anatomy EXAM 1: ch 1-3, 5
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/174
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
175 Terms
1
New cards
physiology
study of the functions of the structures of the human body
2
New cards
anatomy
study of the structures and the relationship among the structures
3
New cards
embryology
the first 8 weeks after fertilization when the sperm cell donates its chromosomes to the egg cell
4
New cards
surface anatomy
use surface markings to understand deep structures
5
New cards
radiographical anatomy
study of structures w/ visualizing through xrays
6
New cards
xrays
the use of electrons that run through the body to be captured on a negative film
7
New cards
pathological anatomy
the study of structural changes from gross to microscopical associated with disease
8
New cards
chemical level in the human body
atoms are organized into molecules
9
New cards
cellular level in the human body
molecules are organized into cells which are the basic structural and functional living units of an organism
10
New cards
the cell
* smallest living unit in the human body
* basic unit of life
* basic unit of life
11
New cards
tissue level
* cells are organized into tissues
* groups of similar cells that usually have similar embryonic origins and perform specialized functions
* groups of similar cells that usually have similar embryonic origins and perform specialized functions
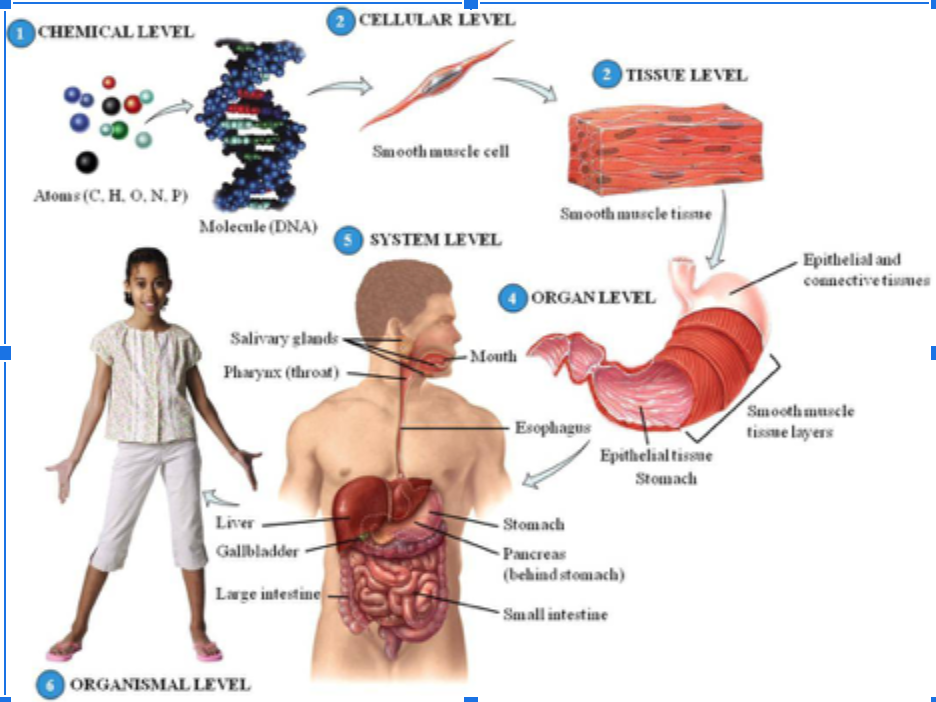
12
New cards
organ level
* 2 or more tissues organized into systems
* functionally related groups of organs that cooperated to perform a common general function
* functionally related groups of organs that cooperated to perform a common general function
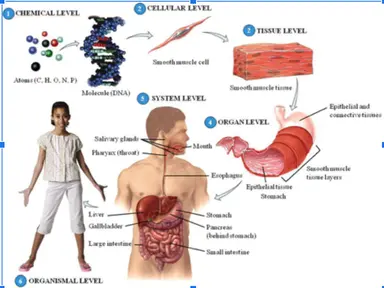
13
New cards
organism level
* all the systems are structurally integrated and function cooperatively to constitute the total organism
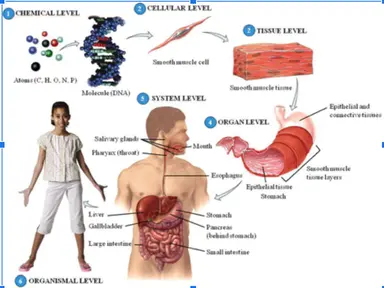
14
New cards
anatomical position
a standard position to ensure directional terms are used accurately
1. the body is erect w/ the feet flat on the floor
2. the upper extremities are at the side w/ the palms facing forward
3. prone position: the face is facing down
4. supine position: the face is facing up
5. it is always the specimen’s left and right side
1. the body is erect w/ the feet flat on the floor
2. the upper extremities are at the side w/ the palms facing forward
3. prone position: the face is facing down
4. supine position: the face is facing up
5. it is always the specimen’s left and right side
15
New cards
