casting: materials gauntlet
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms

aluminum/ zinc alloys
process = ingot casting
shapes = looks like gold bars
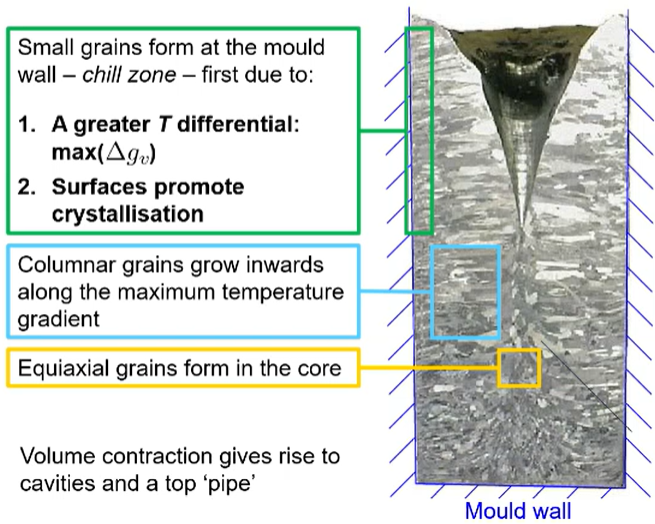
features/microstructure = small grains at mold wall (chill zone) / surface promotes crystallisation/ grains grow inwards along maximum temp grad/ large grains in the core
application =
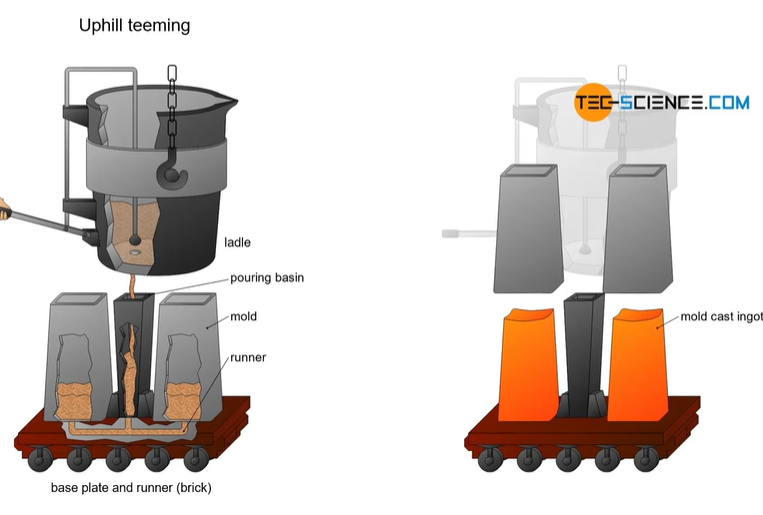
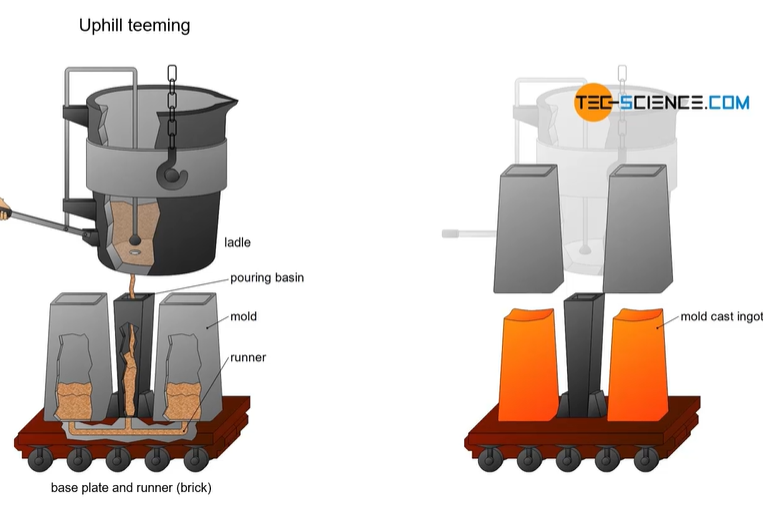
ingot casting
taking a ladle from a furnace, which is filled with molten metal and heated to high temperatures in a furnace
then removed from the furnace and positioned over a platform which holds the molds on a base plate
so the mold is a container made from different materials or refractory bricks/ ceramics/ cast iron/ graphite mold which allows the molten phase to cool quickly
mold needs to withstand the melting point of the material casted
there is 2 processes = uphill teeming or downhill teeming (teeming = to pour)
open a valve in the ladle and molten phase just pours into the basin and flows below and up into the mold
leave to cool in air and remove mold
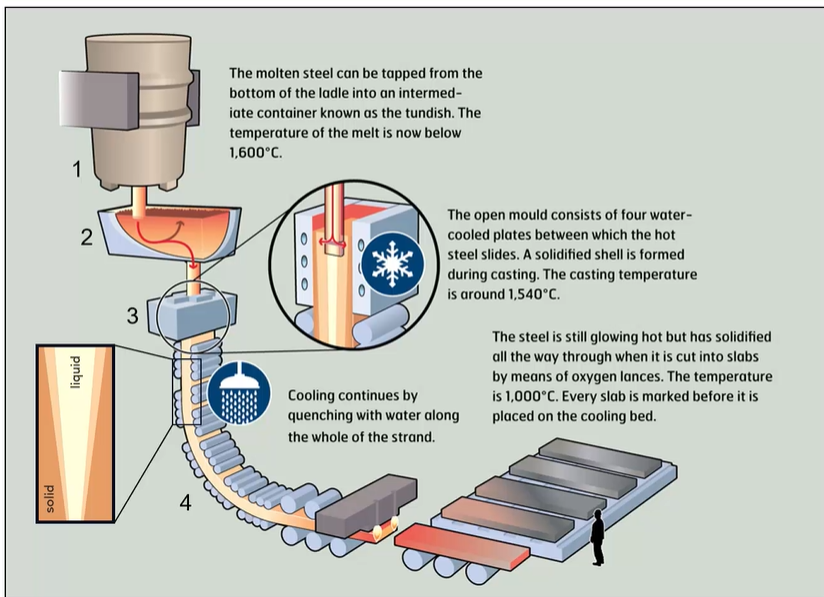
continuous casting
used to produce large scale slabs
continuously pouring and solidifying molten metal into desired shape
have to be post processed - hardened, worked, formed

