
Protein
Lipid
Carbohydrates
Water
Micro Nutrients
Minerals and vitamins
Proteins
Nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen, oxygen and sometimes sulfur and phosphorous
Composed of amino acids
Active machinery of life
Muscle and other tissue
Enzymes
Hormones and antibodies
Shape and behavior drastically changed by heat, acid, salt and air
4kcal/gram
How can we tell something is a protein
It contains hydrogens and nitrogen
Lipids (fats and oils)
Carbon, hydrogen, oxygen
Provide energy
Components of living things
Cooking medium and ingredient
Does not mix with water
9 kcal/gram
Carbohydrates
Carbon, oxygen, hydrogen
Specialty of plants
Sugars, starch, dextrin, pectin, fiber
Mix freely with water
Flavor, bulk and texture
4 kcal/gram
Water
Hydrogen, oxygen
Major components of nearly all foods
Medium to heat foods
Important influence on other food molecules
Solvent
Hydrates
Vitamins and minerals
Essential for nutrition
Vitamins
Sustain life and good health
Minerals
Growth and reproduction