Short Term Memory (9/22)
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
Memory
mental process that enables us to retain and use info over time
What was the significance Atkinson & Shiffrin (‘68)
info passes through three distinct structures and three distinct processes
based on the belief that memories are processed the same way that a computer processes info
What is the Aktinson & Shiffrin Model?
Three Structures of the A-S Model
Sensory → STM → ← LTM
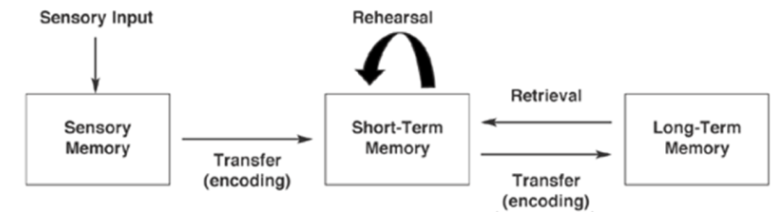
What are the three structures of the A-S Model
Sensory Memory:
STM
LTM
Sensory Memory (A-S Model)
storage of belief sensory events, such as sights, sounds, & tastes
STM (A-S Model)
temporary storage system that processes incoming sensory memory
LTM (A-S model)
the enduring storage of information
What are the three processes of the A-S model?
Encoding
Storage
Retrieval
Encoding (A-S model)
the mental process by which information is transformed into a form that can be easily entered into and retained by the memory system
Storage (A-S Model)
the process of storing information in memory for use at a later time
Retrieval (A-S model)
the recovery of information from our memory so that we are consciously aware of
What are the two types of Sensory Memory?
Iconic (visual) sensory memory
Echoic (auditory) sensory memory
Iconic Memory
immediate, brief memory of a visual image
the shortest-term element of memory
Persistence of Vision
Persistence of Vision ( part of sensory memory)
a sensation lasts for a fraction of a second in memory beyond its real-world duration
Echoic memory (of sensory memory)
momentary sensory memory of auditory stimuli
if attention is directed elsewhere, sounds and words can still be recalled w/in 3 or 4 seconds
→ stores the tail-end of the question temporarily while earlier parts of the message are being processed
estimates of echoic duration are often distorted by retrieval from short term memory
What is the significance of George Sperling et al. (‘60)
conducted classical research on the characteristics and processes of visual sensory memory
Results:
suggest all registered, but some (memories) were no longer available at the time or report (supports decay)
suggested visual sensory store decays rapidly & is relatively large
suggests visual sensory memory lasts about 250-300ms (relatively short)
Short Term Memory (STM)
store house for limited amounts of information for brief periods of time
What is the duration of STM?
Brown-Peterson Paradigm
participants had 5% recall after 18 secs
info decays from STM w/in 20 secs
rehearsal is important in maintaining info - disruption to rehearsal by a distractor task greatly effects recall
Waugh & Norman (‘65)
does not support decay, but interference
What are problems with the Brown Peterson Paradigm
task prevented rehearsal which is a potential sources of interference
→ retroactive interference
Interference from the experimental situation
→ proactive interference
Retroactive interference
occurs when newly learned information interferes with the retrieval of old info
Proactive interference
occurs when previously learned information interferes with the learning of new information
What is the capacity of STM?
can process large amounts of info
creates bottle-neck effect
George Miller (‘56)
results: remembered on average 7 , suggests STM’s magic number is 7 ± 2
Bower & Springston (‘70)
Chunking (or recoding)
if words are reordered into a way that is more meaningful, capacity is maximized
Luck & Vogal (‘97)
suggested STM capacity may be limited to as low as 4 components when STM is not linguistic nature (i.e blocks)
What are the three conditions for important recoding (or chunking) (STM)
sufficient time or resources needed to apply recoding scheme
must be recoded into something meaningful
if the recoding scheme is well learned it requires less time and resources
What are the two position effects?
primary and recency effect
Primary Effect (position effects)
recalling the first items better than the middle items
probability decreases as the number of items increases
result of rehearsal and encoding into long-term memory
rapid presentation eliminated primacy but preserves recency
Recency effect (position effects)
recalling the last items better than the middle items
probability is not affected at the number of items increases
result of items still w/in STM
delayed recall eliminates recency but preserves primacy