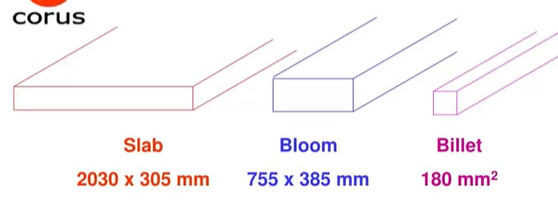
aluminum slabs/ steel billets/ blooms/ slabs
process = continuous casting
features/ microstructure = fewer defects and more consistent microstructure

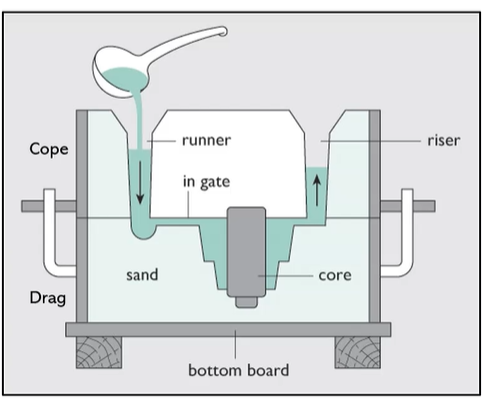
sand casting
is a 2 part mold made from a core and a drag and use a pattern to form a cavity in green sand and pour the molten metal
pattern can be used again
has shrinkage
non uniform grains and no direction associated with the crystal axis when in the center of the cast.
column of grains at the edge

