Crime Mapping, Big Data, and Evaluation Methods in Criminal Justice
1/90
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What is crime mapping?
The process of using a geographic information system (GIS) to analyze crime problems and police-related issues.
What are the three main functions of crime mapping?
1. Provides visual and statistical analyses of crime. 2. Links crime data to other data sources. 3. Communicates analysis results through maps.
What are crime hot spots?
Geospatial locations where crimes are more likely to occur compared to other areas.
How does crime mapping assist law enforcement agencies?
It helps agencies deploy resources more effectively for crime prevention by identifying where crime is likely to occur.
What is big data?
Large and rapidly changing data sets that reveal patterns, trends, and associations among variables.
What defines big data?
A very large data set assessable in a computer-readable form, containing thousands of cases.
What are the characteristics of big data?
High volume, high speed, and high variety.
What is relational data?
Data that measures the connections and ties between units, forming relational systems.
What is risk terrain modeling?
A predictive modeling technique that assesses the probability of future crime based on environmental factors associated with illegal behavior.
How does risk terrain modeling differ from regular crime mapping?
It takes into account environmental features that enable criminal behavior, rather than just mapping past crime occurrences.
What is intelligence-led policing?
A strategy that uses data and analysis to guide police decision-making and resource allocation.
What are the benefits of intelligence-led policing?
Reduces crime effectively, focuses on major threats, saves resources, and improves accountability.
What is social network analysis (SNA)?
An approach to analyzing social relationships in various forms, including face-to-face and online interactions.
What is a sociogram?
A graphical representation of social configurations, showing individuals as points and their relationships as lines.
What are nodes in social network analysis?
The basic units in a graph that represent individuals or other units of observation.
What is an adjacency matrix?
A matrix that defines the relationships between nodes, indicating whether a relationship exists.
What is a binary network?
A network that only indicates whether a relationship exists between pairs of nodes.
What are some advantages of using big data?
Improves decision-making, reveals trends, enables predictions, increases efficiency, and enhances accuracy.
What are some challenges associated with big data?
Generalizability issues, as digital data may not represent the general population due to socioeconomic differences.
How can big data be searched?
One method is through the Google Ngrams site, which allows for analysis of large data sets.
What types of data can generate relational data for SNA?
Surveys, interviews, participant observation, and secondary data.
What is the purpose of using risk terrain modeling in crime prediction?
To statistically compute the probability of specific types of criminal behavior occurring in certain locations.
What is the significance of the presence of gangs and drugs in risk terrain modeling?
Previous research indicates that these factors correlate with a higher likelihood of shootings.
What role does big data play in risk terrain modeling?
It examines multiple data sets that share geographic location as a common denominator.
What is the goal of social network analysis?
To understand the relational dynamics within networks, including criminal networks and social interactions.
What ethical concerns arise from big data?
Big data can reflect the behavior of individuals who did not consent to participate in research, raising issues of subject confidentiality.
What is a key concern when analyzing original records in research?
Subject confidentiality must be maintained by removing identifying information to protect the identities of living subjects.
What is the role of the Institutional Review Board (IRB) in secondary data analysis?
The IRB is responsible for reviewing and approving proposals for secondary data analysis to protect human subjects.
What political concerns are associated with big data?
Big data reflects the influence of political interest groups, necessitating an understanding of changes in demographic categories like race.
What is a needs assessment?
A needs assessment systematically evaluates whether a new program is needed or if an existing one is still required.
What can happen if needs assessments are inadequately conducted?
Failing to properly assess community needs can lead to costly mistakes, such as implementing unnecessary programs.
What is an evaluability assessment?
An evaluability assessment determines if a program can be evaluated effectively before committing resources to evaluation research.
Why might a social program not be evaluable?
Reasons include management's desire for confirmation of success, staff alienation, unclear program goals, or overlap with other services.
What is the purpose of process evaluations?
Process evaluations systematically examine program coverage and delivery to ensure alignment with planned services.
Why are process evaluations crucial for complex programs?
Complex programs may be delivered inconsistently, making it essential to verify that they are implemented according to the design.
What do impact evaluations assess?
Impact evaluations measure the extent to which a program achieves its intended goals after confirming proper implementation.
What is an example of an impact evaluation question?
Did new seat belt laws increase rates of seatbelt usage?
What evaluation is appropriate for a new program?