anatomical position
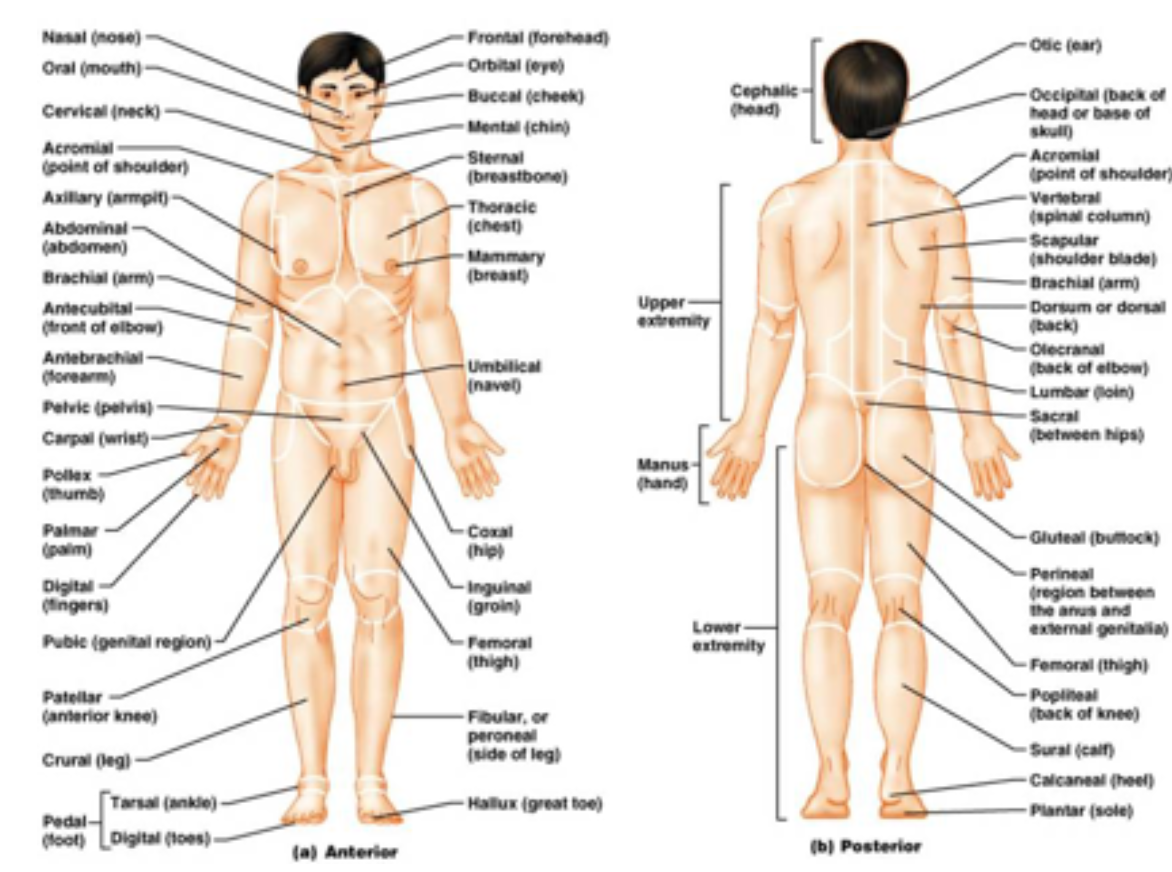
16
New cards
body planes
imaginary flat surface that passes through the body in order to provide an informative view of a specific region of the body
17
New cards
sagittal plane
a vertical plane divides the body into the right and left sides
18
New cards
midsagittal plane
divides the body into equal right and left sides
19
New cards
bilateral symmetry
the right side of the body is a mirror image of the left side
20
New cards
parasagittal plane
divides the body into unequal right and left side
21
New cards
frontal plane
vertical plane divides the body into front and back half
22
New cards
transverse plane
divides the body into the top and bottom half
23
New cards
oblique plane
passes through the body throughout the body not at 90° angle
24
New cards
superior
near the head
25
New cards
inferior
near the tail/feet
26
New cards
anterior
front
27
New cards
posterior
back
28
New cards
medial
middle/midline
29
New cards
lateral
side; away from midline
30
New cards
intermediate
between two structures
31
New cards
proximal
close
32
New cards
distal
far
33
New cards
superficial
close to surface
34
New cards
deep
further from surface
35
New cards
ipsilateral
same side
36
New cards
contralateral
of or pertaining to the other side
37
New cards
parietal
attached to wall of body cavity
38
New cards
visceral
attached to organ itself
39
New cards
body cavities
enclosed spaces within the body that help protect, separate and support internal organs that are located in the cavities
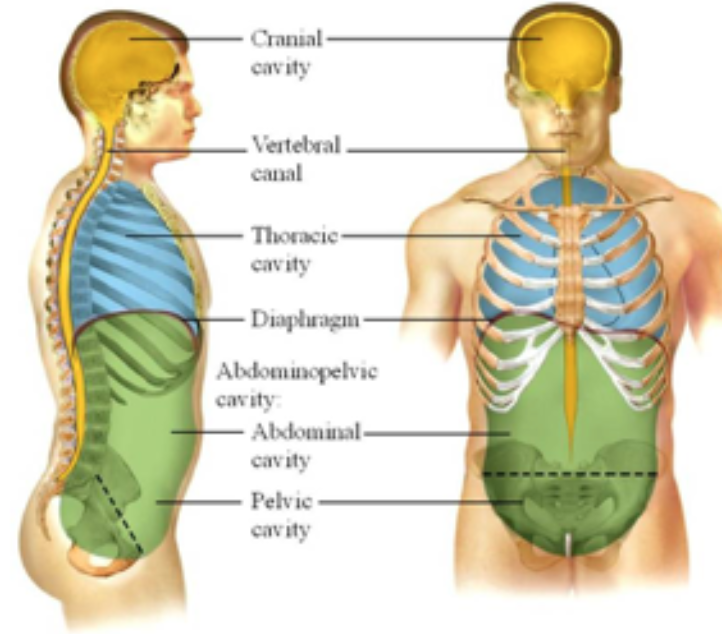
40
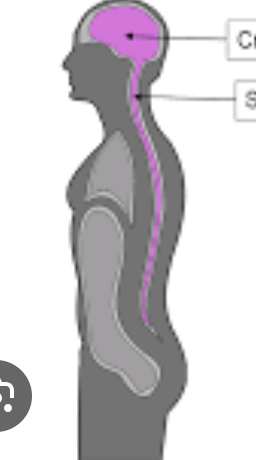
New cards
dorsal body cavity
* cranial cavity
* vertebral / spinal cavity
* vertebral / spinal cavity
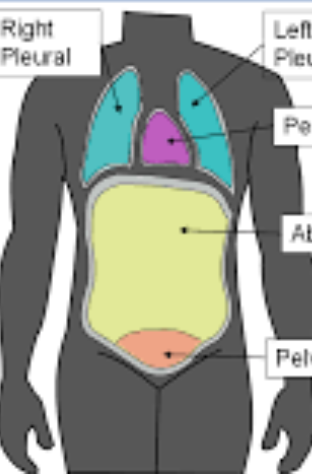
41
New cards
ventral body cavity
* thoracic body cavity
* left & right pleural cavity
* mediastinum
* pericardial cavity
* left & right pleural cavity
* mediastinum
* pericardial cavity
42
New cards
abdominopelvic cavity
* abdominal cavity
* pelvic cavity
* pelvic cavity
43
New cards
serosa
* pleura
* pericardium
* peritoneum
* pericardium
* peritoneum
44
New cards
medical imaging
permit visualization of the interior of the human body used to see tissues in histology
45
New cards
light microscopy
illuminates body tissues with a beam of light
46
New cards
electron microscopy
illuminates body tissues with a beam of electrons
47
New cards
radiography
waves of short wavelength directed at body and absorbed at certain density onto a negative film resulting in a radiograph or xray
48
New cards
