BME 320 - Exam 2
1/166
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
167 Terms
Serous glands
watery solution that contains enzymes
Mucous Glands
secrete mucins that hydrate to form mucous
Mixed Exocrine Glands
contain more than one type of gland cell and may produce two different secretions – one serous and one mucous.
Goblet Cells
Secrete mucins – usually due to
irritating stimulus and not hormones
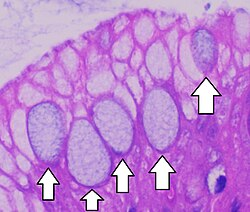
Secretory Sheet
Gland cells form an epithelium that releases secretions into an inner compartment (ie. Mucin secreting cells that line the stomach)
Connective tissue
most abundant, widespread and varied tissue type in the body
Common features of connective tissue
1. Specialized Cells
2. Extracellular Protein Fibers
3. Fluid known as Ground Substance
Functions of connective tissue
1. Establishing a framework for the body
2. Transporting fluids and dissolved materials
3. Protecting delicate organs
4. Supporting, surrounding and interconnecting other types of tissues
5. Storing energy reserves, especially in the forms of triglycerides
6. Defending the body from Invading microorganisms
Classifications of Connective tissue
connective tissue proper
Fluid connective tissue
Supporting connective tissue
Connective tissue proper
- includes many types of cells and extracellular fibers in syrupy ground substance
- Can have very different proportions in terms of # of cells and relative properties and amount of fibers to ground substance
- Loose (ie. Adipose) vs. Dense (ie. Tendon)
Fluid connective tissue
- Distinctive proportions of cells in a watery matrix that contains dissolved proteins
- Blood and Lymph
Supporting connective tissue
- Less diverse cell population and more densely packed fibers than seen in Connective Tissue Proper
- Cartilage and Bone
Limitation of prosthetic control
Limited number of sensor inputs and control features are decided during the initial design
Advantages of electronic prosthetic
various sensor inputs, complex control features via a microprocessor, and post-design feature additions.
C-Leg sensor inputs
knee angle and ankle moment
C-Leg adjustment
PC Sliders software used to optimize and adjust parameters
Genium knee feature
incorporates Inertia Motion Unit (IMU) for Optimized Physiological Gait (OPG)
C-Brace joint unit controls
microprocessor controls hydraulic valves based on knee angle, hydraulic force, and acceleration
Joint (articulation)
any place where two bones meet or join, controlling motion between them
Demands of joints
Stability
Mobility
Transfer of force (energy)
simple joint function
stability, such as sutural joints in the skull
Complex joint function
mobility, such as glenohumeral complex
Synarthrosis joint mobility
Immovable
Amphiarthrosis joint mobility
Slightly movable
Diarthrosis joint mobility
Freely movable (synovial)
Fibrous Joint
To attenuate shock but permit little or no movement
Cartilaginous joint
To attenuate force and allow some movement
Bony Joint
Two bones fused together, resulting in a totally rigid, immovable joint
gomphosis joint
binds teeth to bony sockets in the maxillae and mandible
synchondrosis joint
Articulating bones are held together by a thin layer of hyaline cartilage
syndesmosis joint connection
Bones are connected by a ligament
symphysis joint composition
plates of hyaline cartilage are separated and held together by fibrocartilage
:)
:)
Features of diarthrosis (synovial) joint
joint cavity
articular cartilage
articular capsule
synovial membrane
functions of synovial fluid
lubrication
nutrient distribution
shock absorption
Degrees of Freedom (DoF)
Number of independent coordinates required to completely specify the position of an object in space
Uniaxial
rotation about a single axis
Biaxial
Two dominant rotational motions are possible
Triaxial
Rotation is possible in three planes about three independent axes
Hinge joint
a type of synovial joint that allows movement in a single plane, like the opening and closing of a door
Pivot joint
a type of synovial joint that allows for rotation around a single axis, where a rounded or cylindrical end of one bone fits into a ring formed by another bone and a ligament
Condyloid joint
a type of synovial joint where an oval-shaped bone end fits into a similarly shaped hollow, allowing for movement in two planes: flexion/extension and abduction/adduction
Saddle joint
a type of synovial joint where the articulating bones have both concave and convex surfaces, interlocking like a rider in a saddle
Ball and socket joint
a type of joint where the rounded end of one bone fits into the cup-like depression of another bone, allowing for a wide range of motion in multiple directions. ex. hi
Instantaneous center of rotation
Hypothetical point for any rotating body where velocity is zero.