A needs assessment is conducted to determine if the program is needed.
What evaluation is appropriate for a program in its early stages?
A process evaluation assesses how the program operates.
What evaluation is appropriate for a mature program?
An impact evaluation determines the program's overall impact.
What is the stakeholder approach in evaluation research?
The stakeholder approach encourages responsiveness to program stakeholders and involves them in the evaluation process.
What is action research or participatory research?
This approach engages program participants as co-researchers to help design, conduct, and report the research.
Why might there be differing conclusions about a program's impact in stakeholder evaluations?
Stakeholders may have varying perspectives and assessments of the program, leading to multiple conclusions.
What is the main emphasis of social science approaches in program evaluation?
The importance of researcher expertise and maintaining autonomy to develop trustworthy and unbiased evaluations.
How do evaluators using social science approaches derive program theory?
From information on how the program operates and existing social science theory, rather than from stakeholder views.
What is goal-free evaluation?
An evaluation approach where researchers do not learn the goals of program stakeholders.
What are potential disadvantages of ignoring stakeholders in program evaluation?
Participants may be uncooperative, reports may go unused, and future projects may remain unfunded.
What are the risks of neglecting social science procedures in evaluation?
Standards of evidence may be compromised, leading to invalid conclusions about program effects.
What do integrative approaches to program evaluation aim to achieve?
They seek to balance stakeholder concerns with the goal of obtaining objective and scientifically trustworthy results.
What is evidence-based policy?
Policy that has been evaluated with rigorous methods and proven effective, using empirical research to determine what works.
What methods are prioritized in evidence-based policy?
Randomized trials, systematic reviews, and cost-effectiveness analyses.
What is triangulation in mixed methods research?
Using multiple methods to validate findings and gain a clearer picture of the social reality being studied.
What does mixed methods research combine?
Qualitative and quantitative methods in investigating the same or related research questions.
What is convergent parallel design in mixed methods?
Both quantitative and qualitative methods are implemented simultaneously, and findings are integrated.
What is explanatory sequential design?
A mixed methods design where qualitative methods are implemented first, followed by quantitative methods.
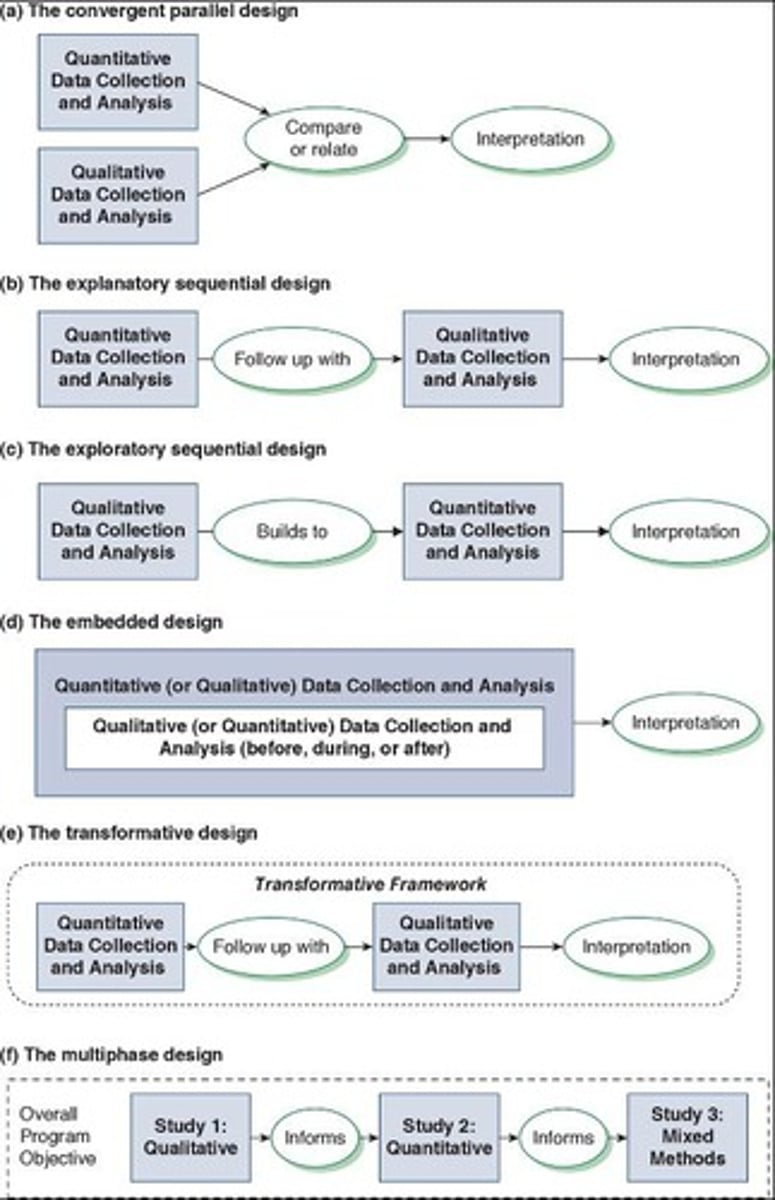
What is exploratory sequential design?