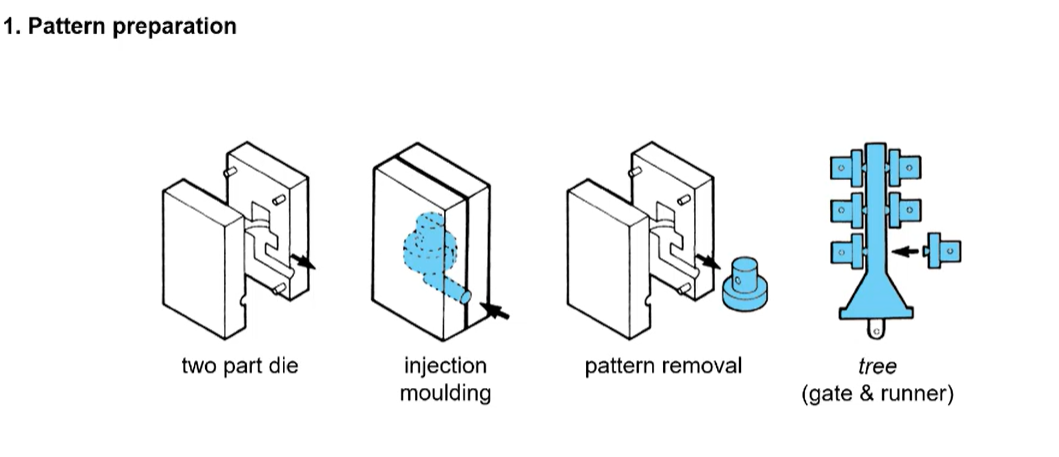
investment casting
can give finer details than sand casting
used for complex shapes with finer features
wax is injected in the die and separated to get the pattern.
the pattern than be stuck to a wax tree to cast multiple objects at the same time
dipped into slurry and refractory sand is then thrown on it building a thick layer for 6-7 mm
the autoclave then hardens the ceramic and creating a hard shell and the wax is loss due to the high heats
cool at room temp and remove the ceramic coating (via high pressure washing or vibration)

