W3 BONE MATRIX, CALLS AND STRUCTURE
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Ground substance (Bone matrix)
jelly like substance
aids in exchange of nutrients
helps with movement for collagen fibres
Collagen fibres (bone matrix)
contributes tensile strength
ability ti twist and bend
Calcium phosphate crystals (Bone Matrix)
provides compressive strength
Osteoprogenitor cells
stems cells that differentiate into osteoblasts

Osteoblasts
bone building cells, secrete collage fibres and ground substance
osteoblast - build
secretes bone matrix
osteocytes /bone-lining cells
mature bone cells that maintain the matrix
inactive osteoblasts
over see/sight - watching to see what’s going to happen
there if we need to build up bone again
osteoclasts
bone resorbing cells, break down matrix and release stored materials
osteoclasts = clear
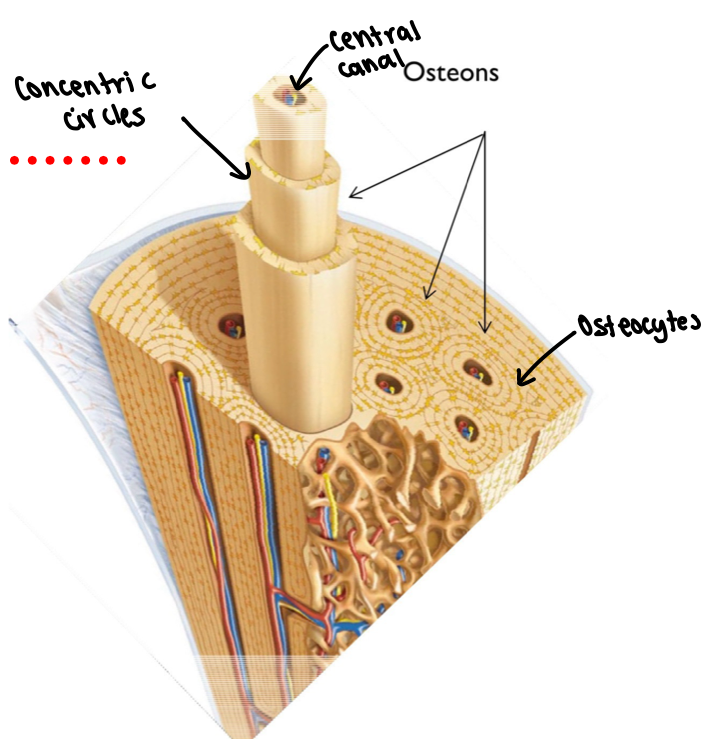
Compact bone (bone tissue)
dence and protective
compact tissue is arranged into osteons
runs parallel to the long axis of a bone (i.e. the shaft)
act as tiny weight bearing pillar
components of osteons
central canal - containing blood vessels and nerves
concentric circles - hollow cylinders of matric
osteocytes - lie between the cylinders of matrix
spongy bone (bone tissue)
lighter and more “adaptive”
osseous tissue arranges into a irregular lattice of this needle like stuctures called trabecule
precisely orientatated to resist forces from all directions and transfer weight without breaking
lighter than compact bone
in long bones, mainly found in the proximal and distal epiphysis
bone marrow can be found between gaps
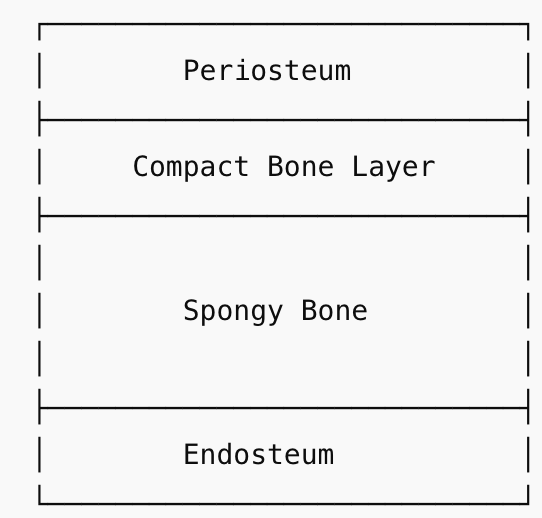
Structure of bone
outer layer is dense, smooth compact bone
internal layer of spongy bone
periosteum - outer connective tissue membrane
covers compact bone
contains blood vessels and nerves
endosteum - internal connective tissue membrane
covers spongy bone
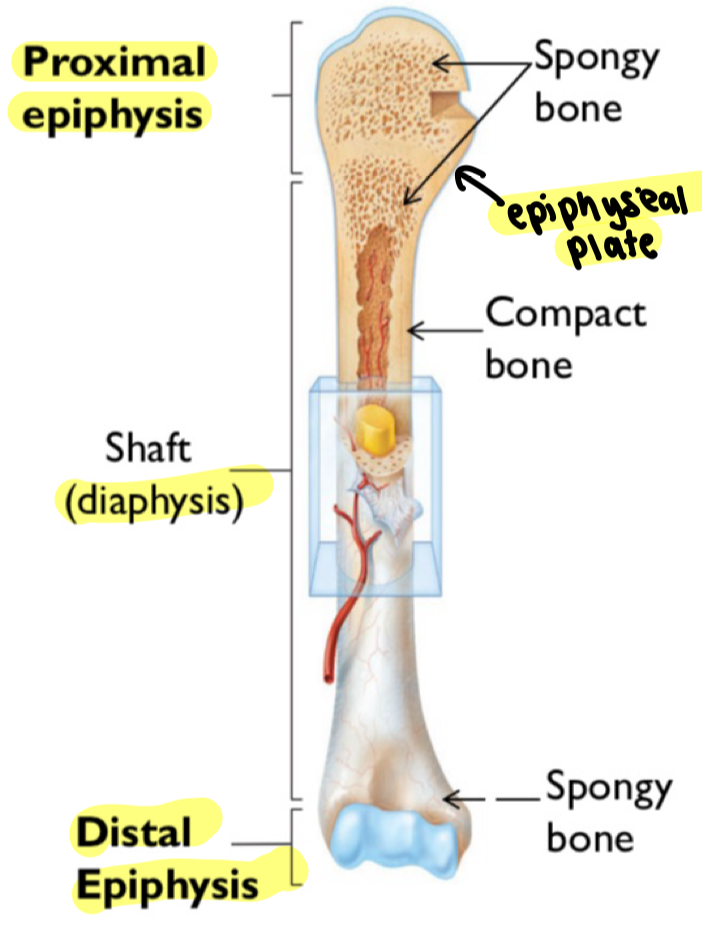
epiphysis (long bone)
“epi” means on top
composed mostly of spongy bone
red bone marrow stored in the spaces
epiphyseal plates (long bone)
also called growth plates
site of new bone growth
increasing bone length during childhood and adolescence
Diaphysis (long bone)
“dia” means through
composed mostly of compact bone
strength and support
Long bone
Types of bones