A mixed methods design where qualitative methods are implemented first, followed by quantitative methods.
What is embedded design in mixed methods research?
A primary method (qualitative or quantitative) is supplemented by the other component for additional insight.
What is transformative design in mixed methods research?
A design that uses a theoretical perspective focused on social justice.
What is multiphase design in mixed methods research?
A design involving a series of quantitative and qualitative designs where each informs the next phase.
What is a meta-analysis?
A quantitative method for identifying patterns in findings across multiple studies addressing the same research question.
What is effect size in research?
A standardized measure of association between independent and dependent variables across multiple studies.
What are true experimental designs strongest for?
Testing nomothetic causal hypotheses and studying treatment effects.
What do surveys typically use in research?
Standardized, quantitative measures of attitudes, behaviors, or social processes.
What do qualitative methods like participant observation and intensive interviewing presume?
An exploratory measurement approach based on direct observation or in-depth commentary.
What are key considerations for designing a mixed method analysis?
Purpose, timing, weighting, integration, and data analysis.
What is the purpose in mixed methods research design?
To clearly define the research question and justify the need for a mixed-methods approach.
What does timing refer to in mixed methods research design?
Deciding if quantitative and qualitative data will be collected concurrently or in separate phases.
What does weighting refer to in mixed methods research design?
Determining the emphasis placed on quantitative versus qualitative aspects of the study.
What is integration in mixed methods research design?
Identifying when the quantitative and qualitative data will be merged and analyzed together.
What is the first step in designing a mixed method analysis?
Formulate the research problem by identifying a problem that requires both quantitative and qualitative evidence.
What are the two specific designs used in mixed methods research?
Convergent and sequential designs.
What does triangulation in mixed methods refer to?
Comparing results from qualitative and quantitative findings.
What is the purpose of integrating data in mixed methods?
To combine qualitative and quantitative findings for a more comprehensive conclusion.
How is the primary method indicated in a mixed methods project?
Written in all caps (QUAN or QUAL).
What does the notation QUAL→quan signify?
Qualitative data is collected first, followed by quantitative data.
What is the mode in statistics?
The most frequent value in a distribution.
What characterizes a bimodal distribution?
It has more than one mode due to two values having the highest frequency.
What is the median?
The 50th percentile or the score in the middle of a rank-ordered distribution.
What is the mean in statistics?
The arithmetic average of all scores in a distribution, symbolized by x-bar.
What is the purpose of chi-squared tests in inferential statistics?
To estimate the probability that an association is not due to chance.
What does a correlation coefficient (Pearson's r) indicate?
The strength and direction of a linear relationship between two variables.
What is a normal distribution?
A symmetric distribution where the mean, median, and mode are equal.
What does a positive skew in a distribution indicate?
The presence of high outliers, resulting in a tail on the right.
What type of graph is best for displaying categorical data?
A bar chart, which reflects distinct categories.
What is a histogram used for?
To show the distribution of quantitative variables on a continuum.
What is the primary use of a pie chart?
To show parts of a whole for nominal variables.
What is the purpose of a line graph?
To visualize trends and changes in quantitative variables over time.
What does a joint display in mixed methods research facilitate?
The integration of quantitative and qualitative results.
What is the first step in analyzing data in mixed methods?
Analyze quantitative data using statistical software.
How should qualitative data be analyzed?
By transcribing interviews, coding responses, and identifying themes.
What is the significance of drawing meta-inferences in mixed methods?
To interpret insights from integrated data and discuss their relationships.