Physics year 1
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
106 Terms
The thing i always forget to include on wave diagrams
Partial reflection rays
speed of light in another substance equation
speed of light in vacuum/refractive index = speed of light
What does the refractive index show
How much slower that light moves in a substance compared to when its in a vacuum
How do wave properties change when it enters a substance of higher refractive index
Bends towards the normal, and wavelength and speed decrease while frequency remains constant
Conditions for total internal reflection
The medium change is from higher to lower refractive
The angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle
Why do diamonds sparkle
The critical angle is very small, so there is a higher probability that light rays are reflected many times before they emerge so the colours will be more spread out
What is the phenomenon that allows fibre optics to work
Total internal reflection
What layers are there in optical fibres
Core, cladding and sheath
What could happen when 2 fibres touch each othee
Crosstalk (loss of signal into another wire)
Why do we use digital signals instead of analogue
When analogue signals pick up noise (superpose with other waves) it is hard to tell where the peaks and troughs are meant to be
What is latency
How quickly a signal reaches its destination
What is bit rate
How much data is sent per second
What must we do to signal to have a high bit rate
Pulses must be quick and close together
What is a potential issue with high bit rate
Multipath dispersion can render the signal undetectable if all the peaks overlap
What does the sheath do
Prevent scratching to core, prevents crossover and add structural integrity
How can a scratch cause signal loss
Light refracts the wrong way due to changed shape
What does the cladding do (5)
Has a lower refractive index so light totally internally reflects in core
Prevents scratching of core
Reduces mobile dispersion
Increase signal strength
Prevent crossover
Attentuation meaning
Decrease in signal strength as it is absorbed by mediums down the wire
How do we prevent attenuation
Use red or infrared as light doesnt absorb those wavelengths
Signal boosters
Material/chromatic dispersion
Pulse widening due to using different wavelengths of light, which travel different speeds in glass
Modal dispersion meaning
Pulse widening due to path difference in optics
How can we reduce modal dispersion
Reducing the diameter of the core or by reducing it enough for single path dispersion
What is the difference between step index and graded index
Graded index changes the refractive index gradually so it bends back toward the centre more often
How can we prevent modal dispersion
Reducing diameter enough so it is a single mode fibre
Wave defintion
Transfer of energy without the transfer of matter by means of oscillation
What can oscillate to form a wave
Matter or fields
What is the difference between longitudinal waves and transverse waves
Transverse waves oscillate perpendicular to energy transfer, and longitudinal oscillate parallel
Example of longitudinal waves
P-waves, sound
Example of transverse waves
S-waves, light, string
What are the parts of longitudinal waves
Rarefaction and compression
How are the two ways waves can be graphed
Displacement against time or distance
Definition of amplitude
Maximum displacement from rest value
Definition of time period
Time for 1 complete oscillation
Definition of frequency
How many waves pass a point in 1 second
What is superposition
When waves overlap, the resulting wave is the sum of the overlapping waves
What is phase difference
Angle between their wave cycles
Coherence definition
Constant phase difference and same frequency
What happens when 2 identical waves travel in opposite directions
A standing wave is formed with 2 * amplitude
What is path difference
The difference in the distances that 2 waves travel between 2 points
In a stationary wave, what is the phase difference
At an odd number of anti nodes away, out of phase, an even number of anti nodes away is in phase
What is polarisation
Restriction of the oscillation of a wave into 1 plane
Why can longitudinal waves not be polarised
Because they can only vibrate in one direction (can’t be restricted to a plane)
What direction of polarisation passes through a vertical polaroid
A vertical polarisation (opposite polarisations can’t get through the polaroid)
How much unpolarised light gets through a polaroid
The intensity halves
How do sunglasses use polarisation
They have a vertical polaroid, which halves the intensity of light from the sun, and eliminates the horizontally polarised light from reflections so it is easier to see
How do we consider polarised light with microwaves
An antennas oscillating electric field forms vertically polarised light so receiving antenna must be the same direction, A vertical metal grid between the source and receiver will block (horizontal polaroid)
What is an easy way to set up a standing wave
Reflecting a wave back on itself with a string
What are the frequencies of a standing wave called
Resonant frequencies or harmonics
How many nodes are there on the nth harmonic
n+1
What pattern does a tube with powder and a loudspeaker show
there are piles of powders equally spaced at the nodes
how does wavelength affect the amount of diffraction
Increasing wavelength increases the diffraction up until when wavelength is greater than the slit width
What are examples of wave behaviour
Interference, diffraction
Examples of particle behaviour
Mass, momentum, photoelectric effect
What determines if something acts like a particle or wave
When de broglie wavelength is larger than the particle, it acts like a wave
Single slit diffraction pattern
A single bright fringe of double usual width, then slits of much lower equal intensity equally spaced
How to set up double slits
Set up a laser in front of a single slit, with double slit behind it so the light hitting the slits has 0 path difference and coherent
Why are lasers helpful in double slit experiments
They provide a source of monochromatic coherent light, so patterns can be clearly seen
Uses of diffraction gratings
reading optical drives
Spectral analysis of stars
What is the path difference of the waves at the dark fringes
n/2 * lambda
What is the path difference at bright fringes
n * lambda
In double slit, why do dark fringes and bright fringes form
At bright fringes. the waves superpose and constructively interfere at bright fringes and destructively interfere at dark fringes
What does single slit diffraction interfere with
It interferes with the waves from different parts of the slit
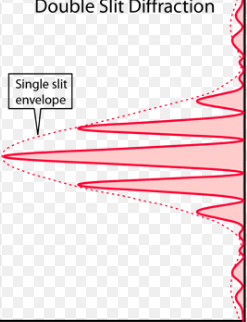
Double slit interference pattern
All are equal width with a high intensity central maximum, fringes much closer together than single slit
Ways to produce monochromatic light (without laser)
Discharge lamps, filters of white light
How many maxima are produced when d/lambda = 3.2 in a diffraction grating
7 (central maxima and 2 sets of 3 maxima)
Why can’t we calculate fringe spacing for diffraction grating
Because the fringes arent equally spaced
Why are there large areas of dark in diffraction gratings
Because at these positions all the different waves superpose and cancel each other out, it is lots of waves to constructively interfere
Double/single slit pattern with white light
A central white maxima, with fringes showing the colour spectrum from red closest to the outside and violet on the inside, with the spectra becoming wider further from the central maxima, shrinking the dark fringes
Diffraction grating with white light
Central white maxima, with spectra with violet on inside and red on outside where maxima would be. Maxima increase in width with increasing order.
