Radiography I: Radiation Concepts
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
151 Terms
Key Terms
- Bucky tray
- Cathode
- Collimating device
- Electromagnetic spectrum
- Energy
- Frequency
- Heel effect
- Rotating anode
- Stationary anode
- Wavelength
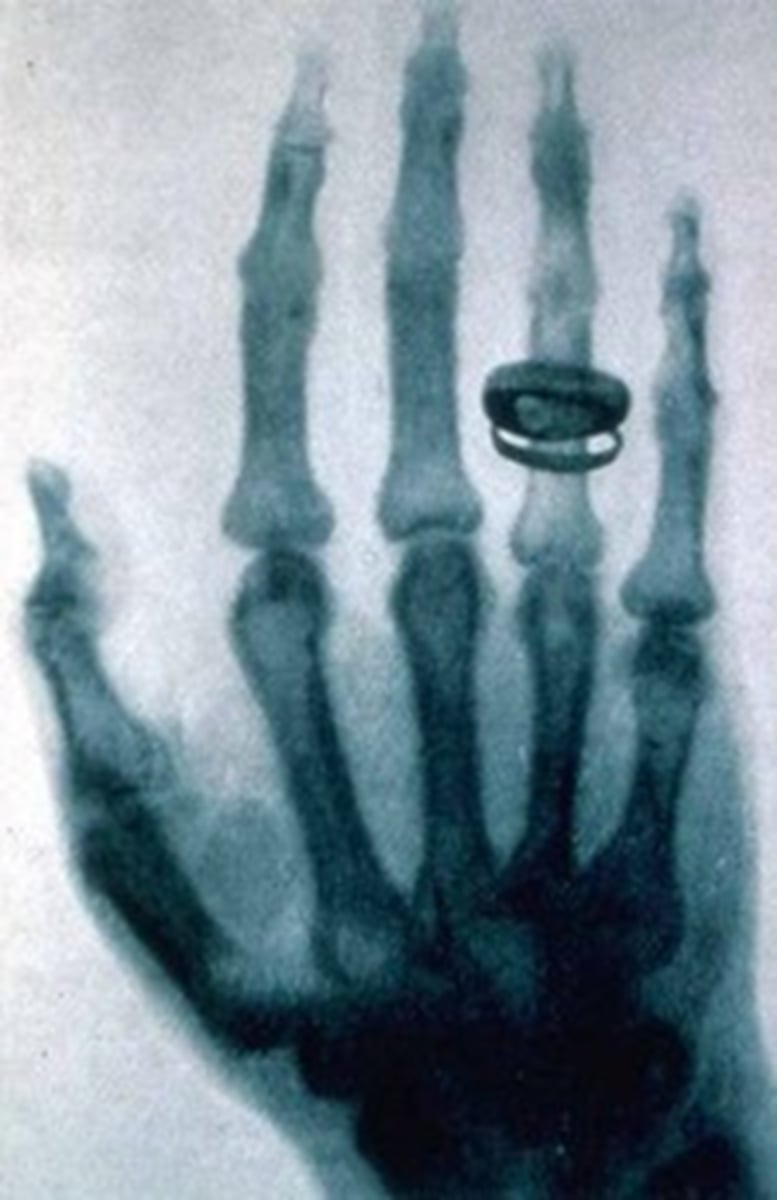
The Discovery of Xrays
- Wilhelm Conrad Roentgen discovered Xrays in 1895
- His wife was said to be his first "patient"
- Xrays were first used in a medical application in 1896
- For the first time doctors could see what was going on inside a patient
History of Radiography
- Therapeutic use (radiation therapy) of radiation began after people reported changes in their skin color and "sunburn"
- The x-ray tube was developed to control the generation of energy of x-rays

Electromagnetic Spectrum is more than the
Visible Spectrum
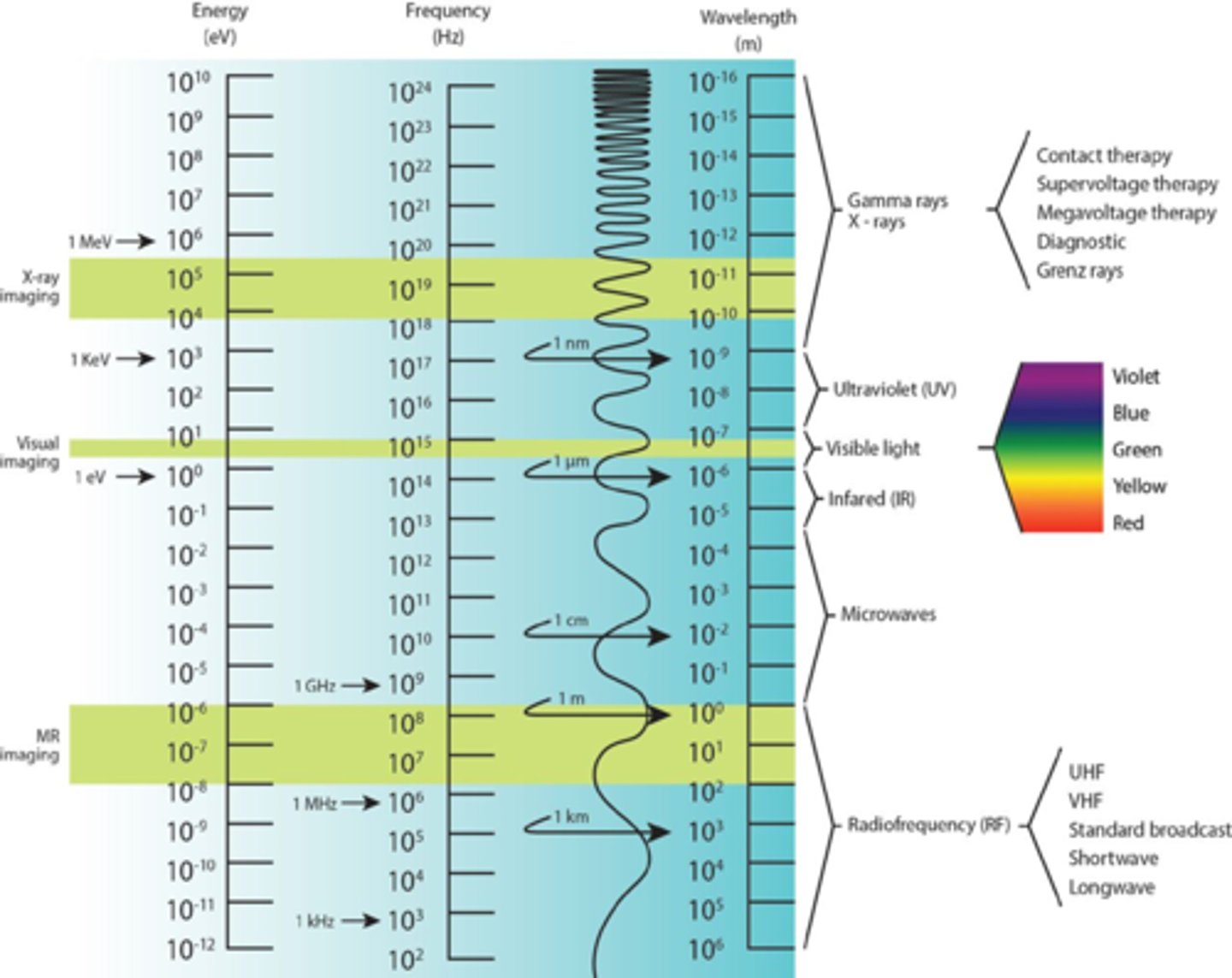
Basic Concepts of Electromagnetic spectrum
1. Energy (eV)
2. Frequency (Hz)
3. Wavelength (λ)
Electromagnetic Spectrum
lA method of transporting energy through space
lMay be waves
lMay be particles of energy called photons
lRadiography deals with EM waves
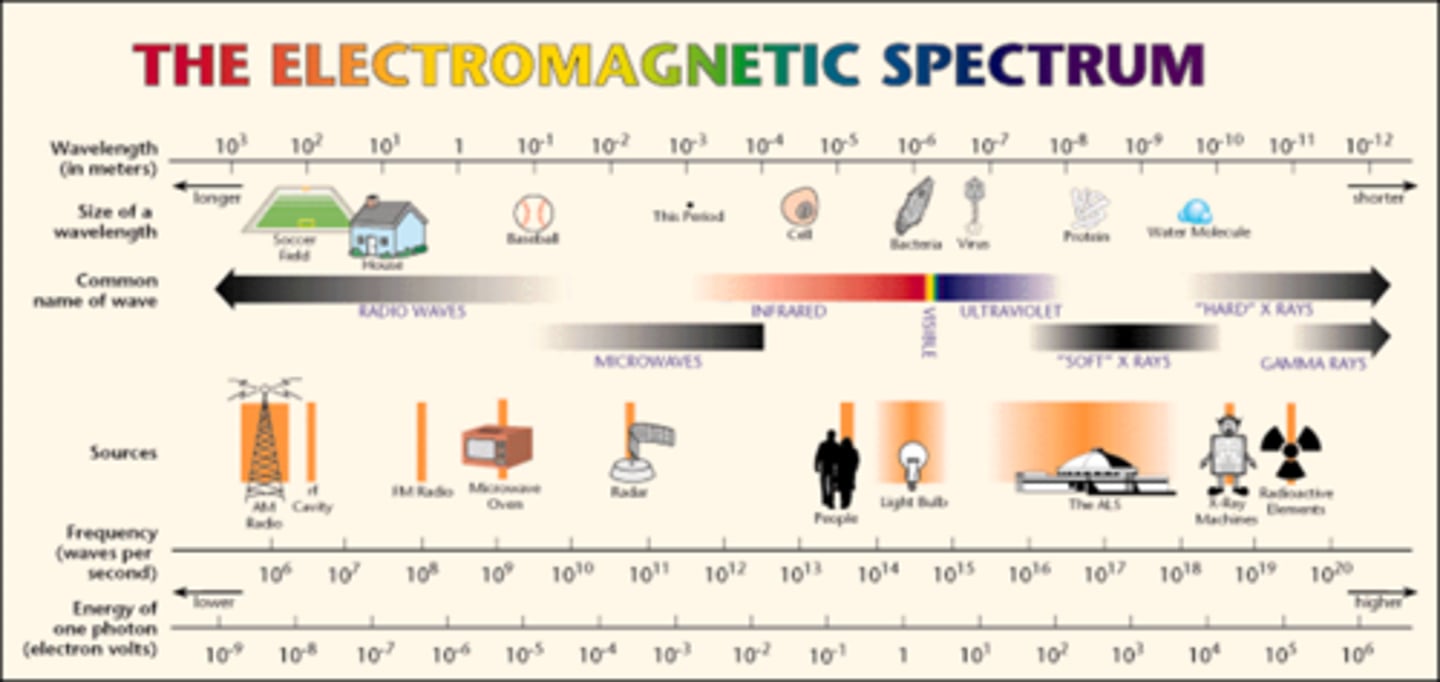
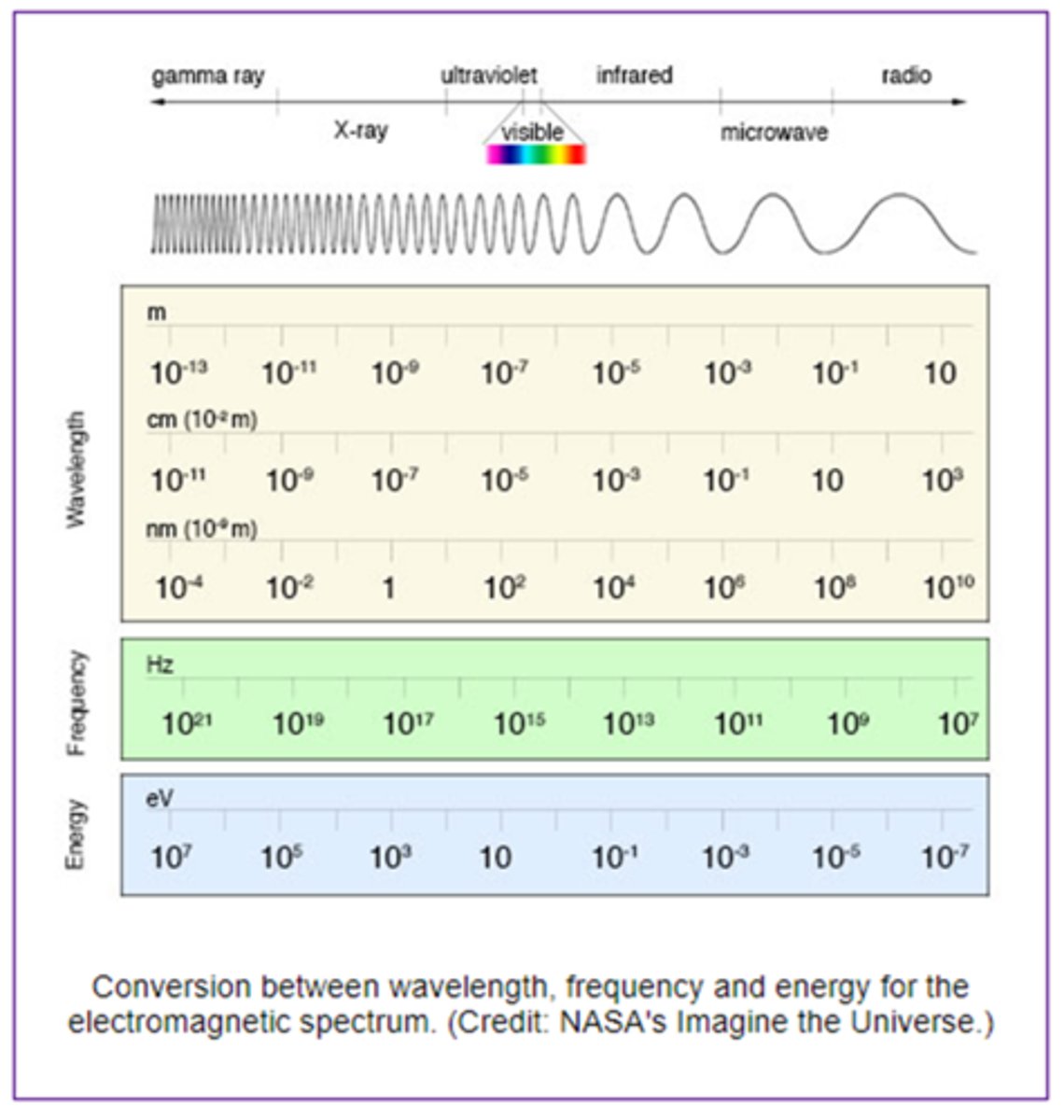
The Electromagnetic Spectrum
- Energy of the waves is arranged from high to low
- Highest = gamma