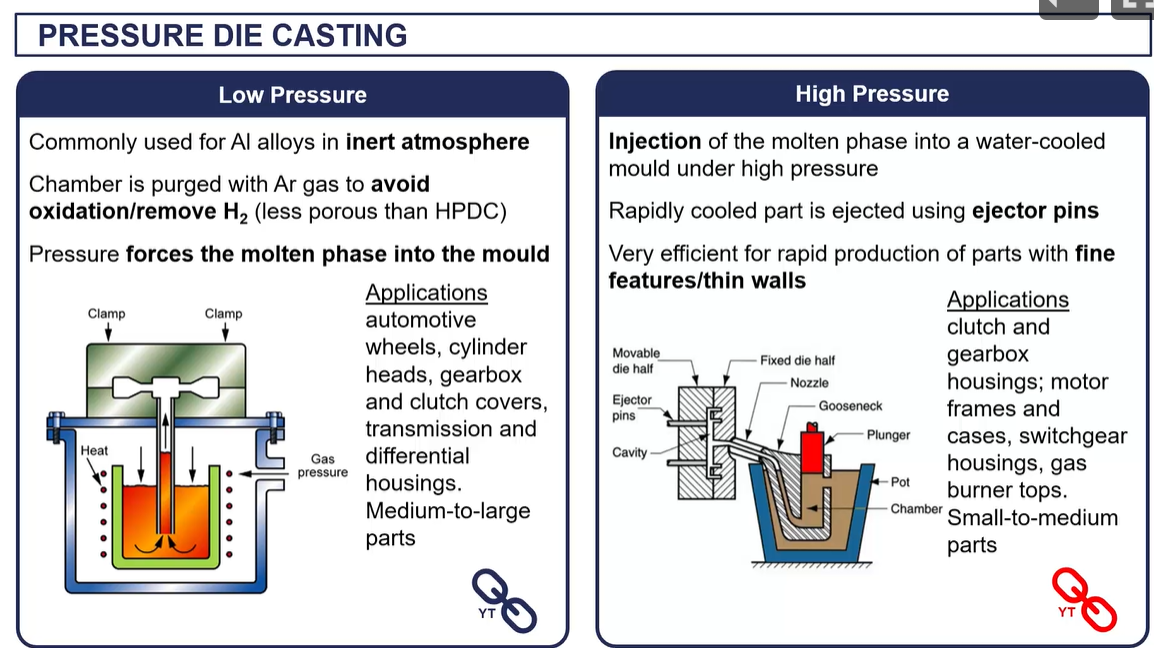
die casting
mass production process
used for non ferrous metal (zinc, aluminum magnesium)
uses a reusable metal mold (high thermal conductivity) and water cooling
3 types = gravity die casting/ pressure die casting low/ high pressure die casting
3D metal objects/ any metal alloy
process = sand casting
features = surface finish is rough and the pits are associated with the sand in the molds
application =
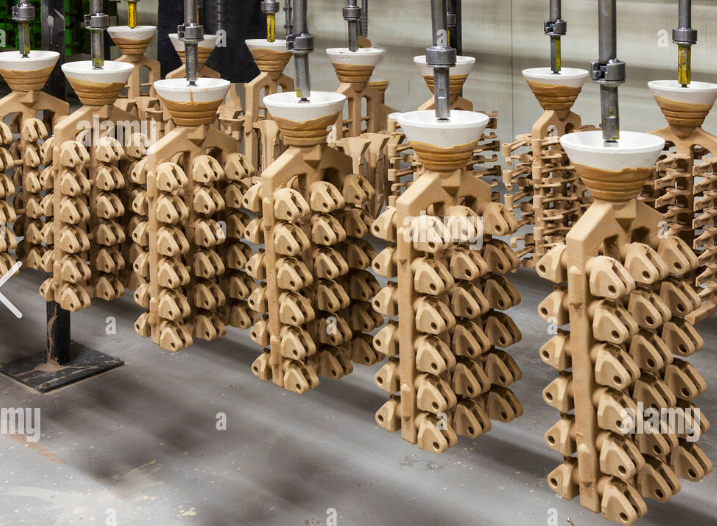

aluminum tree / turbine blades
process = investment casting - use this method because it you can make alot at the same time and they are all consistent
features/ microstructures = tree shape with multiple components on it / has a good surface finish as good as wax pattern
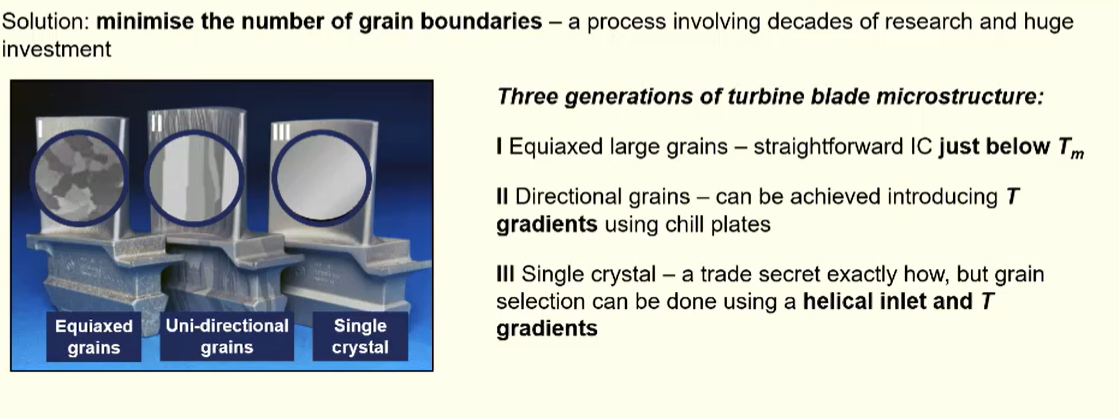
for blades they need excellent creep resistance
single crystal = no grain boundaries = no creep

