OPT 329 Retinal Lasers/Injections
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
laser energy absorbed by the tissue creates heat and denatures proteins = kill off some areas of retina to save other areas
What is photocoagulation?
putting energy into eye for therapeutic effect (decrease exudate/fluid, make RPE work more effectively, etc) without damaging retina
What is a subthreshold laser?
Xenon arc = not a true laser, just an intense light source = not much control over therapeutic effect and lots of S/E such as CNV, peripheral vision loss
What was the first retinal laser used in the 50s?
1960s
When were the Ruby red (694nm) and Argon blue-green (488nm, 514nm) lasers introduced?
multiple burns at once
more uniform distribution and control of burn spots (still some damage tho)
higher intensity burns for shorter duration
What is the PASCAL 532nm freq-doubled Nd:YAG laser from 2006?
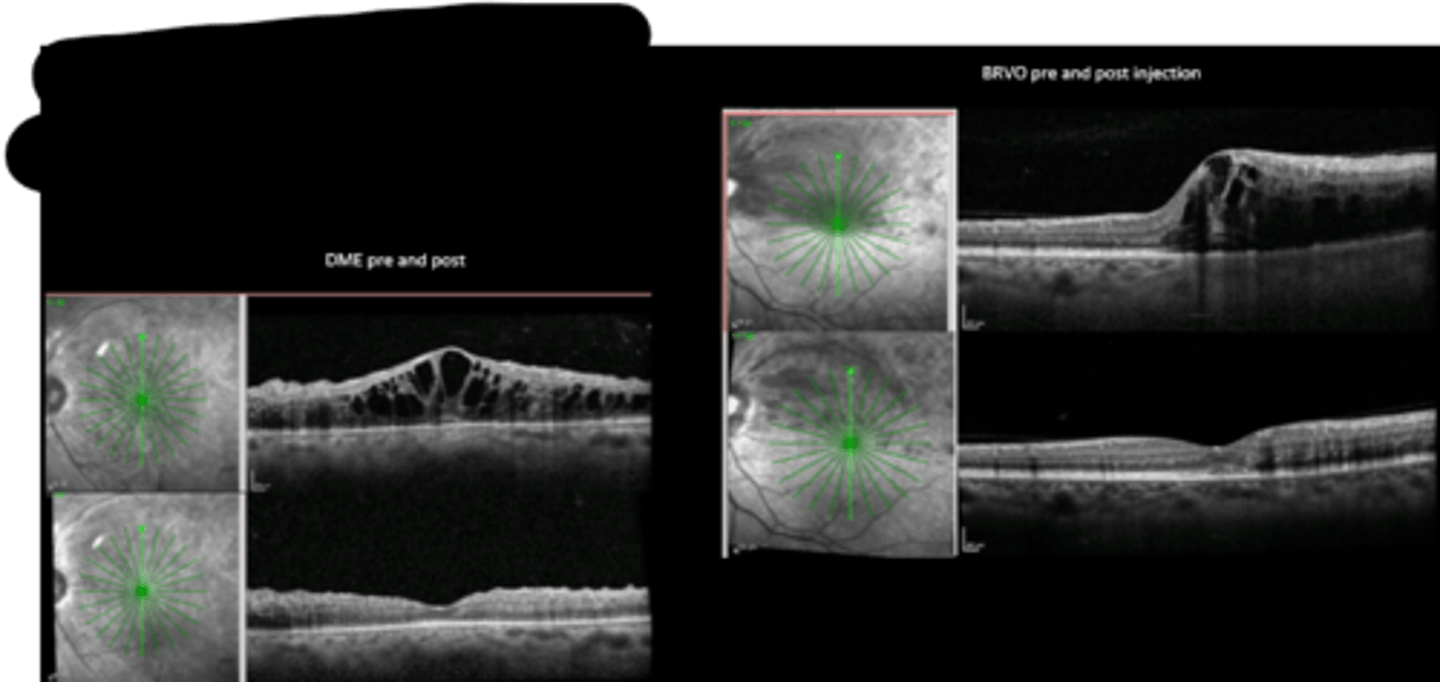
macular edema = DME, ME from BRVO
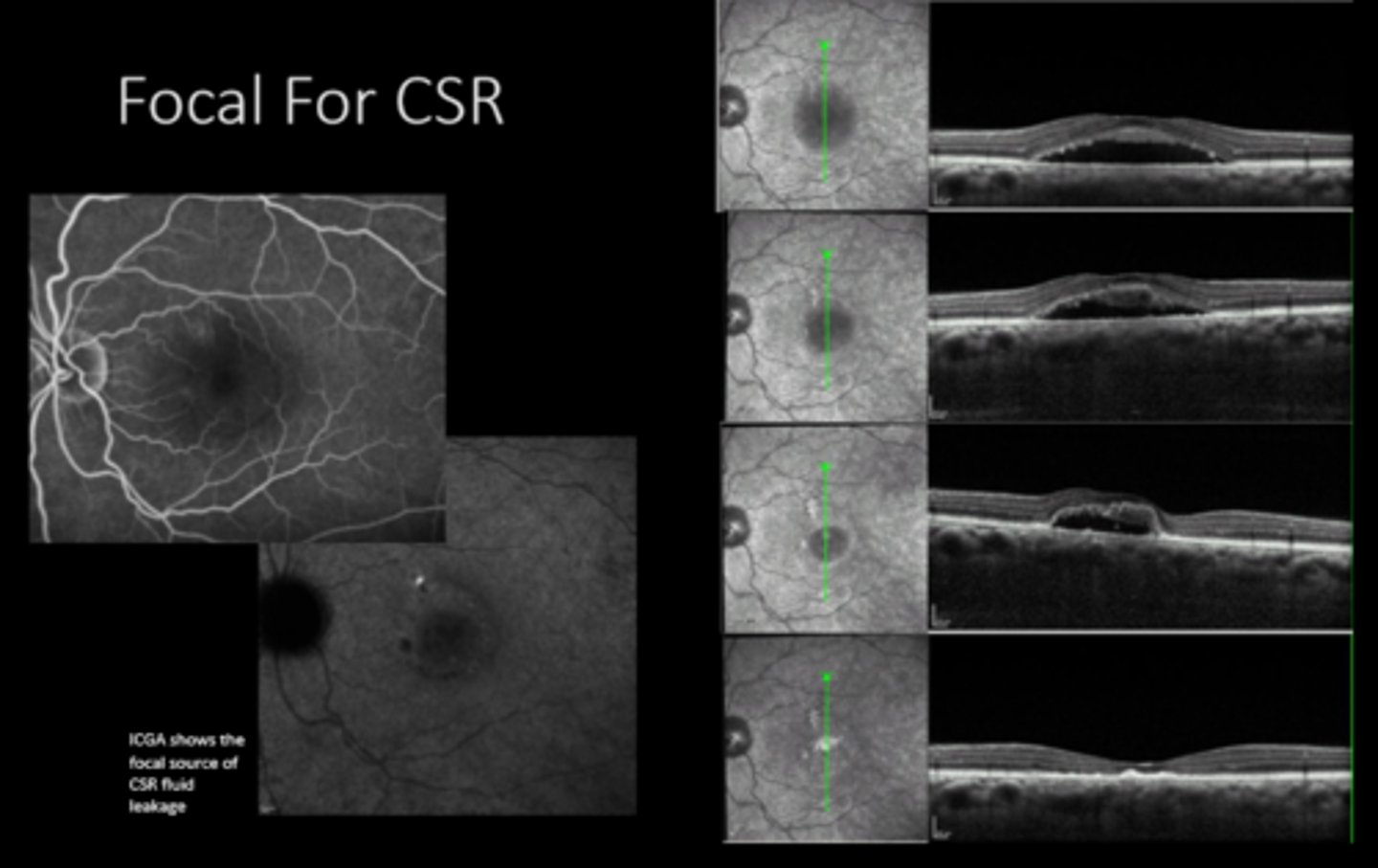
CSR
macroaneurysms = arterial, Coat's
CNV
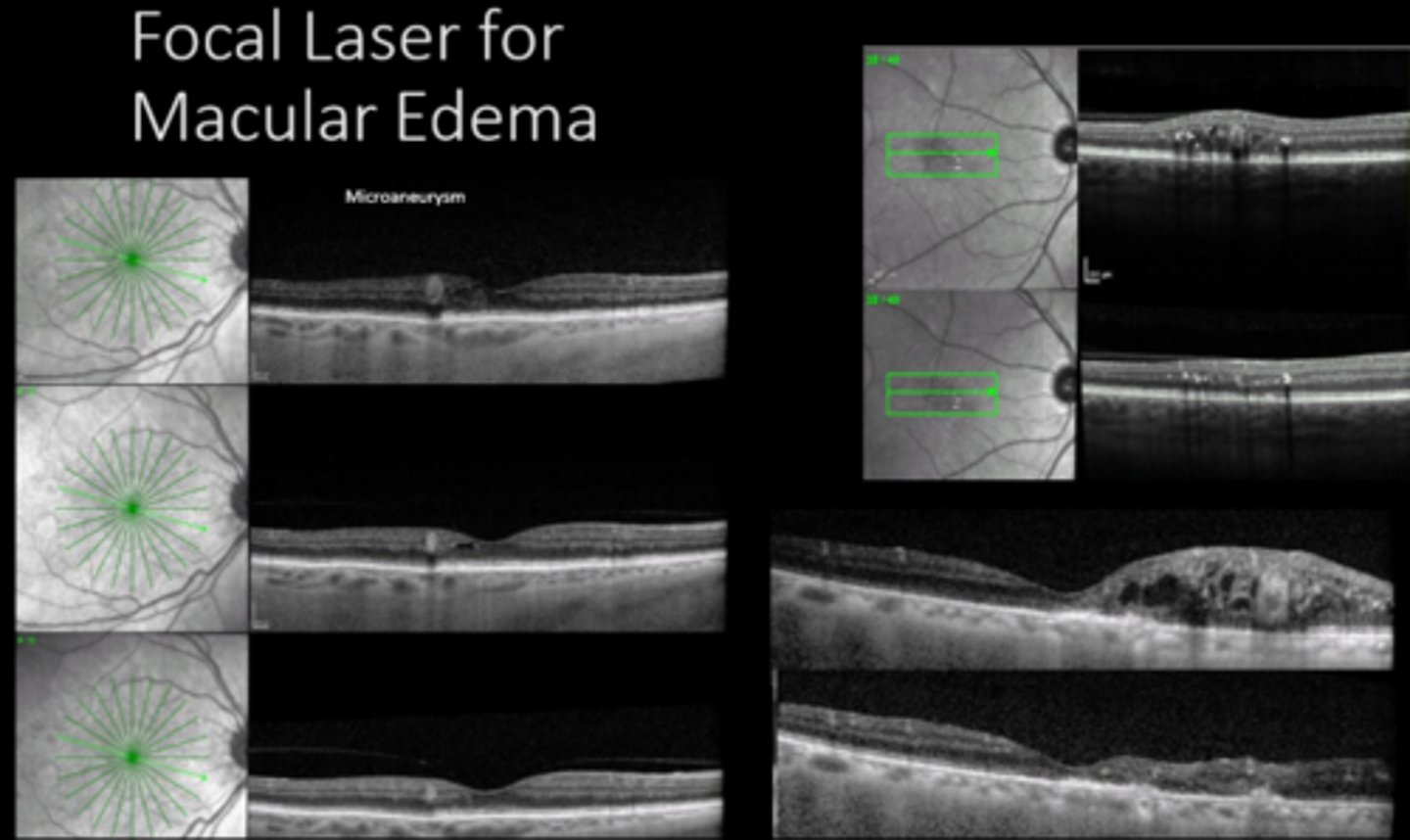
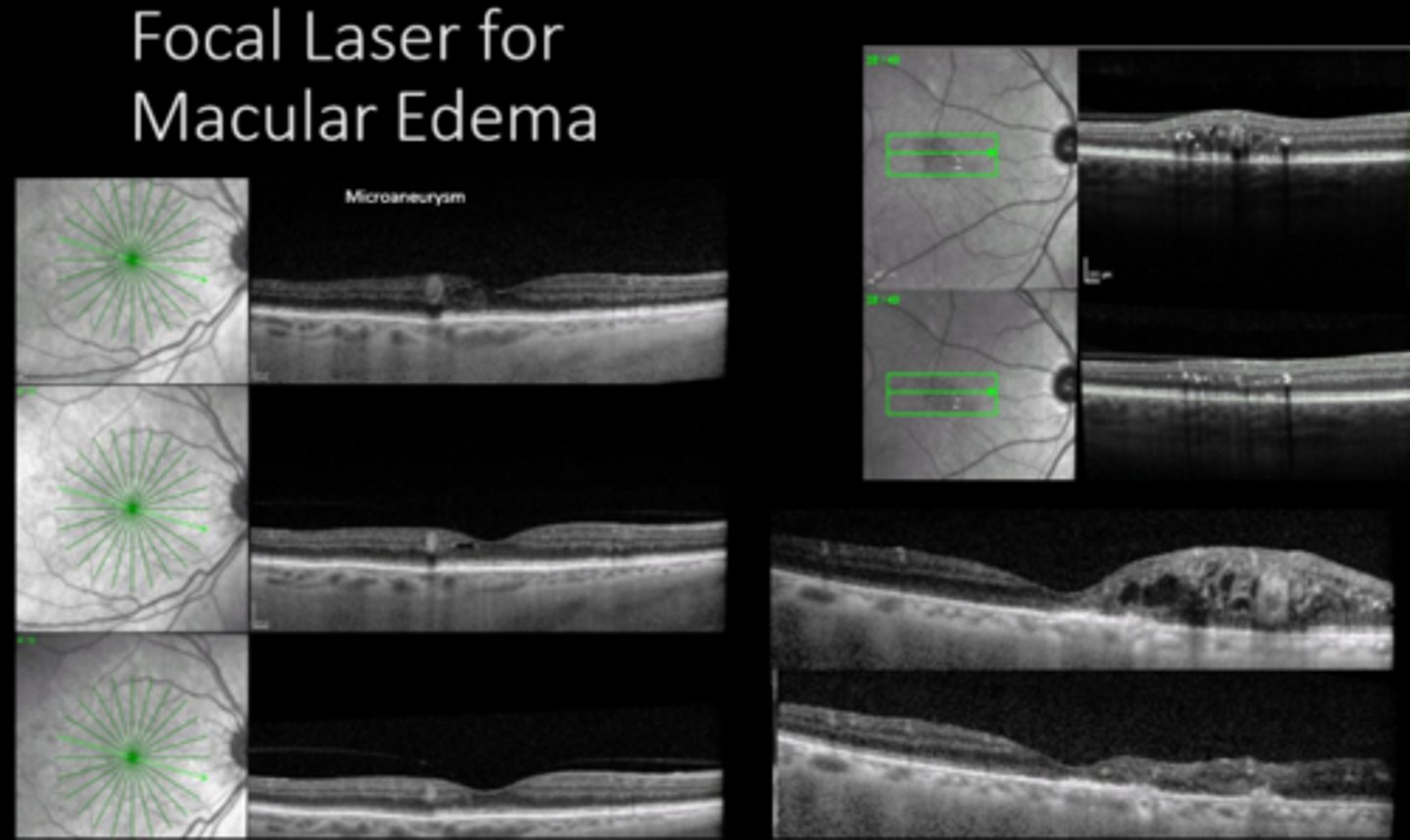
What do we use focal laser for? 4 things.
focal/grid Argon laser for ME decreased risk of vision loss by 50%
also established definition of CSME
What were 2 outcomes of the ETDRS 1989 study?
BVOS found laser was helpful in BRVO
CVOS found no benefit in CRVO
How did the outcomes of the BVOS and CVOS studies differ?
anti-VEGF (PROTOCOL I supported it as better than laser)
steroids
vitrectomy
What are some alternative tx for macular edema?
