Properties of Conjugate Acid-Base Pairs-Unit 22C
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Ka
The acid dissociation constant, indicating the strength of an acid in solution.
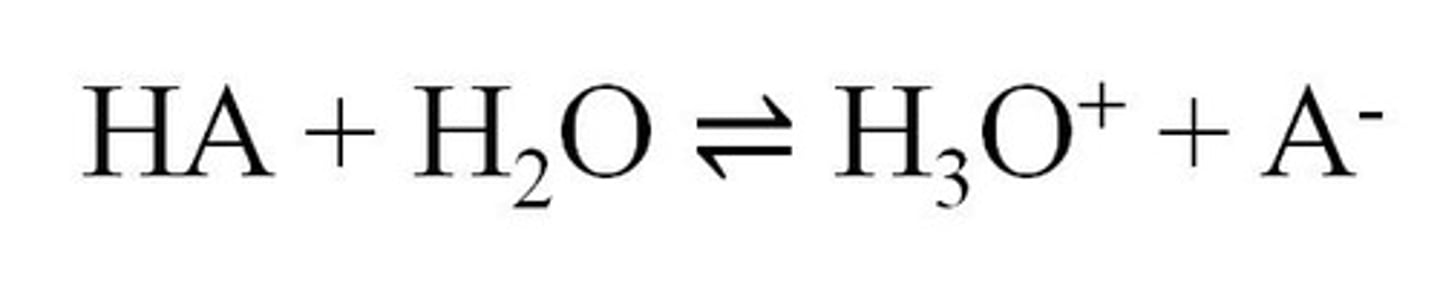
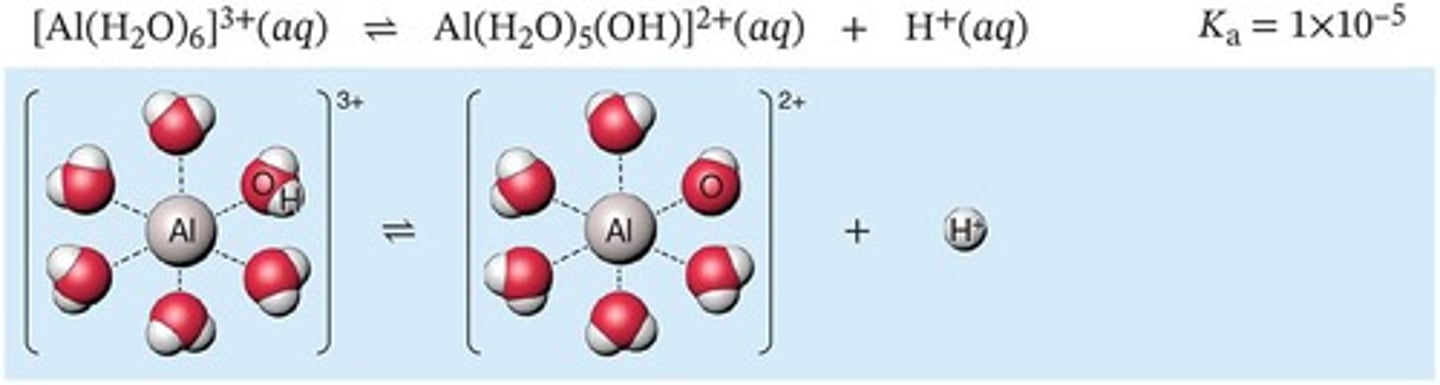
Kb
The base dissociation constant, indicating the strength of a base in solution.
pKa
The negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (pKa = -log(Ka)).
pKb
The negative logarithm of the base dissociation constant (pKb = -log(Kb)).
Kw
The ion product constant of water, equal to 1.0 × 10^-14 at 25°C.
Relationship between Ka and Kb
Ka × Kb = Kw.
HF
A weak acid with Ka = 6.3 × 10^-4.
F-
The conjugate base of HF.
NH3
A weak base with Kb = 1.8 × 10^-5.
NH4+
The conjugate acid of NH3.
pKw
The negative logarithm of Kw, equal to 14 at 25°C.
Acid Strength
As acid strength increases, Ka increases and pKa decreases.
Base Strength
As base strength increases, Kb increases and pKb decreases.
Weak Acid
An acid that partially dissociates in solution.
Weak Base
A base that partially dissociates in solution.
Conjugate Acid
The species formed when a base gains a proton.
Conjugate Base
The species formed when an acid loses a proton.
Strongest Conjugate Acid
The conjugate acid of the weakest base has the strongest acid strength.
pKa and Acid Strength
The lower the pKa value, the stronger the acid.
Conjugate Acid-Base Pair
A pair consisting of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid.
pKc
The negative logarithm of the equilibrium constant Kc.
pKa
The negative logarithm of the acid dissociation constant (pKa = -log Ka).
pH
The measure of the acidity or basicity of a solution, calculated as pH = -log[H3O+].
Strong Acid
An acid that completely dissociates in solution.
Strong Base
A base that completely dissociates in solution.
Acidic Solution
A solution with a pH less than 7.
Basic Solution
A solution with a pH greater than 7.
Neutral Solution
A solution with a pH equal to 7.
Hydrolysis
The reaction of a substance with water, leading to the formation of ions.
ICE Table
A table used to calculate the concentrations of reactants and products at equilibrium.
NH4+
Ammonium ion, a proton donor and weak acid.
F-
Fluoride ion, a proton acceptor and weak base.
H3O+
Hydronium ion, the form of water that carries a positive charge.
NaF
Sodium fluoride, a salt that dissociates into Na+ and F- in solution.
HF
Hydrofluoric acid, a weak acid that donates protons in solution.
NH3
Ammonia, a weak base that accepts protons in solution.
pH relationship
pH = pKw - pKb.