BioChem Quiz 10: Transcription & Regulation of Gene Expression
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
How is RNA synthesized?
5 to 3 direction (same as DNA replication)
Where does energy to drive bond formation come from?
hydrolysis of high-energy bond of incoming nucleotide
What are the substrates for both DNA and RNA?
4 nucleotide triphosphates (3 of the same, one diff)
How does DNA transcription and Replication use enzymes?
use enzymes to select the appropriate nucleoside triphosphate in a template-directed manner following base-pairing rules
What must occur to the DNA helix to gain access to the genetic info?
2 strands of the DNA helix must be transiently separated
What are the linkages formed between RNA and DNA nucleotides?
3'-5' bonds with chain growth occurring in a 5' to 3' direction
How many strands in DNA?
two strands
sense strand and template strand
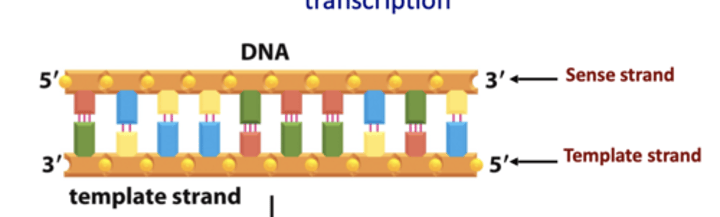
How many strands in RNA? What is it identical to?
one
RNA is identical to sense strand of DNA template except U replaces T and ribose replaces deoxyribose
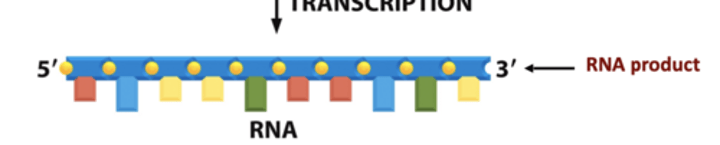
What is true as the RNA chain is synthesized? (difference between replication and transcription)
it does not remain hydrogen-bonded to the DNA template
What is mRNA? What is its role and what % is it of the total RNA?
messenger RNA
DNA transcript, 3%
What is rRNA? What is its role and what % is it of the total RNA?
ribosomal RNA
functions in translations, 80% or more
What is tRNA? What is its role and what % is it of the total RNA?
transfer RNA
deciphers code in mRNA, 15%
Describe the size and shape of RNA molecules in transcription
discrete in size, defined by transcriptional start and stop sites
Which direction does transcription occur along a DNA molecule?
either direction
How many copies does replication make of a genome?
one
How many copies does transcription make of a RNA?
many
Describe the initiation step of transcription
RNA polymerase binds at the DNA start site, known as the promoter, and forms the first bond of the RNA chain
most regulated step
Describe the elongation step of transcription
nucleotides are sequentially added to 3'- end of growing chain in template-directed manner
Describe the termination step of transcription
both the RNA product and RNA polymerase are released from the DNA
What are promoters?
the DNA sequences that the RNA polymerase binds to and initiates transcription
What is the rate at which RNA polymerase utilizes the promoter sequence regulated? What does it determine?
highly regulated
largely determines the rate of transcription and often controls gene expression
What is a repressor?
proteins that bind to DNA that overlaps with the promoter, blocking RNA Polymerase binding and inhibiting transcription
What is an activator?
proteins can bind to DNA and promote RNA Polymerase binding, increasing transcription
Describe strong promoters
have strong (high affinity) interactions with RNA polymerase through the formation of many bonds
more likely to initiate transcription and lead to mRNA synthesis
Describe weak promoters
have weaker interactions with RNA polymerase through the formation of fewer bonds
weaker bonds and fall off the DNA
What represents the strongest affinity site possible for binding?
