UNIT 4 SCIENCE TEST
1/25
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ahhhhhhhhh
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
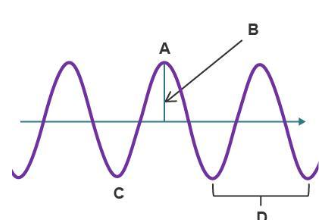
label the parts of the wave
a. crest
b. amplitude
c. trough
d. wavelength
what are the types of EM waves?
radio, microwave, infrared, visible, ultraviolet, x-ray, gamma ray
what is the difference between frequency and amplitude?
Frequency refers to the number of wave cycles passing a point per second, and the amplitude is the maximum displacement of the
wave from its rest position.
how is frequency and energy related?
Frequency and energy are directly proportional, meaning a higher-frequency wave carries more energy.
What is a wavelength?
The distance between two corresponding points on a wave, such as from crest to crest, or trough to trough.
How are wavelength, frequency, and energy related?
Wavelength and frequency are inversely related. Longer wavelength means lower frequency, and shorter wavelength means increased frequency.
What are the three types of waves and how do they move?
Transverse waves have particles moving perpendicular to the wave direction, while longitudinal waves have particles moving parallel to the wave direction. Surface waves are the third type of wave and are a combination of the other two types.
what is an example for radiowaves?
radio, garage door opener, TV
what is an example for microwaves?
microwaves, cell phones, satellite communication
what is an example for infrared waves?
remote controls, thermographs
what is an example of visible light
red, orange, yellow, green blue, indigo, violet
what is an example for UV waves?
sterilization, causes sunburn, can cause cancer cells
what is an example of gamma rays?
killing cells and creating cancerous cells
what is an example of an x-ray?
images of bones
What is the distance from the crest to the trough of a wave in terms of
amplitude?
The distance from the crest to the trough of a wave is twice the amplitude, meaning the wave height is equivalent to two times the amplitude
what is a medium
the material of which a wave travels
what is the hr diagram and how does it organize stars
The HR diagram plots stars by their surface temperature and luminosity
how does the hr diagram organize stars
Based on their characteristics and life stages,
with most stars falling along a diagonal band called the main sequence
How can a low-mass star be classified through its life cycle on the
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram?
Main sequence→ red giant→ white dwarf
What are the different Life Cycles of stars? How do you know which cycle a star will follow?
High mass vs low mass and it is easy to determine by color. Blue and sometimes blue white are high mass. All others are low mass.
What happens to stars when they die?
A low-mass star will shed its
outer layers (red giant stage) and become a white dwarf. A high-mass star, however, will supernova before either turning into a neutron star or a black hole
How does a star’s size and temperature affect its brightness?
Size and temperature help determine the brightness because it is a measure of how much energy the star puts out. Therefore, the greater the surface area and the greater the temperature, the brighter the star.
What must a hypothesis be in order to be considered valid?
A valid hypothesis should be testable and written in an if/then format.
What are units used to measure volume?
Depending on what is being measured, volume is measured in liters, milliliters, and cm3
Describe the similarities and differences of primary and secondary
succession?
Both types of succession are characterized by ecosystems striving to reach a climax community with a great range of biodiversity. Both processes take a long time, though primary succession takes much longer. This is due to the fact that in primary succession no soil is present and rock must be broken down to create soil by pioneer species such as lichen.
What are some causes of primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession takes place after volcanic eruptions, glacial movement, and landslides. Secondary succession takes place after fires, floods, and plowing the land.