Minimum Photon Frequency for Electron Liberation
The photon's energy, determined by its frequency, must be greater than the work function (energy needed to break bonds holding the electron) in order for an electron to be emitted.
What happens if a photon has a frequency higher than the threshold frequency?
The electron will be liberated, and the remaining energy becomes the kinetic energy of the electron.
Effect of Increasing Light Intensity when Photoelectric Emission Does NOT Occur
Increasing light intensity has no effect because each photon still carries the same amount of energy, which is not enough to liberate an electron.
Work Function
The minimum energy required by an electron to overcome the metallic bond holding it in the metal.
Electron Volt
The kinetic energy of an electron that has been accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1V.
How a Fluorescent Tube Works
High voltage applied across mercury vapor accelerates fast-moving free electrons, which collide with the mercury atoms, exciting them. Mercury electrons return to the ground state, releasing a UV photon. The tube's phosphorus coating absorbs the UV photons, and its electrons are excited, they cascade down the energy levels and emit visible light photons.
Evidence for Discrete Energy Levels in Atoms
Line emission and absorption spectra, as the lines appear at discrete points which show where a light photon of specific frequency and wavelength has been absorbed or emitted, this shows electrons can only absorb an exact amount of energy to be excited to the next discrete energy level.
Wave-Particle Duality
All particles have both particle and wave properties. Waves can have particle properties, e.g., light acts as a particle in the photoelectric effect and as a wave when it is diffracted.
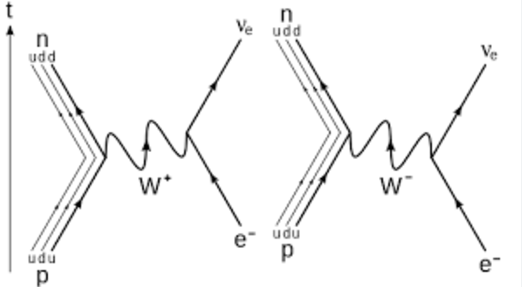
Feynman diagram for electron capture
(Theres 2)
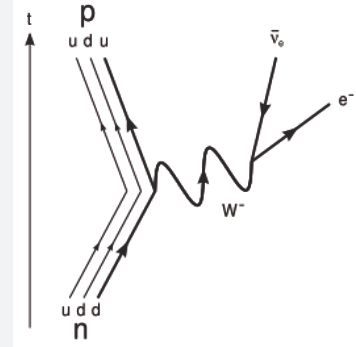
Feynman diagram for beta minus decay
Feynman diagram for beta plus
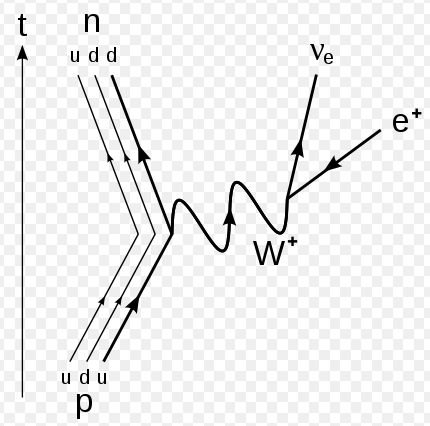
Feynman diagram for decay of a down quark
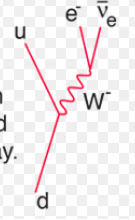
Exchange particle definition
A virtual particle that gives rise to forces between 2 other particles by transferring momentum/energy
Ionisation definition
An atom losing or gaining electrons
Isotope definition
The same number of protons but different number of neutrons in atom
Stable baryon
Proton
Anti kaon neutral
Anti down and strange
Kaon neutral composition
Anti strange and down
Possible quarks in pion neutral
Up and anti up or down and anti down
What do kirchoffs law state
The charge (current) into a junction must be the same as the charge out of said junction
The sum of the voltage of 1 loop is equal to 0
What is emf
Electromotive force, energy gained by unit charge (by a cell)
Resistivity is a physical property of a metal
How to find resistivity experimentally
Change the length of test wire and measure the new resistance, plot gradient if resistance-length graph and multiply by area of wire

What is a superconductor
A material which tends to 0 resistance at low temperatures/pressure
What are superconductors used for
MRI scans, trains, reducing energy lost in national grid
Frequency and voltage of mains
50Hz 230V
What is a rheostat
A variable resistor
Brightness of a bulb depends on what
Power
What is ohms law
The current between 2 points is directly proportional to the potential difference across the 2 points at a constant temperature
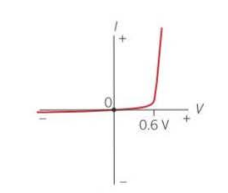
IV graph for diode