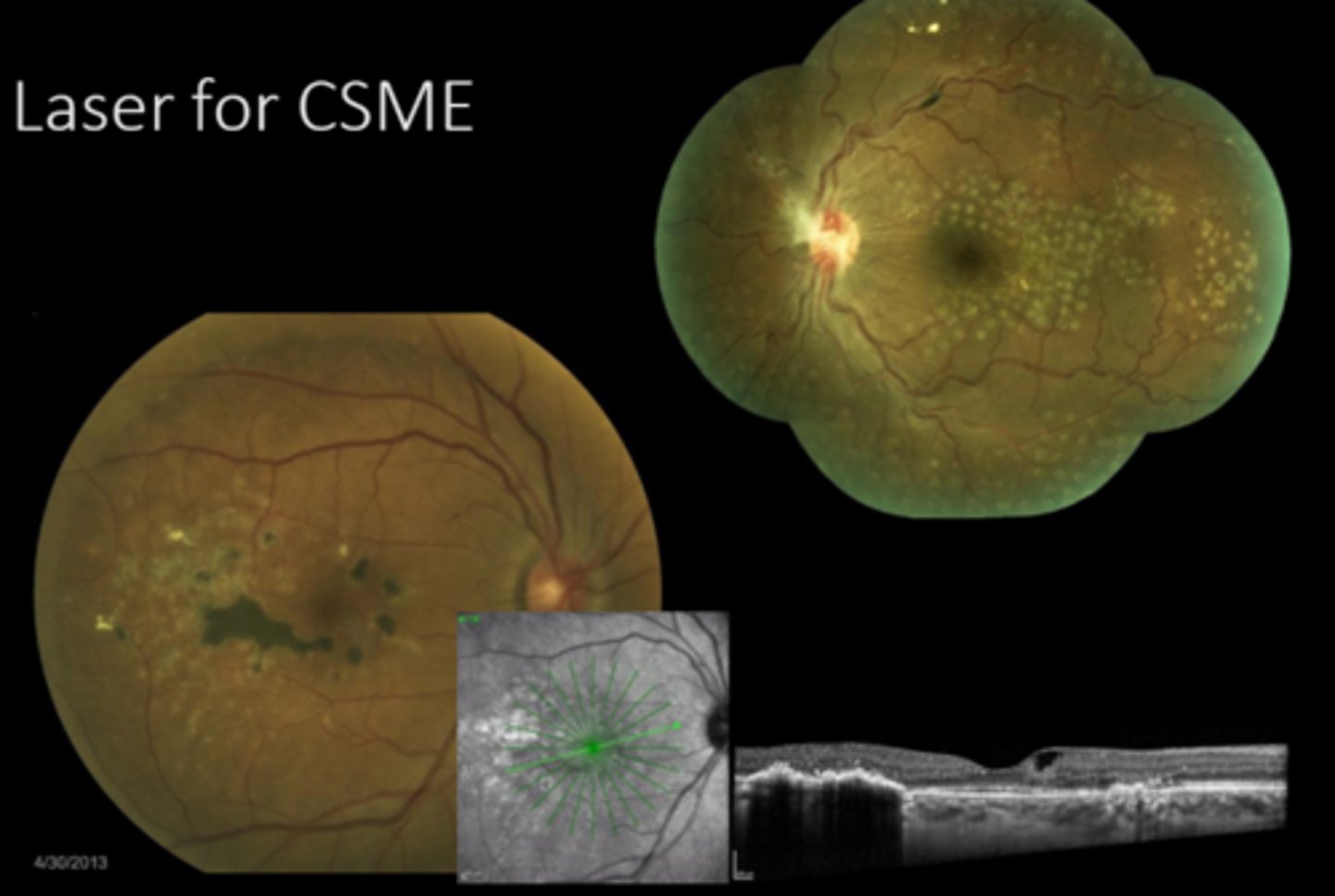
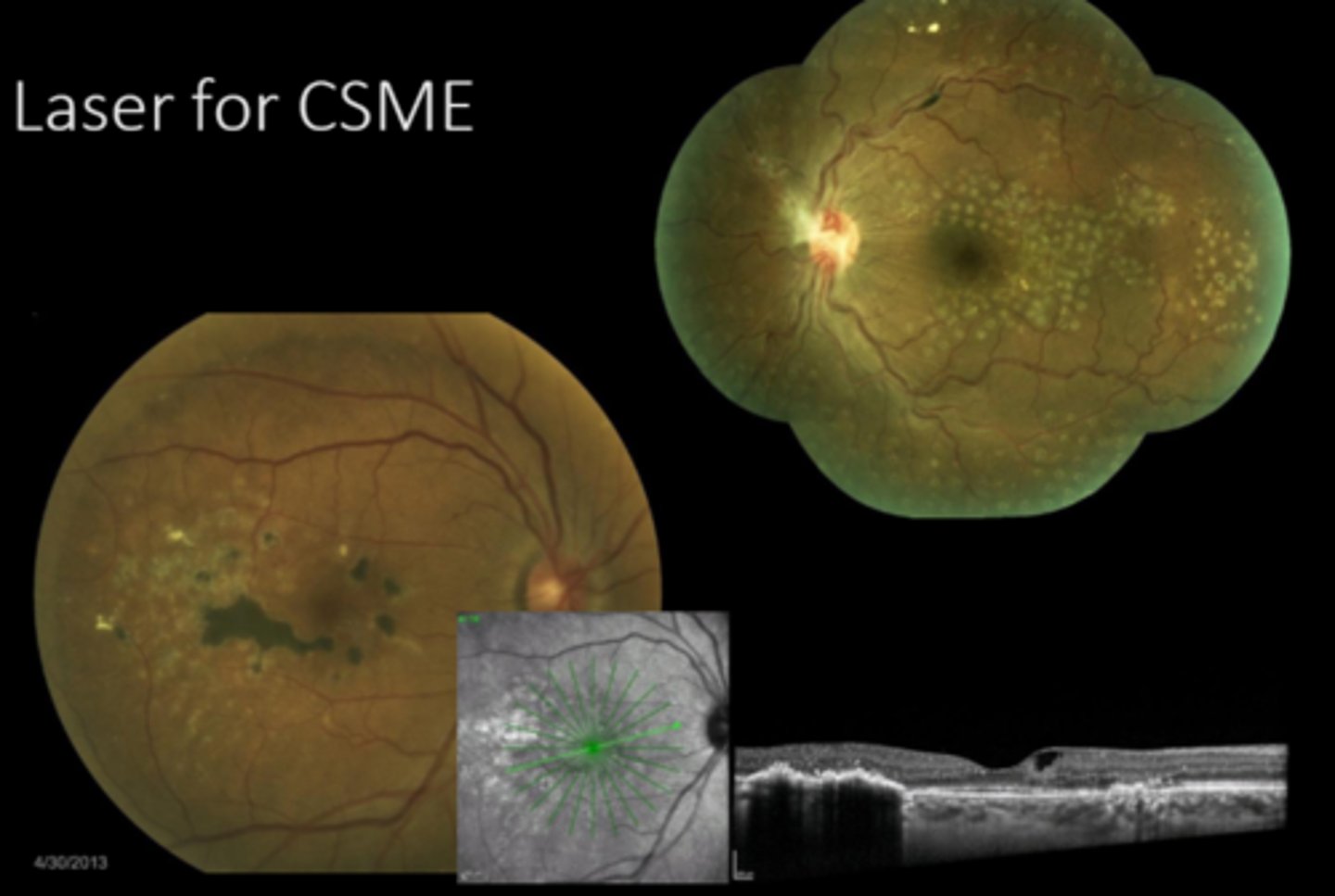
diffuse mac edema is difficult to tx with laser
proximity to fovea = don't want to damage central VA
fixation/cooperation
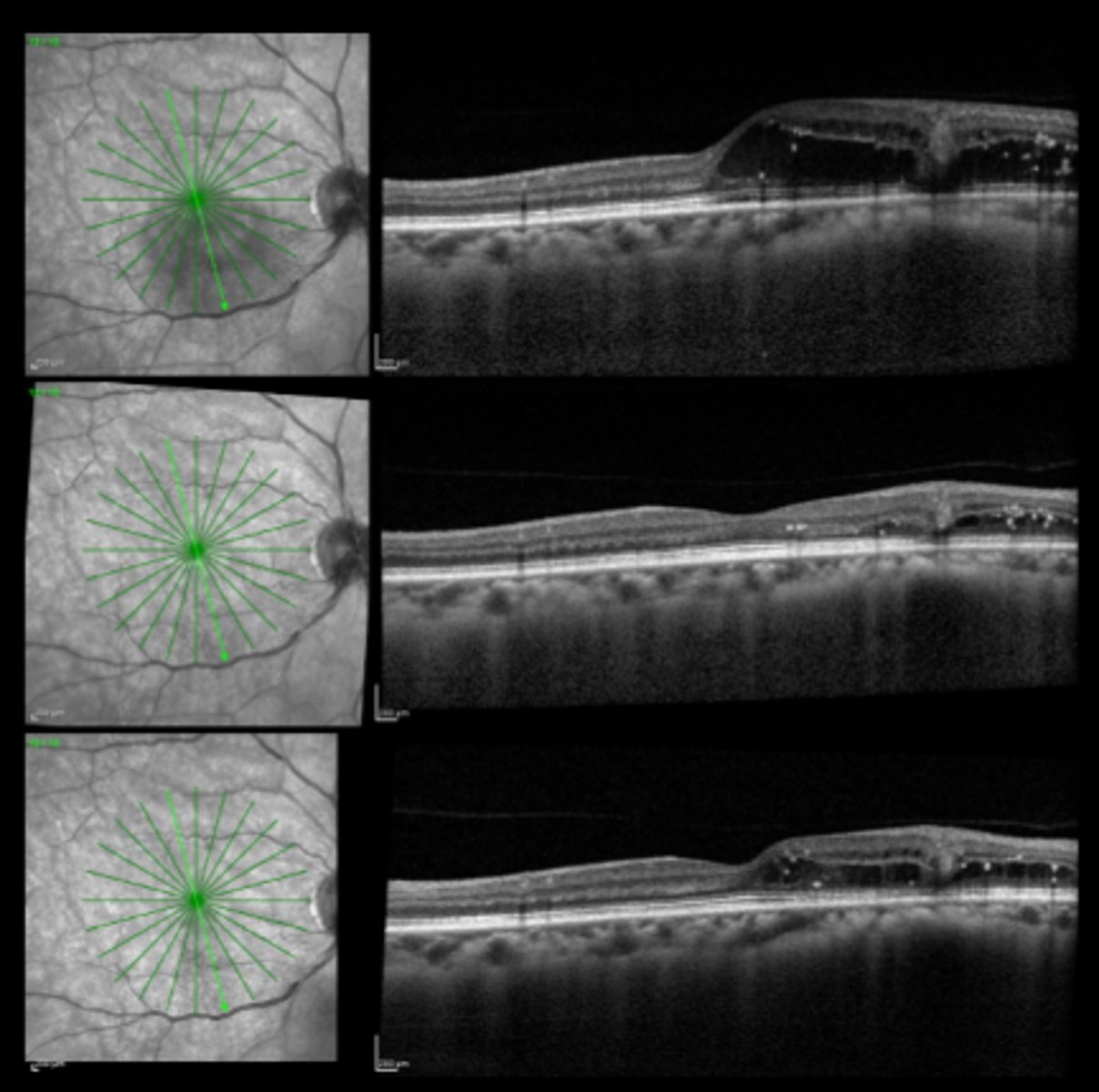
What are 3 limitations to laser for mac edema?
non-urgent (2 week) referral = not as urgent bc PR's are not damaged as easily here
f/u 4-6 weeks after
What is the referral and f/u timeline for macular edema tx with laser/anti-VEGF?
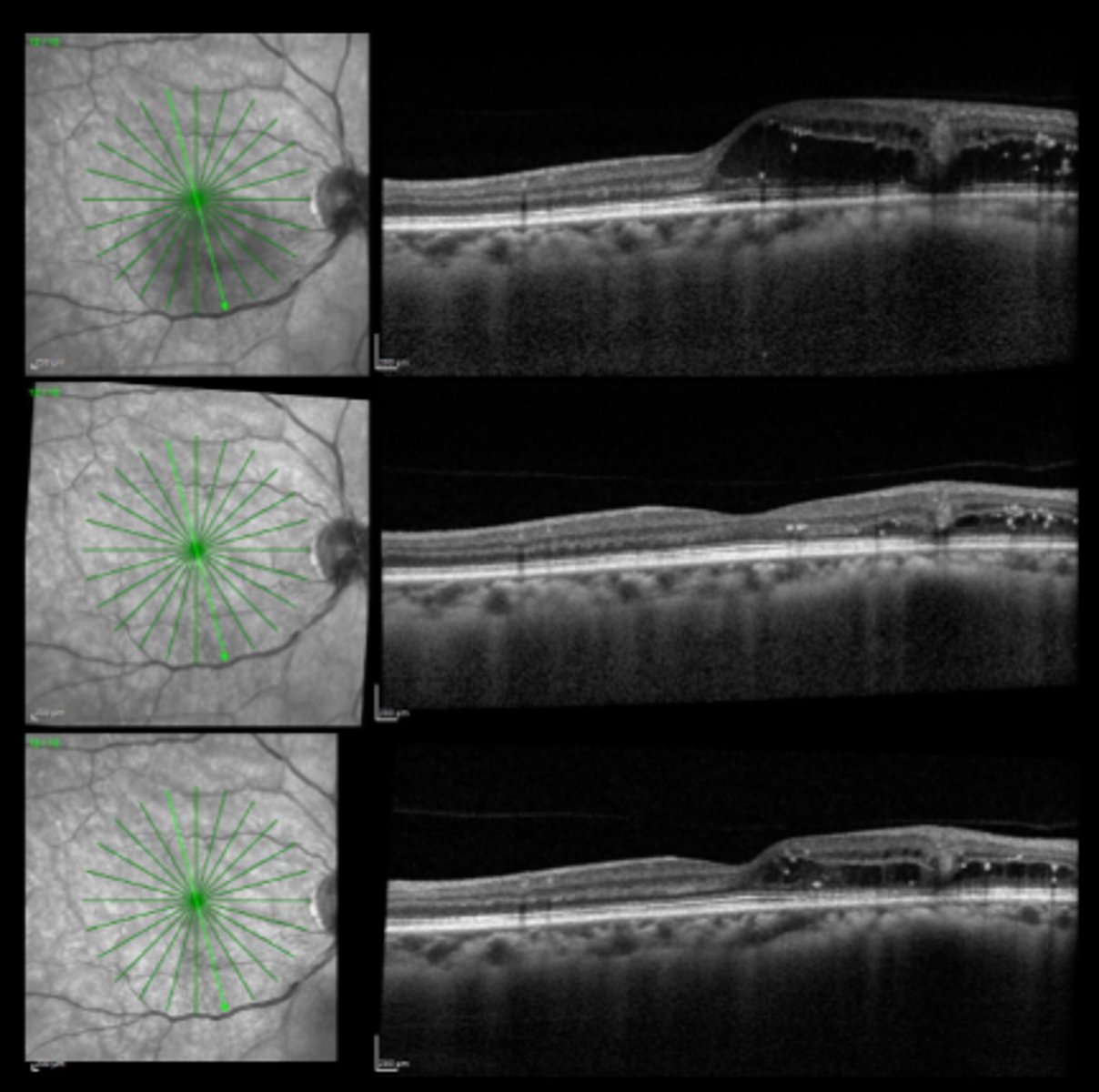
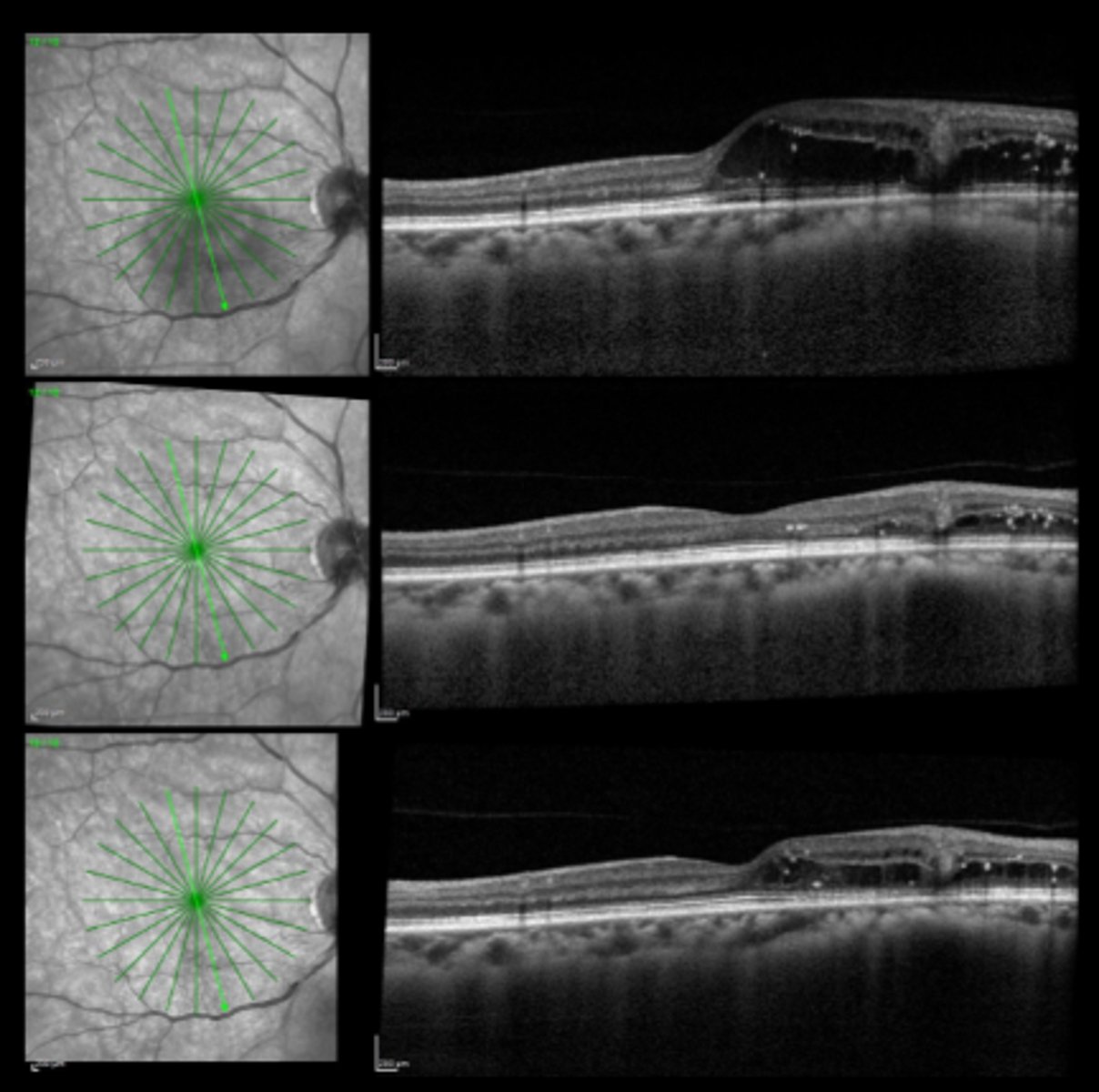
3-6 mos = monitor bc anything that damages outer retina can lead to CNVM
How long do we want to wait between repeating focal laser for macular edema?