high conserved consensus sequence --> TATA box
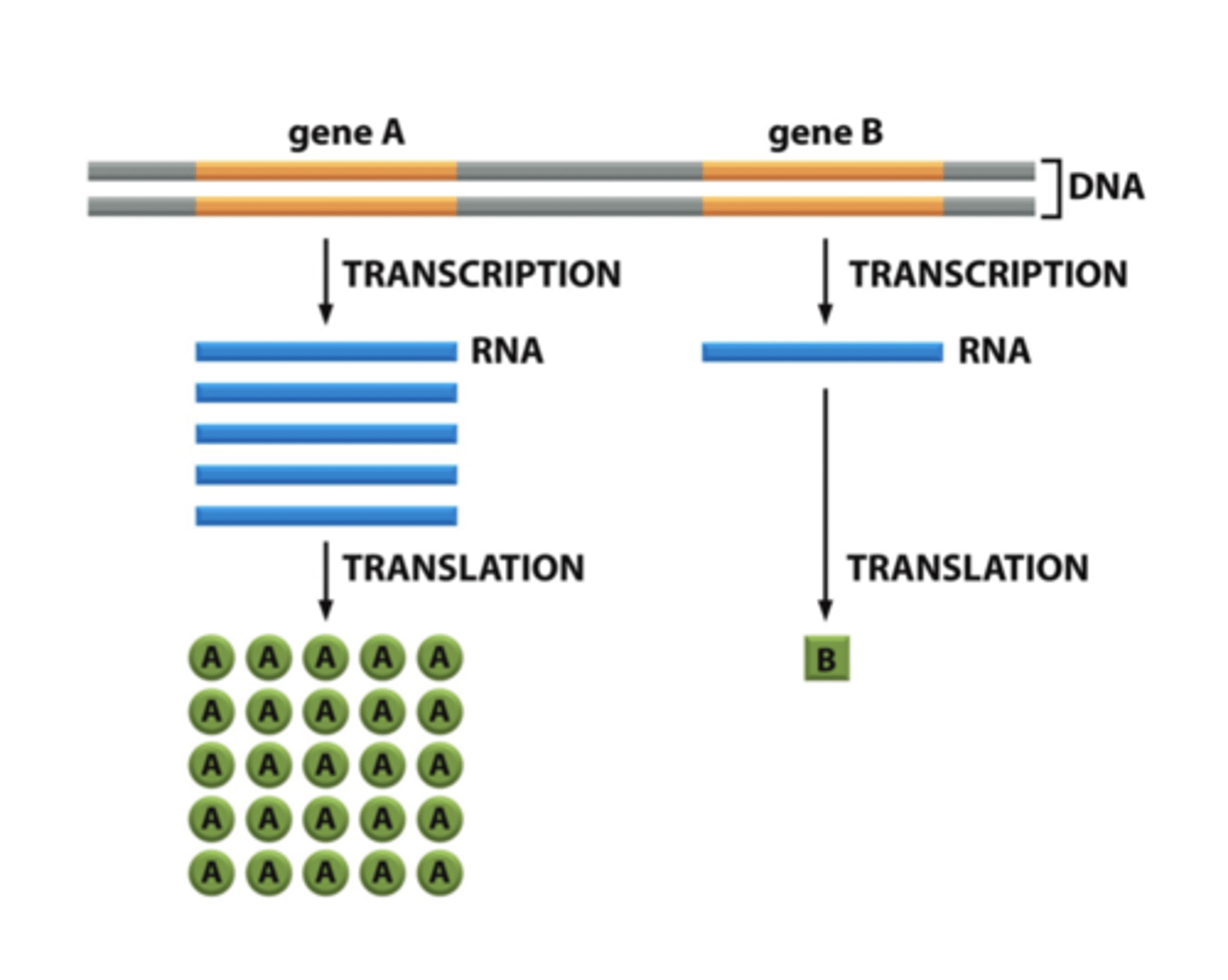
How has evolution tailored each promotor?
tailored each promoter to provide the appropriate amount of RNA and protein for the corresponding gene
Which gene has the stronger promoter?
Gene A
Gene B has a weaker promoter bc less copies
When are promoters in prokaryotes expressed? (no nucleus in prokaryotes)
in the presence of lactose and the absence of glucose
What does DNA Replication use?
DNA polymerase & 4 dNTPs (A, C, G, T)
What does RNA Transcription use?