- Lowest = radiowaves
- Visible light is one small portion of the EM spectrum
Radiography
- Radiology is the study of electromagnetic radiation
- Radiography is the utilization of x-rays to produce photographic images
Image of electromagnetic spectrum
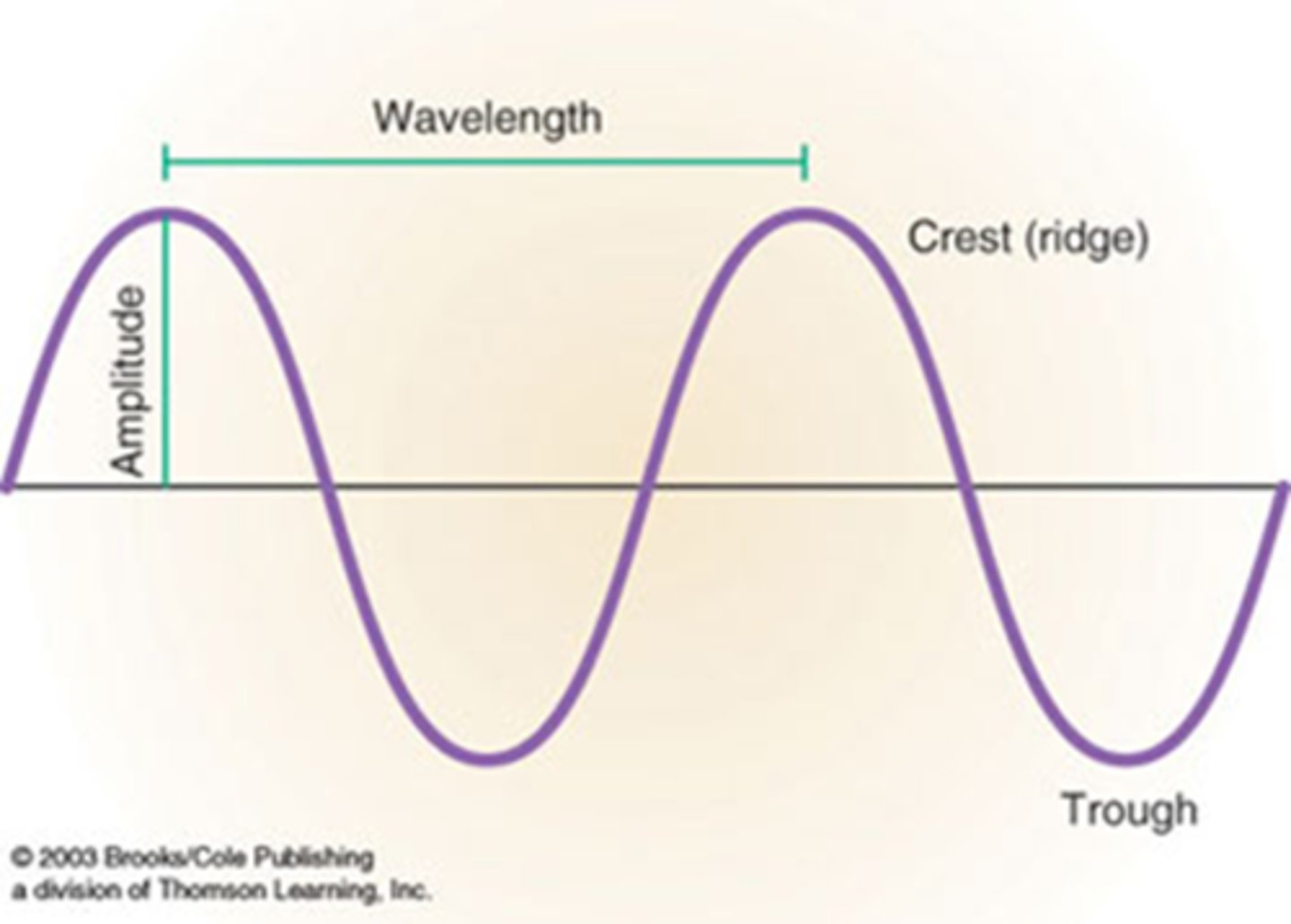
Wave Theory
- The height of a wave is called amplitude
- The highest point is called the crest
- The lowest point is called the trough
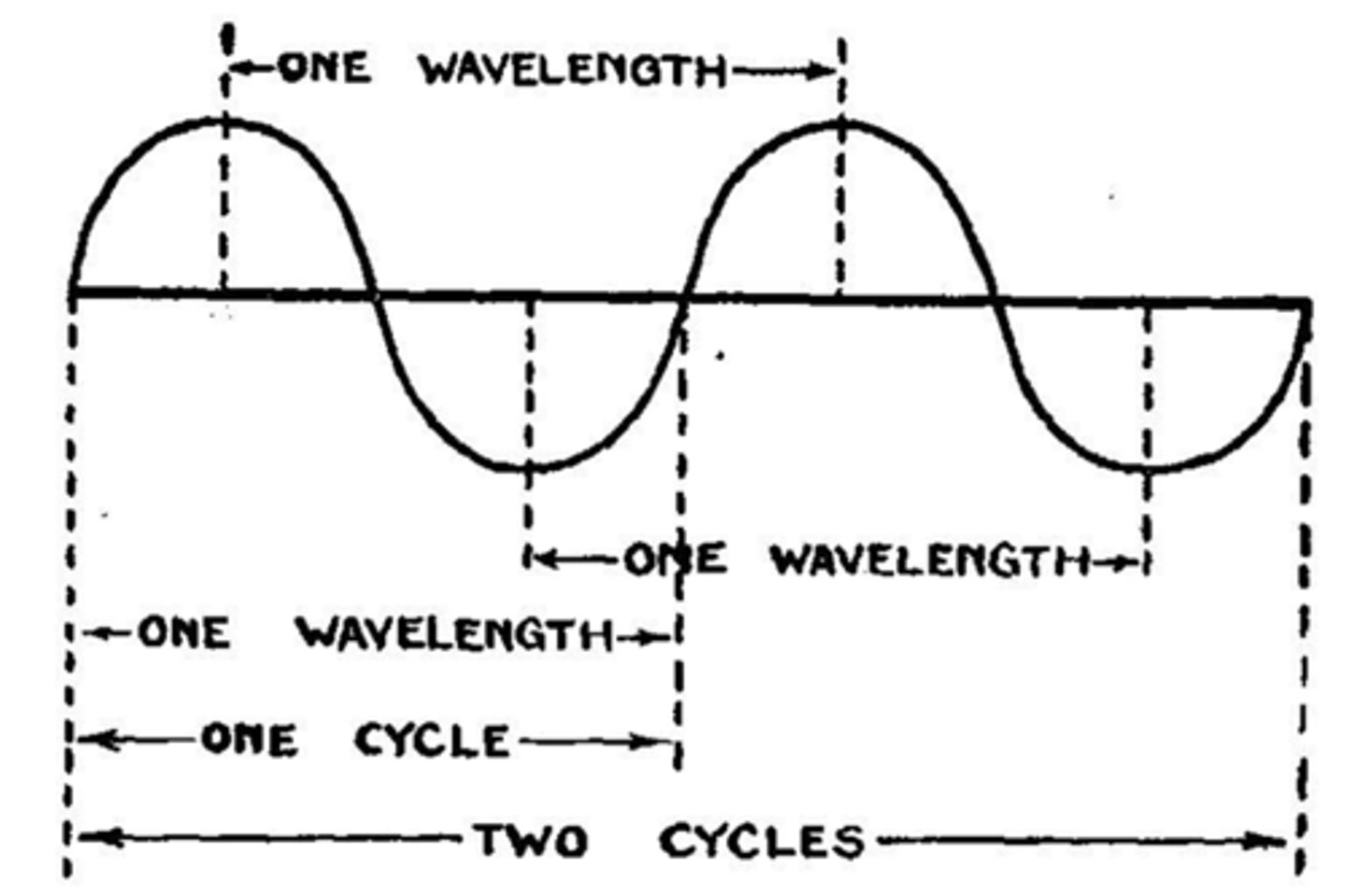
- The distance from one crest to another is called wavelength
Wave Theory: Frequency
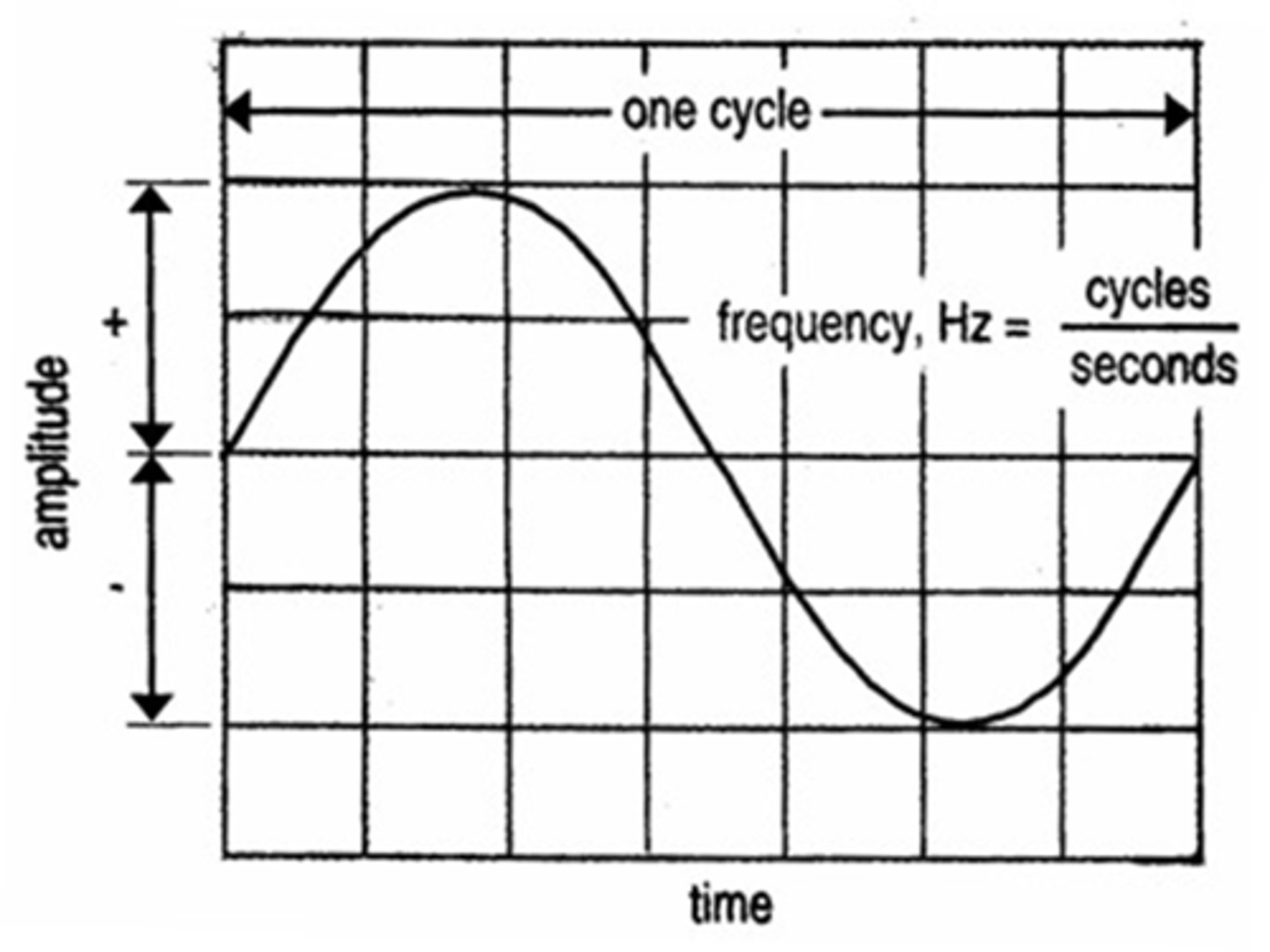
- Frequency is how often a wave occurs in a given time period
- The length of time one wave takes is called a cycle
- Eg 60 cycles/second
The symbol for frequency is Hertz (Hz)
60 cycles/sec = 60 Hz
The Relationship: The longer the wavelength the
lower the frequency the lower the energy
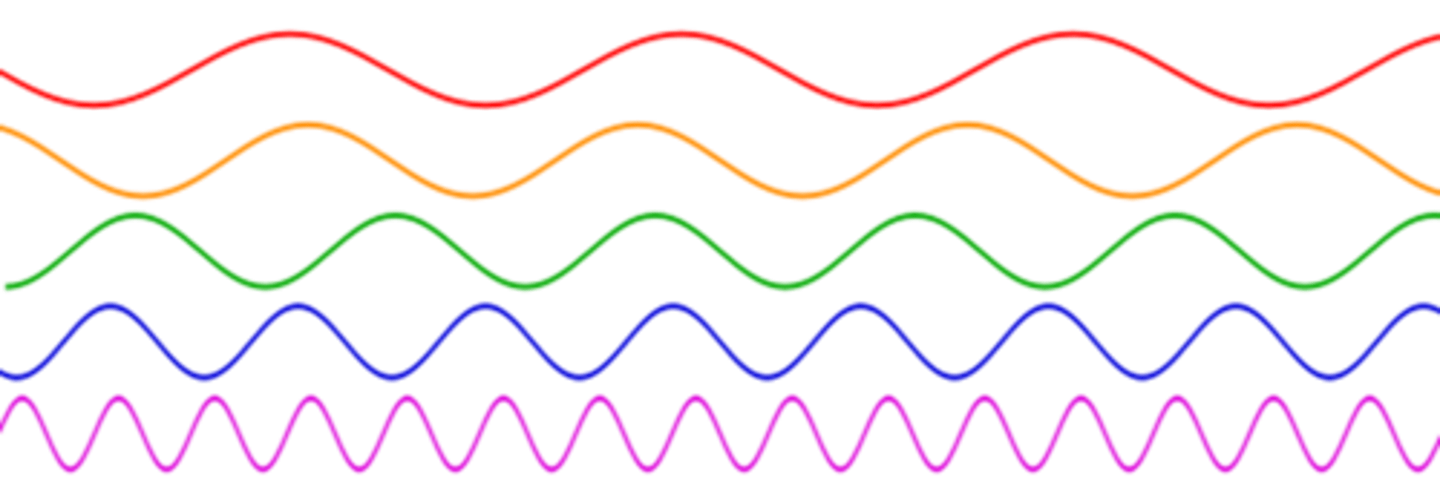
The relationship: The shorter the wavelength the
higher the frequency the higher the energy
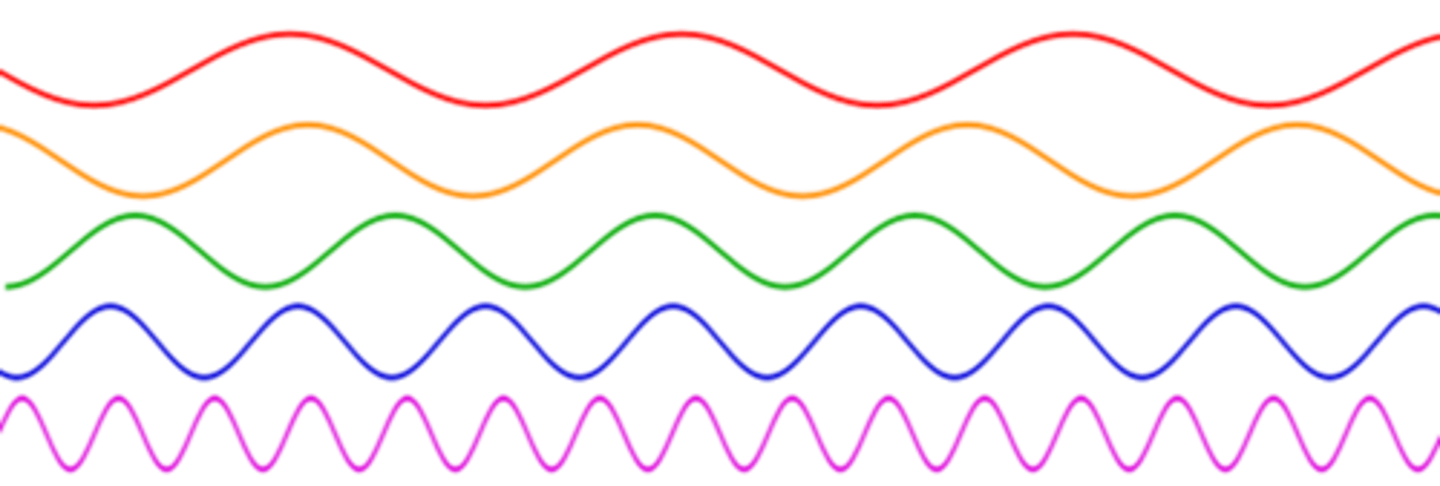
Energy, Frequency and Wavelength
The lower the frequency →the lower the energy →the lower the penetration
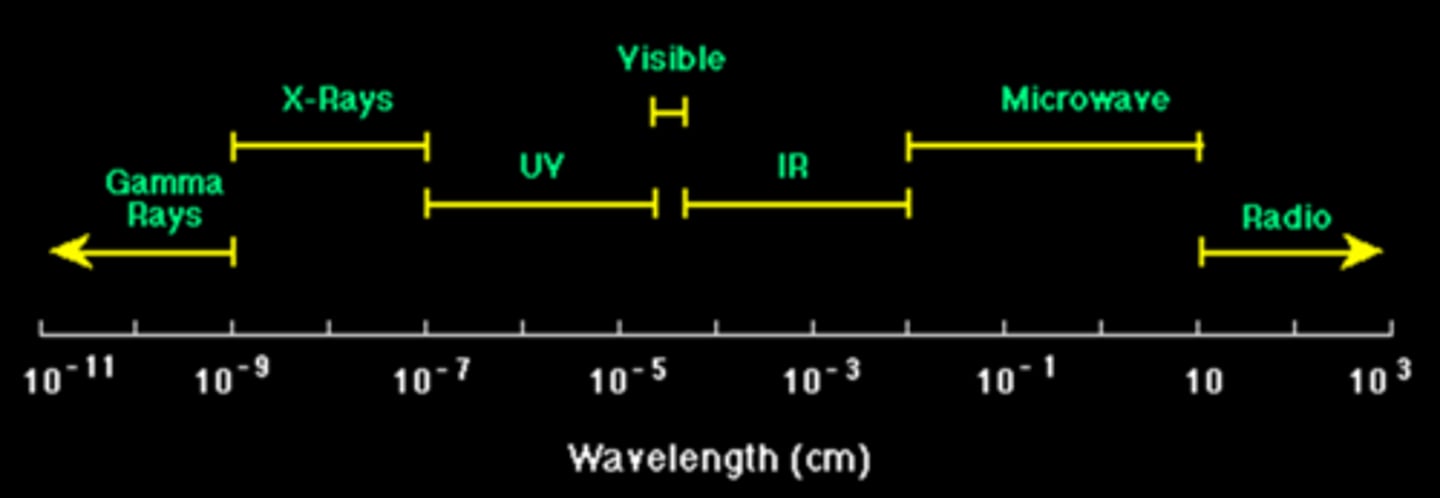
Conversion between wavelength, frequency, and energy for the electromagnetic spectrum (image)