recurrence/worsening of fluid
CNV from laser scars or the underlying disease
additional complications of the underlying disease (e.g. neo)
What are we looking for at the post-laser f/u for mac edema?
proliferative retinopathies:
PDR is most common
CRVO
BRVO
sickle cell retinopathy
OIS
ROP
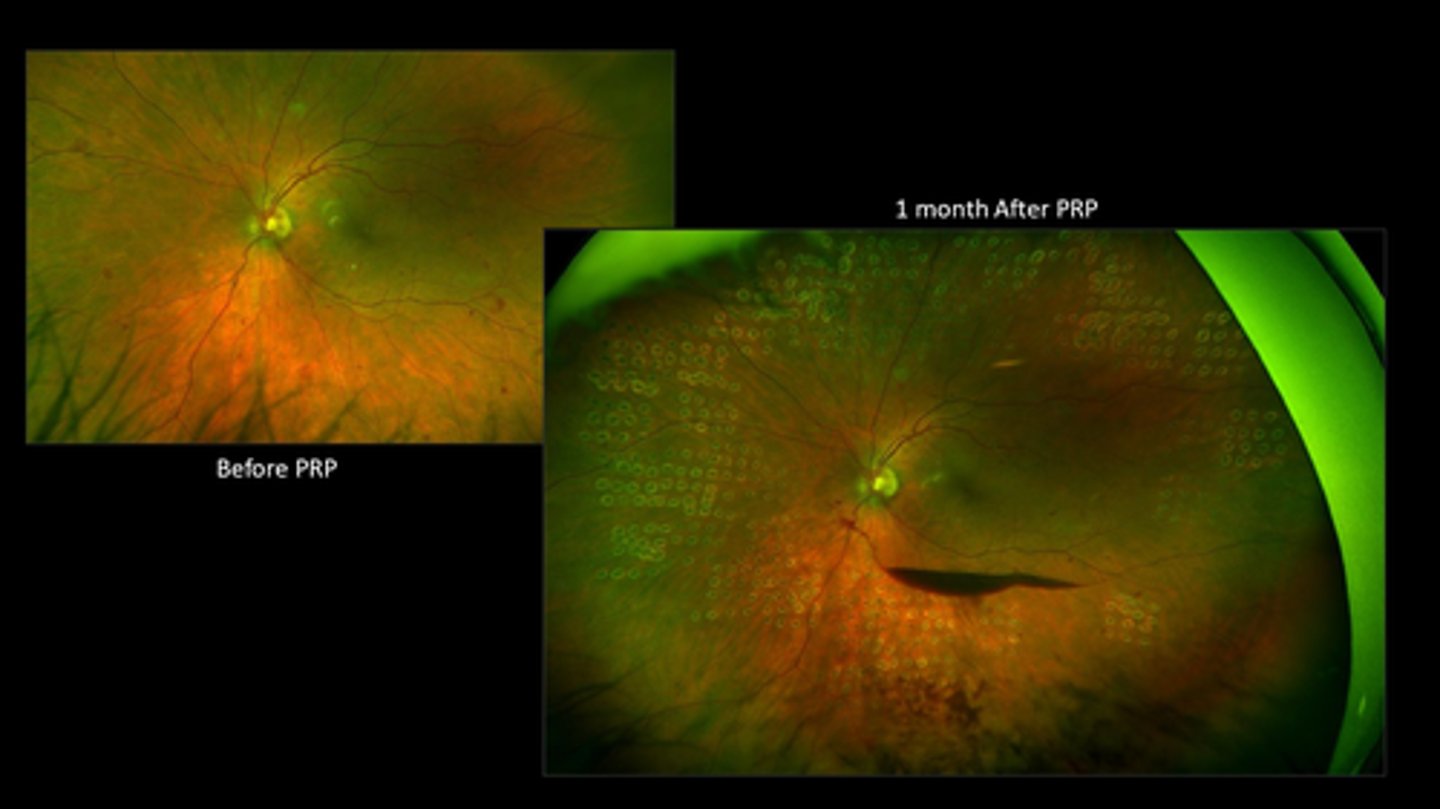
When do we perform panretinal photocoagulation (PRP)?
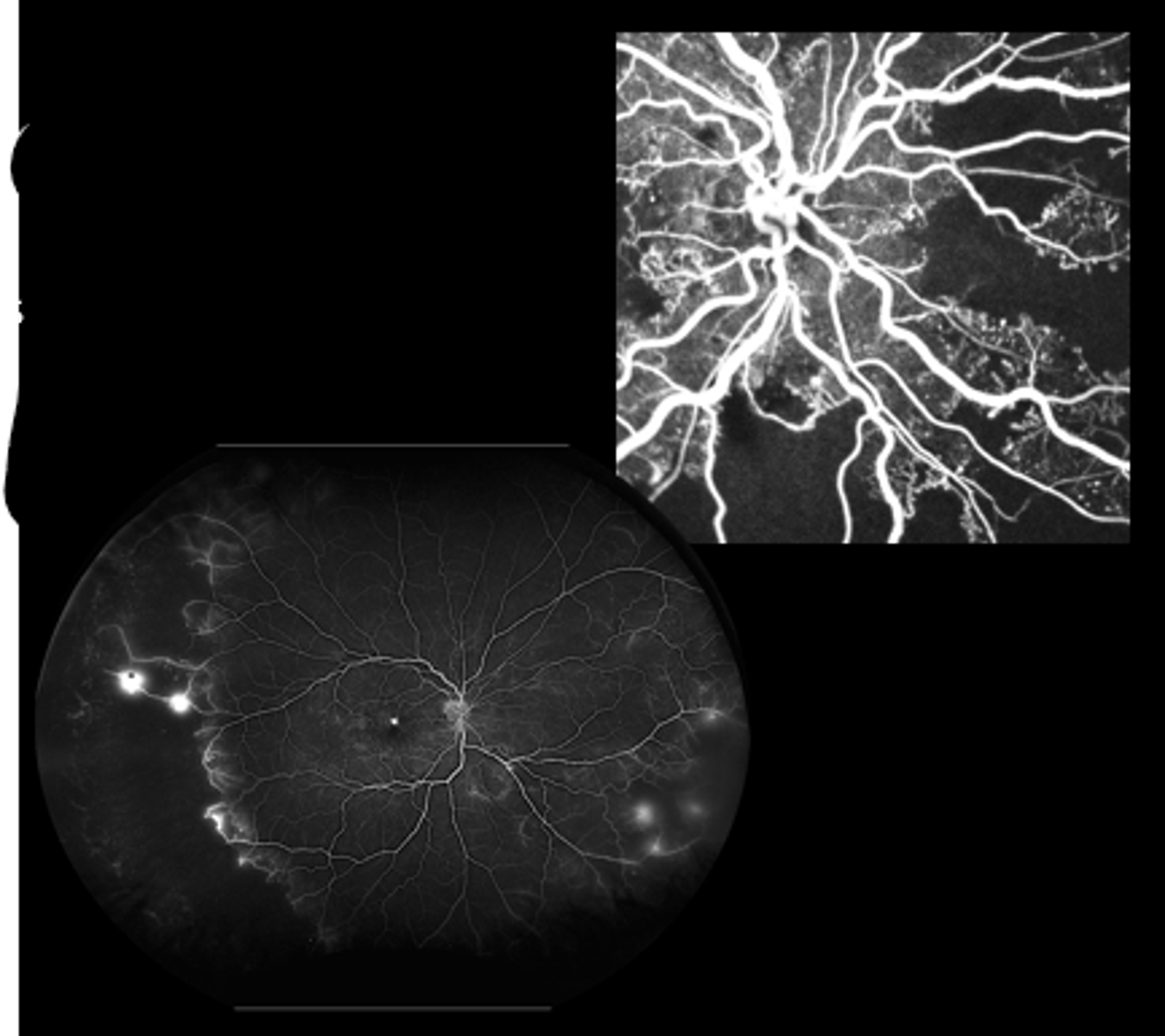
destroys retinal tissue = reduces oxygen demand = less VEGF released = neovasc involutes
What is the MOA of PRP?
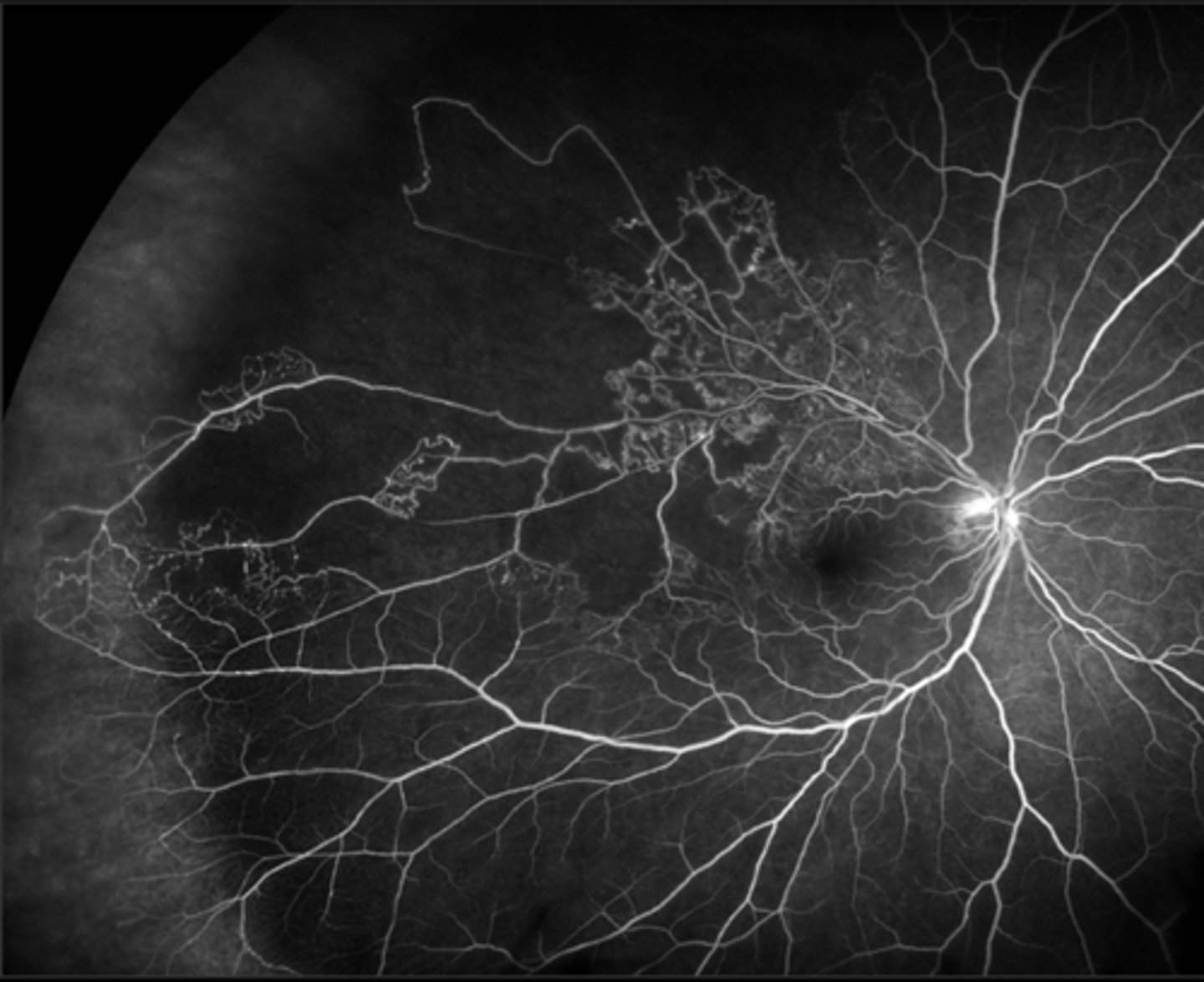
beneficial to prevent vision loss but benefits don't outweigh S/E until high risk PDR:
NVD at least 1/4 disc areas in size
NVD with pre-retinal heme or vitreous heme
NVE greater than 1/2 disc areas with preretinal or vitreous heme
What did the Diabetic Retinopathy Study (1979) find about using PRP for high risk PDR?
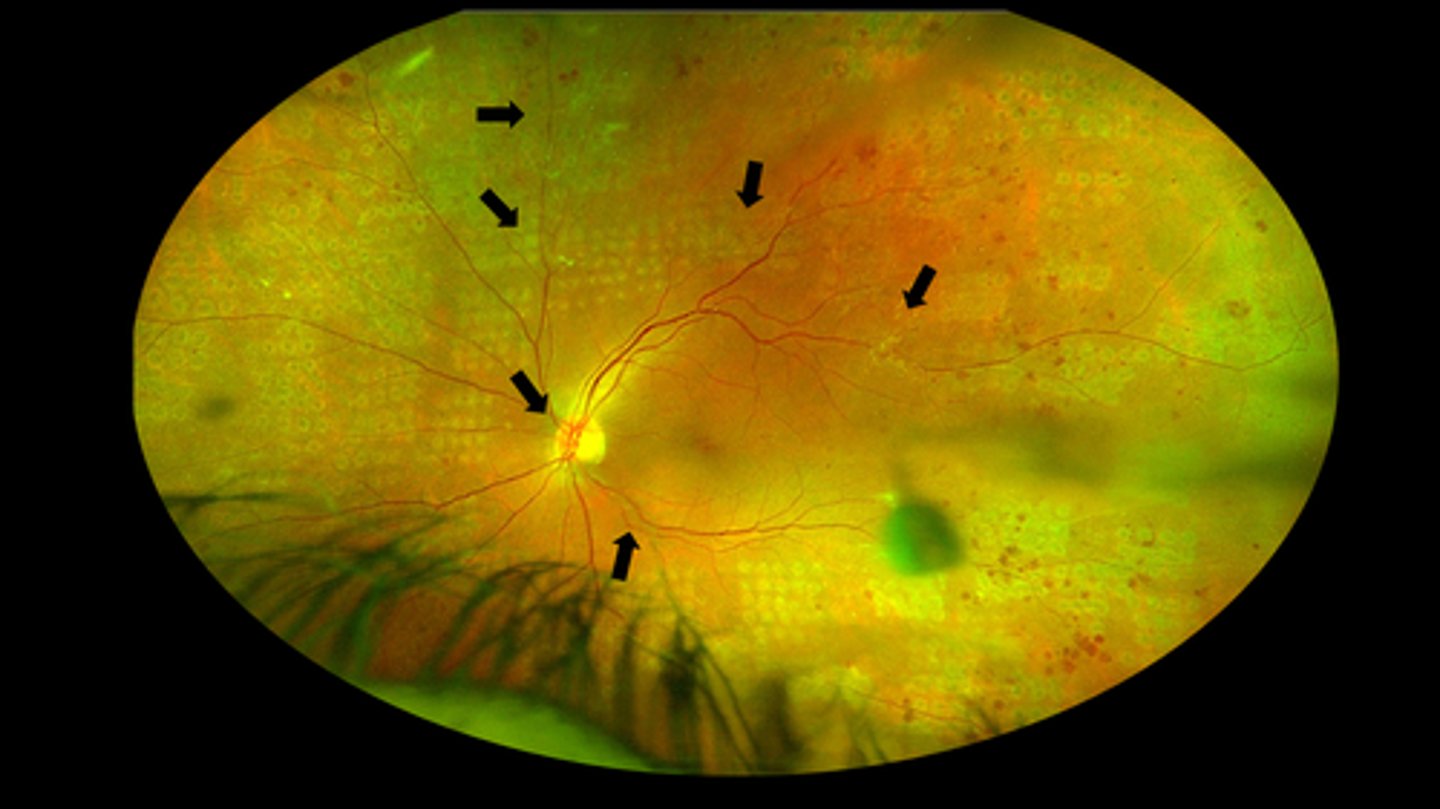
consider PRP in severe NPDR and PDR
What did the ETDRS study (1989) find about using PRP for DR?