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
the use of radio waves and magnetic field images to view soft structures
49
New cards
advanced xray techniques
* computed tomography (CT)
* series of xray images at different angles around a section of the body
* series of xray images at different angles around a section of the body
50
New cards
sonography (ultrasound)
use of pulses of high frequency sound waves the reflect or echo of body tissues
51
New cards
positive emission tomography (PET)
use of isotopes to be absorbed at concentrated parts of the body
52
New cards
endoscopy
use of an endoscope to view internal structures and projected onto a monitor
53
New cards
3 major cell components
1. plasma membrane
2. cytoplasm
3. nucleus
54
New cards
bilayer phospholipid
2 layers of fat w/ phosphate
55
New cards
proteins
* peripheral: on surface
* integral: stuck
* integral: stuck
56
New cards
cholesterol
provides rigidity to the plasma membrane
57
New cards
cytoplasm
1. all the cellular content between the cell membrane and nucleus
2. includes the cytosol and organelles
58
New cards
cytosol
1. the fluid portion of the cytoplasm
2. made up of water and some particles
59
New cards
intracellular fluid
blood inside the cell
60
New cards
extracellular fluid
body fluid not contained in cells
61
New cards
passive process
substances move across a plasma membrane due to their own kinetic energy, down a concentration gradient
62
New cards
diffusion
process in which substances move down a concentration gradient w/out aid of membrane components
63
New cards
osmosis
diffusion of water
64
New cards
facilitated diffusion
process in which substances move down a concentration gradient with aid of membrane transport carrier protein
65
New cards
active transport
process in which substances move against a concentration gradient with aid of membrane transport carrier protein
66
New cards
endocytosis
extracellular molecules surrounded and enclosed and brought into the cell by invagination
67
New cards
exocytosis
intracellular vesicle-enclosed substances are released in the extracellular fluid by membrane fusion secretory vesicles with the plasma membrane
68
New cards
microfilaments
* thinnest structure (microvilli)
* involve in muscle cell contraction
* involve in muscle cell contraction
69
New cards
microtubules
* largest structure determine cell shape
* function: intracellular transport of organelles
* flagella: propel the sperm cell in motility
* cilia: move materials past surfaces of the cells
* centrioles and mitotic spindles: involved in mitosis