Radiography and Wavelength:
X-rays are short wavelength, high energy waves
Wavelength for x rays
0.03-3.0 nanometer wavelength
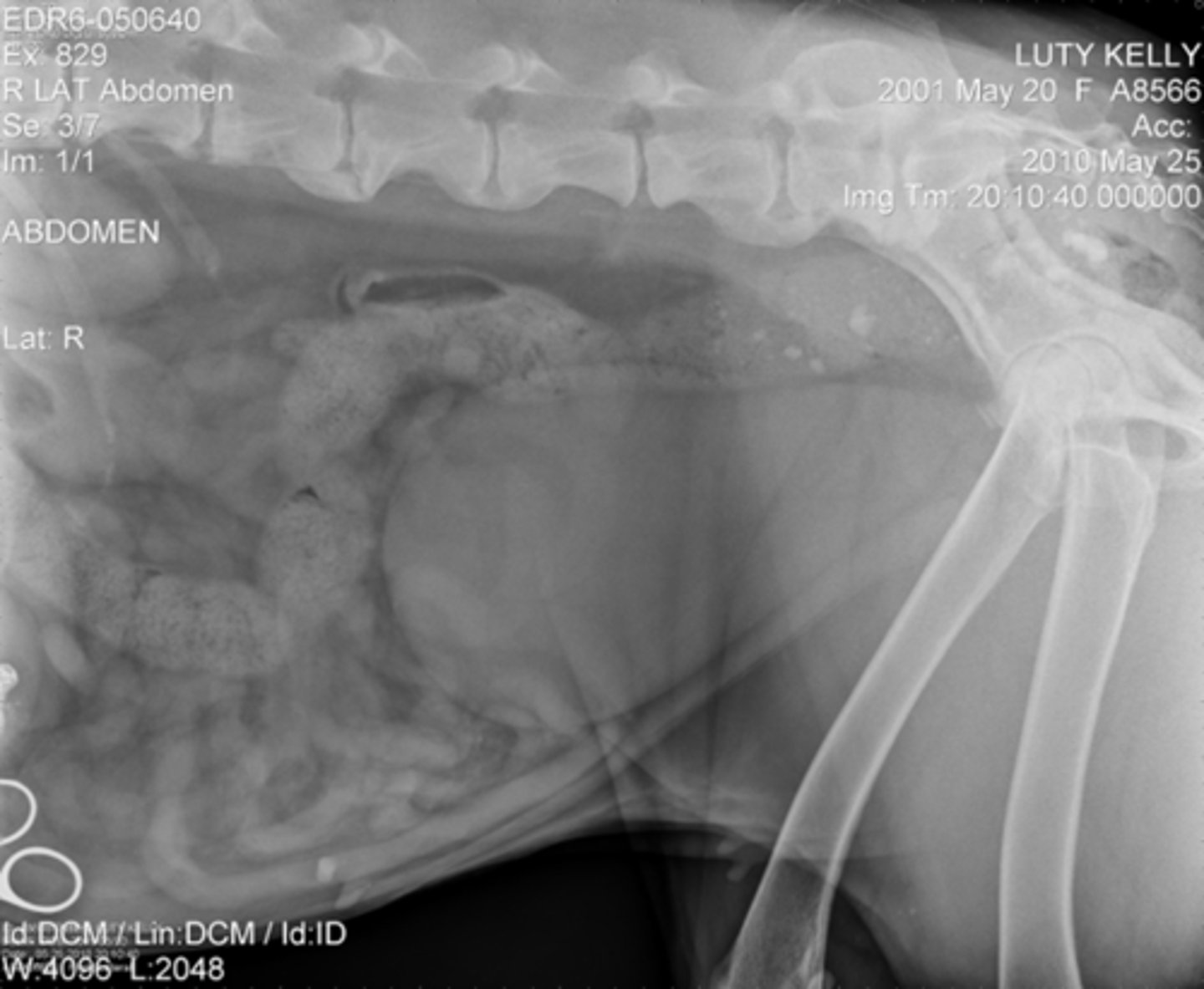
X-rays penetrate
tissue to produce an image on film
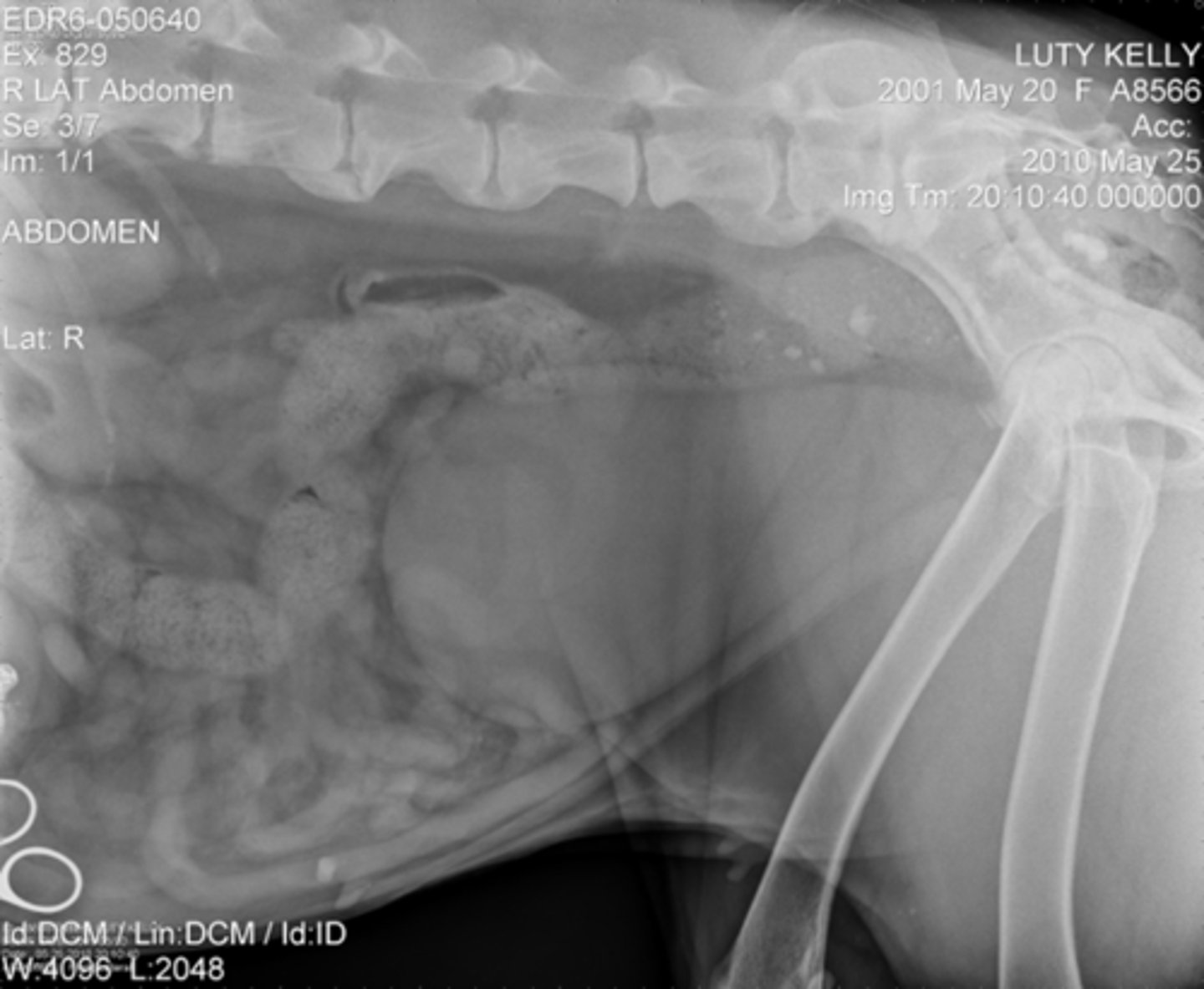
The energy of the x-ray controls the
type of tissue it can penetrate and the depth of penetration
How Roentgen's properties of x-rays are there?
12
First property of x-rays
Highly penetrating invisible rays that form electromagnetic radiation
Second property of x-rays
Electrically neutral
Third property of x-rays
Produce wide variety of energies and wavelengths
Fourth property of x-rays
Release small amount of heat as they pass through matter
Fifth property of x-rays
Travel in straight lines
Sixth property of x-rays
Travel at speed of light in a vacuum
Seventh property of x-rays
Ionize matter
Eighth property of x-rays
Fluorescence of specific crystals
Ninth property of x-rays
Not focused by lens
Tenth property of x-rays
Affects photographic film
Eleventh property of x-rays
Chemical/biological changes in matter due to ionization and excitation
Twelfth property of x-rays
Produce secondary and scatter radiation
Roentgens properties of x rays (1-3)
invisible penetrating form of electromagnetic radiation, are not affected by magnetic or electrical fields, and can have a wide variety of energies and wavelengths