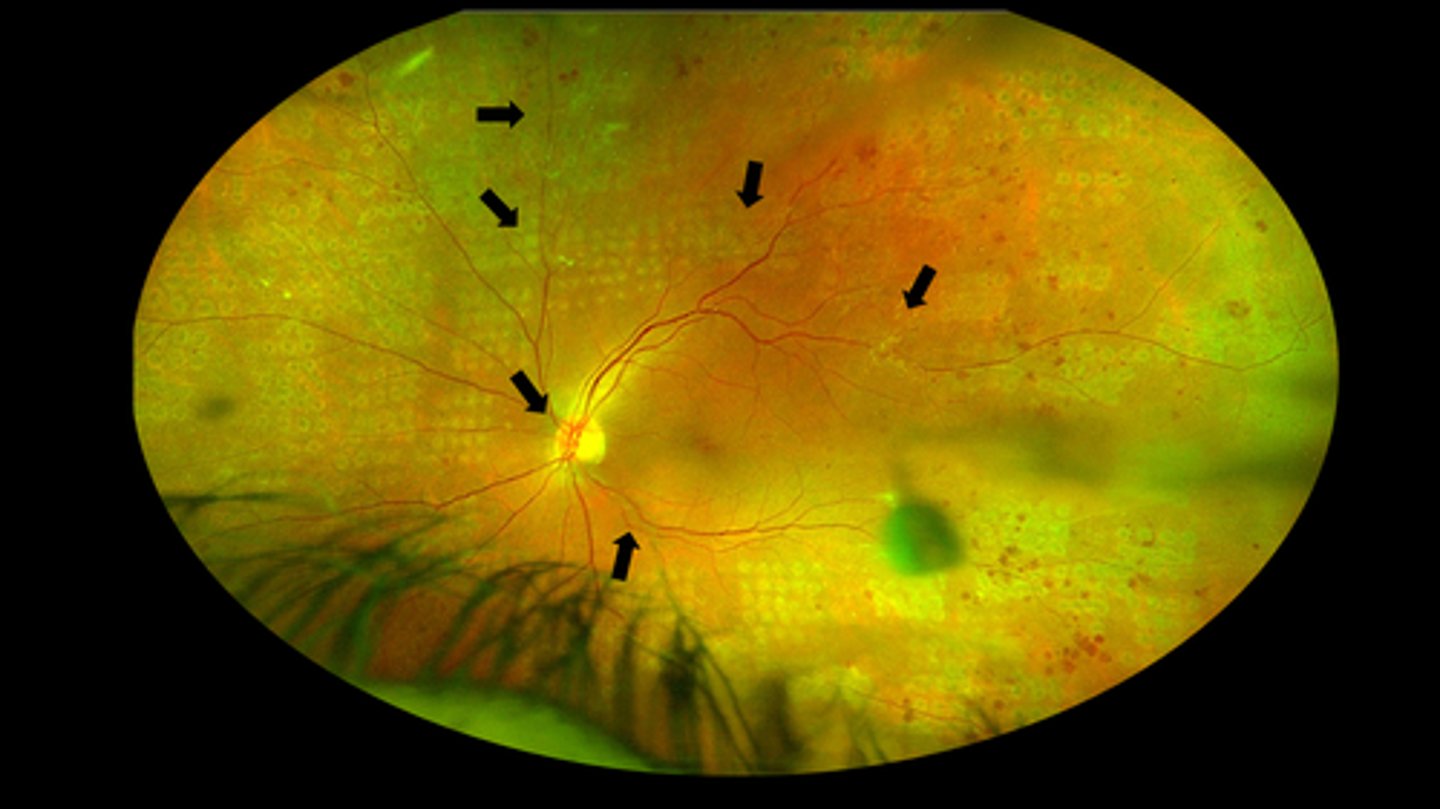
ranibizumab anti-VEGF alone can work but need more appts, more f/u, etc.
What did Protocol S suggest about PRP vs anti-VEGF for DR?
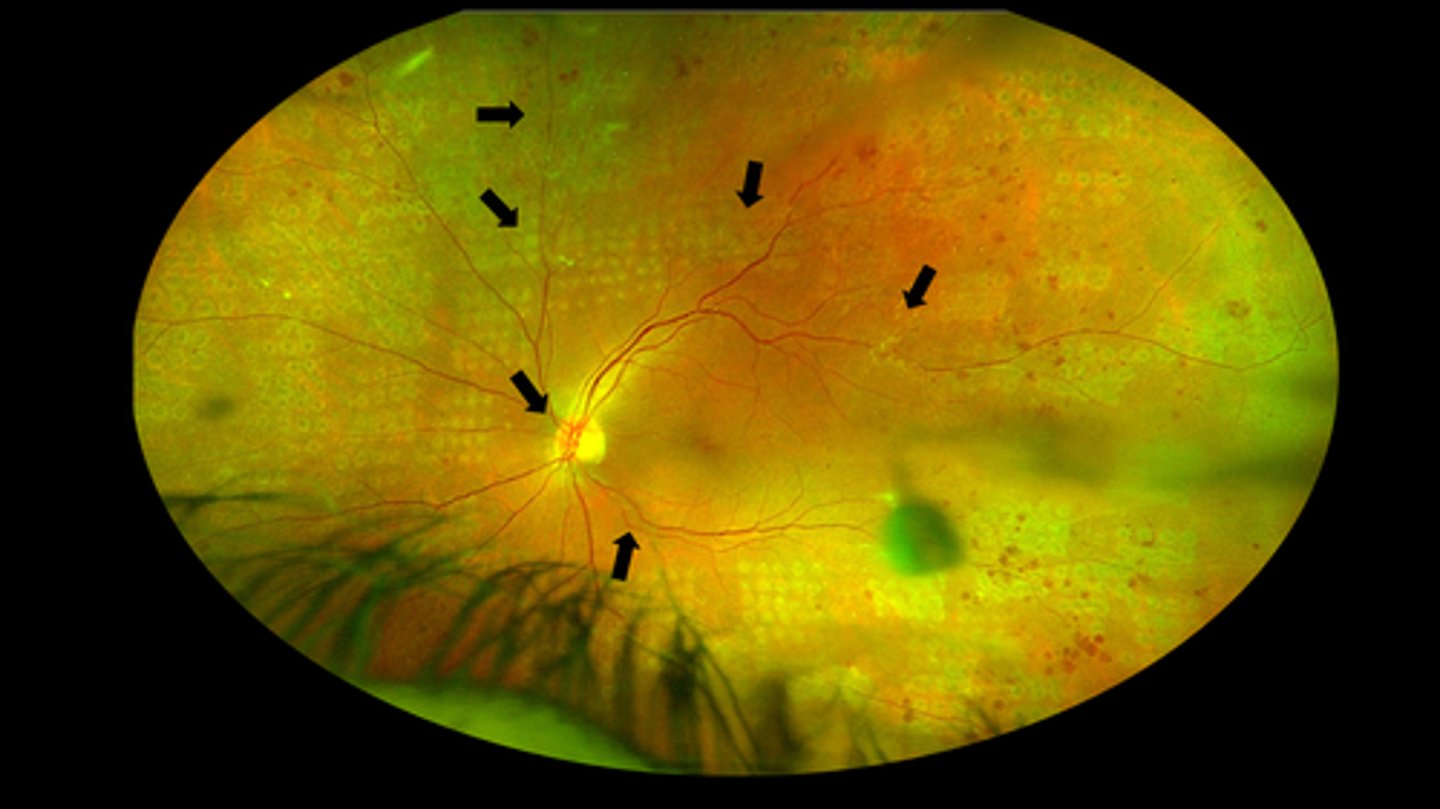
Eylea anti-VEGF for moderately severe to severe NPDR
What did PANORAMA suggest about anti-VEGF for DR?
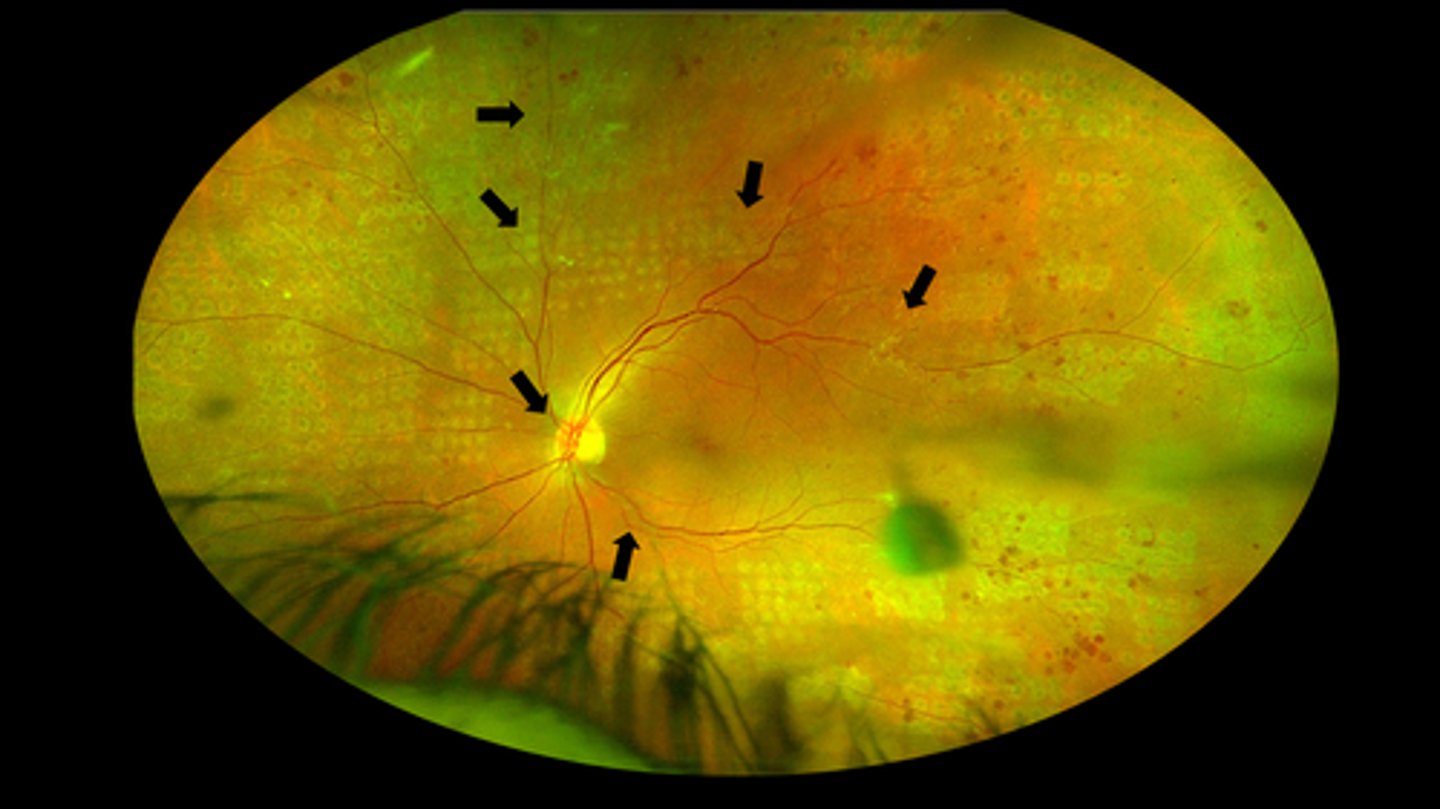
as the neo involutes, there can be hemes
Why are vitreous hemes sometimes a side effect of PRP?
98%
What % of pts with diabetic retinopathy that simply attend appt's will not suffer severe vision loss (not even considering how they control their DM)?
patient cooperation, fixation
media opacity = cortical cataract, hemorrhage
too much treatment/scarring
What are some limitations to performing PRP?

non-urgent (2 week) referral = not as urgent
f/u 4-6 weeks after
can extend out 4-6 mos if PDR quiescent
What is the referral and f/u timeline for proliferative retinopathy treated with PRP?
emergent = refer asap
What is the referral and f/u timeline for neovascular glaucoma treated / iris neo?
NVE
TRD
NVI
pre-retinal heme
vitreous heme
additional complications of disease (DME)
What are we looking for at the post-laser f/u for proliferative ret?
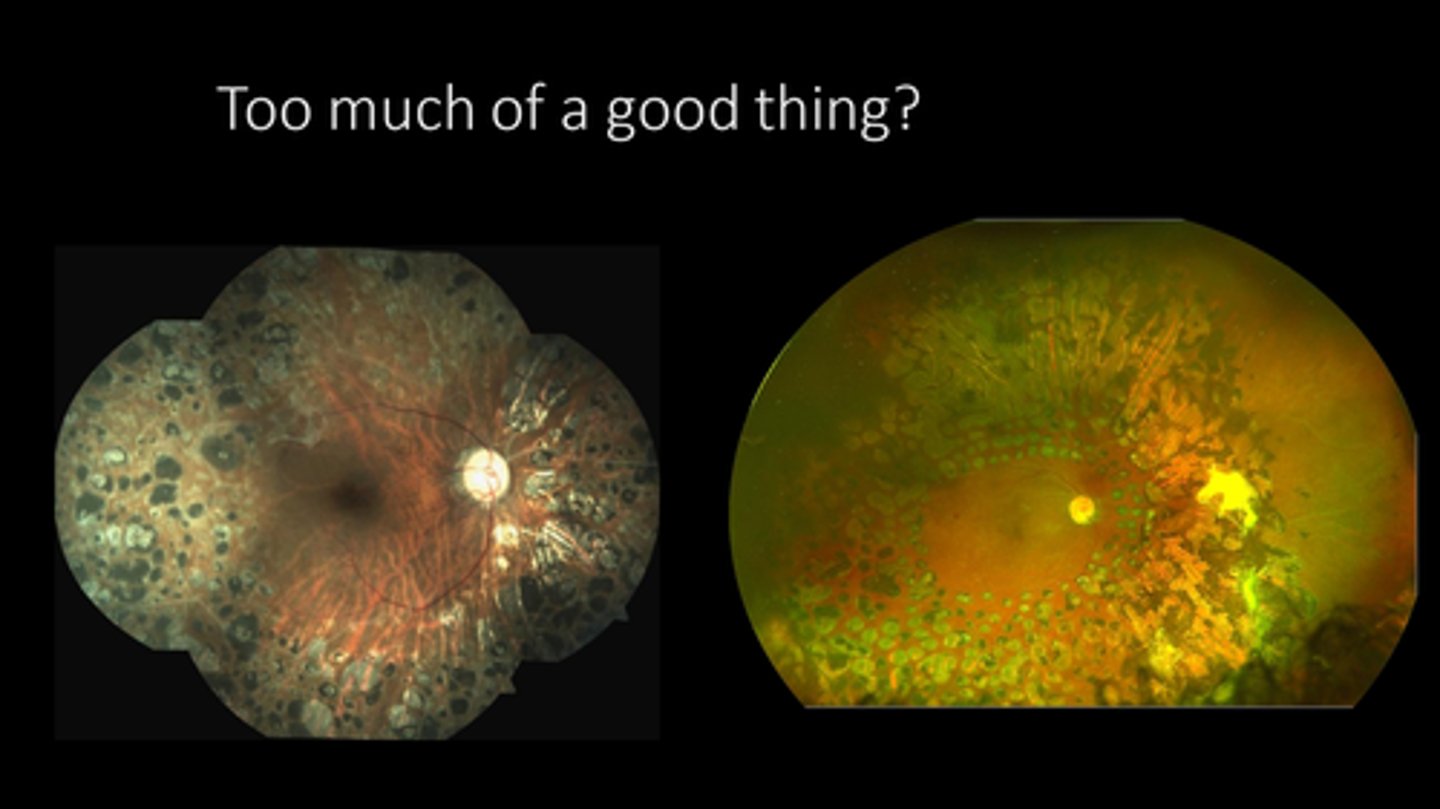
retinal holes/tears
subclinical RD
What do we use laser retinopexy for?
