Animal Behavior ch18
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
wilson’s characteristics for Eusociality
reproductive division of labor
cooperative brood care
overlapping generations
Cornwallis et al.
study suggested that cooperative breeding is more likely to evolve in populations where females mate with fewer males
Paul Sherman
studied alarm calls in Belding’s ground squirrels and tried to determine if the alarm calls were directed at the predator or at kin.
He found that the answer varied with the circumstances.
nepotistic society
where most interactions occur between females and their offspring and kin
Benefits of group living?
improved foraging
decreased predation risk
conserving heat & water
conserving energy
information sharing
improved foraging by observing the behavior of group members.
informational centers
communal roosts or colonies where animals can observe the foraging success of conspecifics and follow the successful ones to food sites.
Costs of group living?
increased intraspecific competition
increased risk of disease & parasites
reproduction interference
kin selection
refers to apparent strategies in evolution that favor the reproductive success of an organism's relatives, even at a cost to the organism's own survival and reproduction.
coefficient of relatedness
r
Hamilton’s rule
developed a theorem for determining how the coefficient of relatedness affected altruism
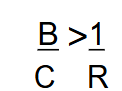
kin recognition
refers to an animal's potential ability to distinguish between close genetic kin and non-kin.
4 ways that an animals may be ale to tell kin from nonkin:
location
familiarity
phenotype matching
recognition alleles (green beard effect)
Location kin recognition
works well in species with established distribution patterns.
familiarity kin recognition
involves animals learning to recognize individuals with whom they were raised.
Phenotype matching
allows animals to identify kin even if they had never previously met. Family members tend to share phenotypes so phenotypic similarities can be used to determine relatedness.
recognition Alleles
involves an inherited allele or group of alleles that the individual can use to recognize others with the same allele.
ex: green beard effect
Cooperative breeding
social system in which individuals contribute care to offspring that are not their own at the expense of their own reproduction.
was first observed in birds
Benefits of cooperative breeding
increase inclusive fitness
gain parental experience
group augmentation
Costs of cooperative breeding
unable to increase own direct fitness
expending energy on someone else’s offspring
The benefits of cooperative breeding will only occur…
in a population only if it is better to stay and help other individuals than to move somewhere else and attempt breeding.
Other reasons for cooperative breeding?
habitat saturation
lack of mates
Eusociality
term used for the highest level of social organization in a hierarchical classification
usually find a queen and unsterile workers
examples: insects (ants, bees, wasps, and termites)
Narrow definition of eusociality
specifies the requirement for irreversibly distinct behavioral groups or castes
sterility in lower castes
Broader definition of eusociality
allows for any temporary division of labor or non-random distribution of reproductive success
Isopterans
termites
hymenopterans
bees, wasps, and ants
Haplodiploidy
Sisters are more related to each other than to their offspring
"supersisters" who share 75 percent of their genes on average—> workers will invest more care into their sisters over having their own offspring
Evolution of Eusociality
haplodiploidy
shared defensible resource
extended parental care and lasting sibling associations