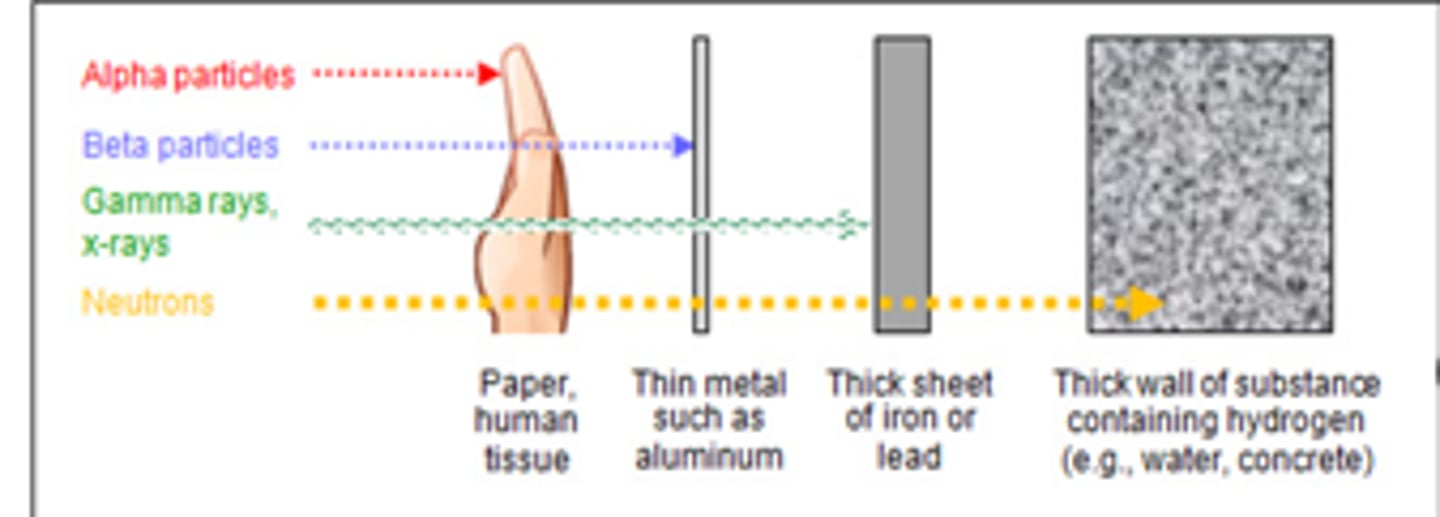
Roentgens properties of x rays (4-7)
release small amounts of heat when passing through matter, travel in straight lines, travel at the speed of light, and can ionize matter
Roentgens properties of x rays (8-10)
cause fluorescence, cannot be focused, and affect photographic film
Roentgens properties of x rays (10-12)
Produce chemical and biological changes in matter and produce secondary and scatter radiation

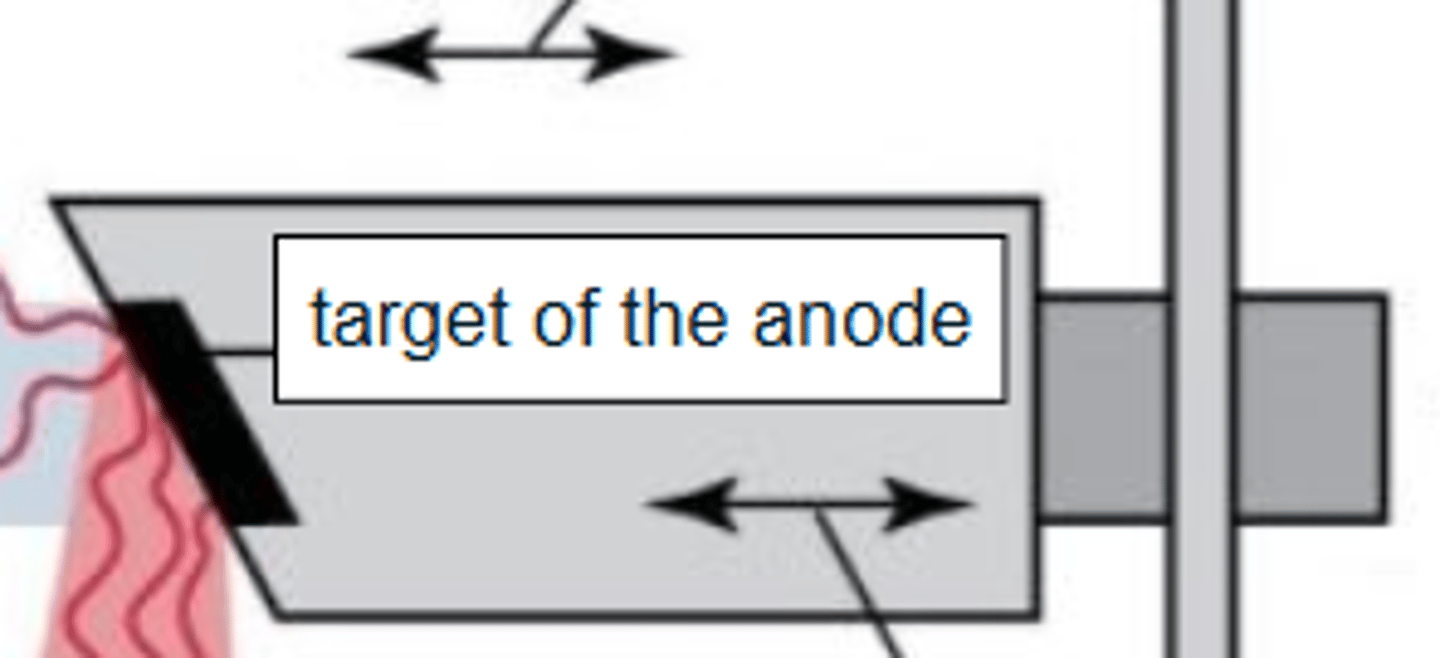
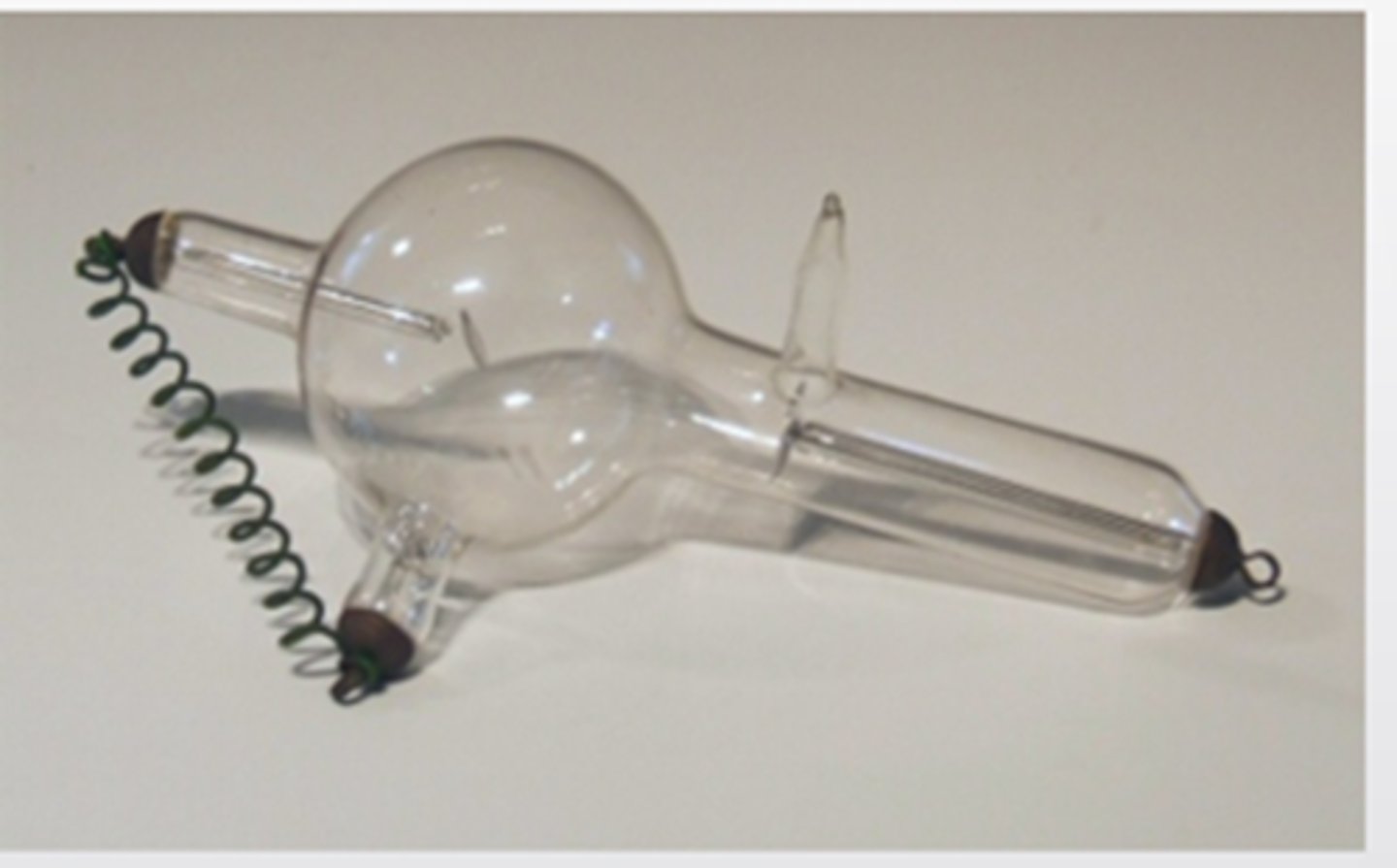
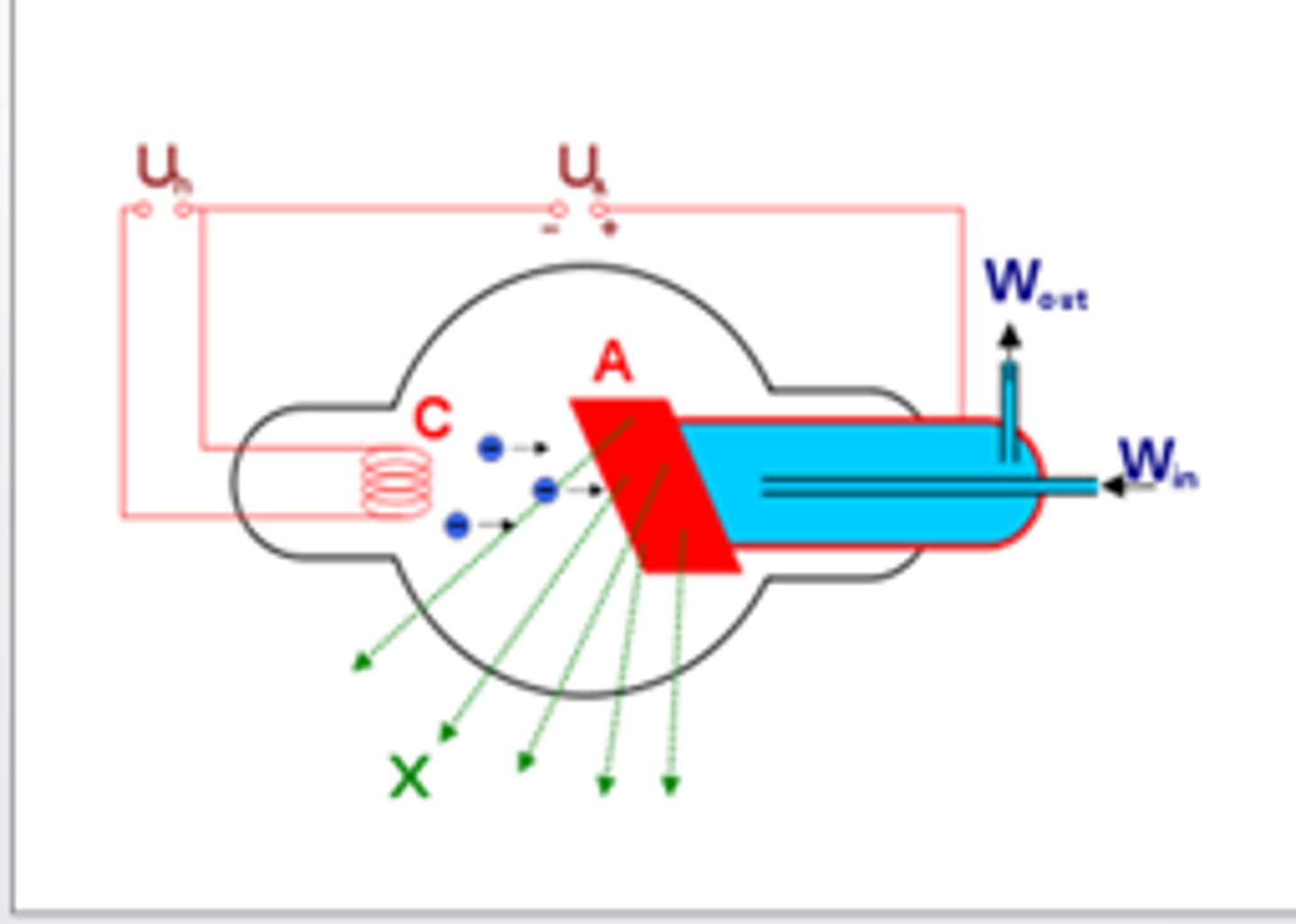
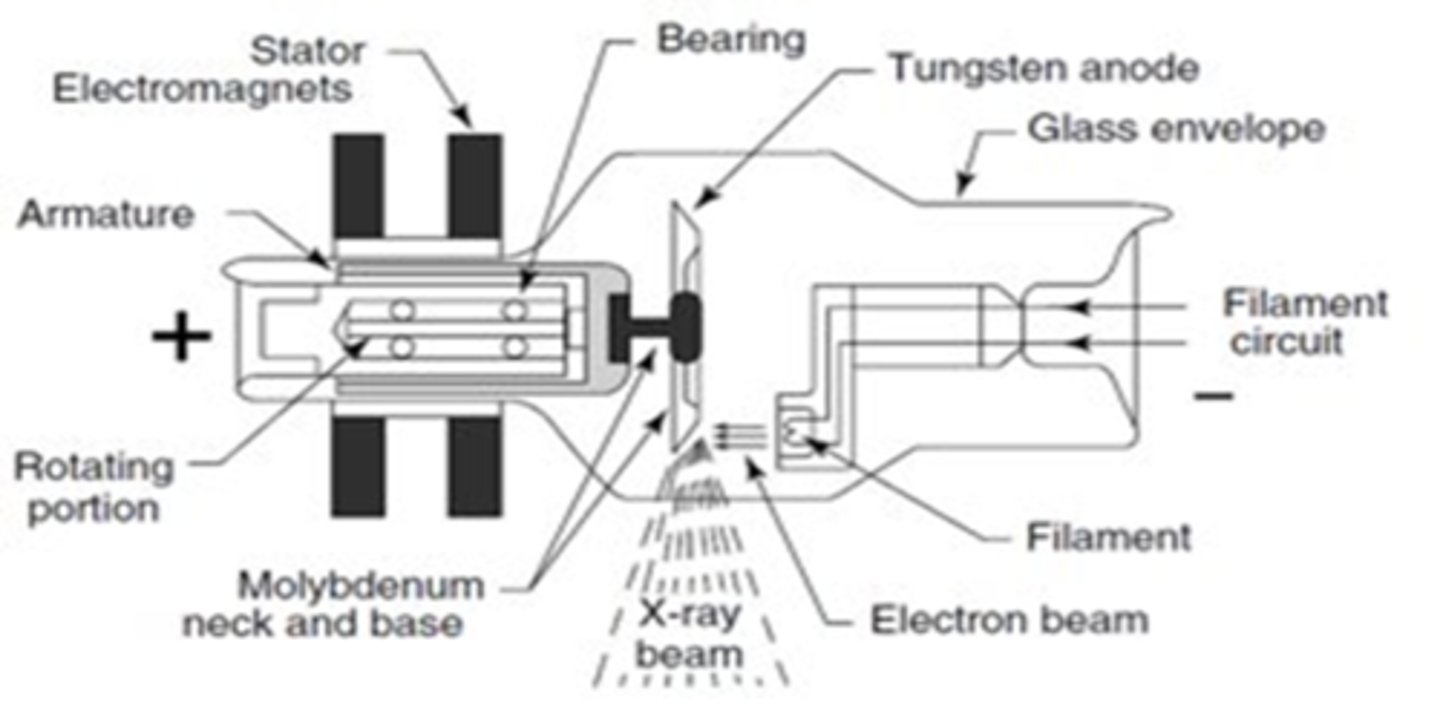
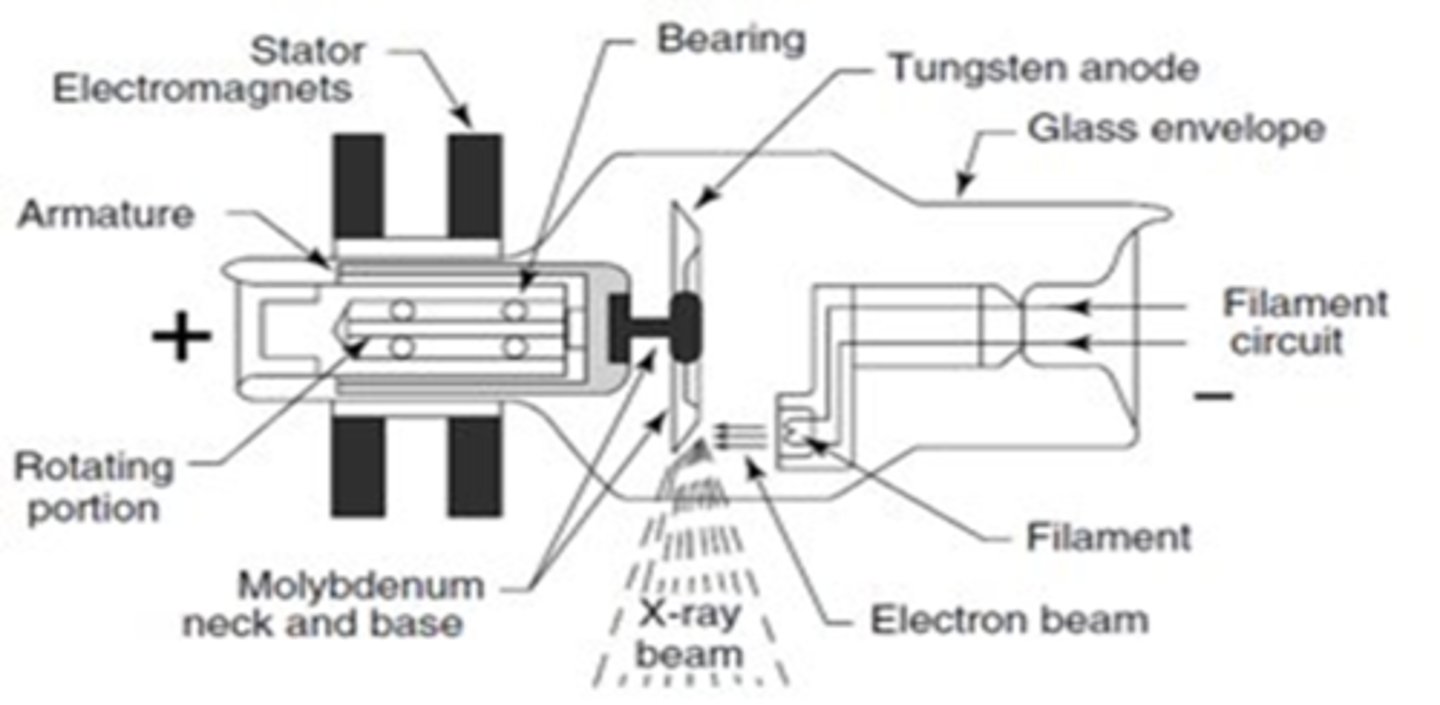
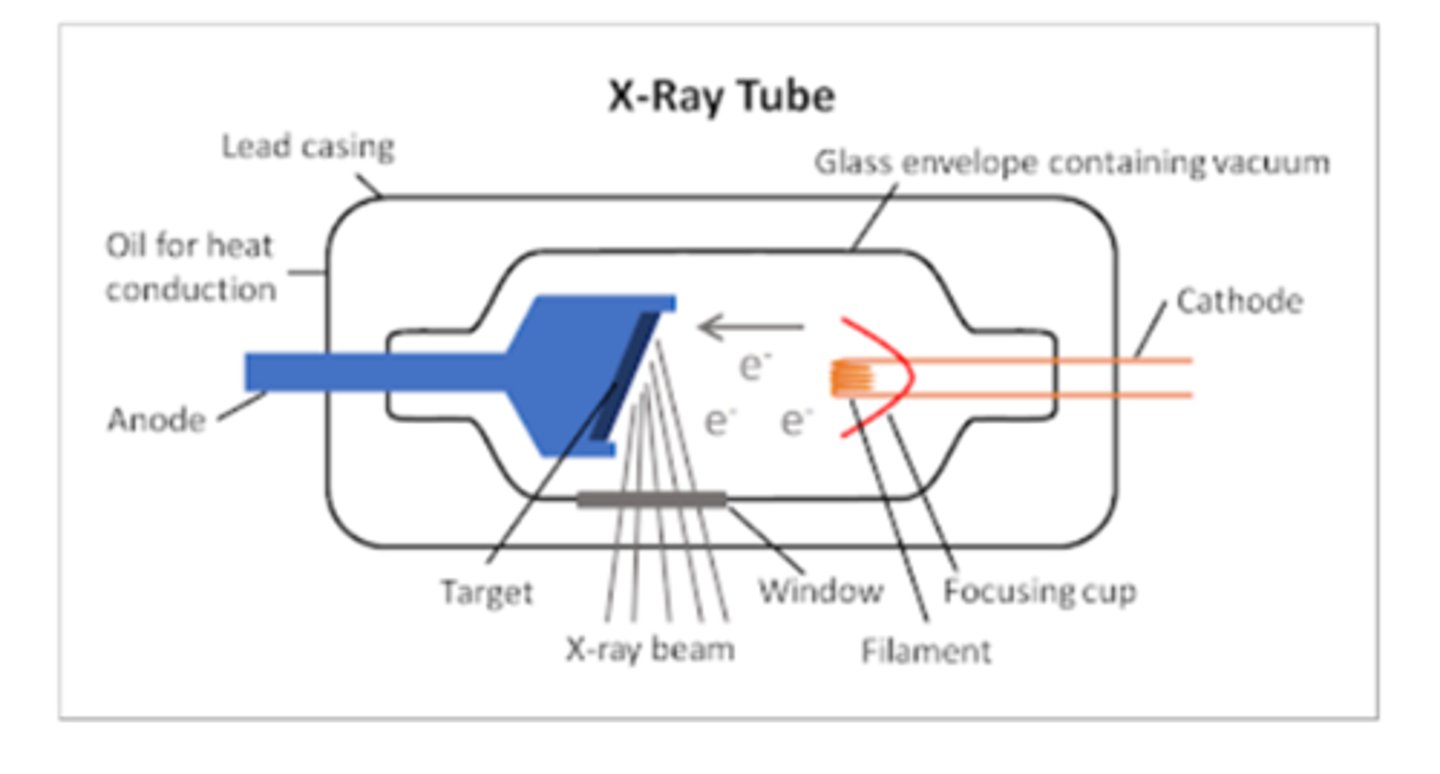
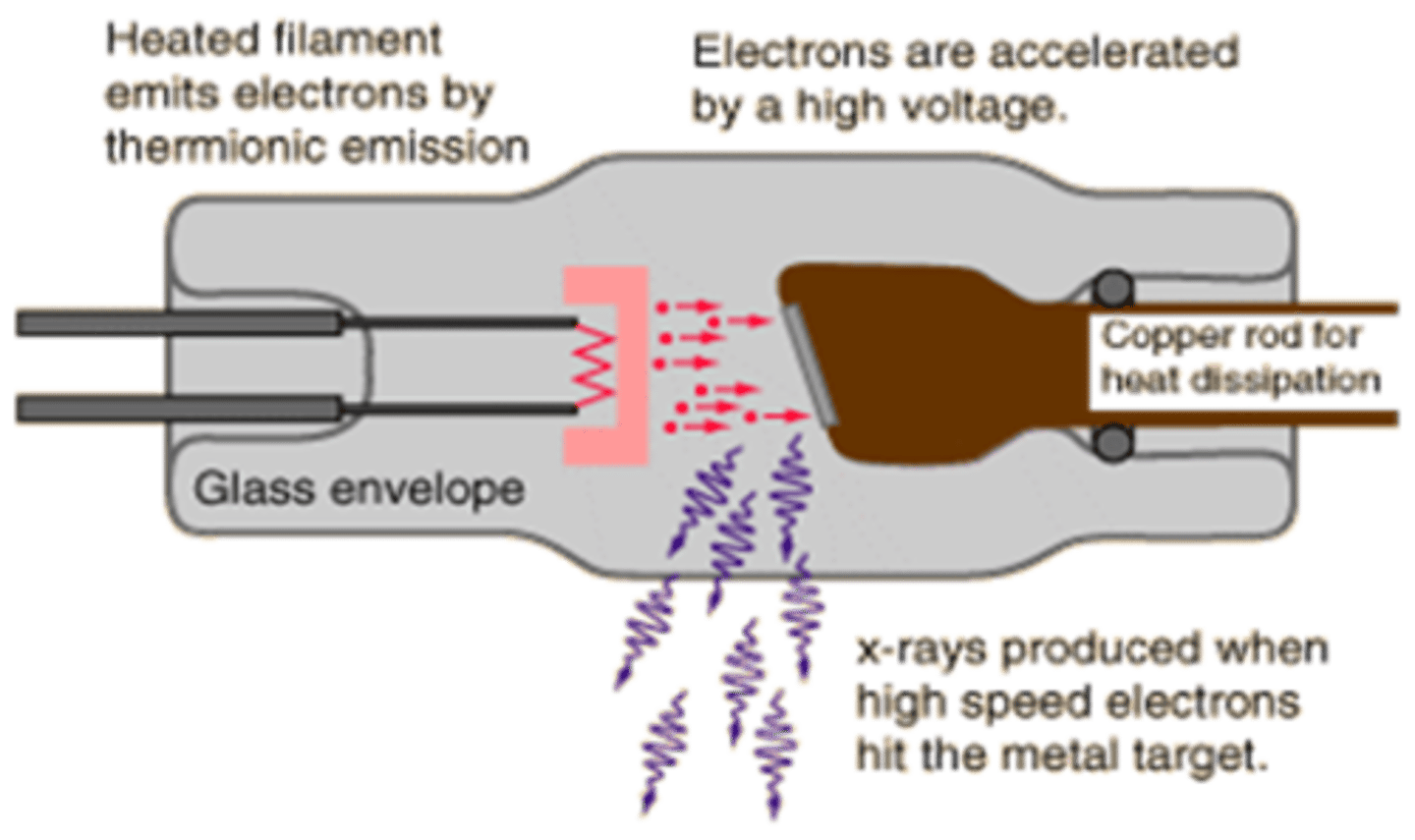
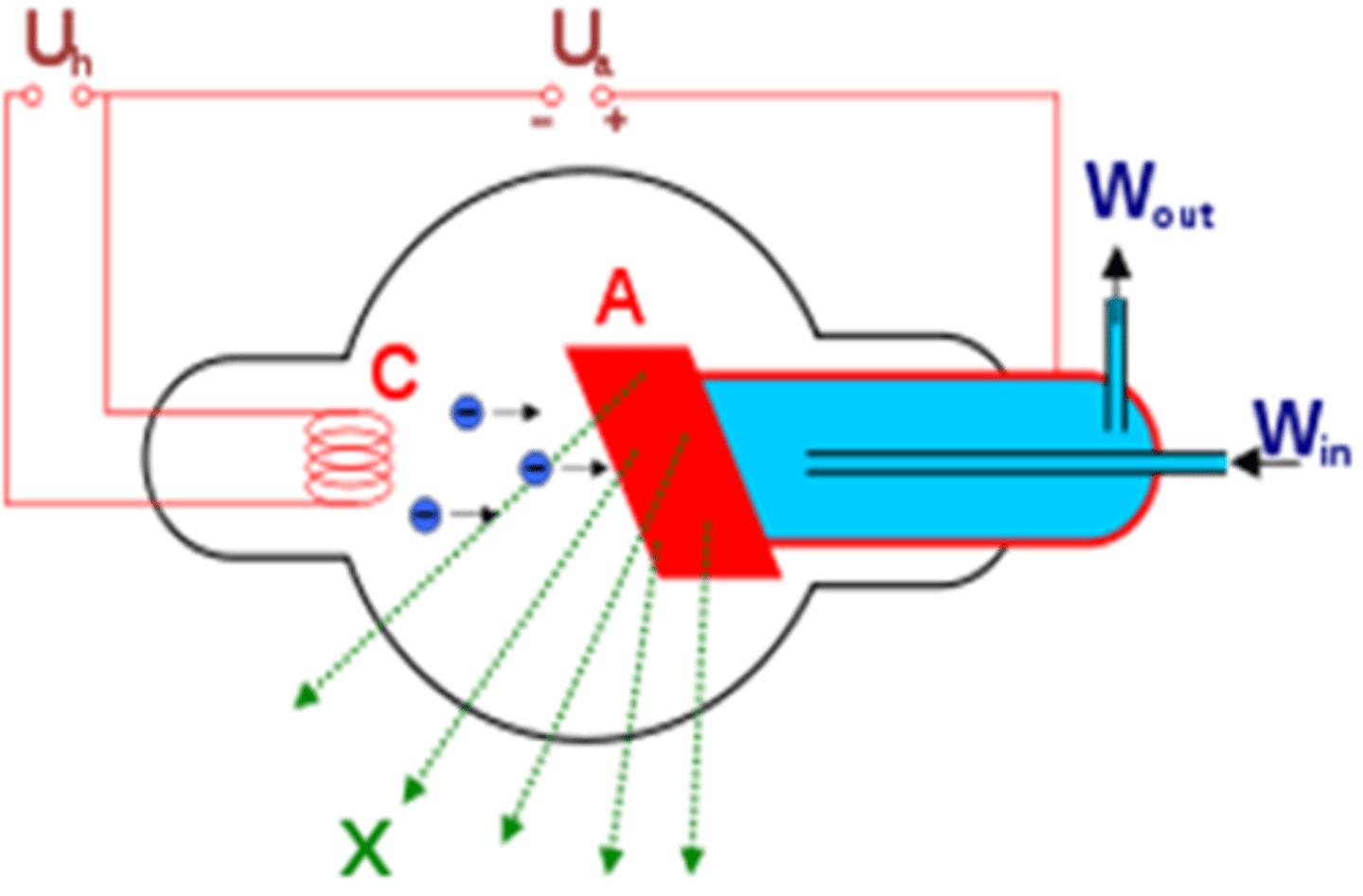
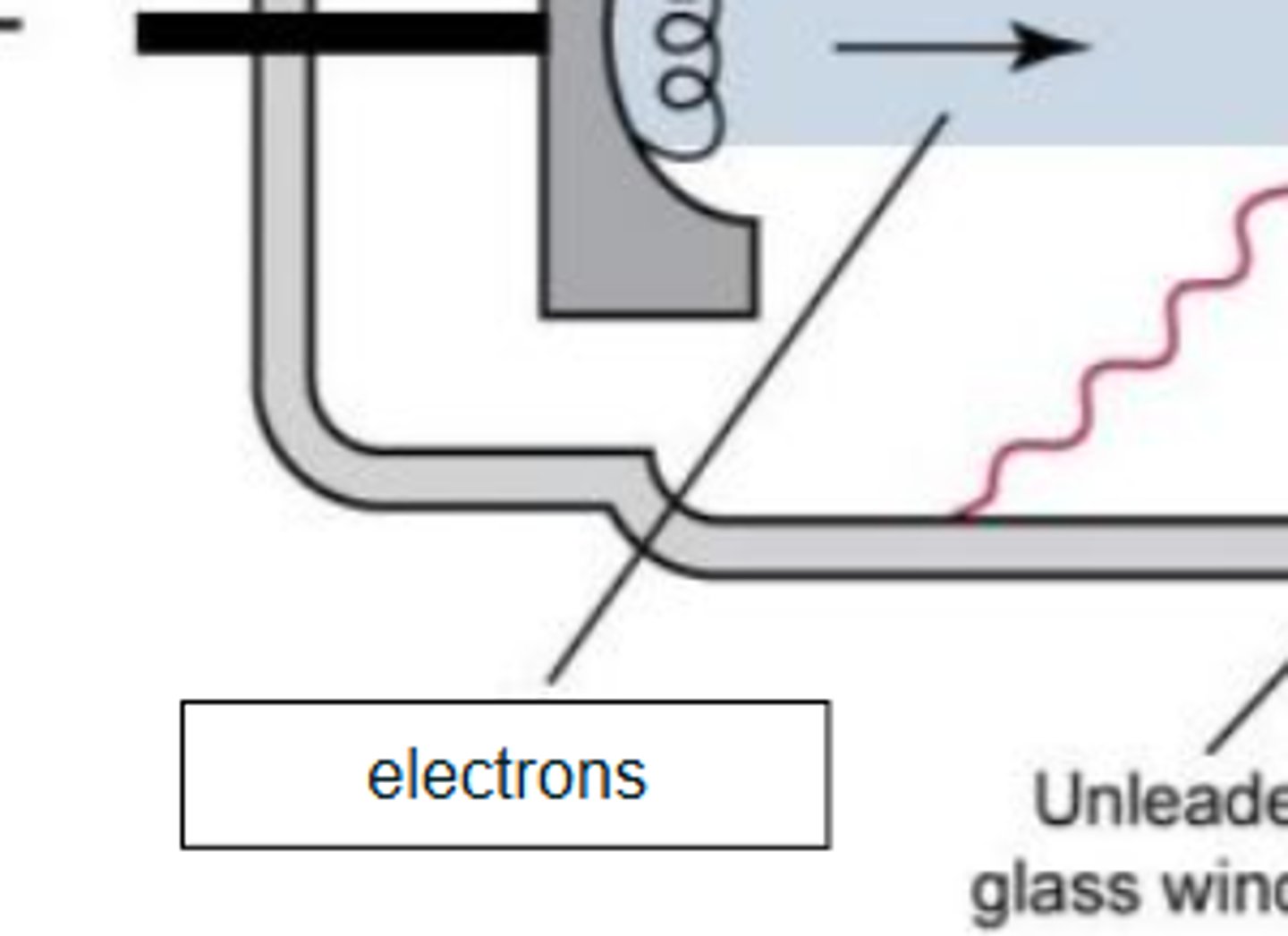
X-Ray Tube Anatomy includes
- Cathode
- Anode
- Glass enclosure
- Tabletop
- Transformer and rectifiers

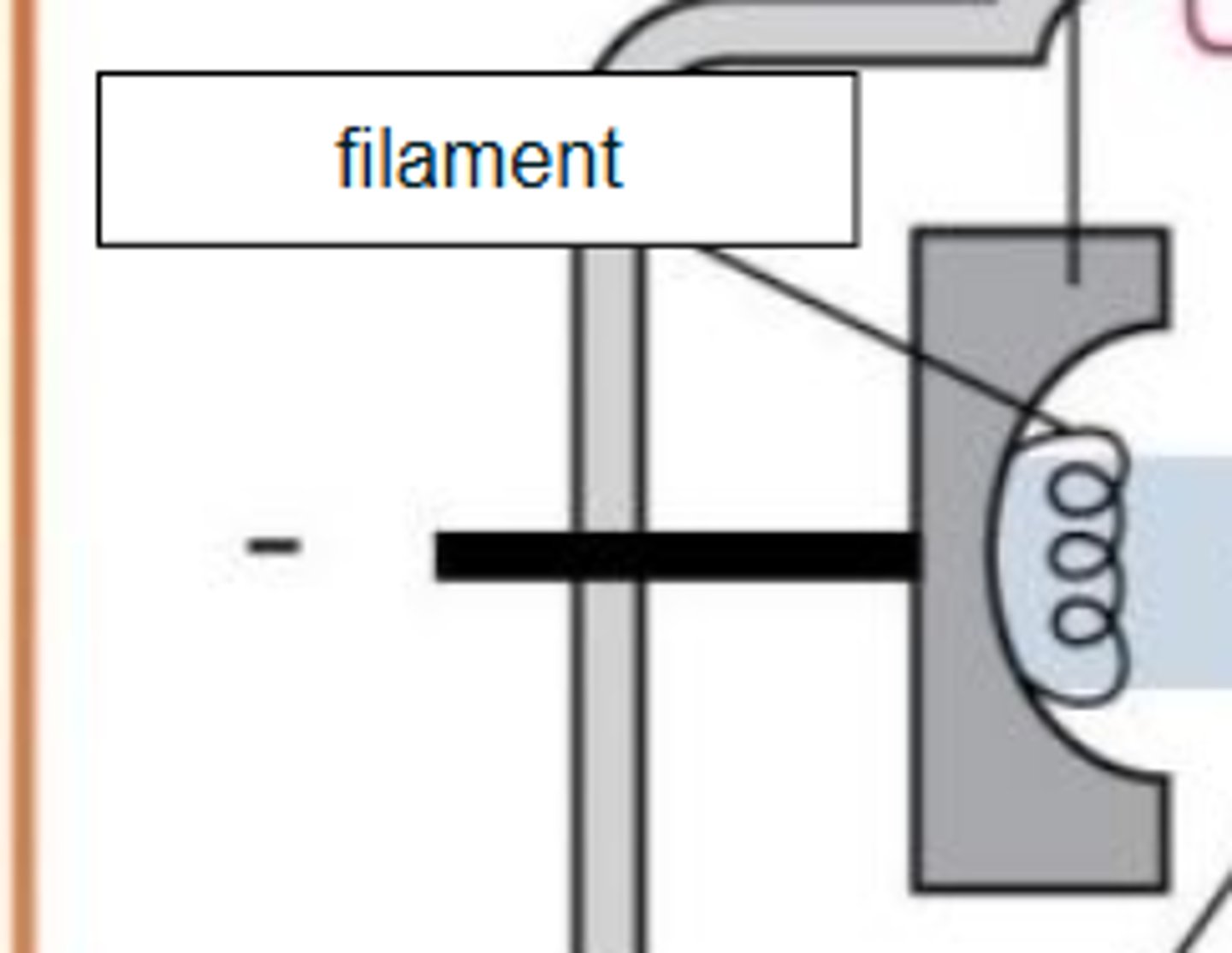
Cathode characteristics
- filament heats up
- electrons "boiled" off (thermionic emission and "space charge)
- focusing cup sends electrons towards target on anode
- electrons repelled by negative charged cathode
Cathode usually have two filaments
- 100 mA (small focus)