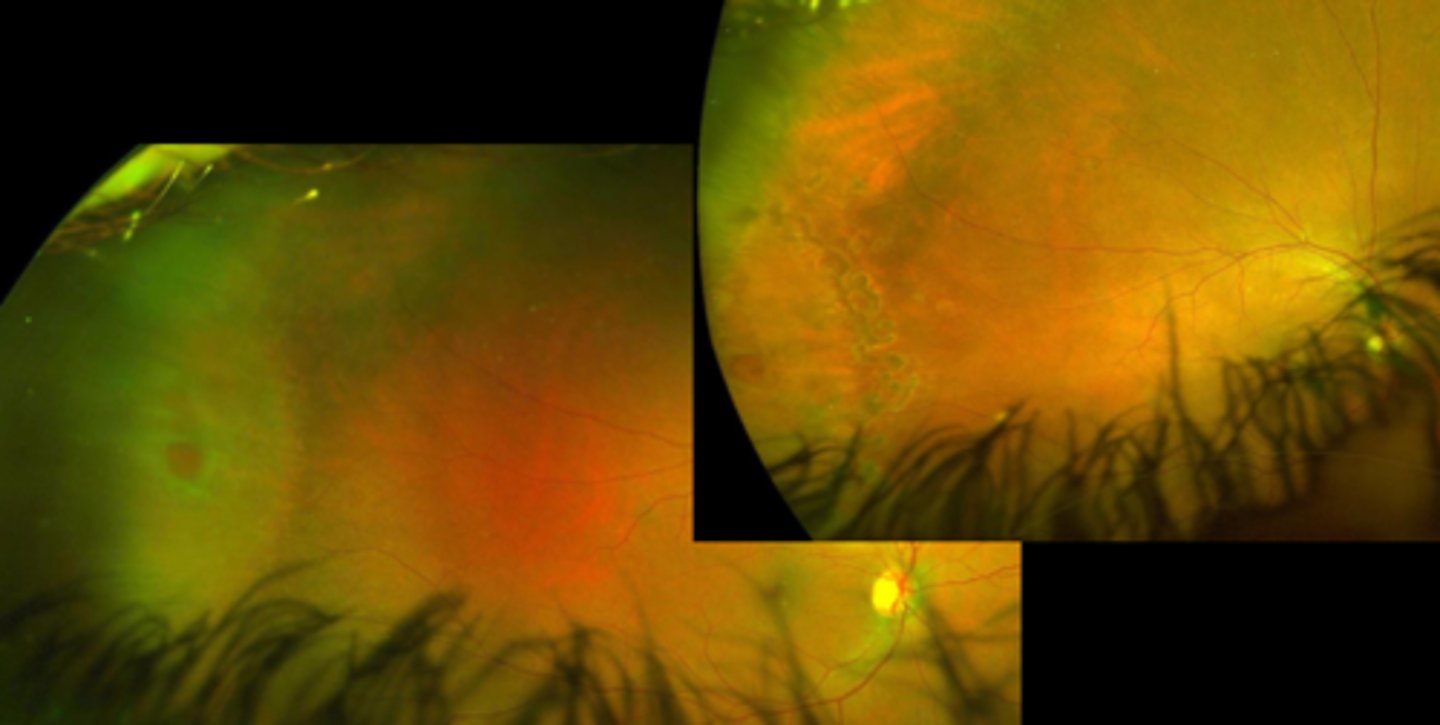
symptomatic horseshoe tear
symptomatic dialyses
traumatic retinal breaks
Dr. Haynes says refer if symptomatic, superior, CAT Sx soon
According to the AAO, what holes/tears should be referred for possible laser tx?
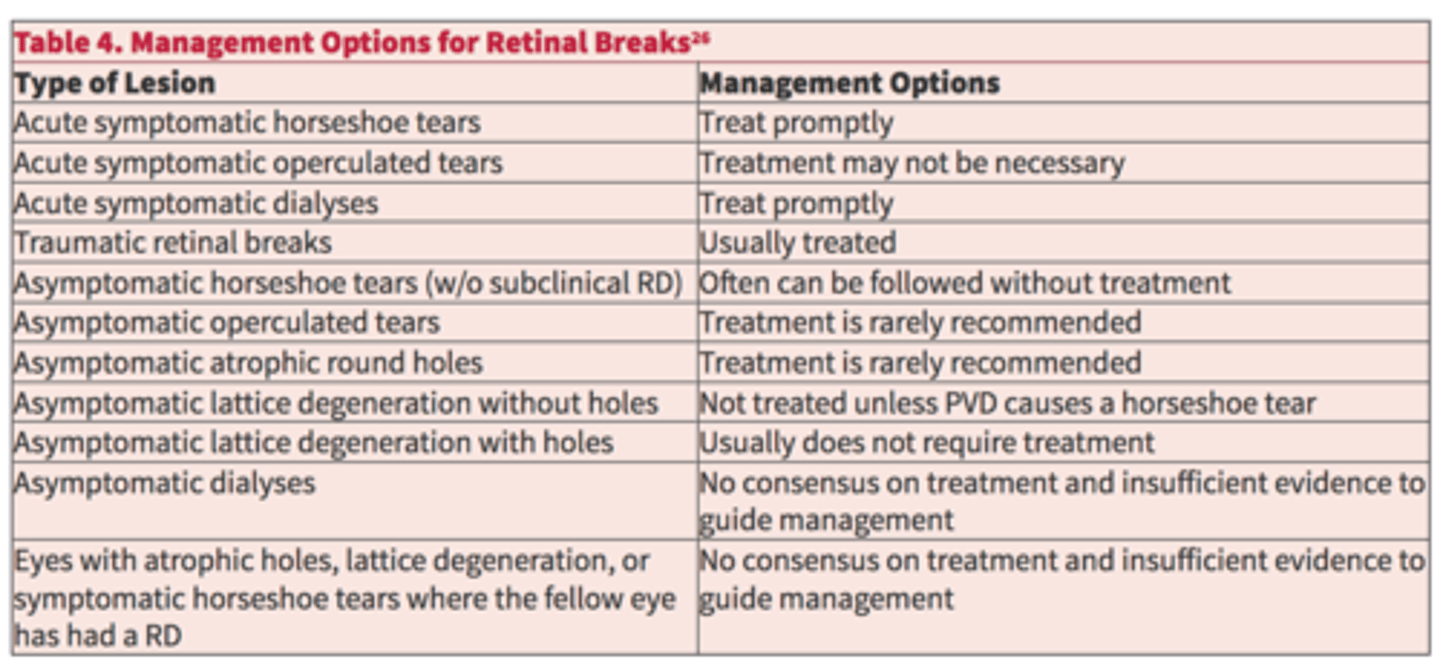
operculated holes (regardless of symptoms)
asymptomatic lattice +/- holes
asymptomatic horseshoe tear
asymptomatic atrophic holes
Dr. Haynes also says inferior holes, asymptomatic, pigmented is safe
According to the AAO, what holes/tears can be monitored only?
view
extent of subretinal fluid (should laser at edge of fluid!)
pt cooperation/fixation
What are some limitations to laser retinopexy?
6 mos to 1 year for atrophic holes, lattice degeneration, retinal tufts
What is the monitoring timeline for holes/tears?
non-urgent (1 month) for asymptomatic atrophic or operculated holes
urgent/emergent for symptomatic operculated hole or horseshoe tear
What is the referral timeline for laser retinopexy?
typically 1 month unless large tear, lots of fluid, difficult laser, high concern for additional breaks, etc.
What is the f/u timeline for laser retinopexy?
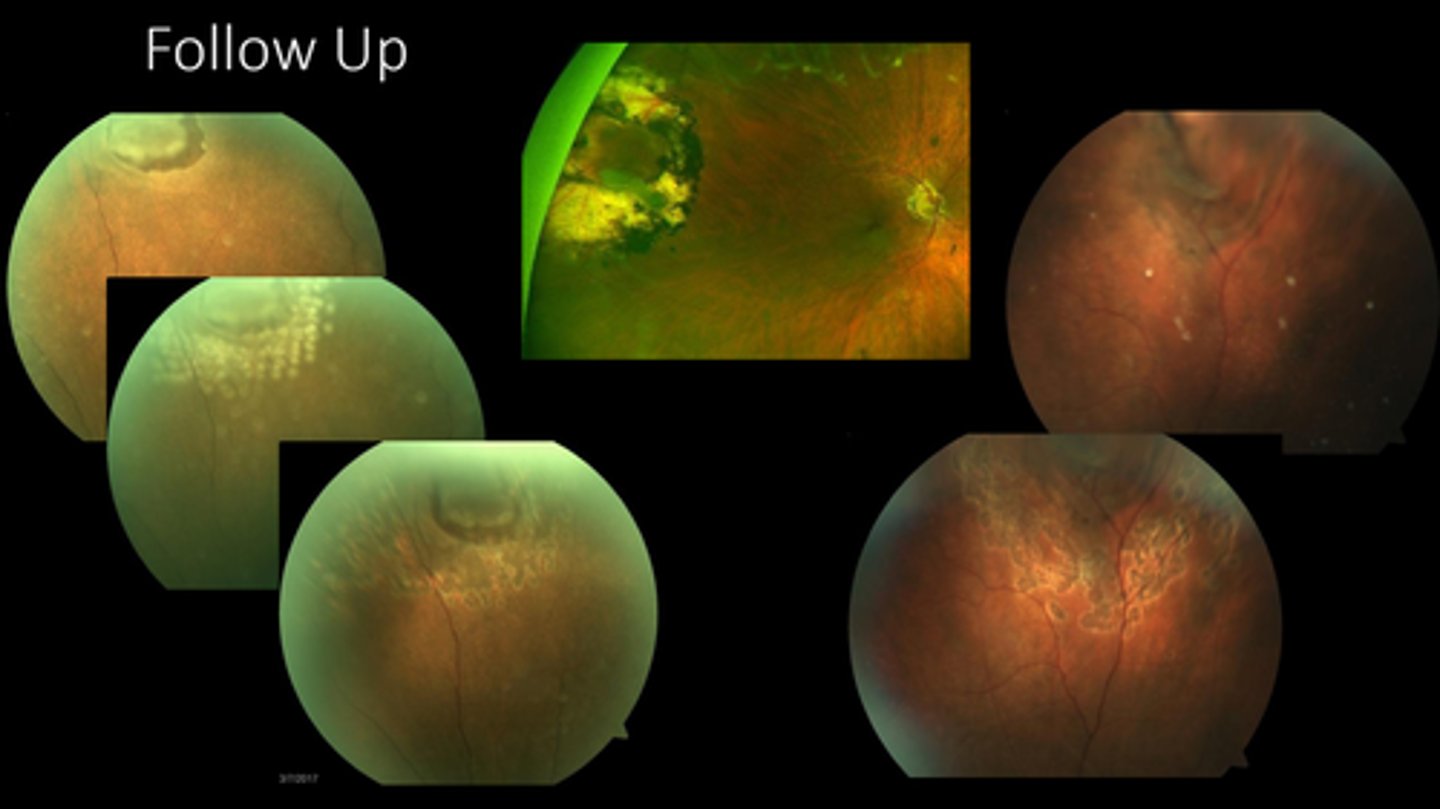
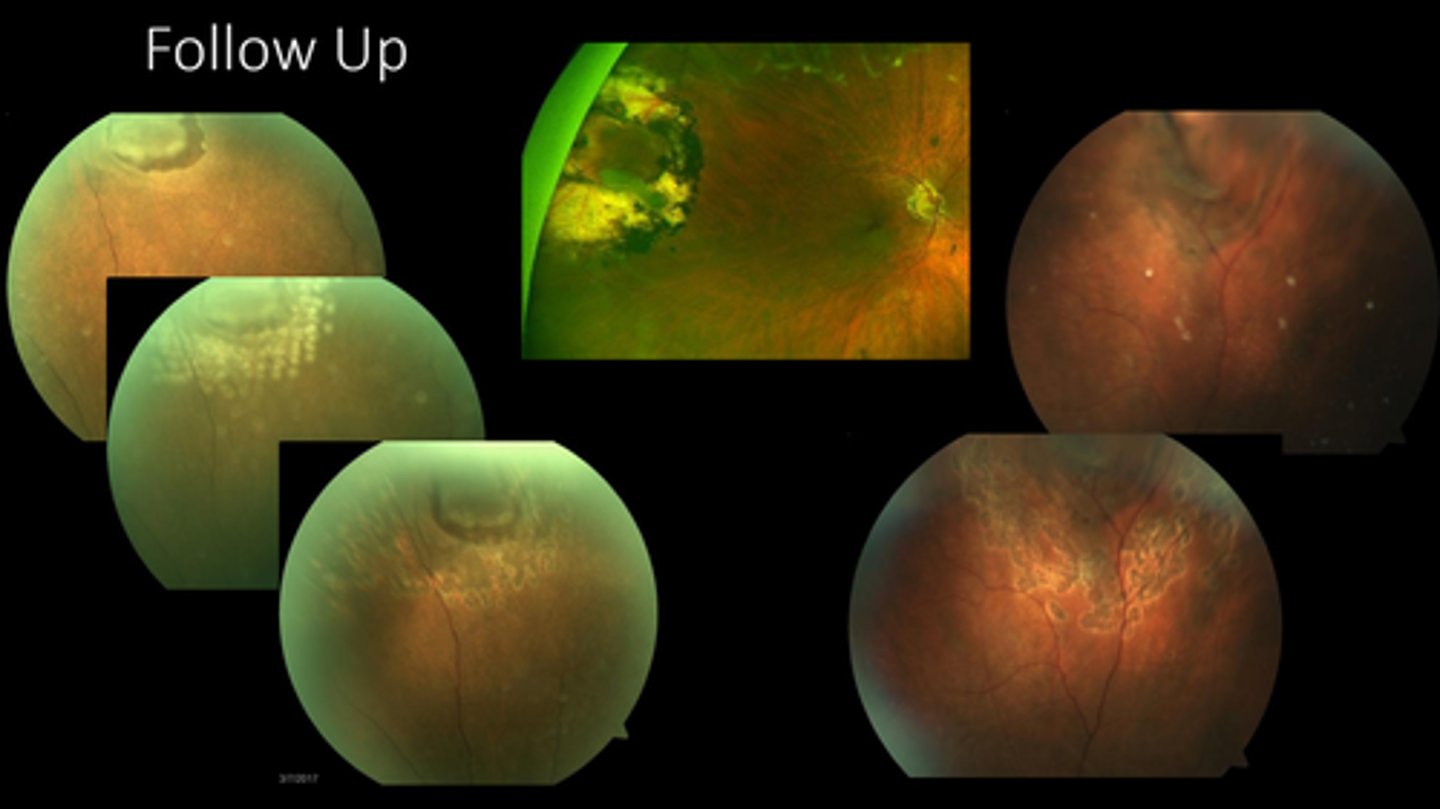
check laser uptake (2-6 mos)
look for additional holes/tears
assess fluid
What are we looking for at the post-laser f/u for laser retinopexy?
cool laser targets verteporfin dye to create an oxidative reaction
What is photodynamic therapy (PDT)?
CSR
polyploidal choroidal vasculopathy
vascular tumors = choroidal hemangioma, hemangioblastoma, metastatic tumors
What is photodynamic therapy (PDT) used for?
confirm the patient, eye, and medication
signed consent
topical numbing drops
betadine
lid speculum = L/L are main source of bacteria entering eye
What is the preparation for intravitreal injections?
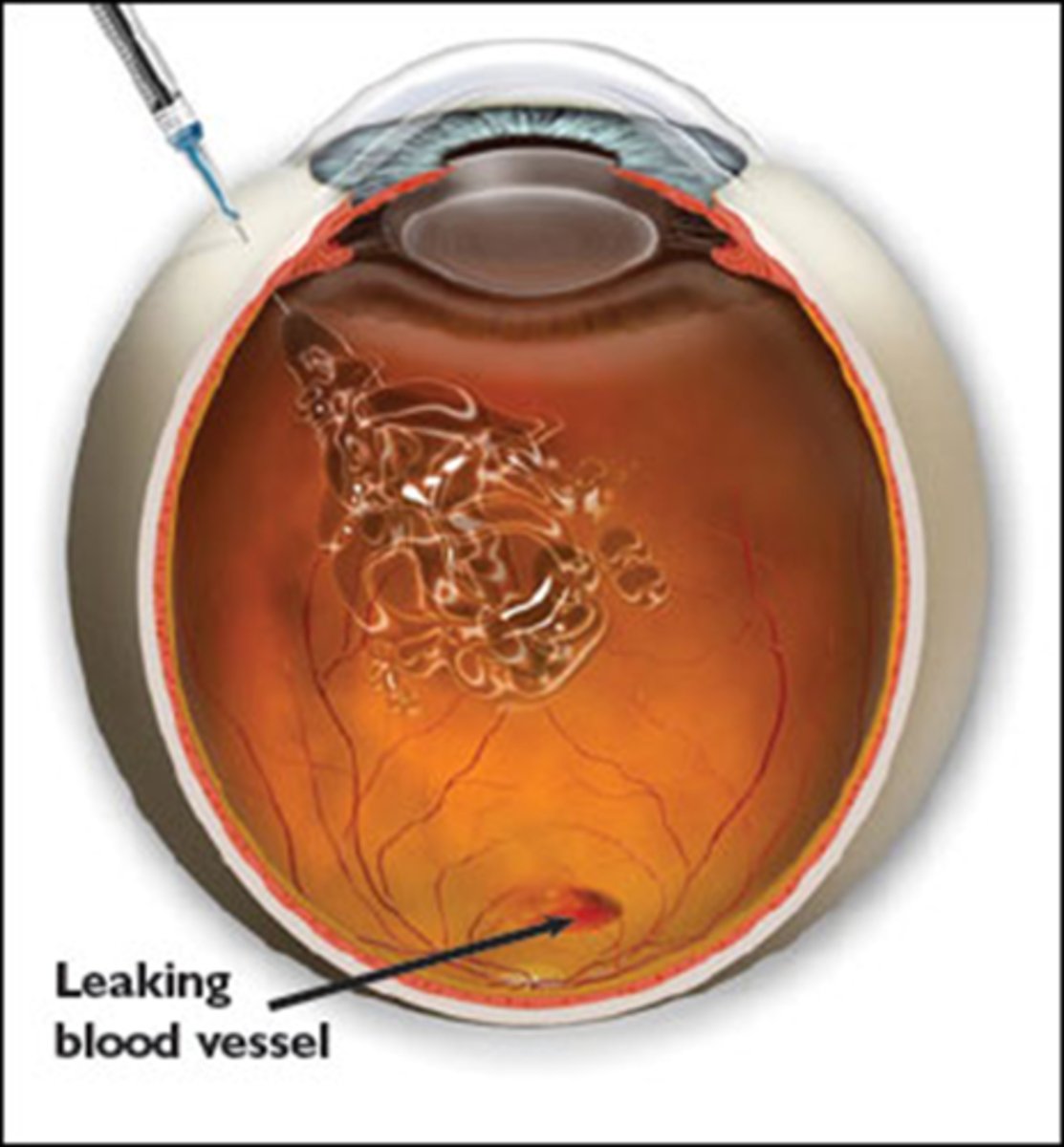
3mm posterior to limbus
Where is the intravitreal injection placed on the eye?
eye rinse
check VA
check IOP
educate about symptoms requiring re-evaluation
recommend ATs
What is the post-op care for intravitreal injections?
betadine irritation/discomfort
What is the most common post-op complaint after injections?
floaters (often just the medication itself)
mild discomfort
subconjunctival heme
punctate keratitis
What are some other common S/E of intravitreal injections?
