ABO Blood Group System
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
84 Terms
transfusion of incompatible blood is associated to what
acute intravascular hemolysis, renal failure, and death
transfusion of incompatible organs is associated to what
acute humoral rejection
which chromsome is the ABO gene on
chromsome 9
what are the four phenotypes resulting from the prescence or abscence of A or B antigen
A, B, O, and AB
what are the genotypes possible for the ABO blood groups
AA, AO, BB, BO, AB, and OO
which gene is the amorphic gene
the O gene because it has no detectable antigen
what structure commonly carries ABO and H antigens on the red blood cell membrane
a glycoprotein (carbphydrates attached to proteins)
where are ABO antigens found on
RBCs, PLTs, lymphocytes, most epithelial and endothelial cells and organs (kidneys, heart, bowel, pancreas, and lungs)
when do ABO antigens show up in the embryo
5-6 weeks into a pregnancy (gestation)
between what age group do you have adult levels of ABO antigens present
2-4 years old
when do the ABO antibodies start to develop
3-6 months of age, peak at 5-10 years old
are ABO antibodies present at birth
no (so you can’t do reverse blood typing on newborns)
are ABO antibodies naturally occurring
yes, they just develop after a few months after being born
what antibody does type A have on its RBCs
anti-B
what antibody does type B have on its RBCs
anti-A
what antibody does type AB have on its RBCs
no antibodies
what antibody does type O have on its RBCs
anti-A and B
what antibody does type A not have on its RBCs
anti-A
what antibody does type B not have on its RBCs
anti-B
what antibody does type AB not have on its RBCs
anti-A and B
what type of immunoglobulins are anti-A and B
IgM
what type of immunoglobulin are found in O patients
IgG and IgM
can ABO antibodies activate complement
yes (both IgM and IgG) at 37 degrees celsius
in group O, IgG individuals can also make
anti-A,B
which antibody can sometimes be found in people with subgroups of A
anti-A1
what temperature do ABO antibdoes react at
37 degrees celsius (room temp cold agglutinin)
what is the source of ABO antibodies
gut and environmental bacteria (enterobacteriaceae)
what antibody is not a combination of anti-A and anti-B but is a different “cross-reacting antibody” that is usually IgG
anti-A,B
what type of chains are the ABO blood group built on
two types of long chains, type I and type II
what are the three genes that modify the chains that ABO blood groups are built on
H gene on chromosome 19
Se chromosome 19
ABO gene on chromosome 9
another name for H gene
Fut 1 gene
another name for Se chromosome
Fut 2 gene
H, Se, and ABO genes produce what kind of enzyme
glycosyltransferases
glycosyltransferases add sugars to the precursors that make H, Se, and ABO, the sugars are known as
immunodominant sugars (responsible for RBCs being able to have their specific antigens)
what are the different types of glycosyltransferases
H(O)-antigen: alpha-2-L-fucosyltransferase
A-antigen: alpha-3-N-acetylgalactoseaminyltransferase
B-antigen: alpha-3-D-galactosesyltransferase
what are the three immunnodominant sugars
H(O)-antigen: L-fucose
A-antigen: N-acetyl-D-galactosamine
B-antigen: D-galactose
structure of H-antigen
formed for the platform on which A and B antigens are made
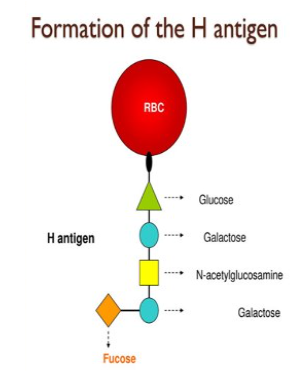
structure of A antigen
H antigen is the docking port that N-acetylgalactosamine can attach to
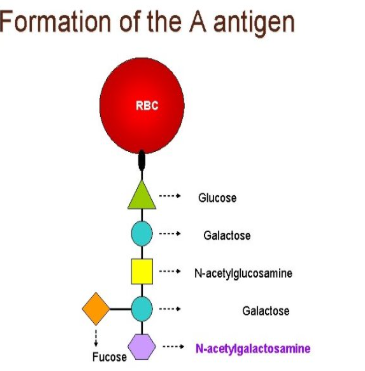
structure of B antigen
H antigen acts as a docking port that galactose can attach to
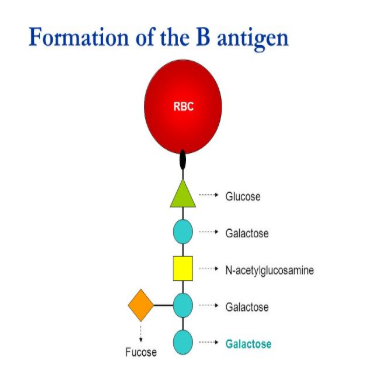
what antigen is the platform of A and B antigen
H antigen
what is the only antigen of the H blood group system
H
what are the two significant alleles of the H blood group system
H (dominant, 99.99% frequency)
h (amorph, rare frequency)
the H gene codes for
the glycosyltransferase L-fucosyltransferase to stimulate L-fucose to become a terminal sugar of type-1 or 2 chain
h is an amorph which means it has _______________________________
no detectable gene product
red cells from an hh individual are the ____________ phenotype
bombay
what immunodominant sugar encodes for the H anitgen
L-fucose