- 300 mA (large focus)
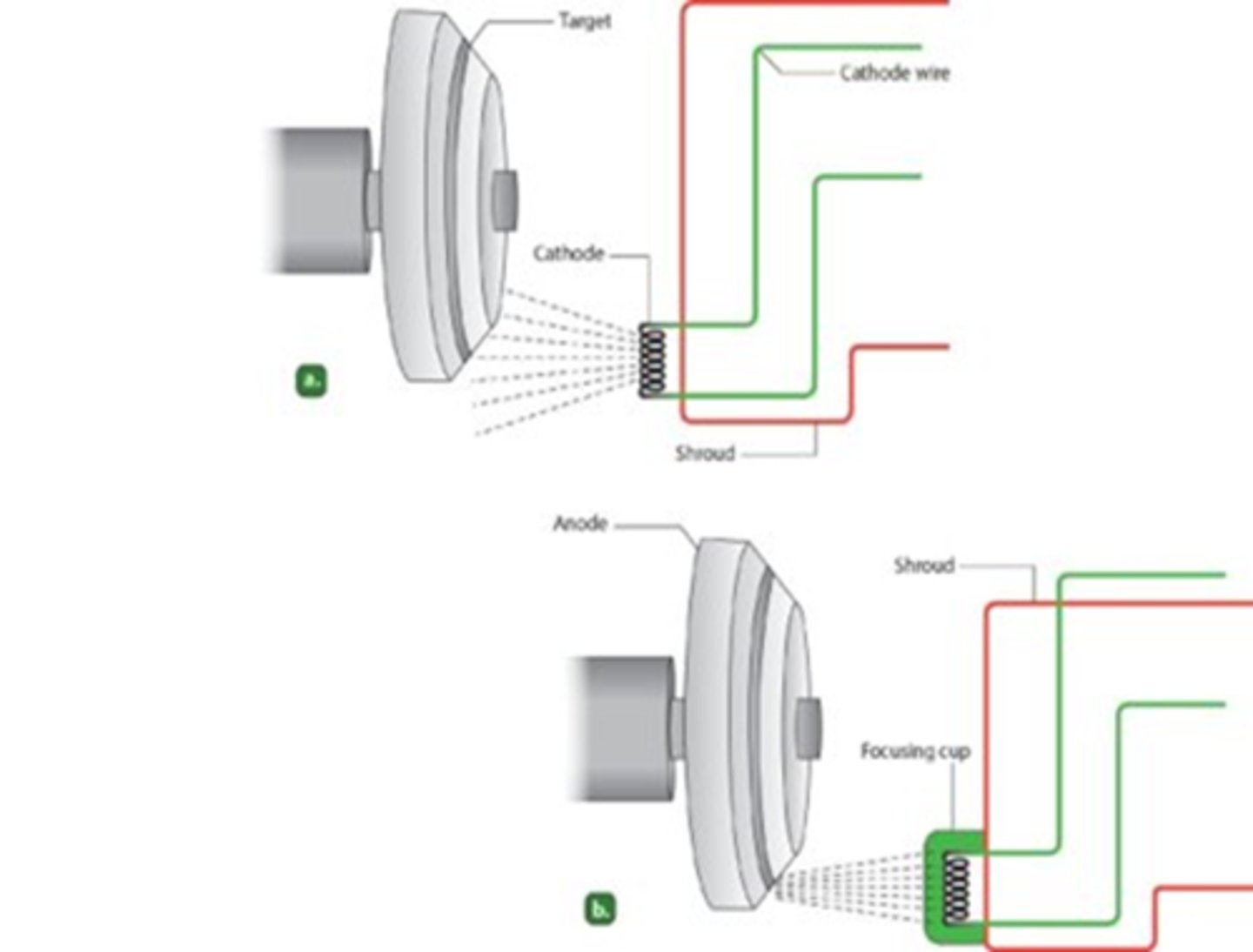
For the cathode, operator can select
which filament to use
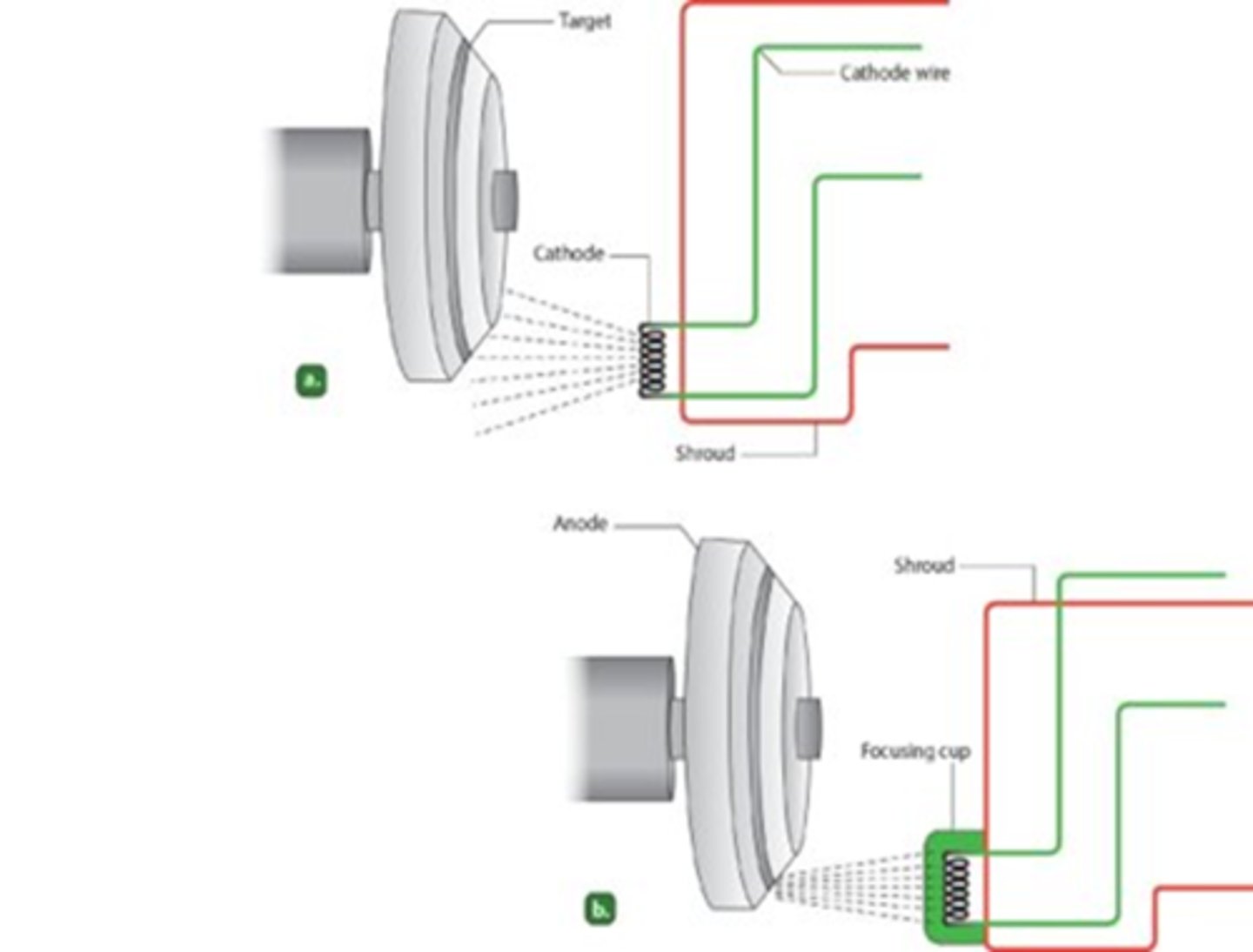
Cathode with more power/electrons from the 300 mA filament→
more x-rays
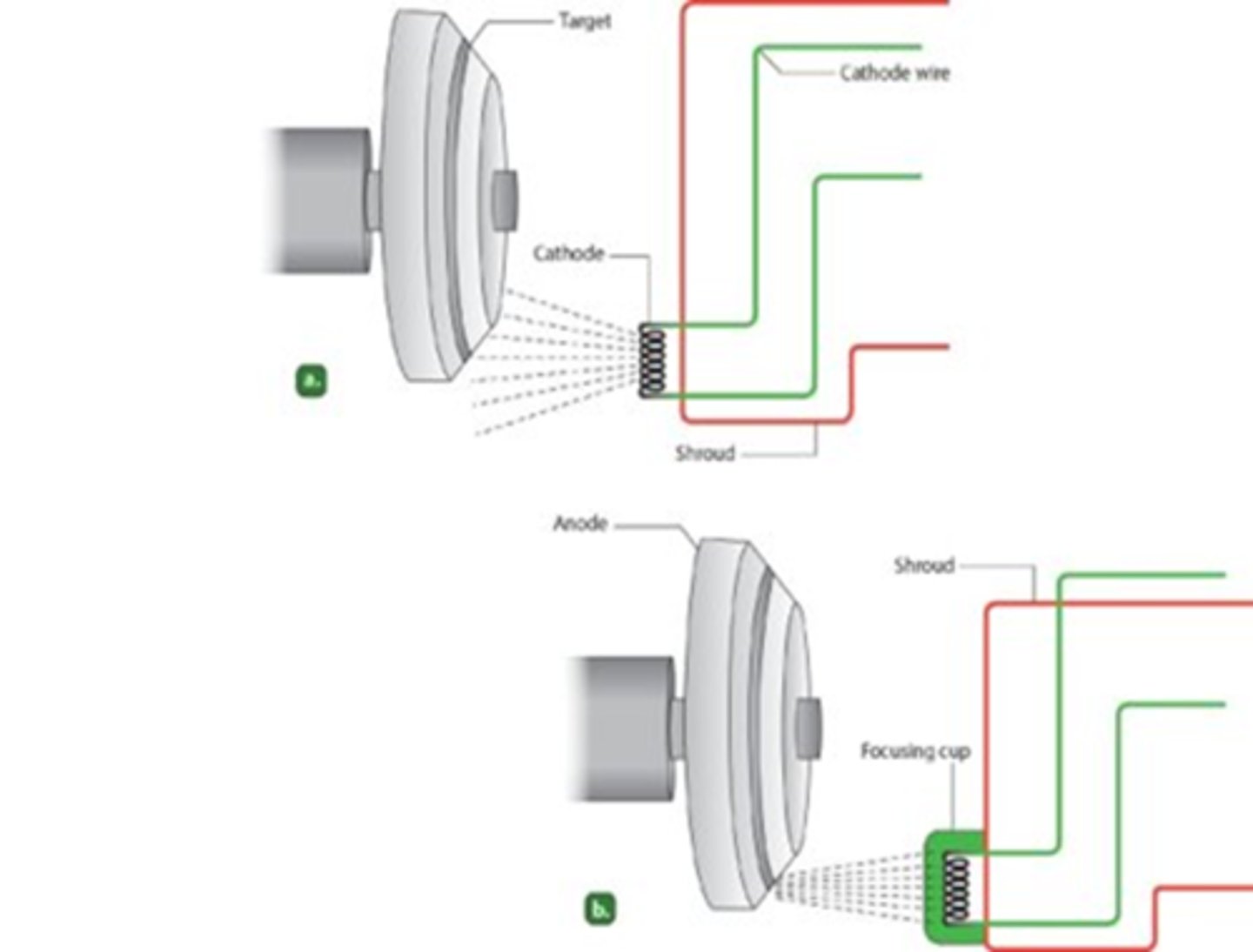
Cathode Filaments are located in focusing cup
- Electrons released in straight pattern
- If there is no focusing cup it results in poor radiograph
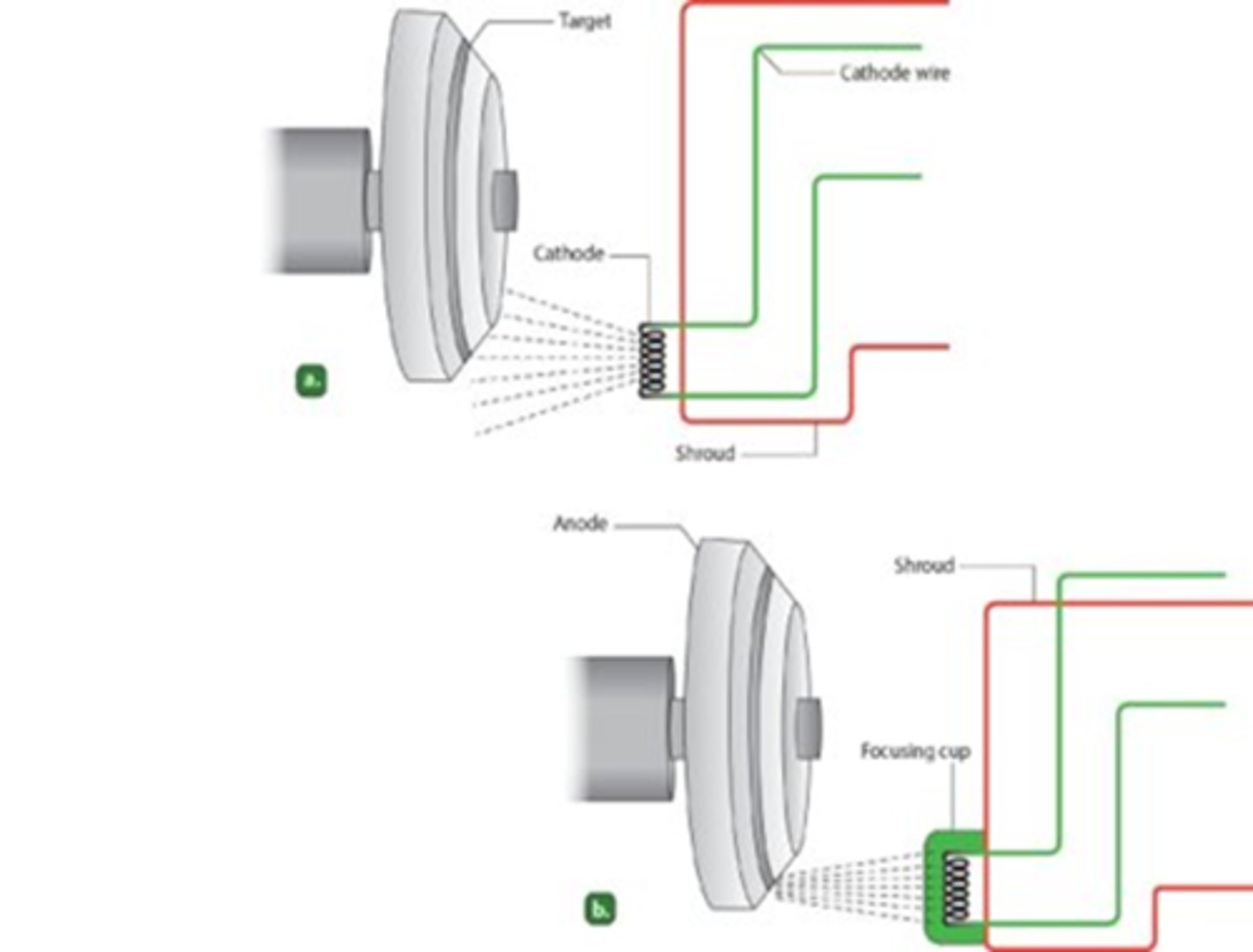
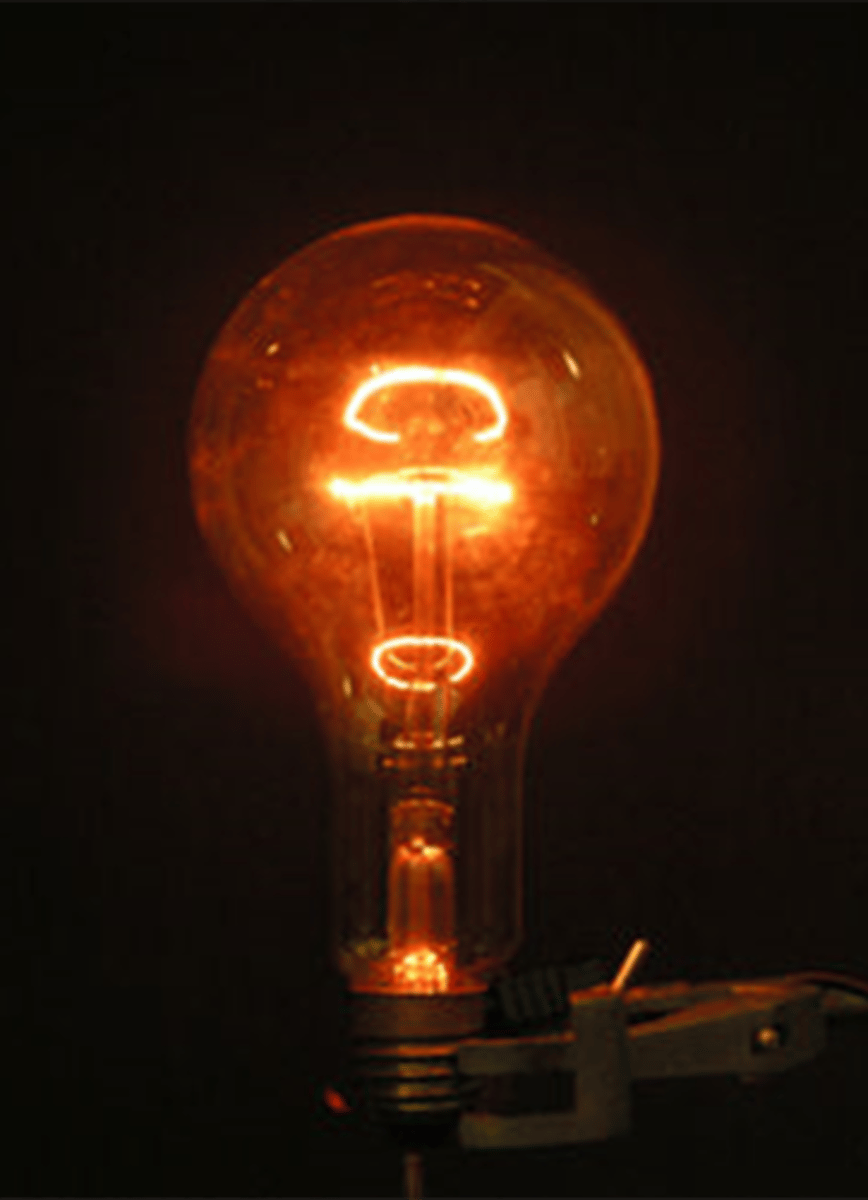
Cathode Filaments similar to light bulb filaments
- Made of thoriated tungsten
- 1%= electrons
- 99%= heat and light

The milliamp rating (300 or 100 mA) controls the number of electrons produced by the
Cathode
300 > 100
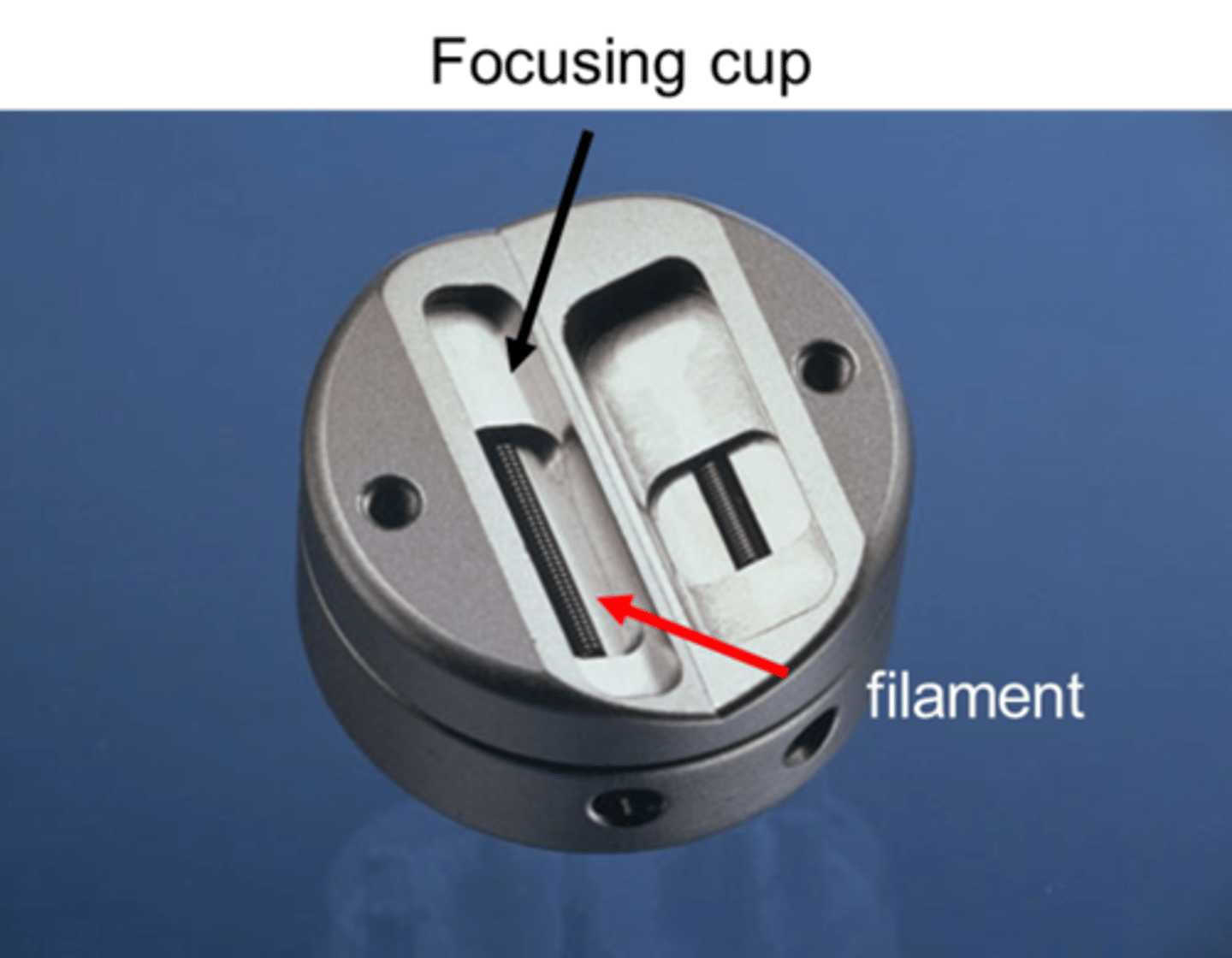
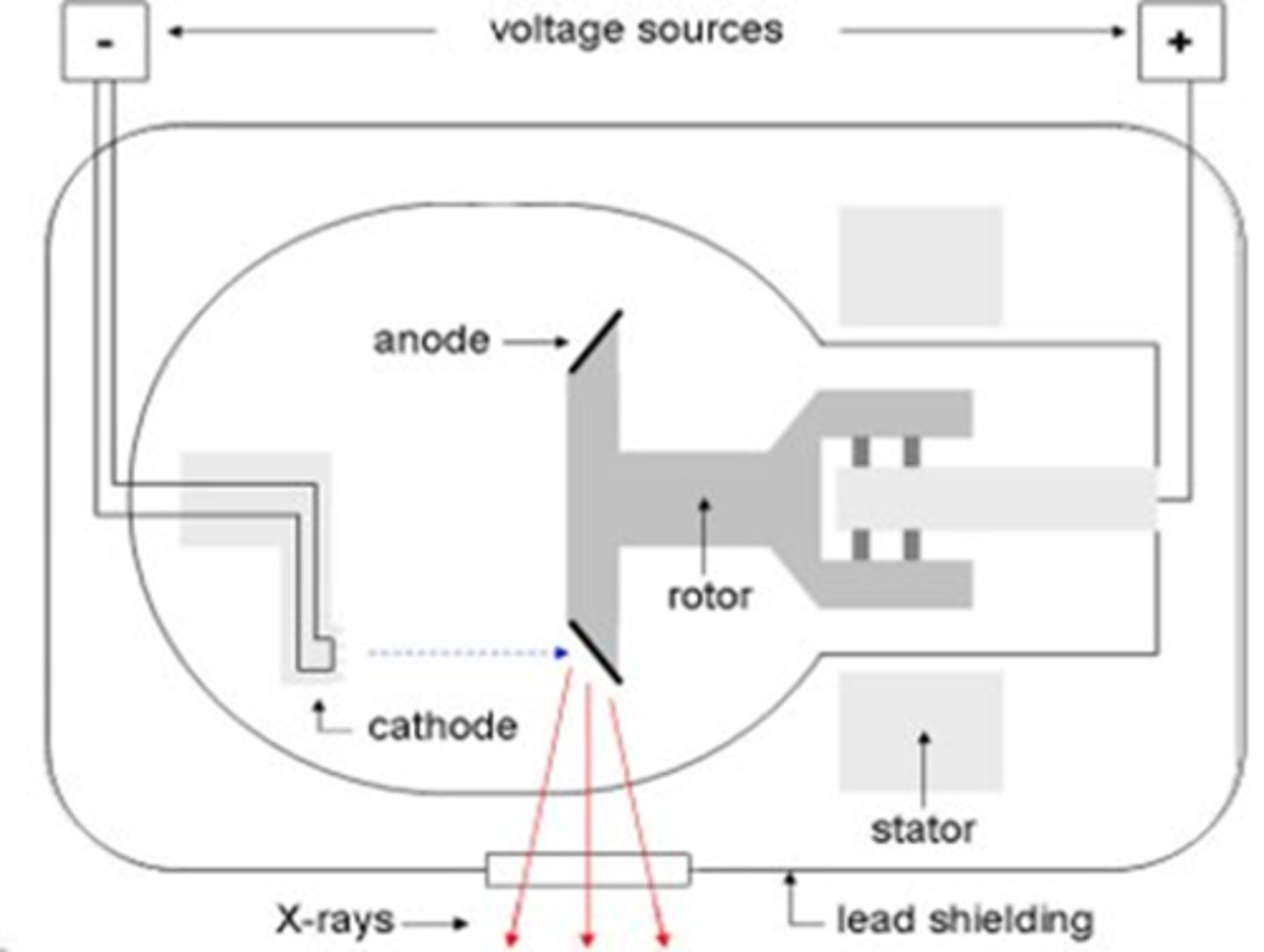
Anode characteristics
- Positively charged
- Electrons attracted to positive charge
- 2 types of Anodes: Rotating and Stationary
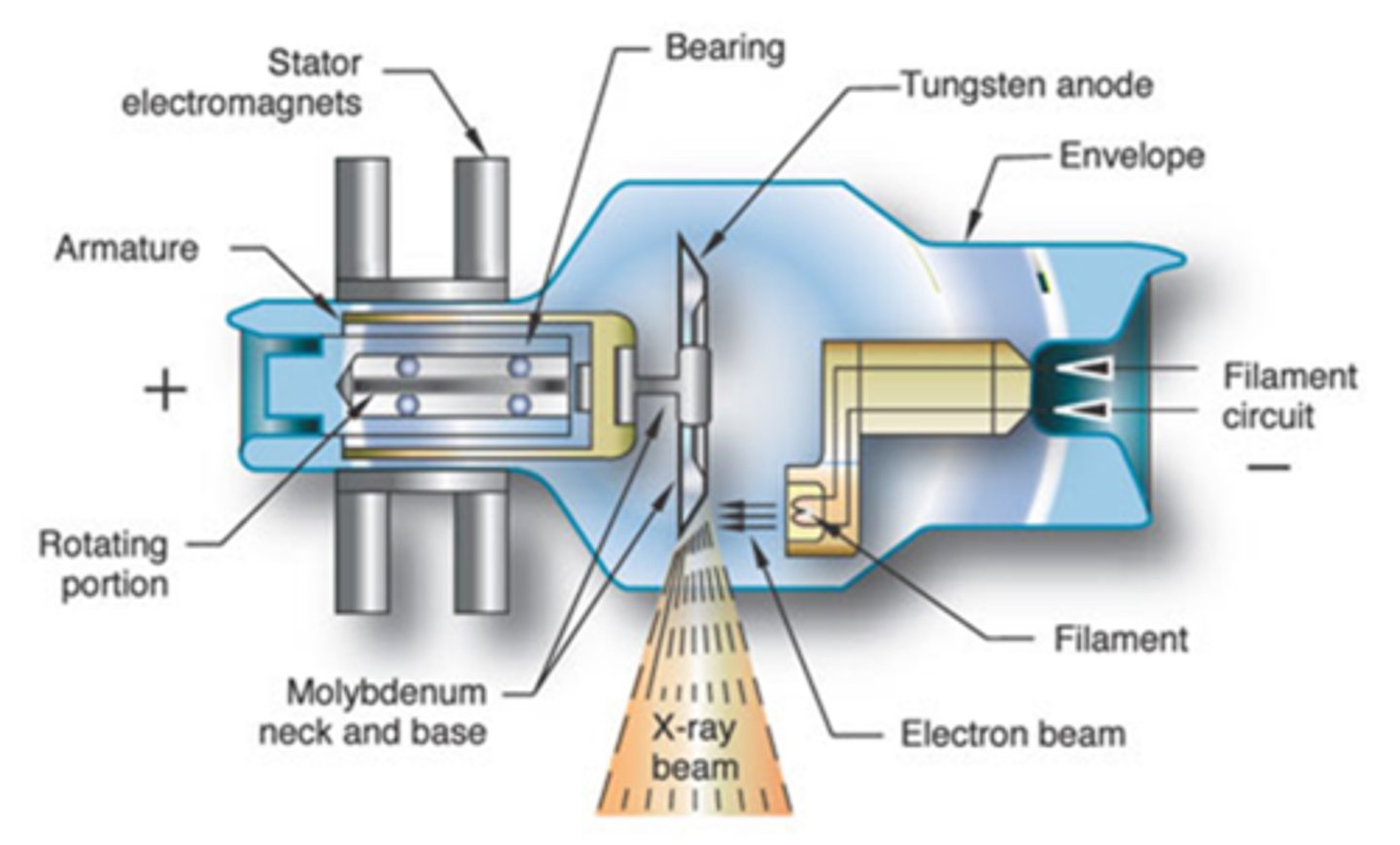
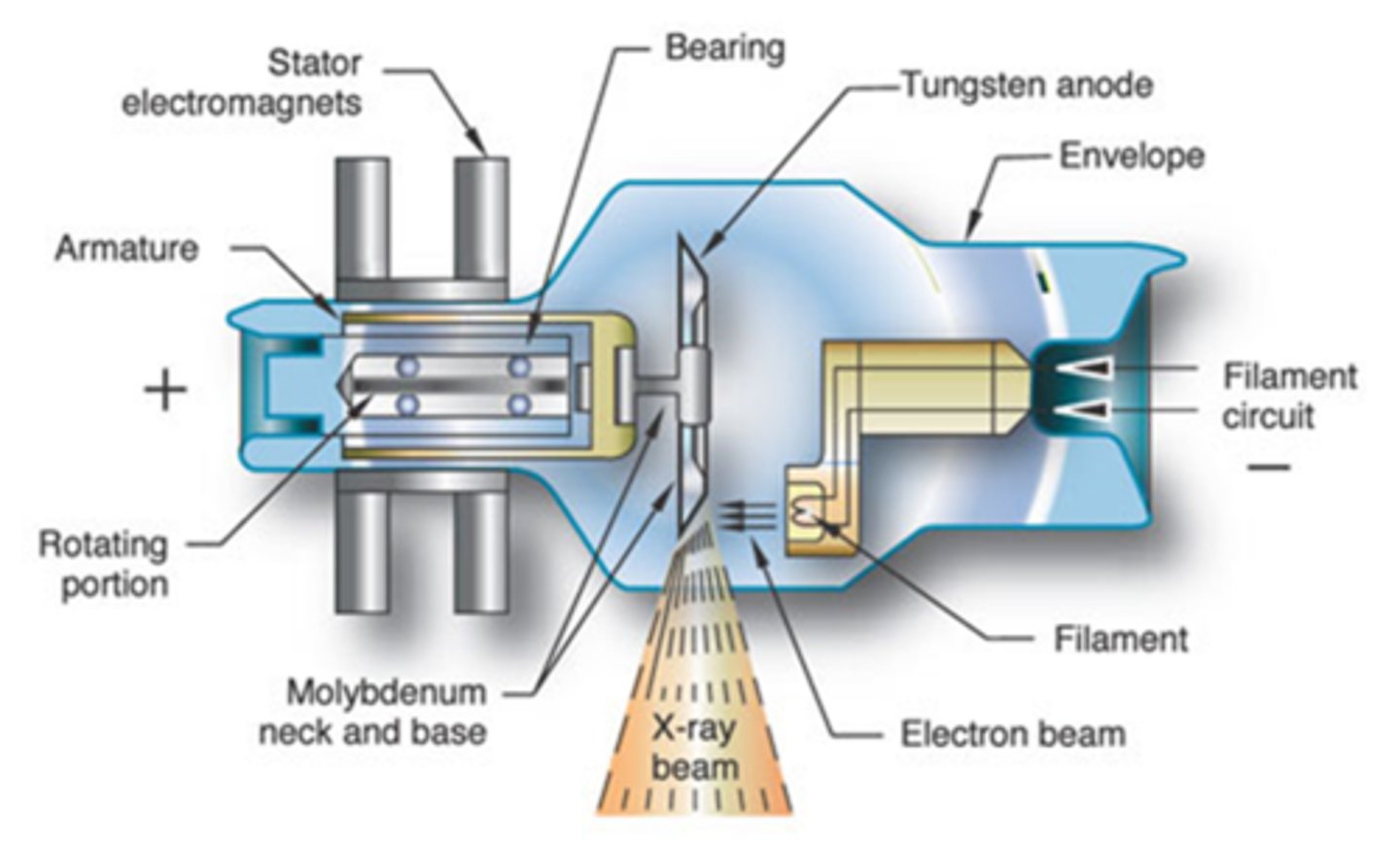
Rotating Anode
- Rotating target helps dissipate heat
- Found in standard x-ray machines
Stationary anode in some models
- Dental units
- Portable units
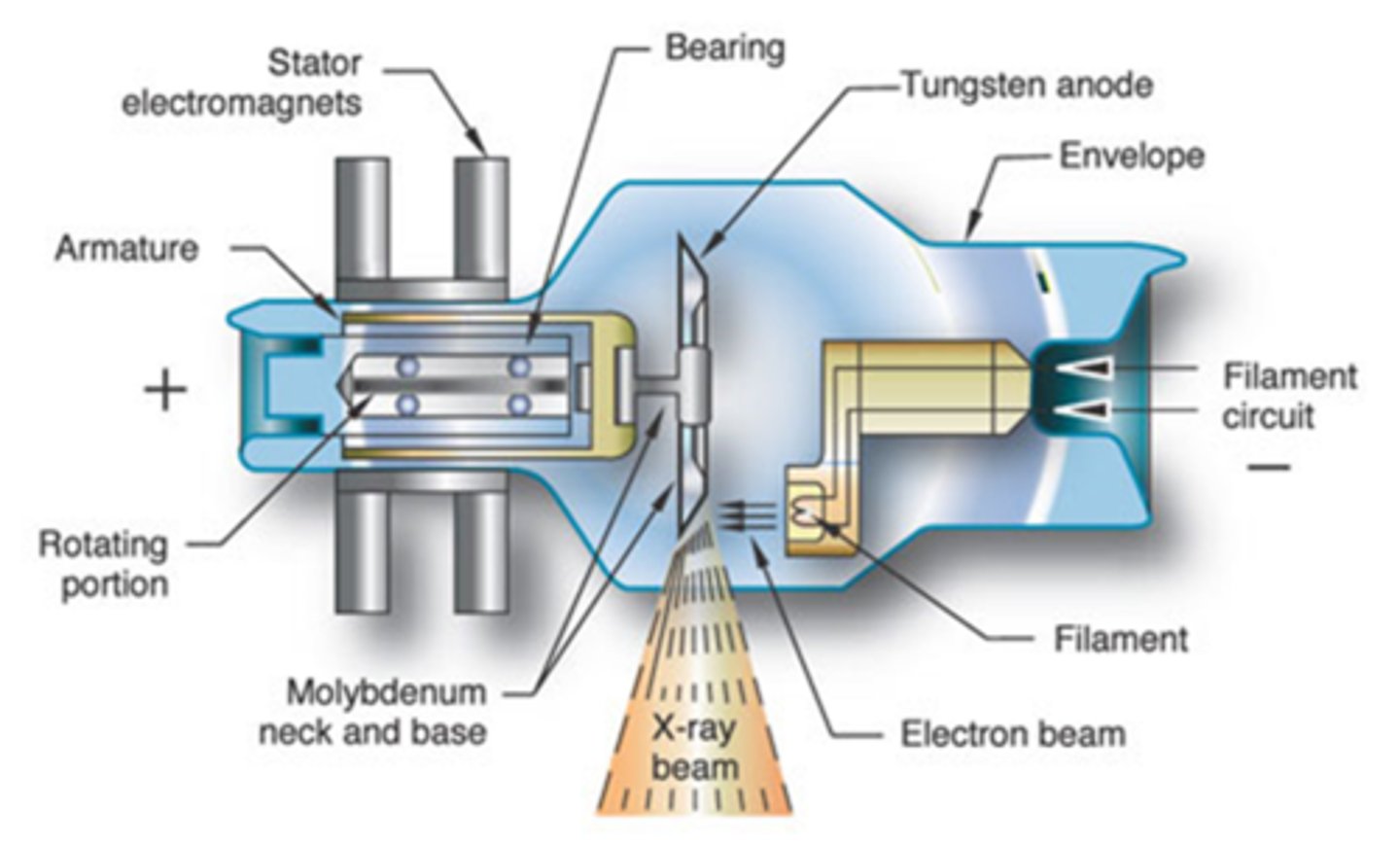
Anode electrons strike target
Target made of tungsten
Does the anode slow down the electrons?