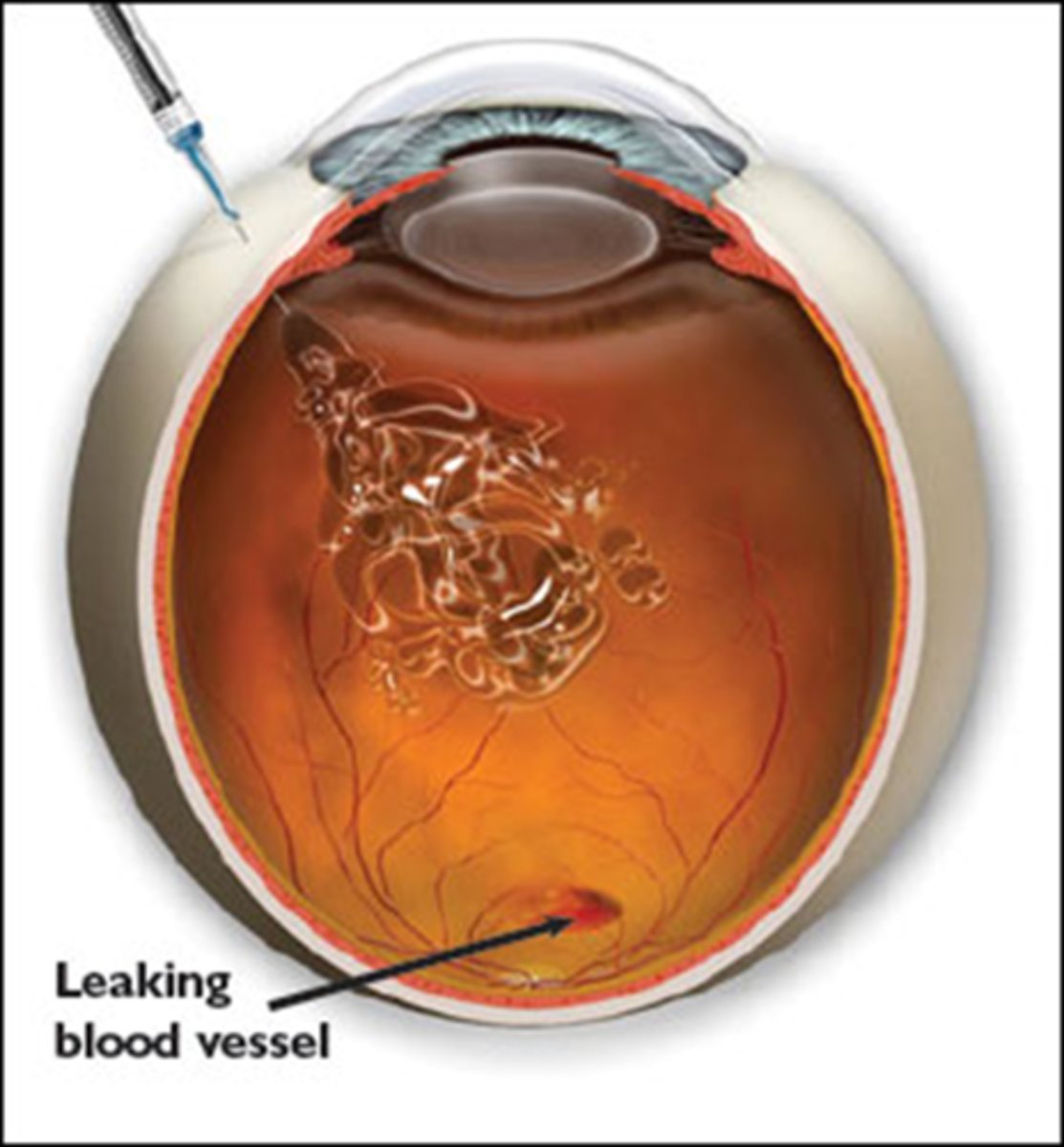
corneal abrasions
increased IOP
endophthalmitis from skin/eyelashes 3-4 days post-op = eye pain, soreness, blur, vitritis, AC rxn, hypopyon
CATs if Dr hits the lens
RD
inflam = sterile endophthalmitis reaction to meds, needle, etc.
What are some other uncommon S/E of intravitreal injections?
macular edema = DME, RVO
wet AMD
NPDR and PDR
other proliferative retinopathies
myopic CNV
What are some indications for using anti-VEGF?
Avastin (bevacizumab)
Which anti-VEGF medication is used off-label bc it's inexpensive?
in DR, VEGF is very high compared to levels in AMD
Why do on-label meds like Eylea, Lucentis, Beovu tend to work better for DR while they work just as good as off-label for AMD?
Avastin and Luctenis were similar to exudative AMD (which responds well to anything) but the benefit of name brand is they can go longer between injections
What did the CATT trial find about Avastin and Lucentis?
avoid permanent PR atrophy especially at the PIL
prevent exudates from depositing
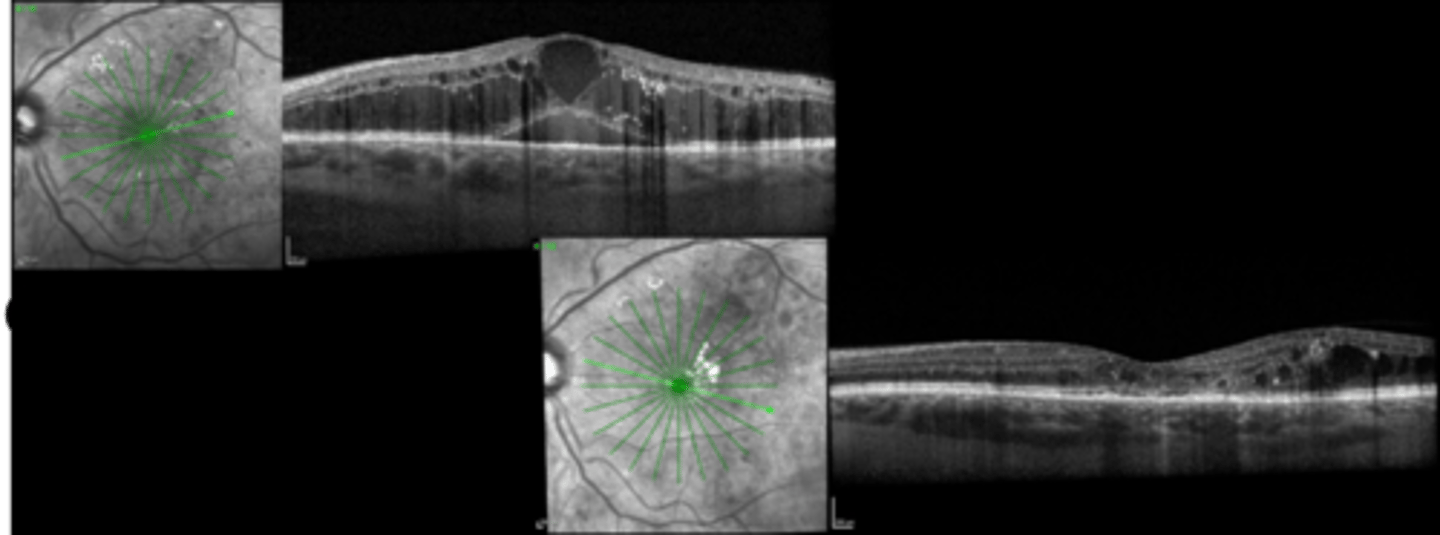
While we consider location of edema, pt symptoms, VA, general level of retinopathy, BG control when deciding whether to tx mac edema, what are 2 big reasons we should treat it?
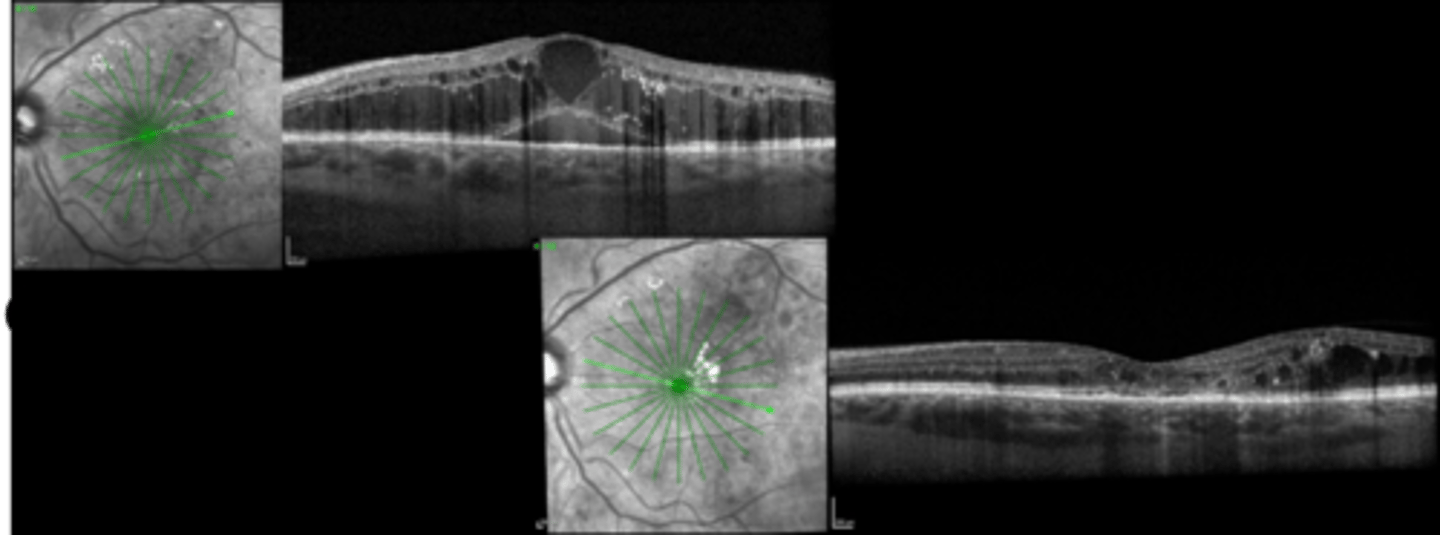
non-urgent (2 week) referral
f/u 4 weeks after if treated (4-8 if just monitoring)
What is the referral and f/u timeline for treating mac edema with anti-VEGF?
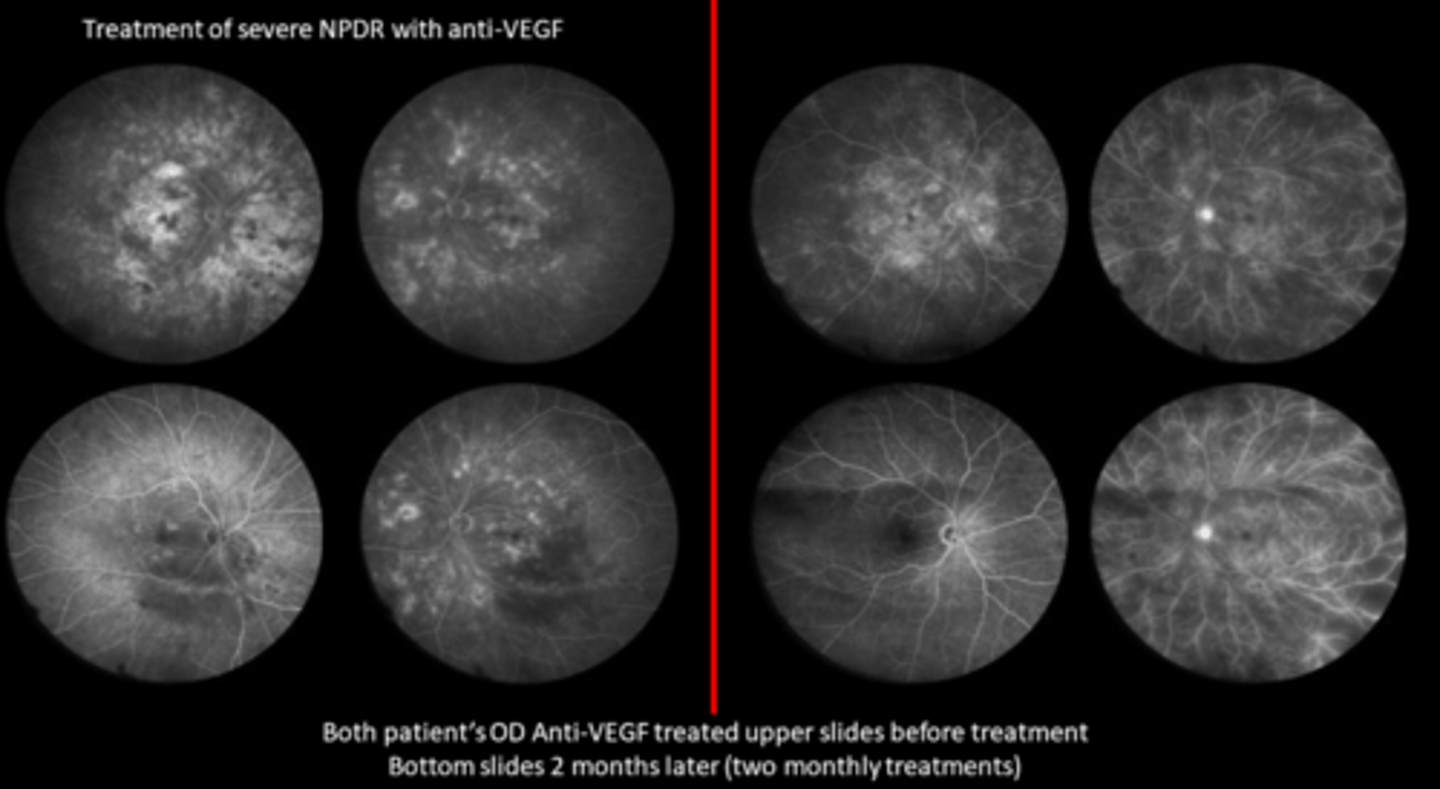
Lucentis has better visual outcomes, less VF loss compared to PRP (but higher tx burden)
What does Protocol S suggest for treating PDR with Lucentis?
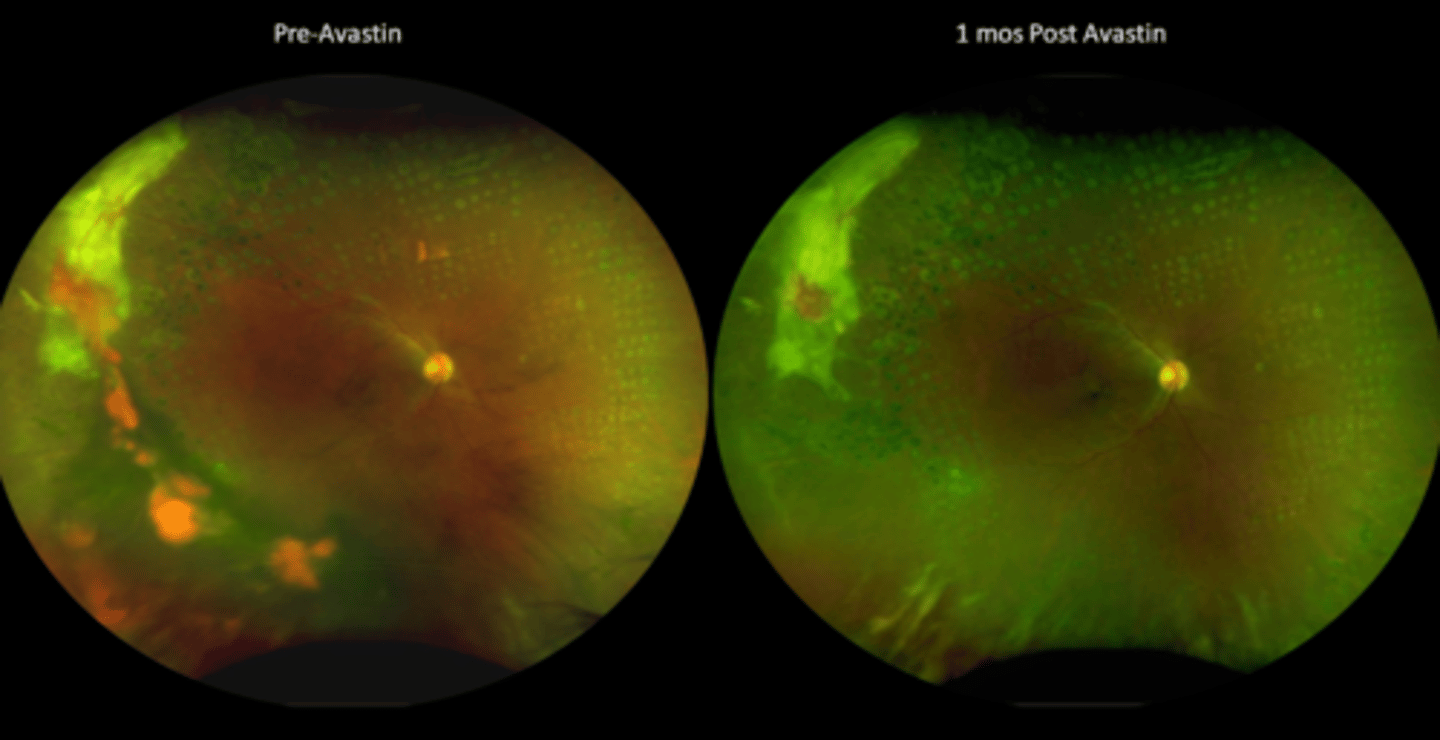
Eylea for moderately severe to severe NDPR resulted in a 2 step reduction in DR severity, decreased risk of sight threatening complications or DME compared to no tx
What does PANORAMA suggest for treating PDR with Eylea?