gearheads
process = die casting
features/microstructure = metal mold and water cooling cause small uniaxial grains to be produced
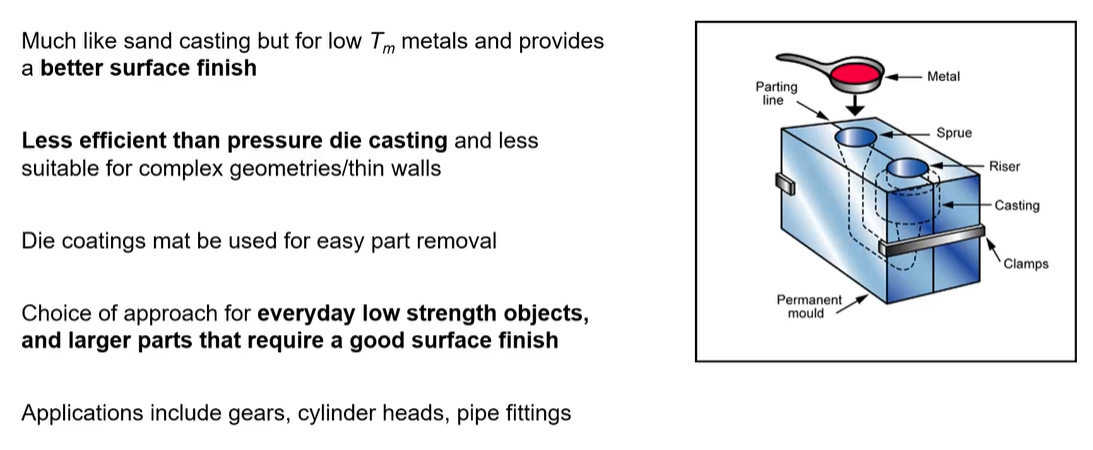
gears/ cylinder heads/ pipe fittings
process = gravity die casting
can reuse the mold, do not have to make a new 2 half of the mold
gives a good surface finish
high and low pressure die casting
look out for sand casting

look out for investment casting

look out for gravity die casting

look out for low pressure die casting

look out for high pressure die casting

when to do sand casting, investment casting or die casting?
determined by the melting temperature/ type of metal you are using/ part size you want to produce/ detail you want to achieve/ surface finish you want/ how much time and money needed in order to prepare
ship anchor
process = sand casting
doesn’t need a good surface finish and is made from a ferrous material
what to make only a few so sand casting is used
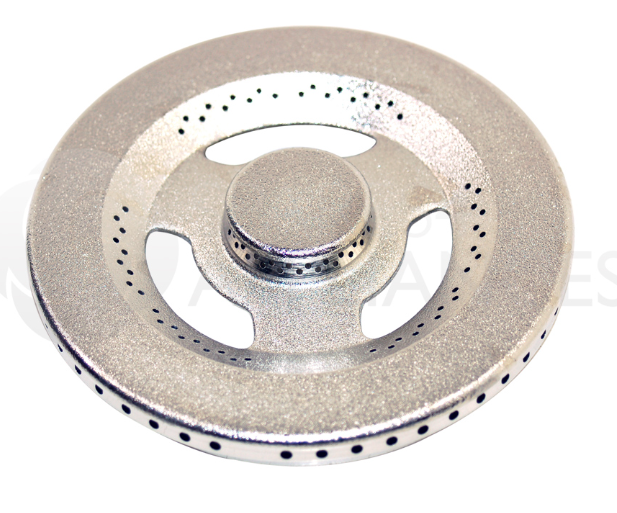

cooker hob/ ring burner
process = die casting
surface finish = good surface finish as it will be in someone’s kitchen
want to make multiple, therefore die cast is used
casting considerations
solidification and shrinkage
gas porosity
want consistently sized parts / uniform mechanical properties / uniform grain size
want to avoid porosity and segregation