Yes
For the anode, energy lost in slowing down the electron is released as
x-rays
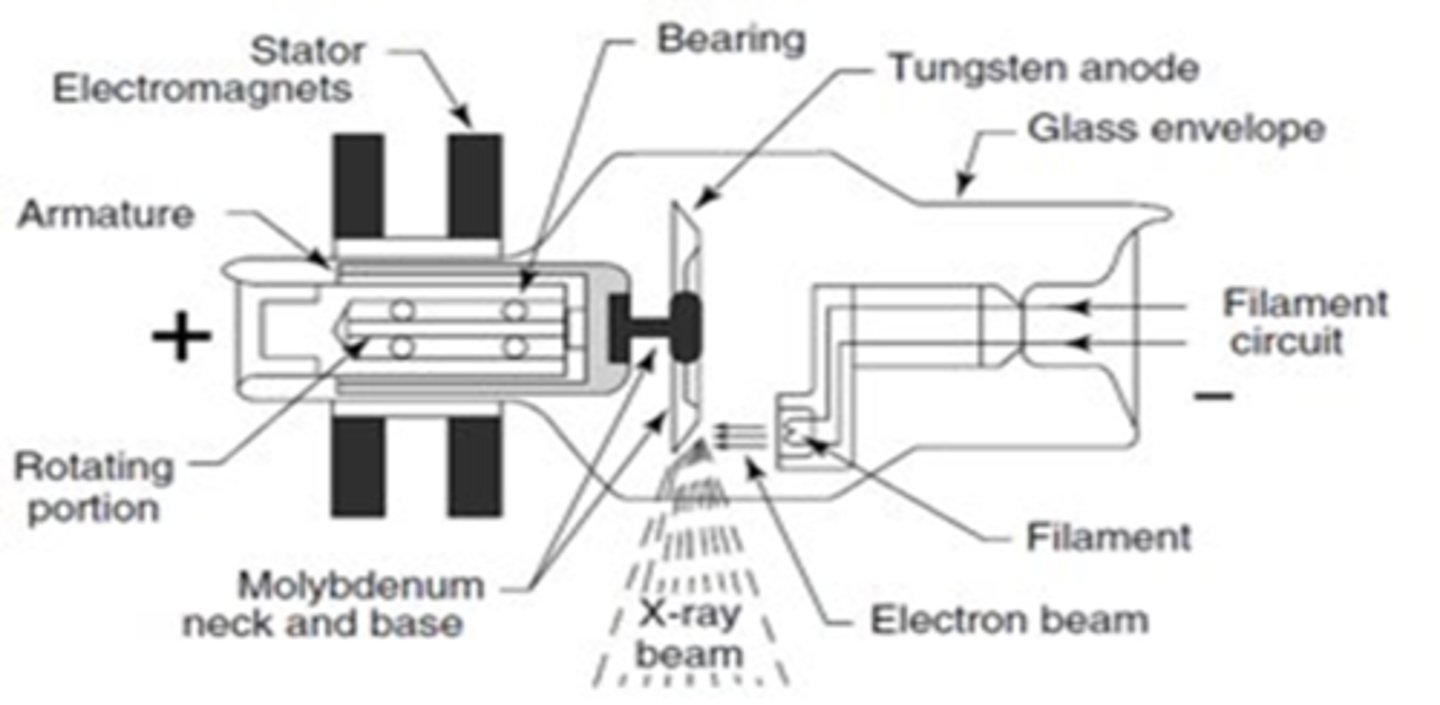
Anode: Beveled edge directs x-rays down toward patient
- This edge is where electrons are aimed from cathode
- Called the focal spot or target area
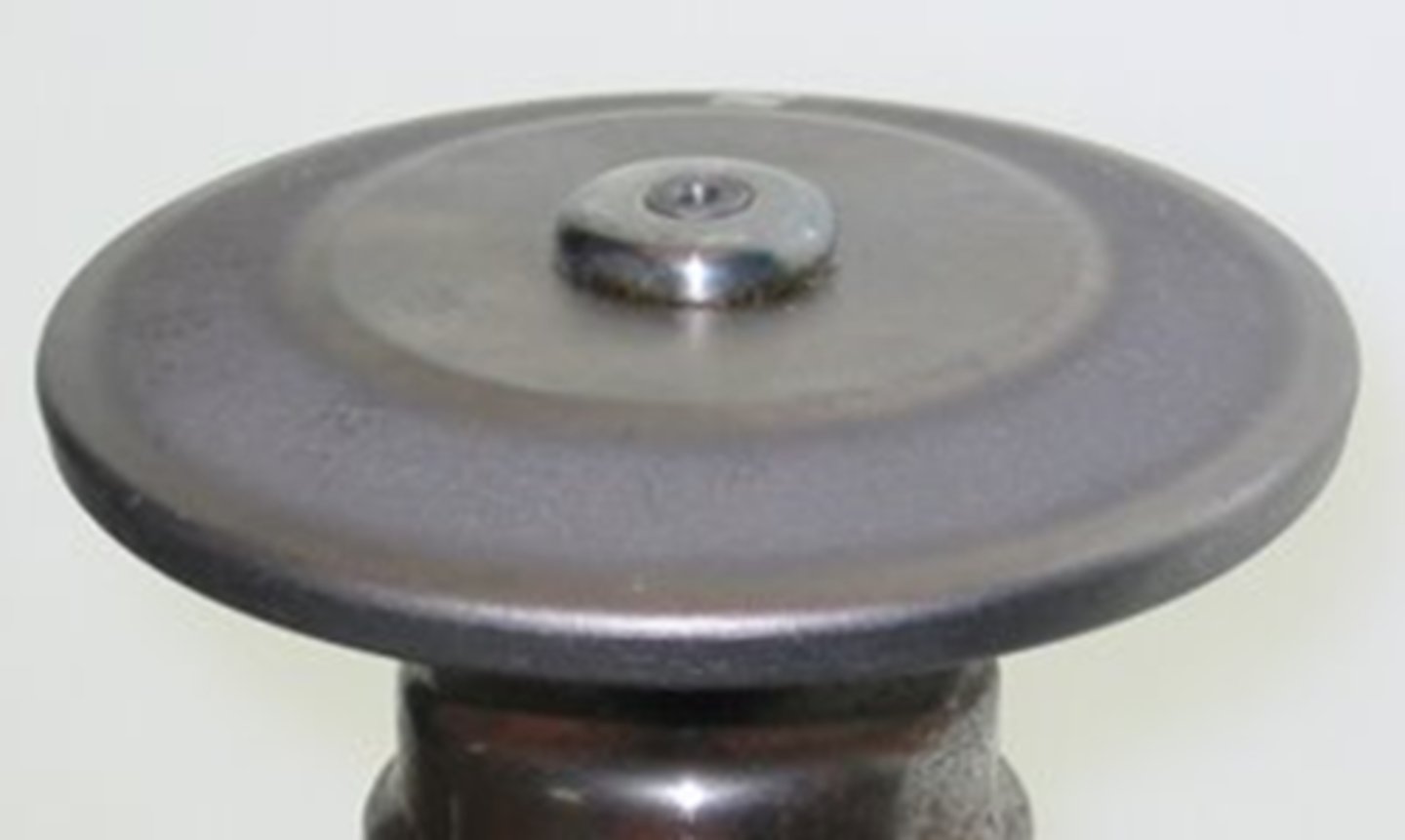

Stationary Anode
- Found in portable units (equine/dental)
- Stem is wide to absorb and dissipate heat
- Must wait between exposures for tube to cool
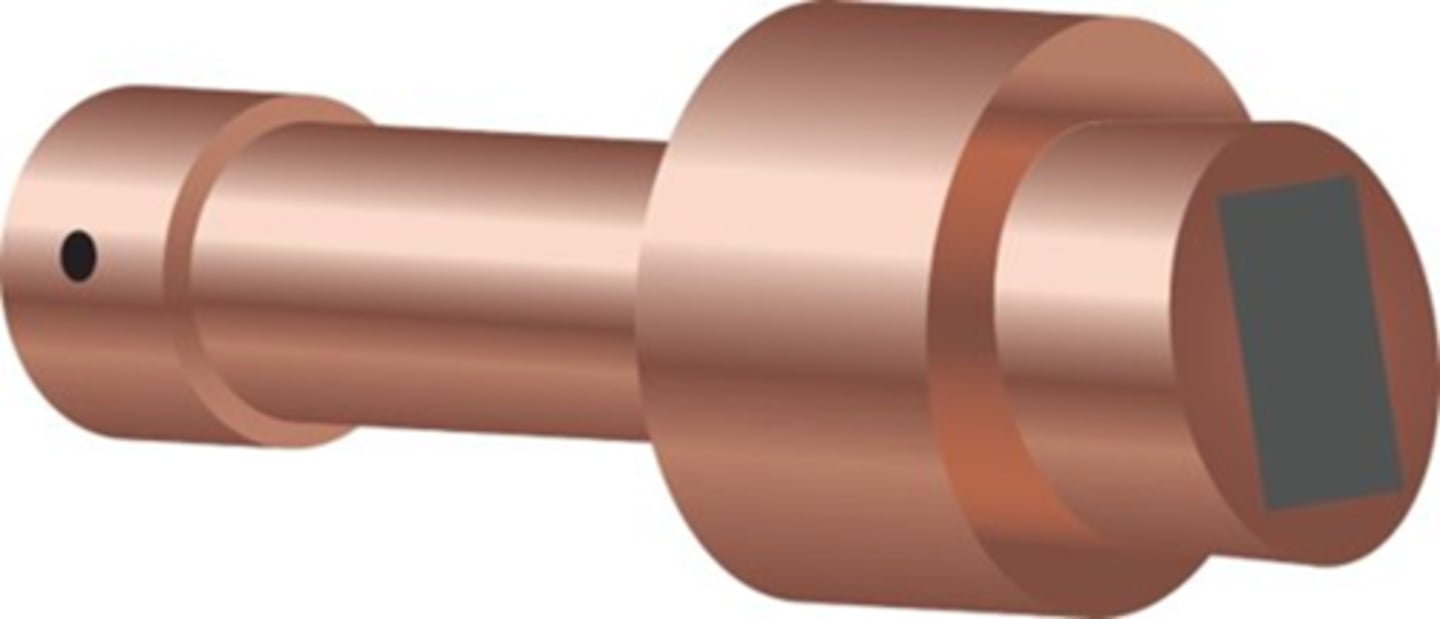
Stationary Anode Pros
small, easily moved, user friendly
Stationary Anode Cons
Inability to withstand large amounts of heat, decreased contrast, cannot x-ray thick structures
Damage seen with stationary anodes:
- Pitting of the target surface
- Radiographs appear lighter than expected
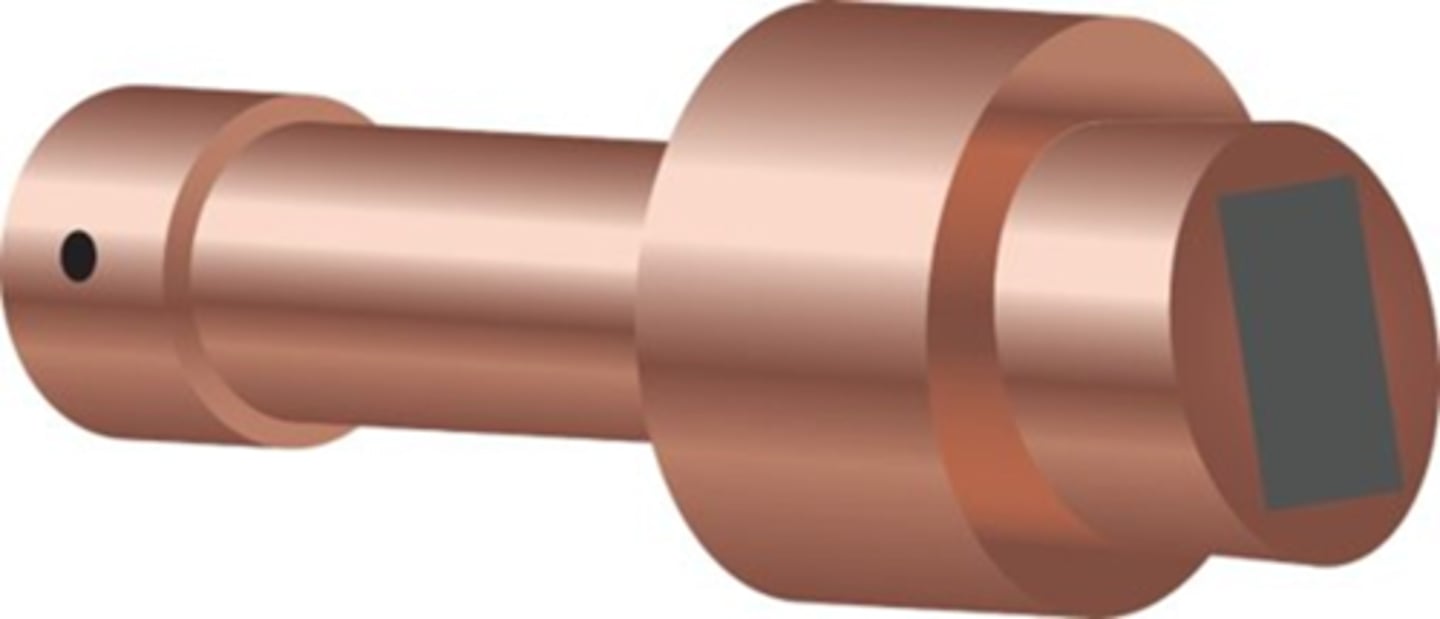
Rotating Anode
In a rotating anode the target spins
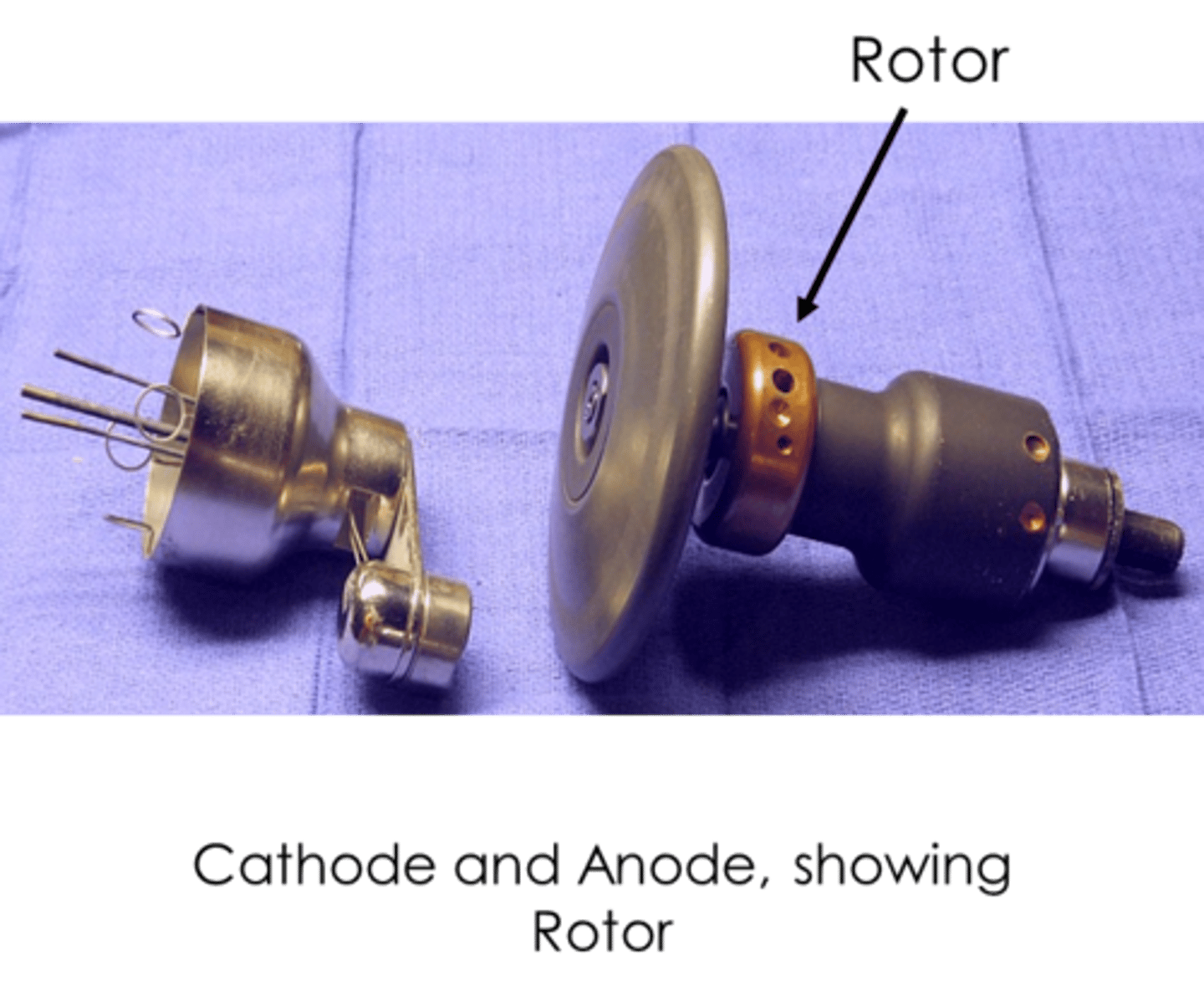
Rotating Anode Pros
- Serves as an electrical conduit unit
- Spreads the heat around (Extends life of tube)
Rotating Anode Cons
Large, bulky units- not portable
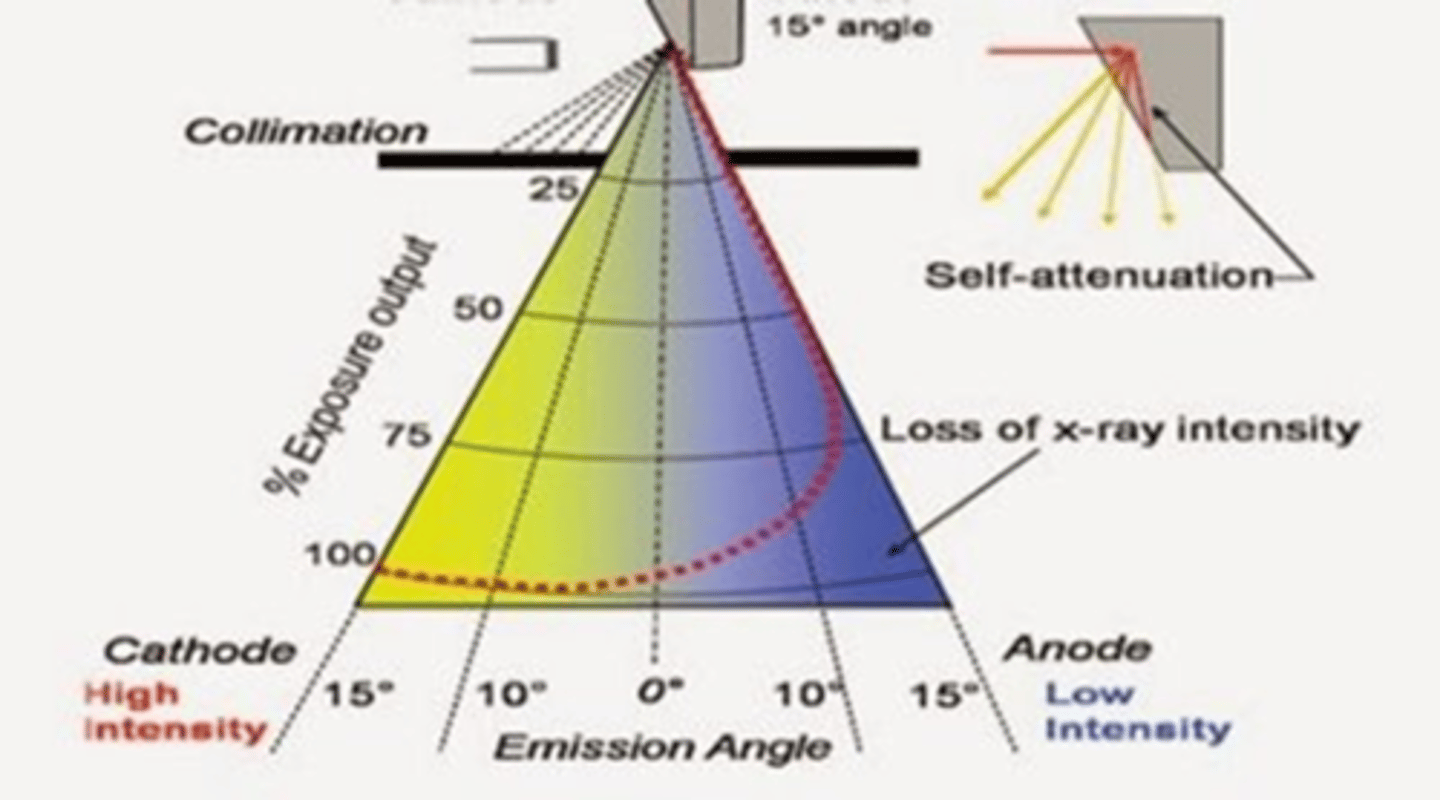
Anode Heel Effect
1. X-rays produced closer to the cathode are higher energy
2. Lose less energy traveling across tube
3. Lose less energy because of bevel
4. More x-rays are directed toward patient at cathode end
Glass Enclosure is where the
Anode and Cathode Live
Glass Enclosure
1. Vacuum-enclosed area
2, Prevents dust interfering with electrons
3, Heat-protected glass with oil to dissipate head
4. Beryllium window
(Allows X-rays to pass from enclosure to patient)
5. Aluminum filters prevent weak X-rays from passing
6. Collimating device present
Tabletop
1. Bucky tray
2. Hold X-ray cassette under tabletop
3. Grid located between table and cassette
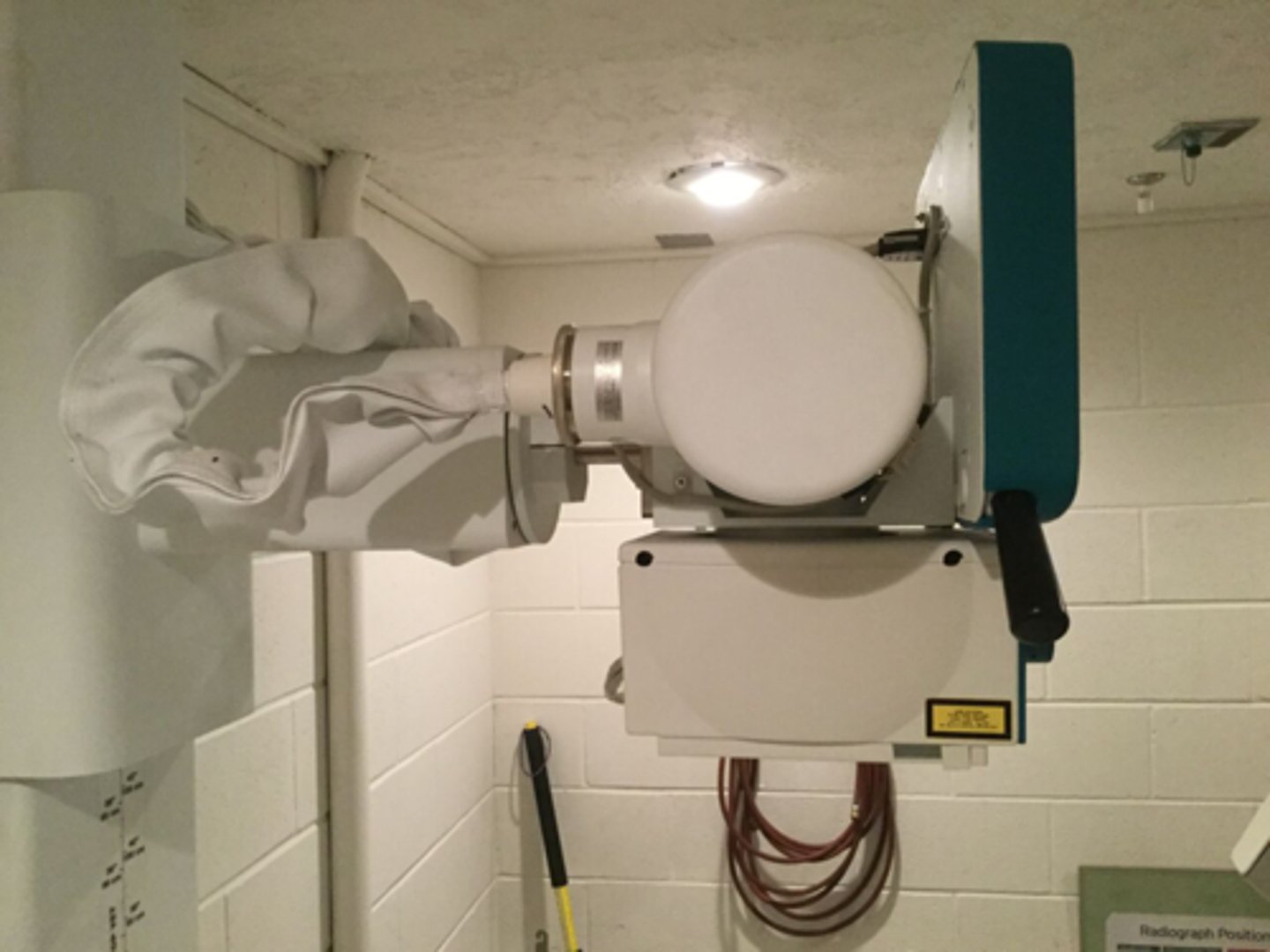
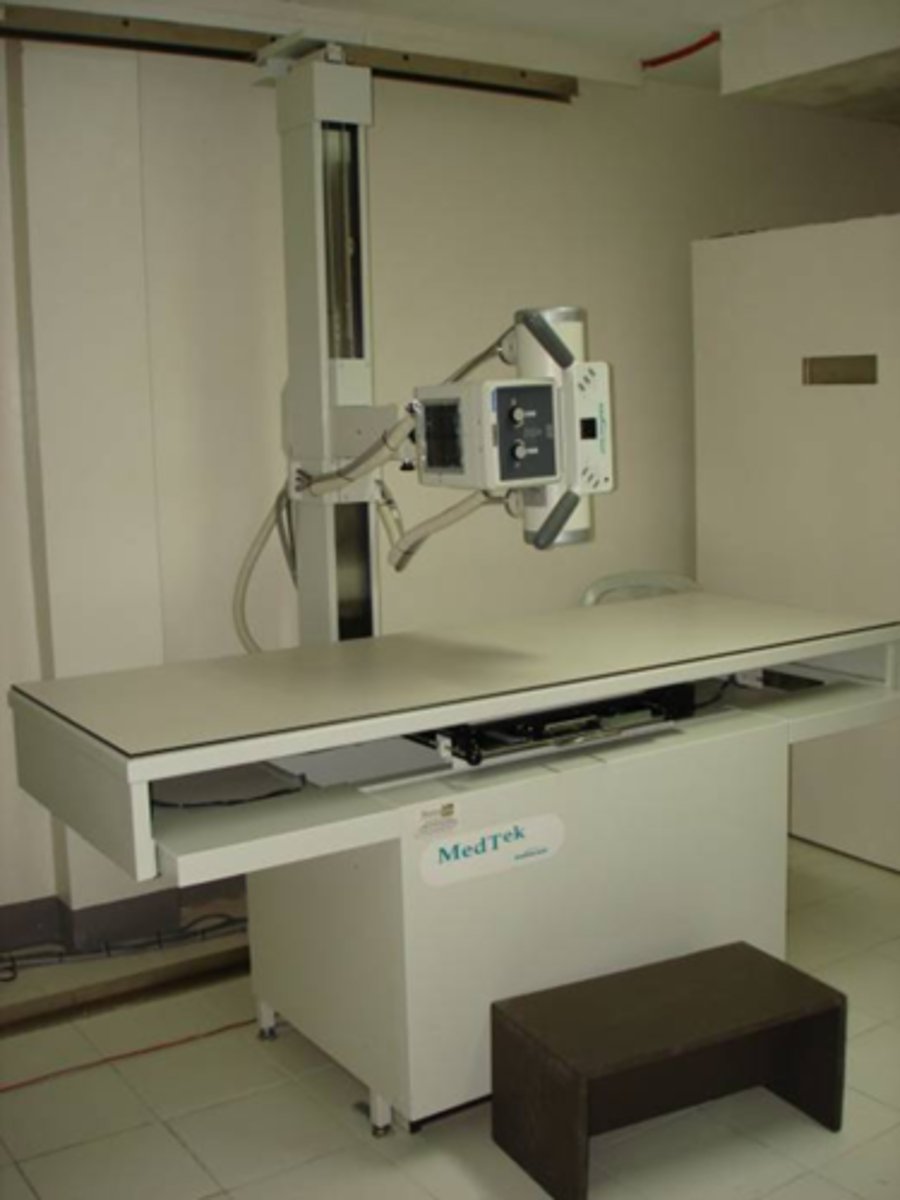
X-ray machine
- 1 = tube stand
- 2 =tube housing/head
- 3 = collimator
- 4 = table top
- 5 = bucky tray

Control Panel (May be built into machine or free standing)
- Power switch
- kVp selector
- mA selector
- Line voltage compensator
- Exposure time control
- Exposure button
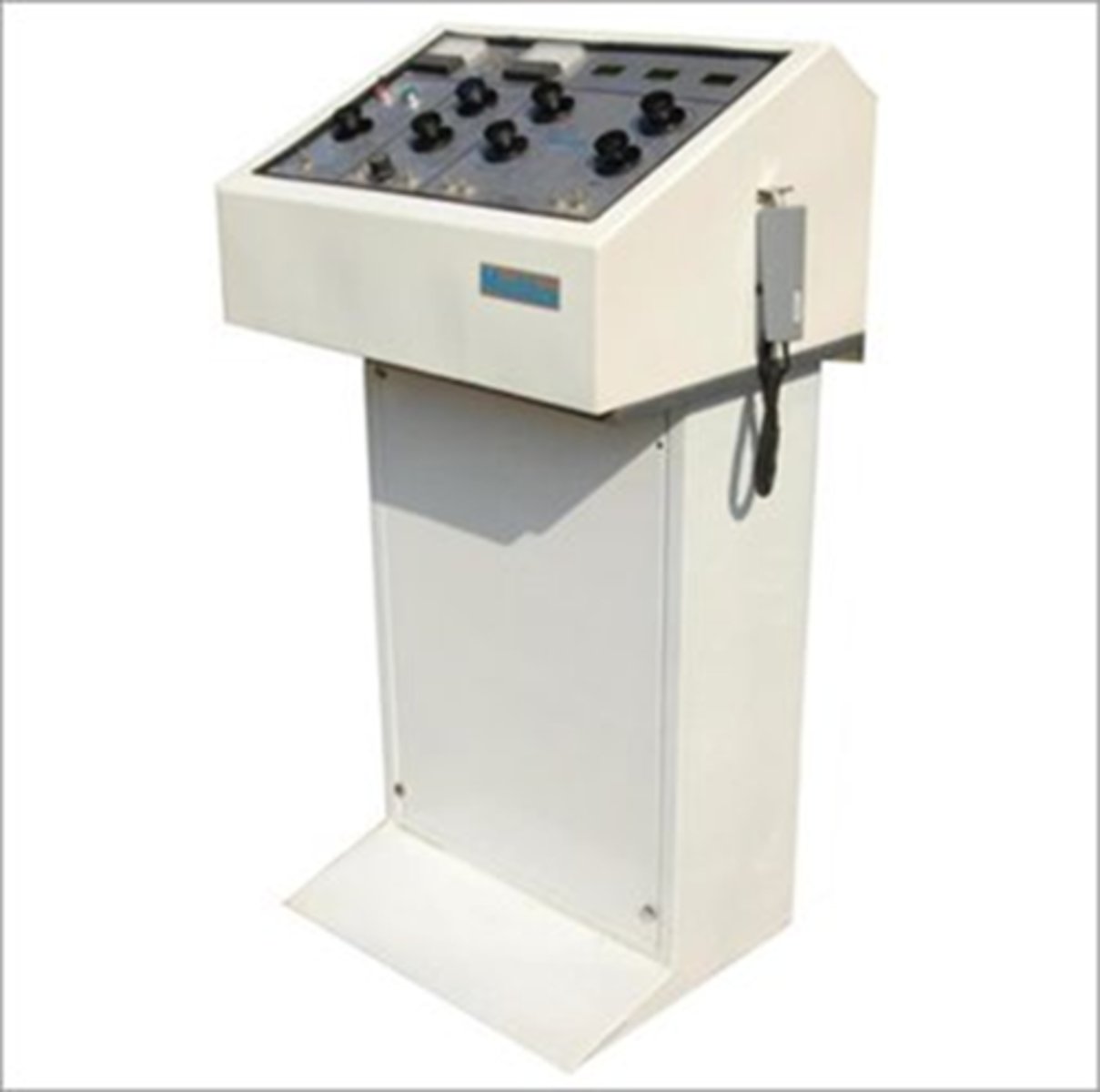

Control Panel (Power switch)
controls power to the unit
Control Panel (kVp selector)
step up transformer, anode
Control Panel (mA selector)