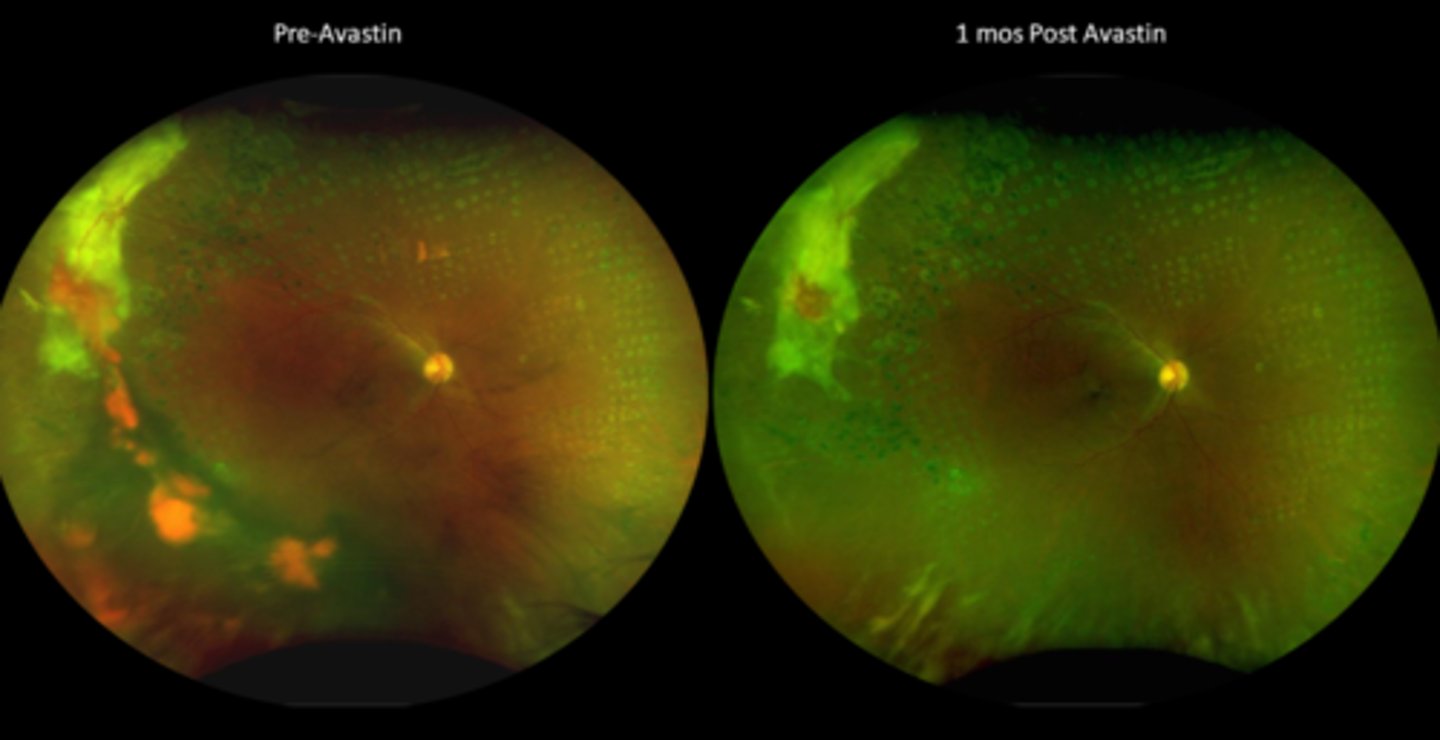
non-urgent (2 week) referral for severe NPDR, PDR, other proliferative ret
emergent/urgent referral for NVG/NVI
What is the referral and f/u timeline for treating proliferative retinopathies with anti-VEGF?
choroidal breaks = laser scars
Histoplasmosis
AMD
myopic CNV
peripapillary CNV
angioid streaks
Best's disease
CSR
MacTel 2
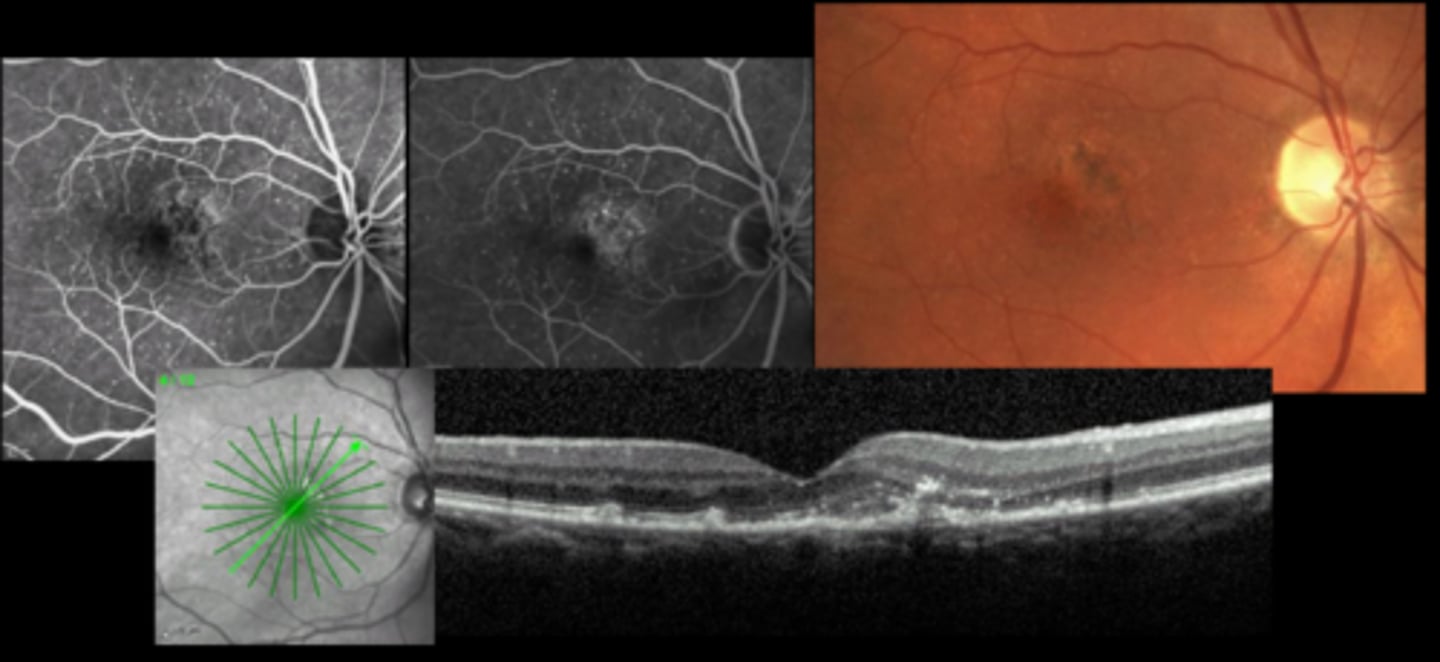
What can cause a CNV?
PDT
focal laser
anti-VEGF is preferred today
How do we tx CNV?
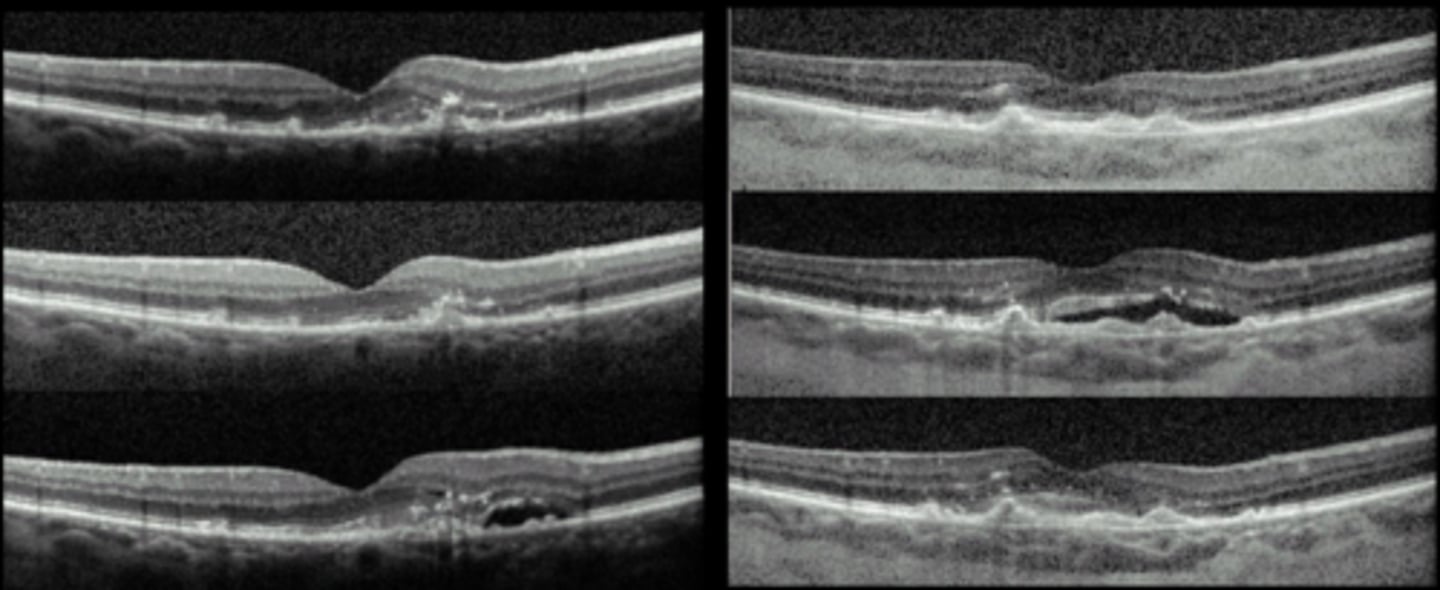
emergent/urgent referral = ASAP bc scarring can cause significant damage to PR's quickly
f/u in 4 weeks after tx to ensure no recurrence, then continue to treat and extend with anti-VEGF
What is the referral and f/u timeline for treating CNV with anti-VEGF?
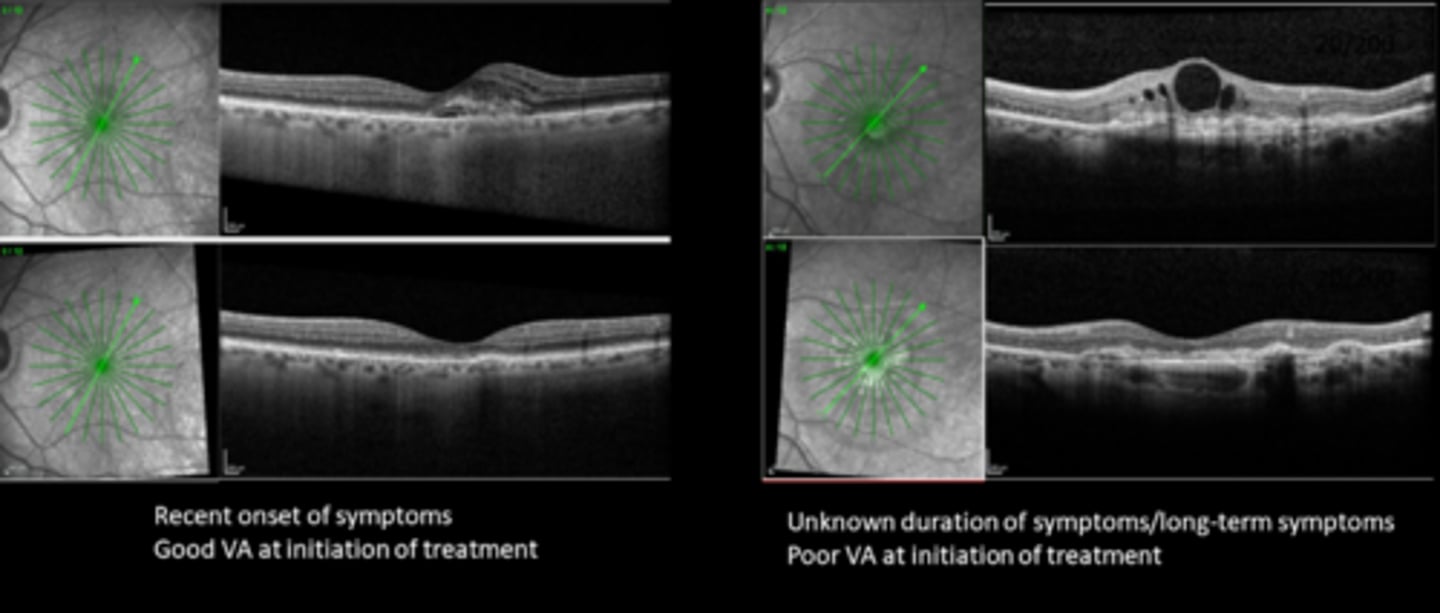
true = only treats CNV that may result from it, cannot treat drusen or GA
True or False: anti-VEGF does not treat AMD.
molecules that last longer in the eye so longer time between tx
What is the main feature being added to the future of anti-VEGF?
cure
Anti-VEGF is a treatment that requires routine f/u and monitoring, not a ___________.
Ozurdex = dexamethasone intravitreal implant
Iluvien = fluocinolone intravitreal implant
Retisert = fluocinolone intravitreal implant
YUTIQ = fluocinolone intravitreal implant
What are some examples of intraocular steroids?
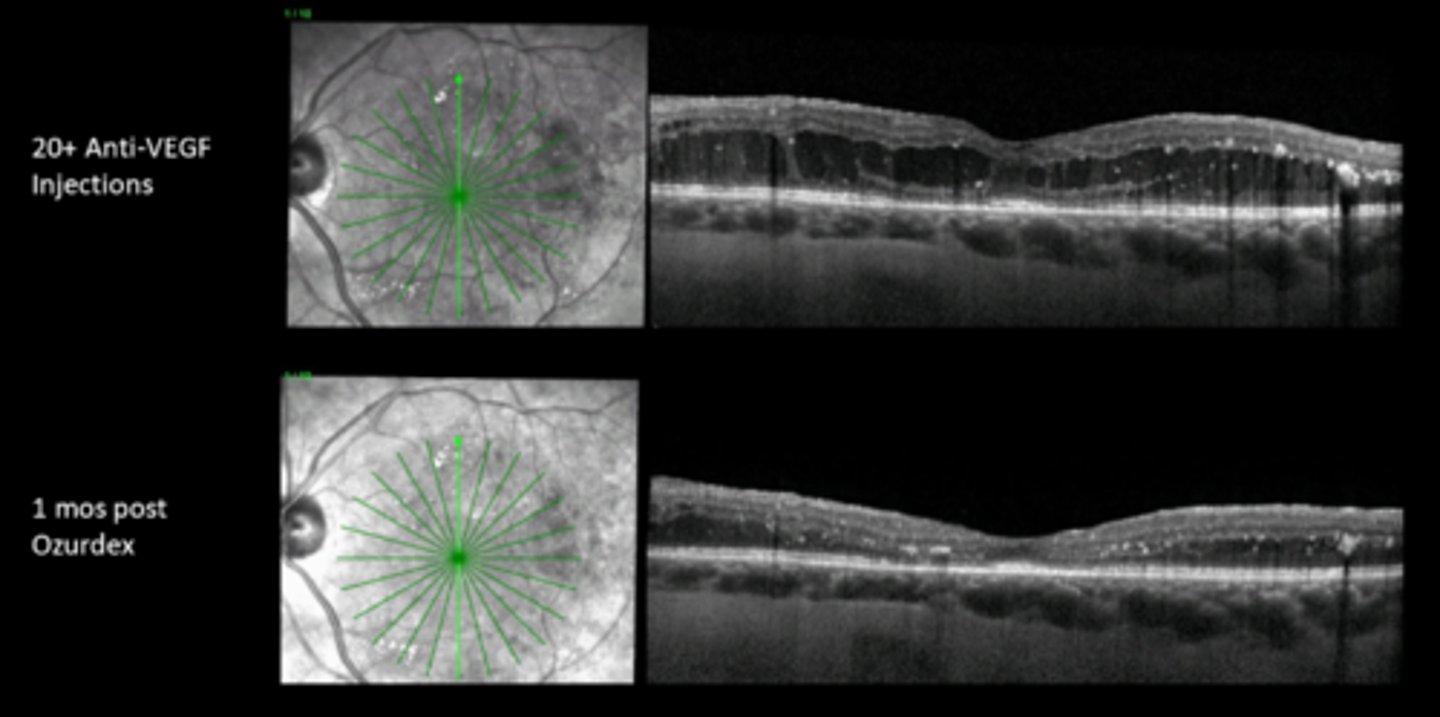
macular edema = DME, RVO
CME (Irvine Gass) after CAT Sx
posterior uveitis after R/O infectious etiology
What are some indications for intraocular steroids?