* function: intracellular transport of organelles
* flagella: propel the sperm cell in motility
* cilia: move materials past surfaces of the cells
* centrioles and mitotic spindles: involved in mitosis
70
New cards
intermediate filaments
* intermediate in size
* function: position organelles and give shape to cell
* function: position organelles and give shape to cell
71
New cards
organelles
* little organelles in the cell
* have specific functions and specific shapes
* have specific functions and specific shapes
72
New cards
centrosomes
* consists of a pair of centrioles
* organize microtubules in non-dividing cells
* organize microtubules in non-dividing cells
73
New cards
centrioles
* a bundle of parallel microtubules
* oriented at right angles
* oriented at right angles
74
New cards
mitotic spindle
organizes microtubules in dividing cells
75
New cards
ribosomes
* granules w/ 2 subunits: proteins, ribosomal, RNA
* 2 types:
1. free floating
2. attached to endoplasmic reticulum
* function: protein synthesis
* 2 types:
1. free floating
2. attached to endoplasmic reticulum
* function: protein synthesis
76
New cards
endoplasmic reticulum
* a network of interconnected flattened sacs
77
New cards
smooth endoplasmic reticulum
* no ribosomes
* function: lipid synthesis
* function: lipid synthesis
78
New cards
rough endoplasmic reticulum
* has ribosomes
* function: protein synthesis
* function: protein synthesis
79
New cards
golgi complex/apparatus
* series of flattened sacs called cisternae, stacked on each other
* function: receive the protein and lipid to package them
* function: receive the protein and lipid to package them
80
New cards
81
New cards
membraneous system
extends from the nuclear membrane to the rough endoplasmic reticulum to the golgi complex/apparatus to the plasma membrane
82
New cards
lysosome
* spherical organelles
* contains digestive enzymes
* contains digestive enzymes
83
New cards
peroxisomes
* spherical organelles
* contains enzymes to oxidize molecules
* found in hepatocytes and renal cells
* contains enzymes to oxidize molecules
* found in hepatocytes and renal cells
84
New cards
proteasomes
* spherical organelles
* contains protease → breaks down proteins
* contains protease → breaks down proteins
85
New cards
mitochondria
* sausage shaped organelles
* 2 membranes: out and inner layer
* function: make cellular energy as adenosine triphosphate
* have own mitochondria; DNA to self replicate (ATP)
* 2 membranes: out and inner layer
* function: make cellular energy as adenosine triphosphate