step down transformer, cathode
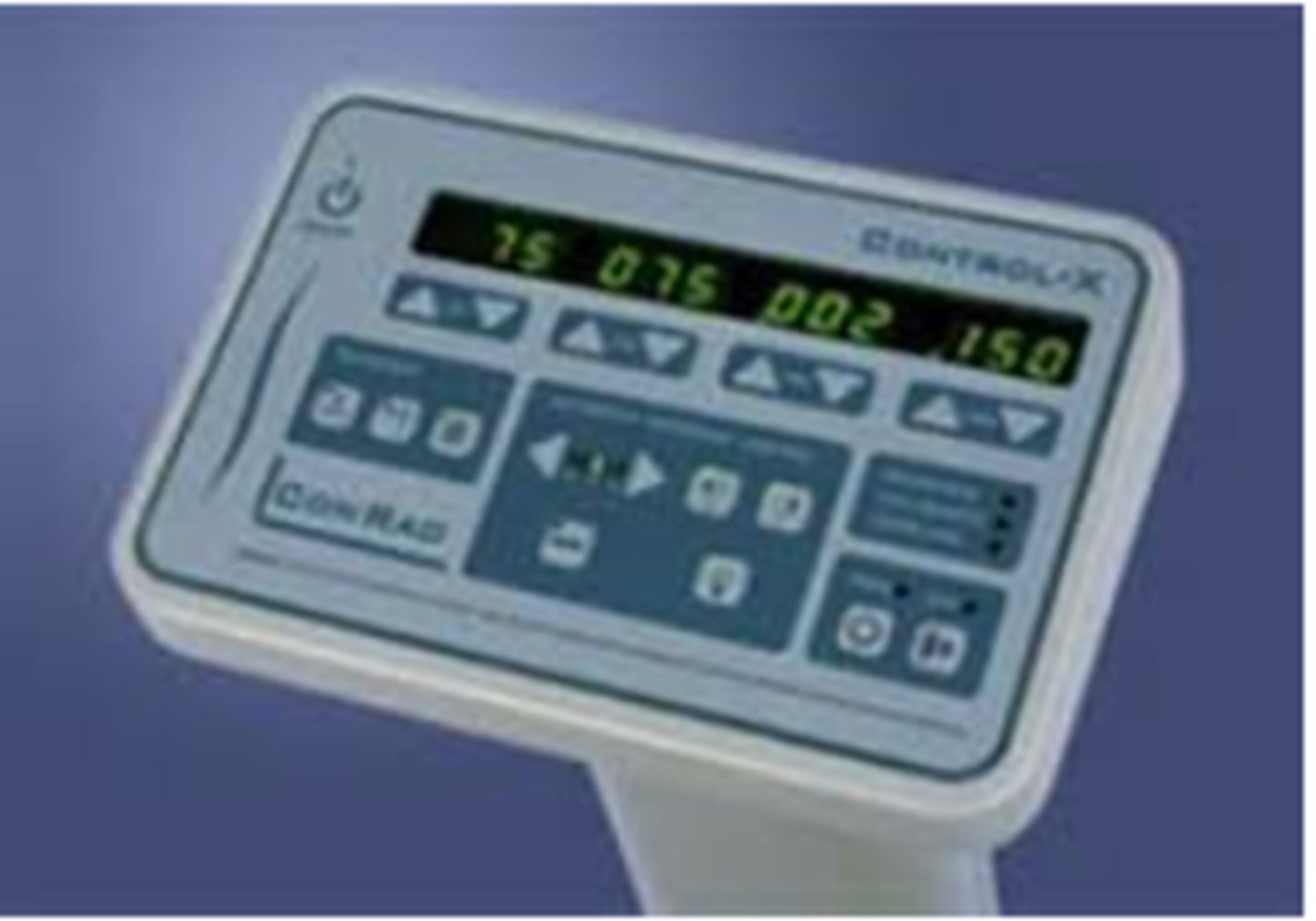
Control Panel (Line voltage compensator)
stabilizes power coming into machine (built into new machines)
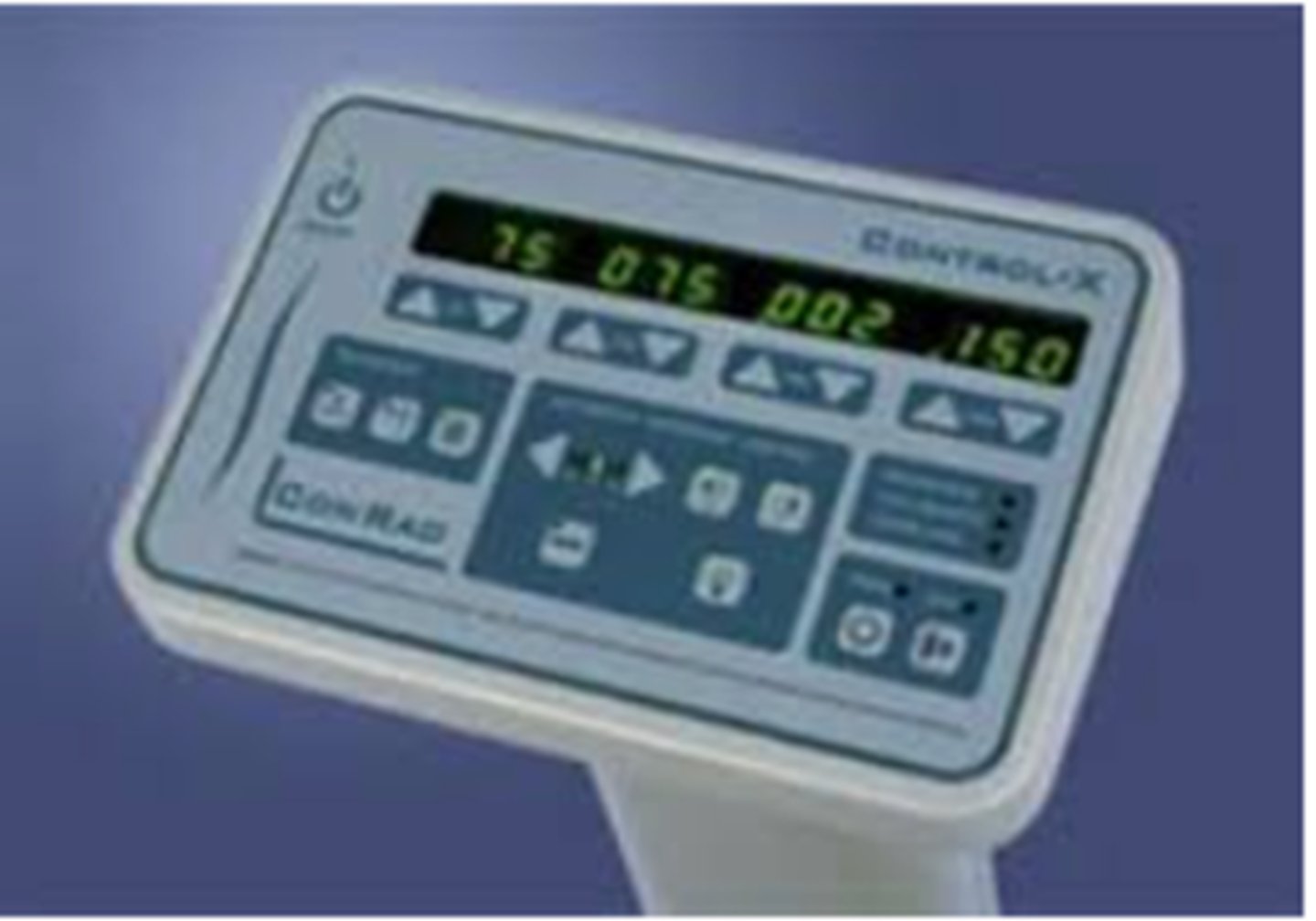
Control Panel (Exposure time control)
how long the x rays are released
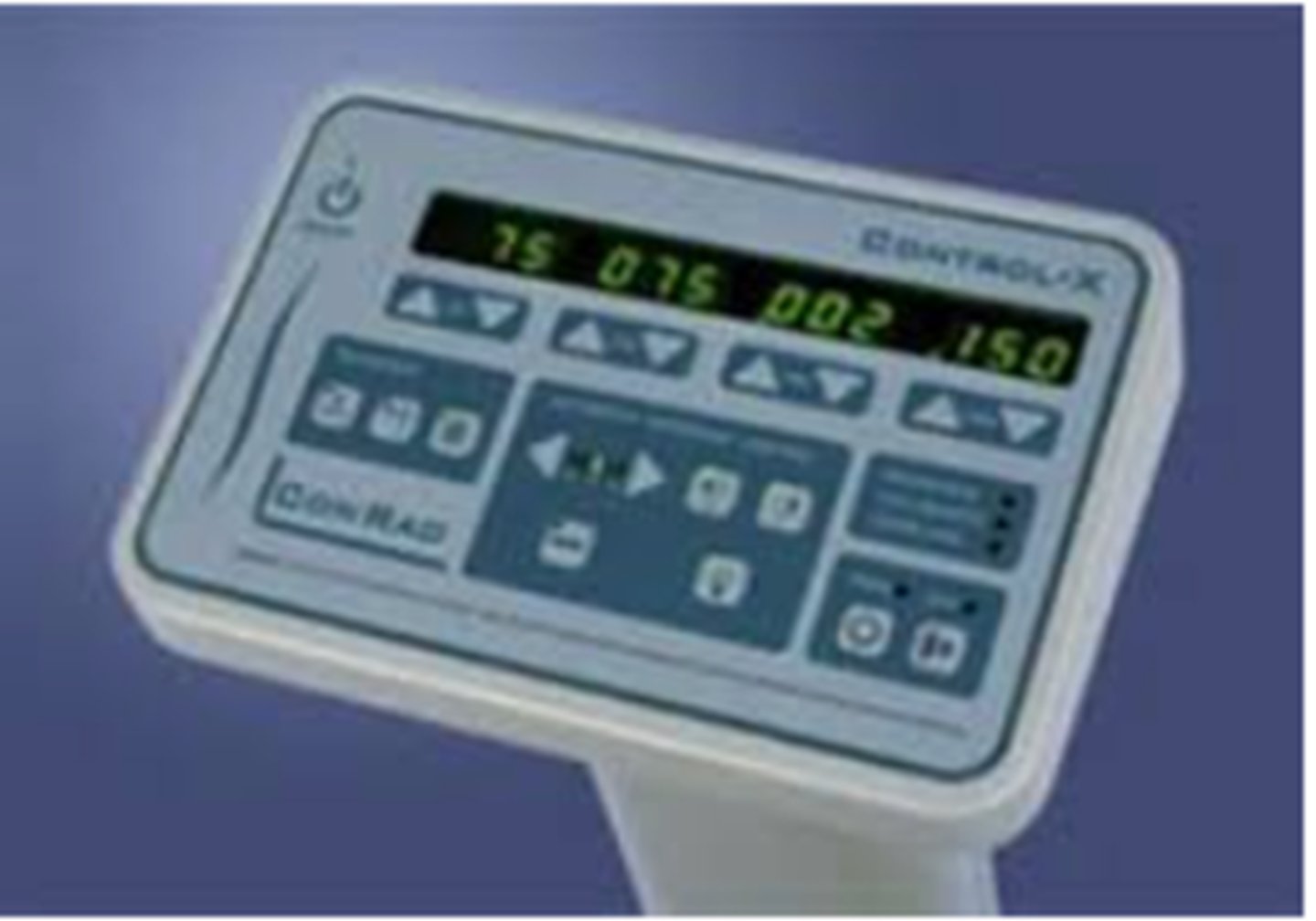
Exposure button:
may also be foot or hand switch
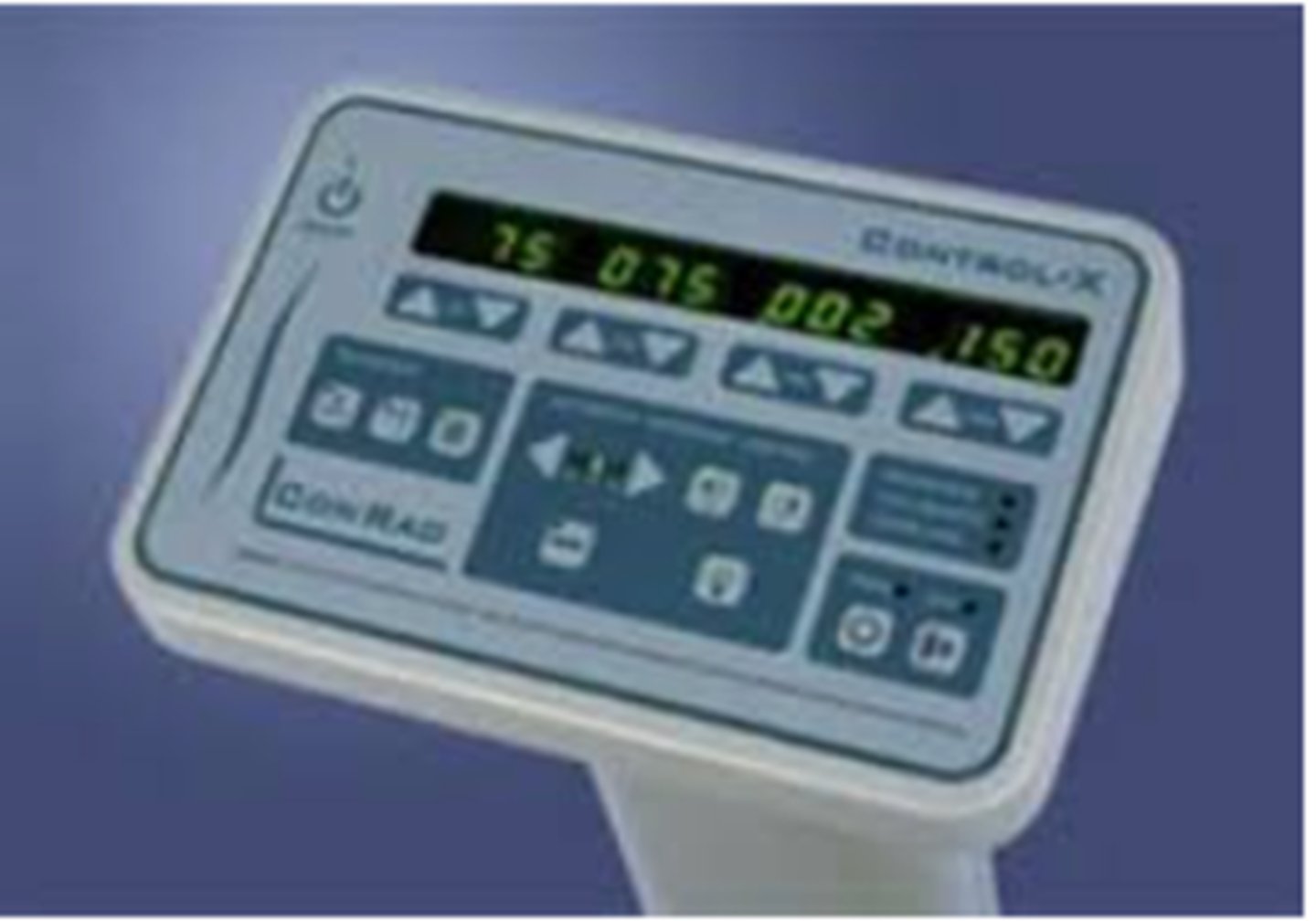
Electrical Circuit
1. Power coming in needs to be adjusted to accommodate an x-ray machine
2. 120V -- 240V
3. Generally has a separate circuit breaker box

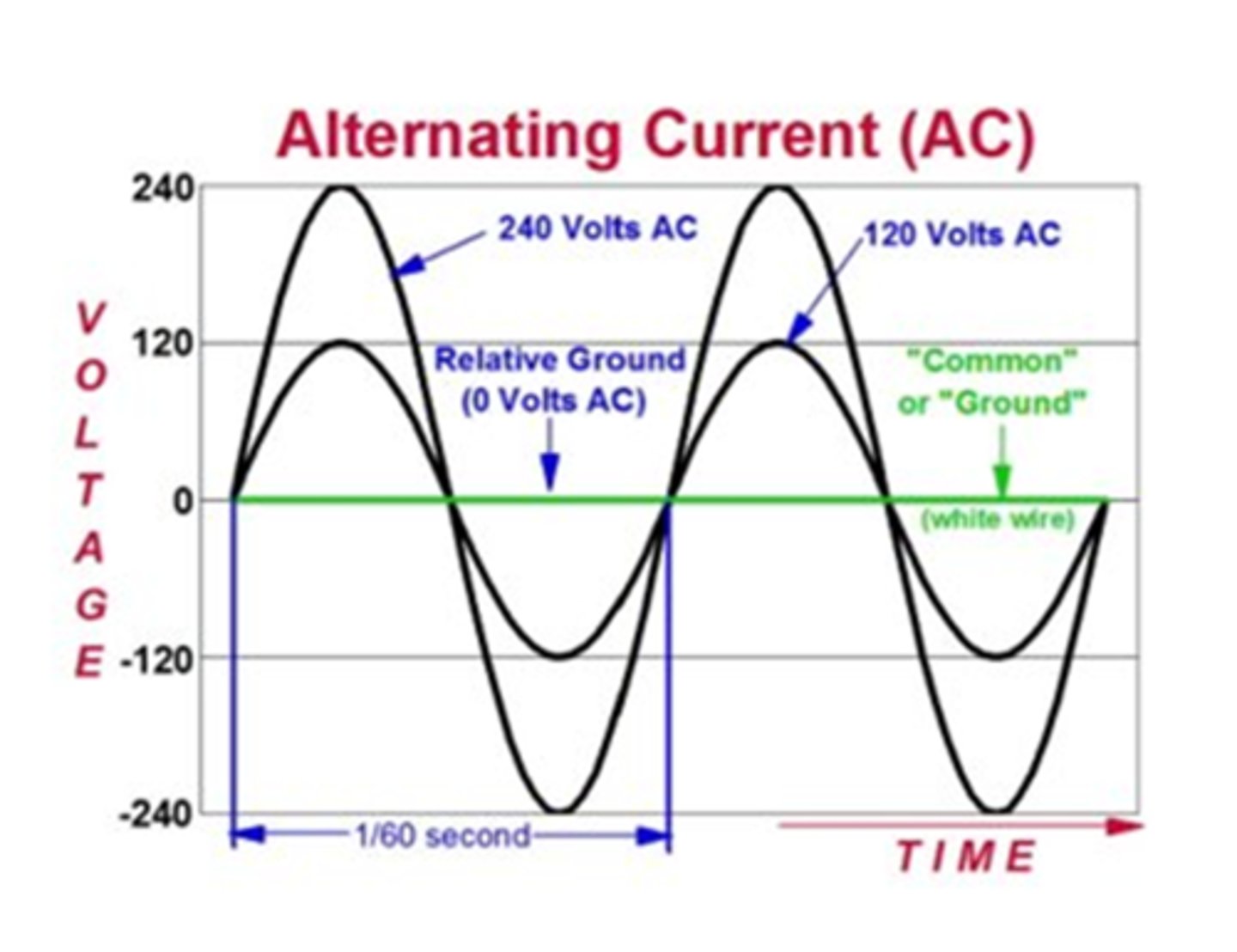
Current Affairs
- Power is alternating current
- 60 Hz in USA
- Power is present on the positive side
- No power is supplied when on the negative side
Step Up Transformers
- Increase power to x-ray tube
- Boosts voltage from 220V to max of 125,000V
Step Down Transformer
- Decreases voltage going to the filament
- From 240V to ≈10V
Amount depends on mA selection
Circuitry
- Step up transformer is at the anode kVp selector: step up transformer, anode
- mA selector: step down transformer, cathode
- 99% heat and light lost, 1% xrays
Rectifiers
- With alternating current power is available only ½ the time
- Rectifiers increase efficiency of power generation
- Negative portion of wave is suppressed or redirected to positive
There are three types of rectifiers
1. half wave
2. full wave
3. three phase
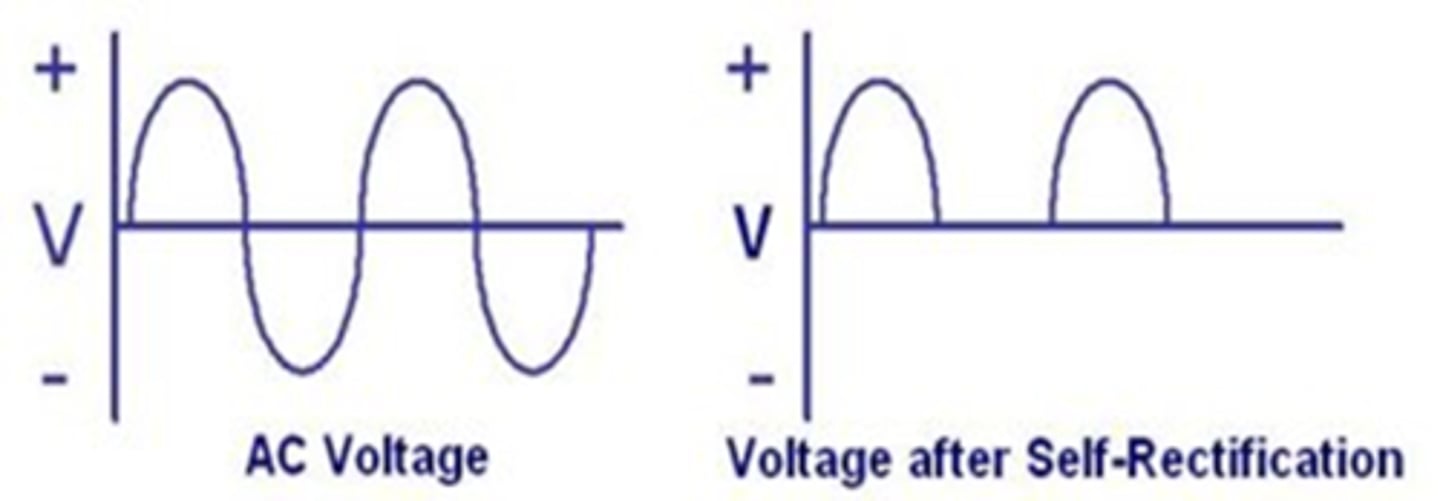
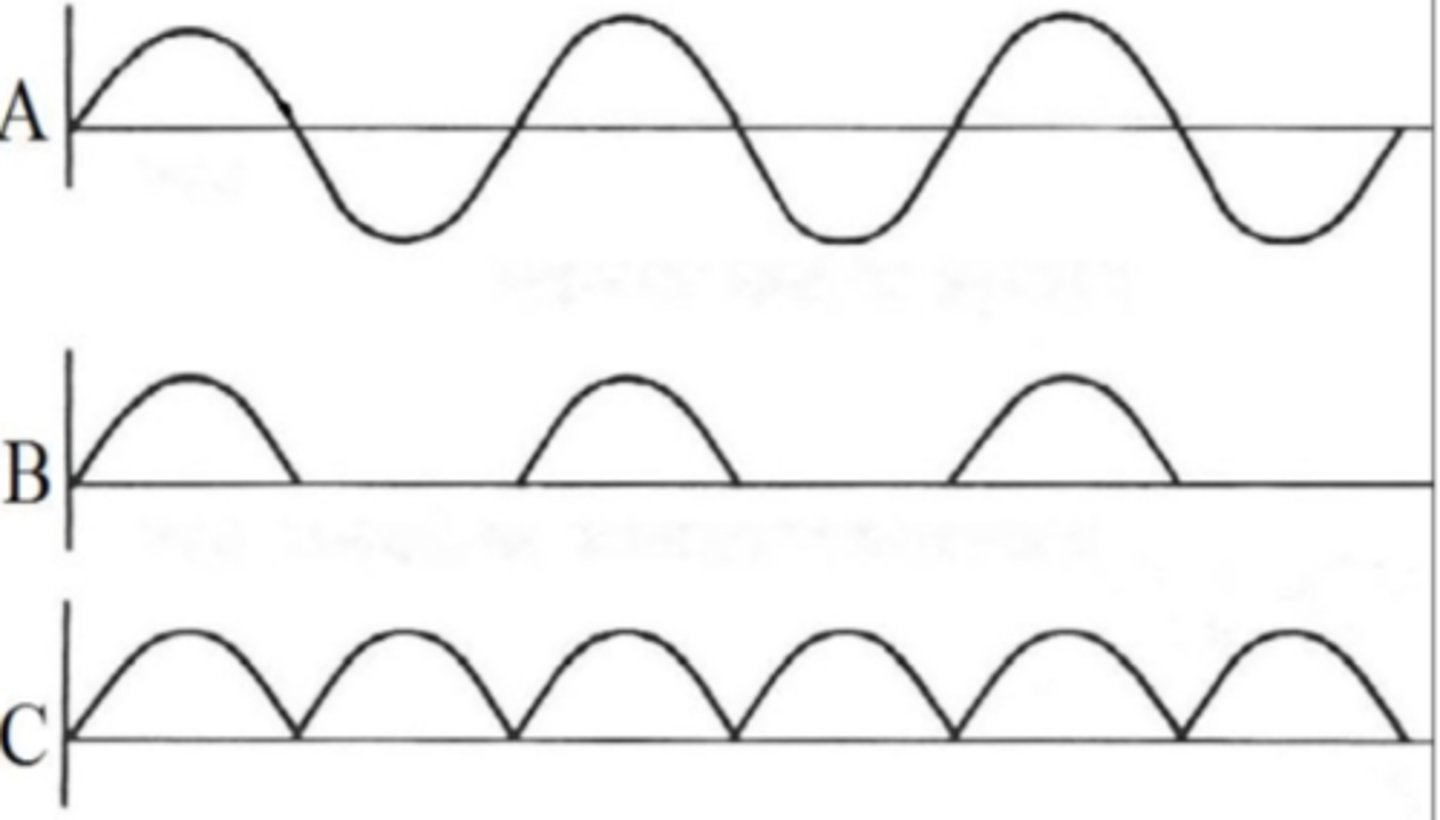
Single phase rectifier or Half-wave rectifier
- Also called self-rectification
- Standard in old XR tubes
- No current is flowing ½ the time
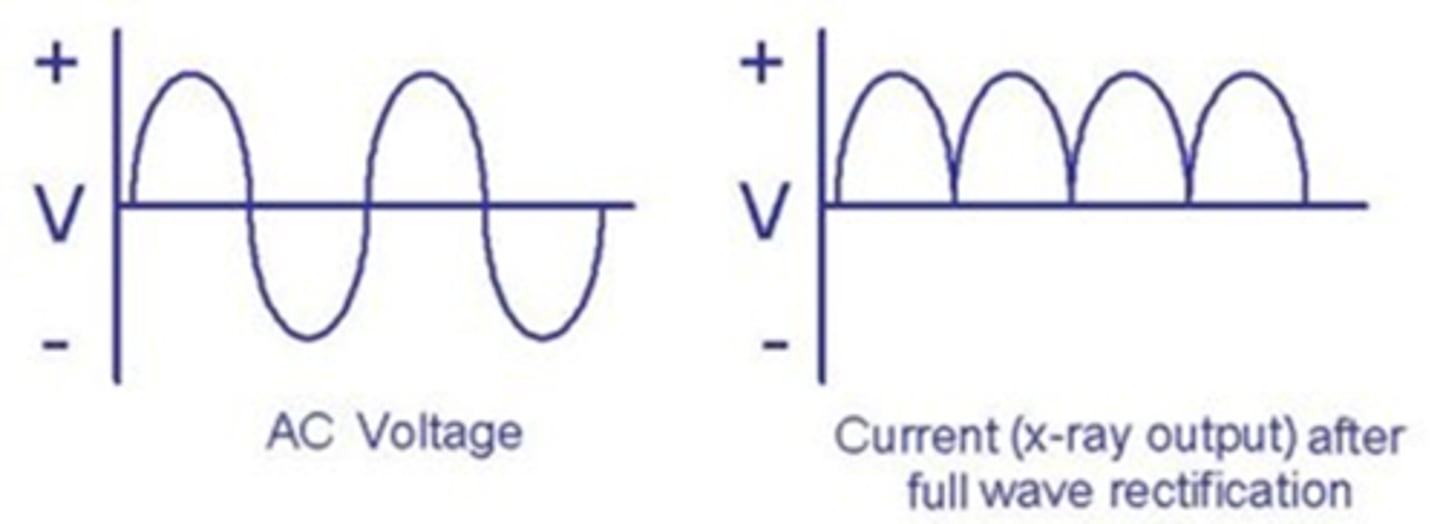
Full Wave Rectifier
- Multiple valve tubes reverse negative portions of wave
- Current flows more consistently
- Faster times and more x-rays produced than half-wave rectifier
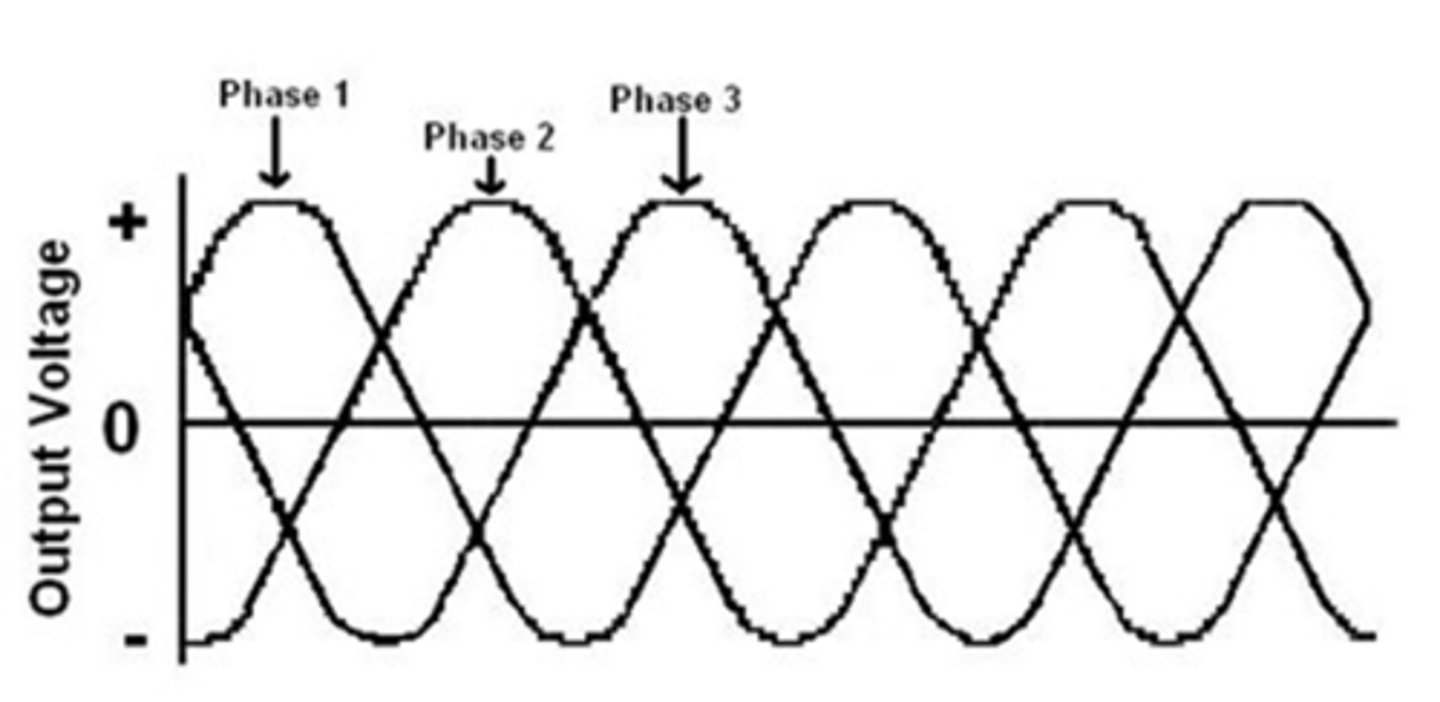
Three Phase Approach
- Require a lot of power
- Used primarily in large referral practices/board-certified
- Three currents each 120 degrees out of phase with the others
- Eliminates power drops between waves
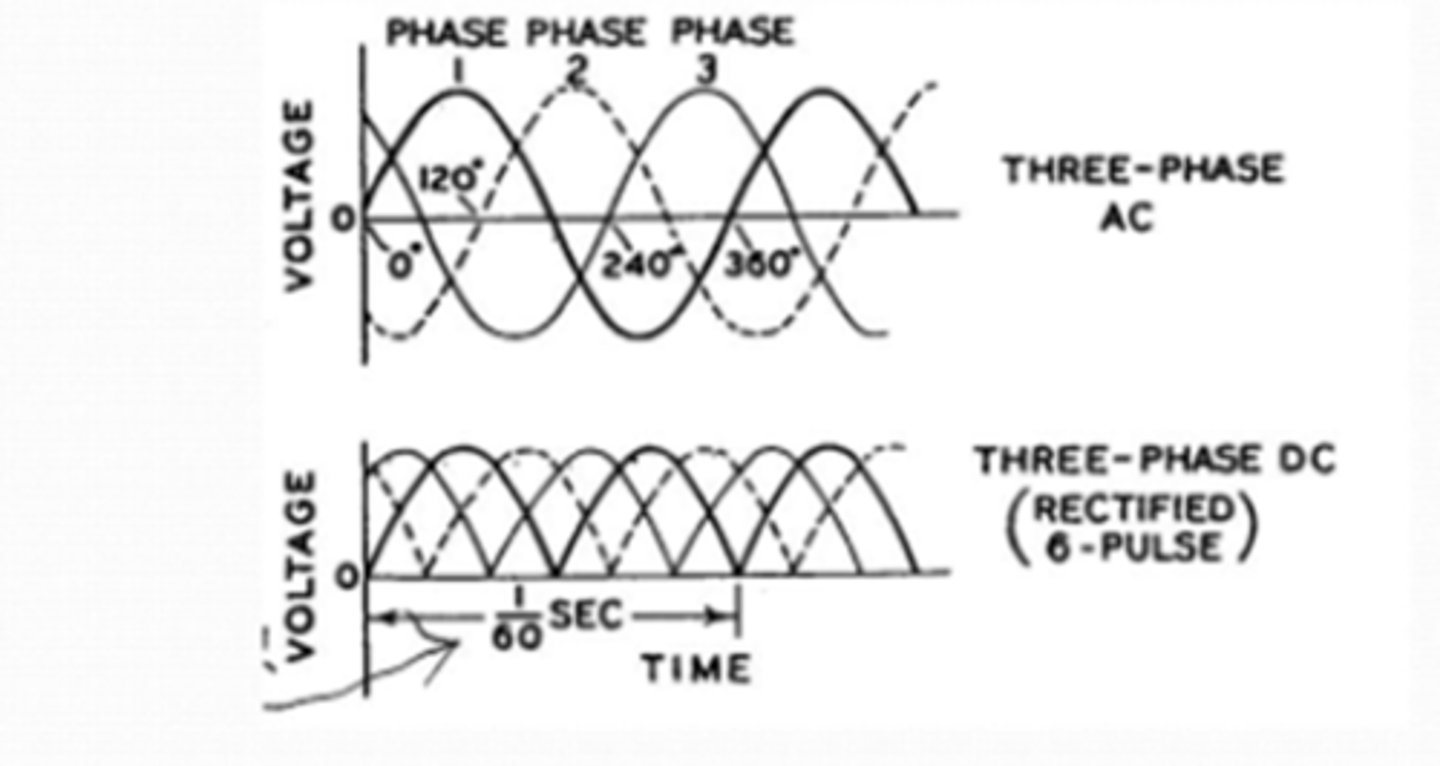
Three Phase Rectifier
1. Each phase is 60 cycles/sec.
2. Three phases = 60 x 3 = 180 total cycles/sec
3. Fully rectified = 180 x 2 = 360 total cycles/sec
4. High efficiency, consistent power