RNA polymerase & 4 NTPs (A, C, G, U)
How many copies of the genome does DNA Replication make?
one
How many copies of the genome does Transcription make?
many
Does DNA Replication copy one strand or both?
both
Does Transcription copy one strand or both?
one - template strand
What happens to the product in DNA Replication?
stays bound to template
What happens to the product in Transcription?
released from template
What is the error rate of DNA Replication?
low error rate, proofreading
What is the error rate of Transcription?
higher error rate, no proofreading
Describe promoters in prokaryotes
Situation: body is creating proteins to break down lactose because glucose is low
1. central dogma is carried out and active repressor is blocking the area that RNA polymerase needs to bind so no protein to break down lactose is being made
2. lactose in the body binds to repressor to remove it from its site so that RNA can bind
3. meanwhile glucose activates CAP with cAMP to induce transcription and active CAP can bind to CAP site
4. CAP is bound to site and RNA polymerase can bind and transcribe and lactase is made
**if we have high glucose, this process is not needed
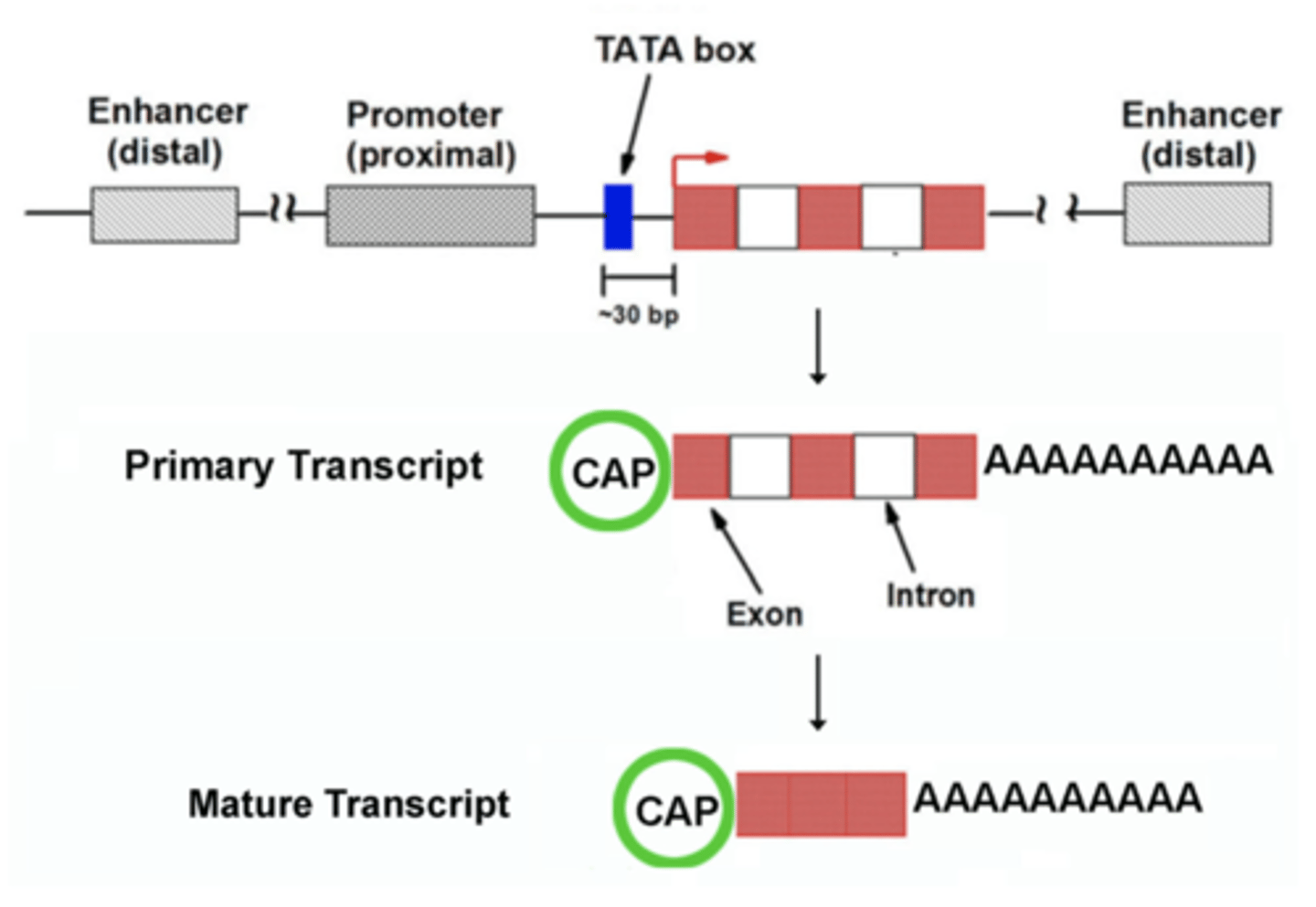
Describe promoters in eukaryotes
connect enhancers or repressors to promoter to stop or start the process
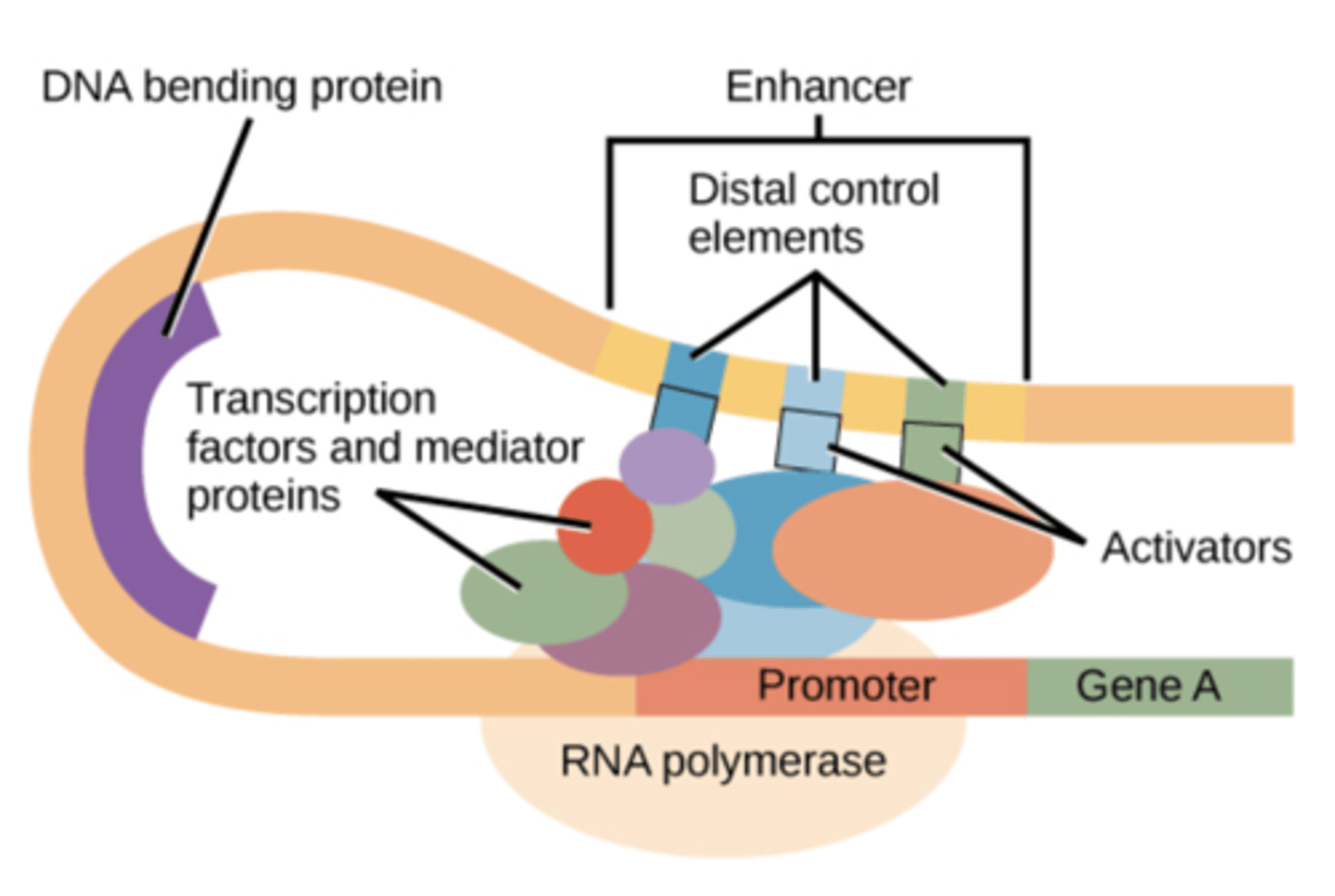
Describe promoters & mRNA processing in eukaryotes
exons exit nucleus
introns stay in nucleus
mature transcript is left with all exons