* have own mitochondria; DNA to self replicate (ATP)
86
New cards
nucleus
1. largest organelle, usually spherical or oval shaped
2. enclosed by 2 layers nuclear envelope or membrane with nuclear pores for movement of substances between nucleus and cytosol
3. have spherical nucleoli where ribosomal subunits and RNA are made
4. contains chromatin (condensed into chromosomes during mitosis) composed of DNA and histone proteins organized into nucleosomes
87
New cards
genes
unit of hereditary information, arranged along chromoeomes
88
New cards
genomes
total genetic information in a cell or an organism
89
New cards
DNA
1. long double helix that resembles a spiral staircase held together by a centromere
2. composed of 4 subunits called nucleotides
1. thymine
2. adenine
3. cytosine
4. guanine
90
New cards
somatic body cells
process that separates replicated DNA into 2 daughter cells
91
New cards
germ cells
undergo reproductive cell division called meiosis to produce gametes
92
New cards
haploid cells
2 stages:
1. meiosis 1, 2 haploid cells
2. meiosis 2, 4 haploid cells
1. meiosis 1, 2 haploid cells
2. meiosis 2, 4 haploid cells
93
New cards
prophase
1. chromosomes condensed and coiled
2. nuclear envelope and nuclei break downs
3. centrosomes move to opposite poles
4. mitotic spindle forms
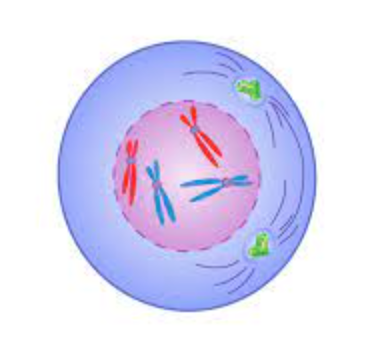
94
New cards
metaphase
chromosomes meet in the middle / equator of the cell
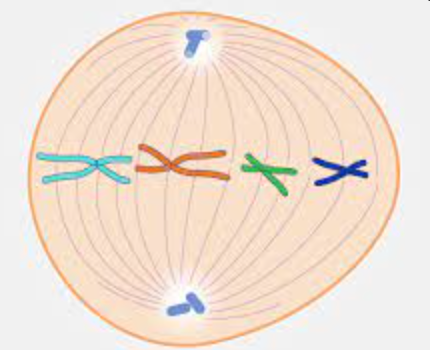
95
New cards
anaphase
chromosomes are pulled apart to opposite poles
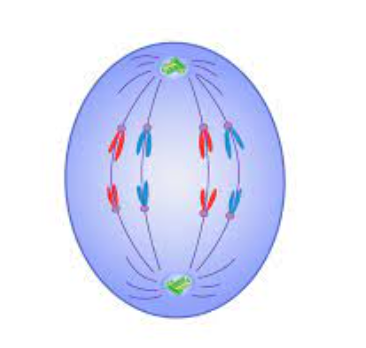
96
New cards
telophase
1. chromosomes uncondensed + uncoiled
2. nuclear envelope and nucleoli reform
3. centrosomes not at opposite poles
4. mitotic spindle break down
5. cytokinesis= end up with 2 identical daughter cells
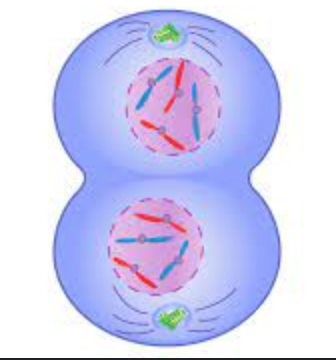
97
New cards
cellular diveristy
1. cells that connect body parts or cover and lines organs
2. cells that produce movement and move body parts skeletal and muscular systems
3. cells that store nutrients adipocytes and erythrocytes
4. cells that gather information and control body functions nervous system
5. cells that fight against diseases immune system
6. cells that reproduce reproductive system
98
New cards
aging
normal process accompanied by progressive change in the body’s homeostatic adaptive responses in order to maintain normal conditions
99
New cards
geriatrics
branch of medicine that deals with medical problems and care of elderly people
100
New cards
gerontology
scientific study of the process and problems associated with aging