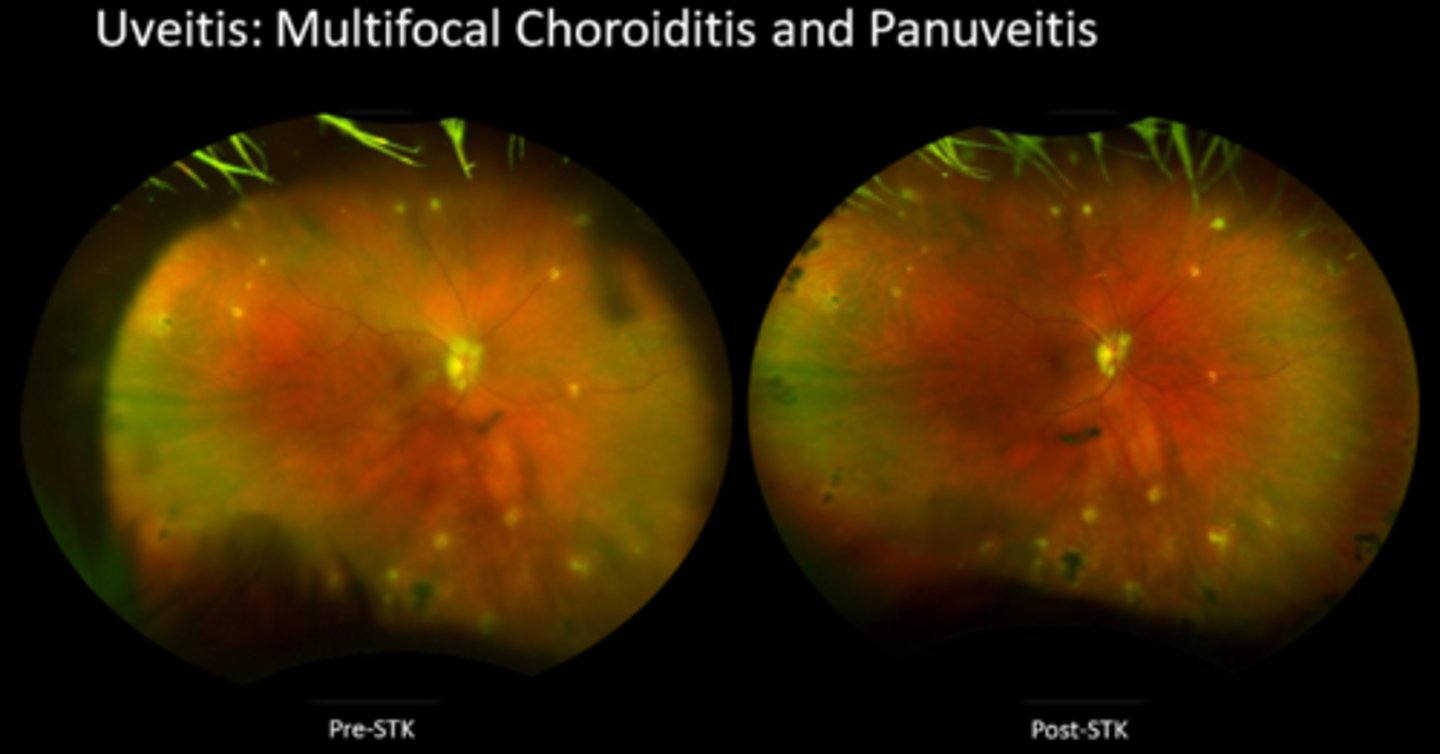
CATs
glaucoma/increased IOP
immunosuppression = infection risk
Recall the main 3 S/E of intraocular steroids are?
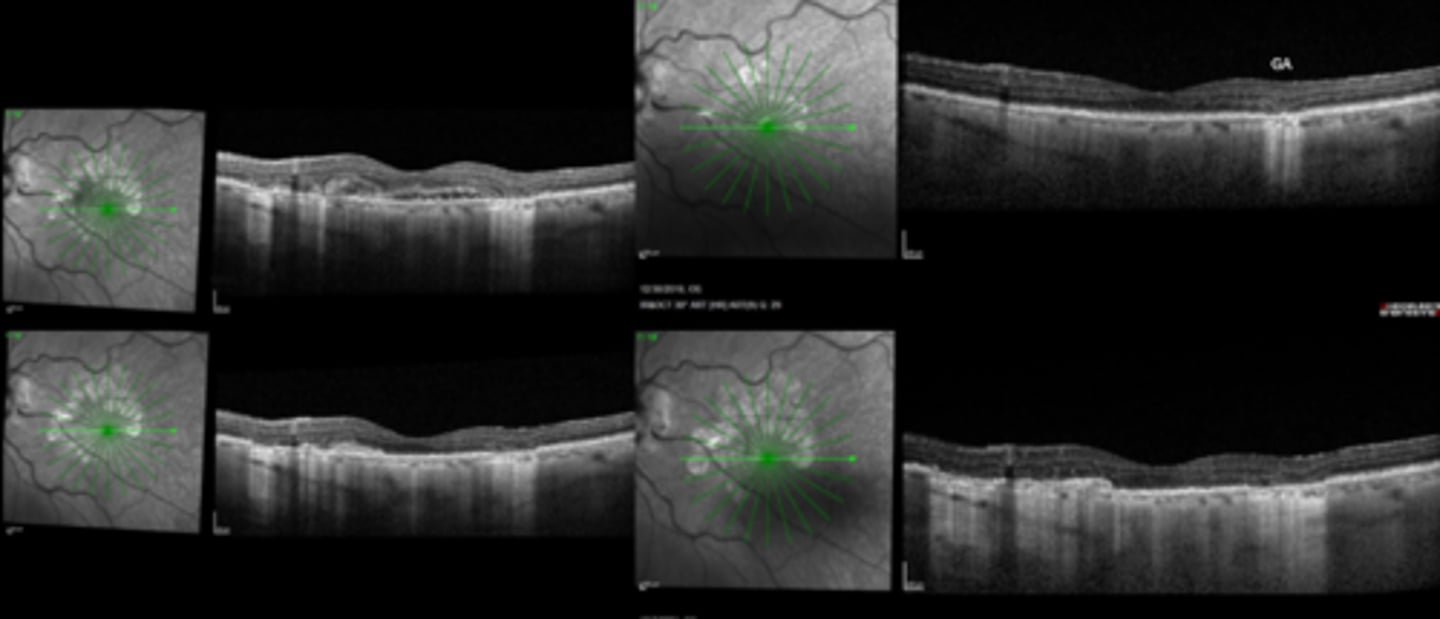
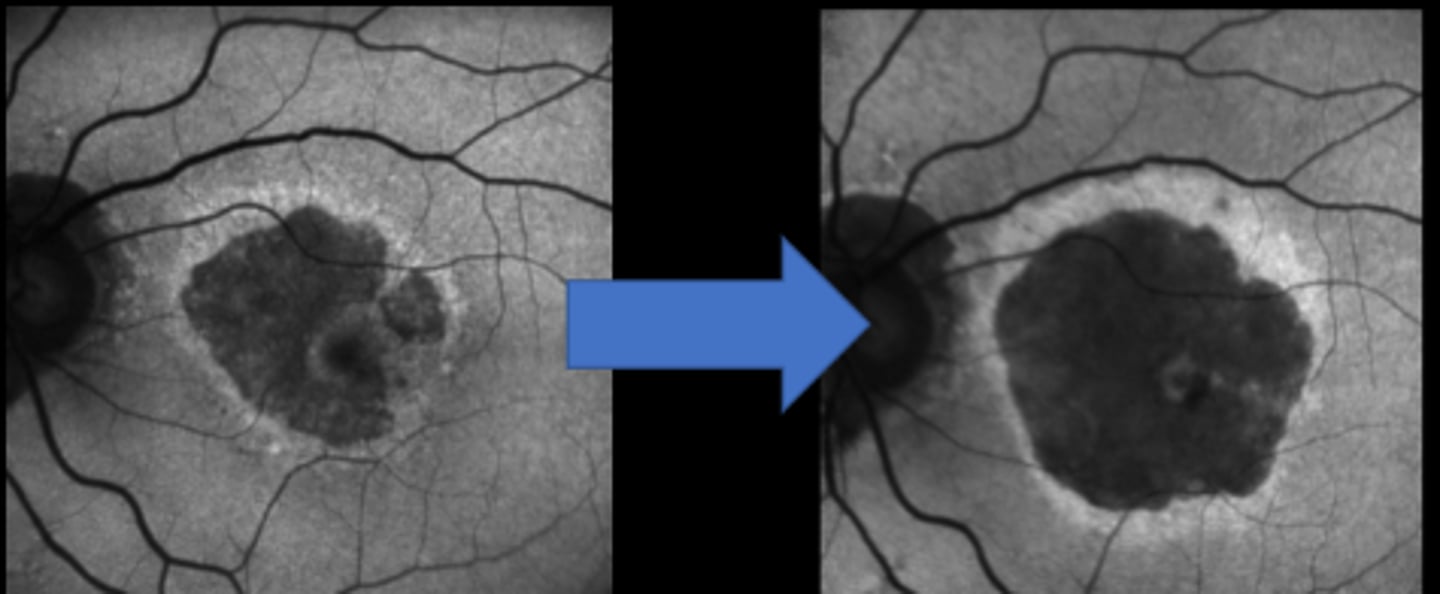
Geographic Atrophy (GA) in AMD
New injectable meds Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) and Izervay (avacincaptad pegol) from 2023 are now available to treat which condition?
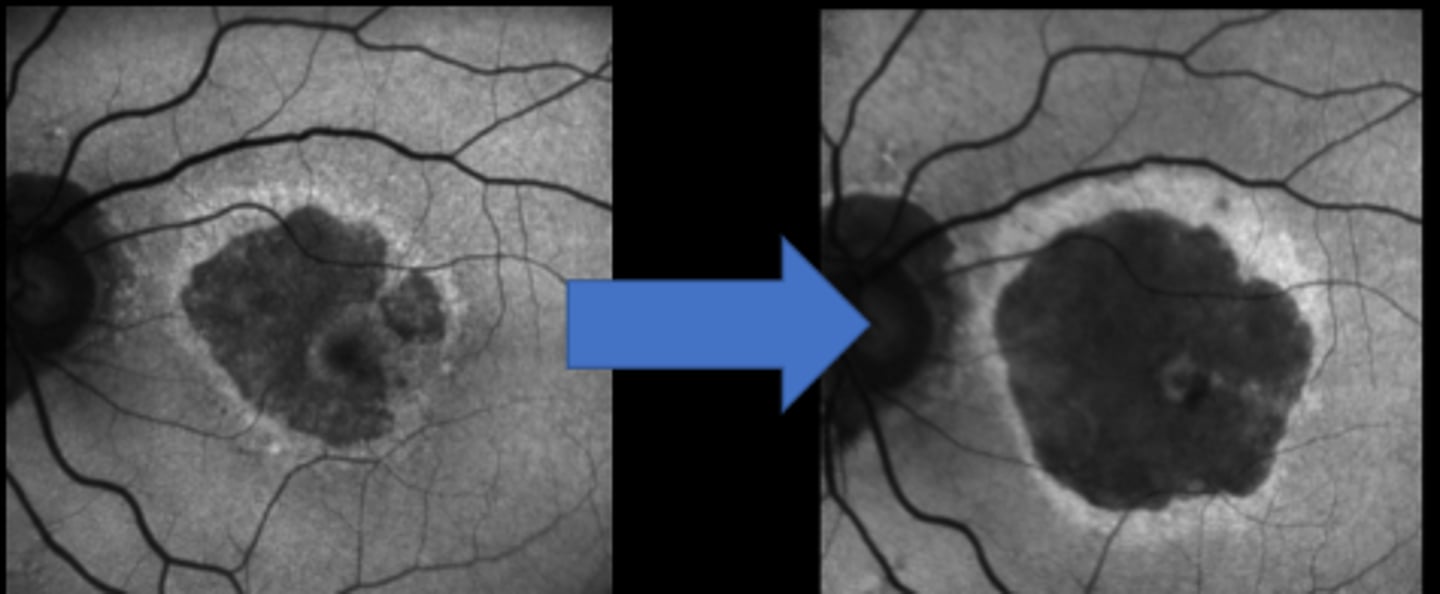
intravitreal C3 complement inhibitor = decreased GA growth by 25%
What is the MOA of Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) and Izervay (avacincaptad pegol)?
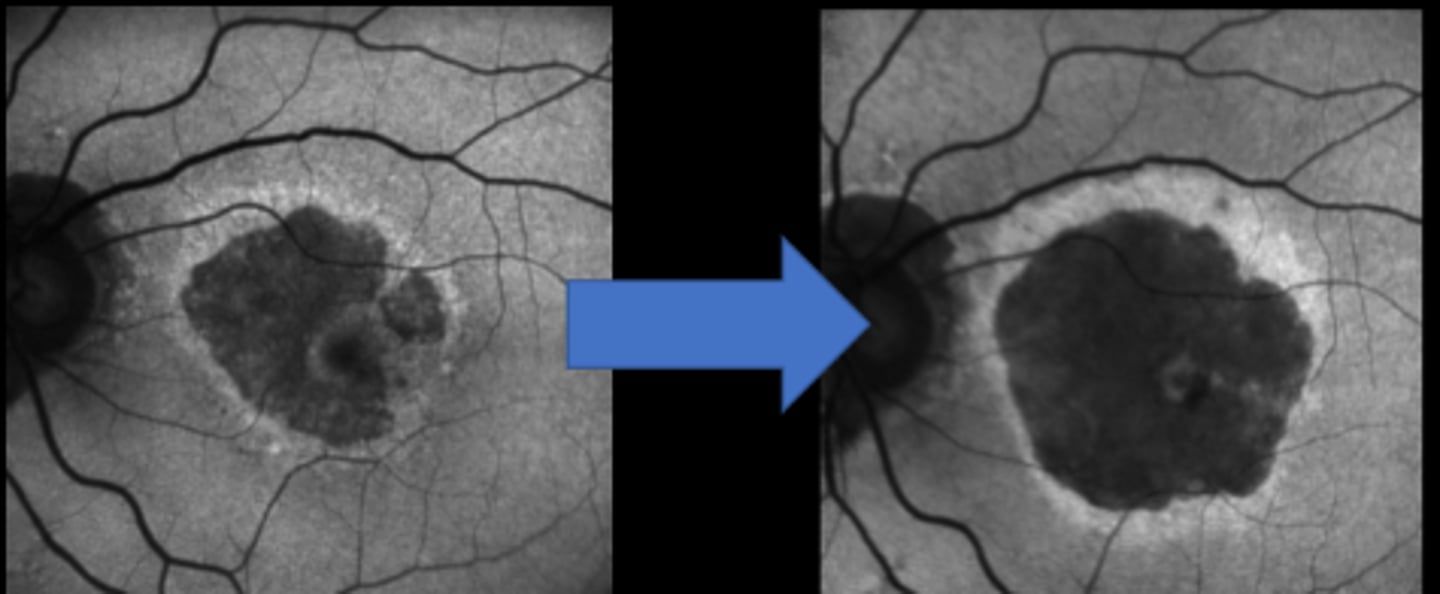
increased risk of CNV formation
What is the main S/E of Syfovre (pegcetacoplan) and Izervay (avacincaptad pegol)?
antibiotics (ceftiazidine, vancomycin, clindamycin) for endophthalmitis, toxoplasmosis
antivirals (foscarnet, ganciclovir) for CMV retinitis, ARN, PORN
antifungals (amphotericin B, voriconazole)
What are 3 classes of intravitreal anti-infective injections?