the Fut 1 gene results in which type of blood group
group O
which blood group has the highest concentration of H antigens
group O
which blood group has the least concentration of H antigen
A1B
greatest to least amount of H antigen
type O > A2 > B > A2B > A1 > A1B
which type of chain is ABH antigens constructed on
type 2 chains (attached and a mixture of glycolipids/glycoproteins)
what is bombay
a rare autosomal recessive phenotype chracterized by the abscence of H, A, and B antigens on RBCs and in secretions
inheritence pattern of bombay phenotype
autosomal recessive
how does the bombay phenotype occur
a mutation in the H gene produces a silenced gene incapable of coding for H transferase
the bombay (Oh) phenotype typing looks like
O blood group but the serum contains anti-A, anti-B, anti-A,B, and anti-H
the bombay phenotype makes anti-H antibodies which can or cannot bind complement
can bind complement
if a patient had the bombay phenotype what kind of blood would they need
blood from another person that has the bombay blood type
how is para-bombay different from the bombay phenotype
it still results from genotype hh and at least one Se but has small amounts of A and/or B antigens on RBCs
since there’s H, A and/or B antigens in their secretions that get absorbed from plasma onto the RBC membrane resulting in weak expression
how is bombay detected
through absorption/elution studies
what antigens will a secretor carry
SeSe (carried by 80% of population
which gene encodes for mucosal protective functions and determines the ability to secrete your blood type antigen in body fluids and tissue
Fut 2
which antigen in plasma can absorb on platelets and lymphocytes but not on granulocytes and monocytes
A, B, and H antigen
in non-secretor how is the degree of protection decreased
IgA and IgG will be decreased in non-secretors, in addition to having decreased mucosal protective functions
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype A
anti-A: positive
anti-B: negative
A1 cells: negative
B cells: positive
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype B
anti-A: negative
anti-B: positive
A1 cells: positive
B cells: negative
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype AB
anti-A: positive
anti-B: postive
A1 cells: negative
B cells: negative
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype O
anti-A: negative
anti-B: negative
A1 cells: positive
B cells: positive
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype Oh (hh genotype with sese bombay)
anti-A: negative
anti-A: negative
A1 cells: positive (follow up with elution studies)
B cells: positive (follow up with elution studies)
expected reaction when preforming ABO typing on RBCs and plasma for phenotype Oh (hh genotype with at least one Se, para-bombay)
anti-A: negative
anti-B: negative
A1 cells: +/Ø
B cells: +/Ø
which subgroups are more common, A or B
A subgroups
which subgroup, A1 or A2 show increased reactivity with the anti-H
A1 reactivity is 80%
A2 is 20%
what A subgroups have the greatest amount of H antigen
A2
what would you use to distinguish the difference between subgroups A1 and A2
the lectin dolichos biflorus
chracteristics of the ABO subgroups
decreased number of antigen sites
variable agglutination with anti-A,B
variable detection of anti-H
anti-A1 may or may not be present
infrequently encountered
dolichos biflorus lectin prefers what antigen
binds A1 and A1B
ulex europaeus lectin prefers what antigen
binds H and O cells
bandeiraea simplicifolia lectin prefers what antigen
binds B
vicia graminea lectin prefers what antigen
binds N
iberis amara lectin prefers what antigen
binds M
what are the two components of routine ABO typing
forward and reverse typing
type 1 chain
a free floating chain found in secretion (saliva, tears, urine, digestive fluid) as a glycoprotein
exist as glycolipids in plasma
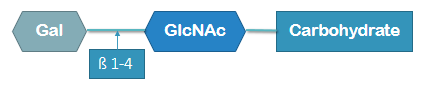
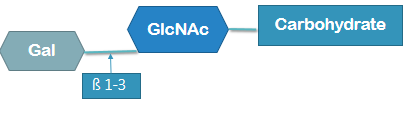
type 1 chain structure
galactose connected with β 1-3 to N-acetylglucosamine and then a carbohydrate
type 2 chain characteristics
attached to the RBC membrane
a mixture of glycolipids/glycoproteins
type 2 chain structure
galactose connected with β 1-4 to N-acetylglucosamine and then a carnohydrate