Record Keeping
- Part of medical record
- Developed films stored in folder or envelope
- All views of one study placed in one folder and labeled
- Label: patient, clinic name, date and view taken

Radiology Log
Used for tracking and cross-referencing
Radiology Log includes:
- Client's name
- Patient's name
- Body part being radiographed
- Position
- KVp and mAs settings used
- Initials or signature of radiographer
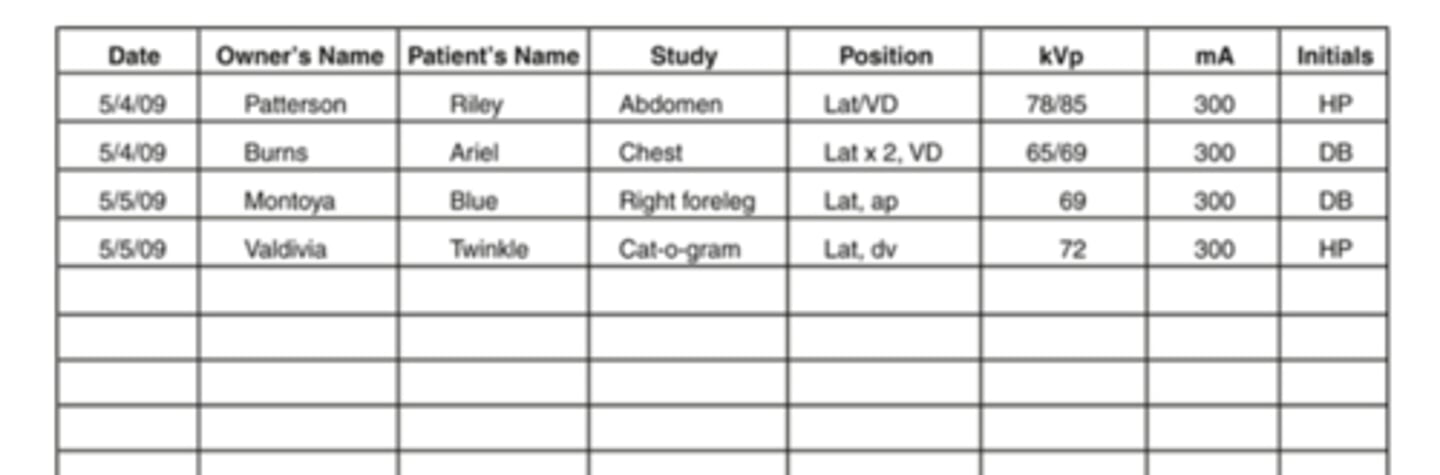
Digital Radiographs for record keeping
- Part of patient's electronic medical record
- Can be copies onto CD or flash drive to be provided to client or referral DVM
- Images provided into a universal format known as DICOM
- DICOM Stands for: Digital imaging and communications in medicine
Comparing wavelengths on the electromagnetic spectrum, what is the order going from lowest frequency to highest frequency? Choose the correct example.
radio waves, microwaves, visible, gamma
In an xray tube, xrays are formed on the
tungsten target on the anode
Regarding the production of xrays in the tube, the
cathode includes the filament and focusing cup
The cathode is on the _____________voltage side of the circuit, and the anode is on the _____________ voltage side.
low, high
The electron cloud is generated at the
cathode
The filament of an xray tube is the
tungsten coil that emits electrons when heated
The purpose of rectifying a current is to ________________________ xray production.
increase efficiency of
The step-up transformer converts the volts coming in to ____________________ going out.
kilovolts
Waveform B represents what type of rectification of current?
single phase or half wave
Identify the parts of the xray tube and circuit by dragging and dropping text into the appropriate box: Filament
Identify the parts of the xray tube and circuit by dragging and dropping text into the appropriate box: Cathode
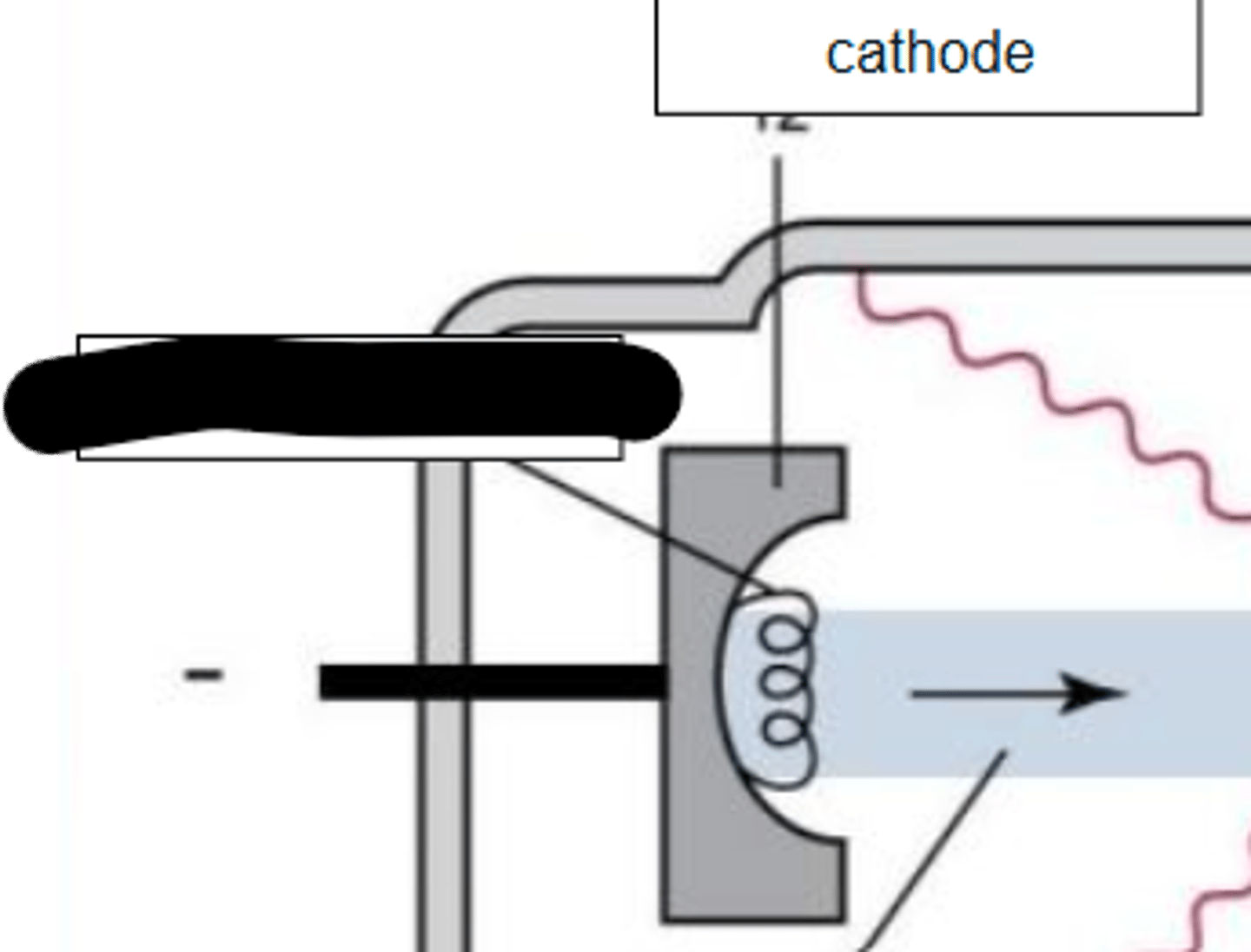
Identify the parts of the xray tube and circuit by dragging and dropping text into the appropriate box: Electrons
Identify the parts of the xray tube and circuit by dragging and dropping text into the appropriate box: Vacuum
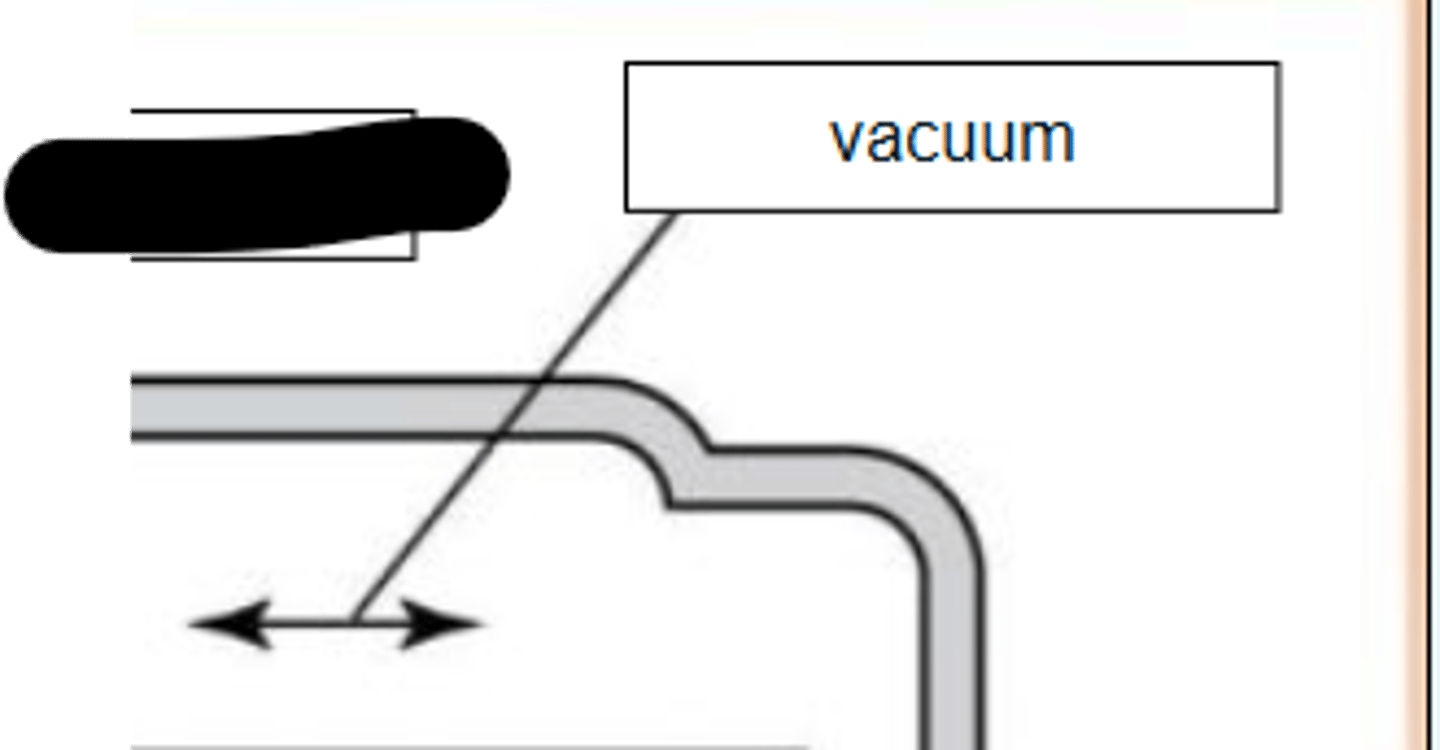
Identify the parts of the xray tube and circuit by dragging and dropping text into the appropriate box: Target of the anode