Convex-Concave Rule
The concave articulating surface moves in the same direction as the shaft of the bony lever
Knee joint compartments
medial and lateral
4 main knee ligaments
medial collateral
lateral collateral
anterior cruciate
posterior cruciate
Menisci function
deepen the joint
distribute load
aid in shock absorption
0 to 140 degrees
knee flexion range
LARS artificial ligament
made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), which encourages biological tissue ingrowth
Shoulder joint composition
three synovial joints (sternoclavicular, acromioclavicular, glenohumeral) and the scapulothoracic gliding mechanism
Glenohumeral joint type
highly mobile, triaxial, ball and socket joint
Glenoid labrum
Fibrocartilage rim that increases the depth of the glenoid fossa articulation by 50%
Scapulothoracic joint
Crucial for allowing the full range of motion of the shoulder, contributing 60 degrees to the 180 degrees of abduction
Anterior dislocations
Account for 85-98% of shoulder dislocations in the ER
Nucleus pulposus
A central gelatinous mass that acts hydrostatically to cushion and distribute loads. the inner, gel-like center of the intervertebral discs in the spine. It is made mostly of water, type II collagen, and proteoglycans, which allow it to act as a shock absorber for the spine. It plays a key role in spinal flexibility and stability by absorbing and distributing the forces placed on the vertebrae.
Annulus fibrosus
Consists of about 90 concentric bands of collagenous tissue that restrain excessive motion
Shear stress
created by spinal rotation
Bone Function
support
storage of minerals
blood cell production
protection
leverage
Two types of bone
compact (dense/cortical) bone and spongy (cancellous/trabecular) bone
Bone matrix composition
2/3 hydroxyapatite crystals and 1/3 collagen fibers
Osteocyte
To maintain and monitor the protein and mineral content of the matrix and participate in bone repair
Osteoblasts
Produces new bone matrix (osteogenesis)
Osteoprogenitor cells
Mesenchymal stem cells that differentiate into osteoblasts
Osteoclasts
giant, multinucleated cells that break down bone matrix (osteolysis)
Osteon
(Haversian system) The functional and structural unit of mature compact bone
Compact bone concentric lamellae
Rings of bone that surround the central canal, making up the bulk of an osteon
Compact bone canaliculi
Tiny interconnecting channels that connect adjacent lacunae and the central canal, permitting cell communication
Spongy bone trabeculae
An open lattice of narrow rods and plates of bone, with space for red bone marrow between them
Periosteum
isolates bone
provides a route for circulatory/nervous supply
participates in bone growth and repair
Endosteum
An incomplete cellular layer lining the marrow cavity that aids in bone growth, repair, and modeling
Anisotropic
elastic modulus depends on the direction of loading (strongest in compression)
Viscoelastic
Stress-Strain relationship depends on the rate of loading
Wolff’s Law
Bone remodels along lines of stress, changes in form and function lead to changes in internal architecture
Piezoelectric effect
Stress on bone produces small electrical fields, to which osteoblasts are sensitive, guiding remodeling
Parathyroid hormone effect
Increases blood calcium levels by stimulating osteoclasts and increasing intestinal absorption
Calcitonin effect
It decreases blood calcium levels by inhibiting osteoclast activity and increasing kidney excretion
Intramembranous ossification
The process where mesenchymal tissue is directly converted into dermal bone, forming bones like the flat bones of the skull, clavicle, and mandible
Endochondral Ossification
Bone develops from a pre-existing hyaline cartilage model, this is how most bones form.
Fracture repair
Formation of a fracture hematoma (blood clot)
Formation of an external callus of cartilage and bone and an internal callus of spongy bone
Cartilage of the external callus is replaced by bone and struts of spongy bone unite the broken ends
Remodeling occurs over time, where the initial swelling marks the location of the fracture
Osteopenia
Condition where bones become thinner and weaker as a normal part of aging, starting between ages 30-40
Osteoporosis
Condition where bone mass is reduced enough to compromise normal function
Animal model
To predict how a treatment will behave in a human wound under clinical conditions
Pig model
Anatomic and physiologic similarities of of its skin to human skin
Porcine epidermis thickness
30-140 micrometers
human epidermis thickness
50-120 micrometers
Porcine skin
Lacks a significant panniculus carnosus, similar to humans, as they are not loose-skinned animals
reepithelialization
how pigs and humans close wounds
Partial thickness wound model
To evaluate the impact of wound agents on healing in the short term, essentially a safety test
Full thickness wound model
To evaluate an agents impact on healing and the nature of the resultant scar, often with induced infection
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death where cells fragment into membrane-bound particles, reducing the inflammatory response
Nanocrystal formation
formed using an advanced materials process called physical vapor deposition (PVD)
Features of connective tissue
specialized cells
extracellular protein fibers
fluid known as ground substance
Constituents of tissue matrix
extracellular protein fibers
ground substance
Connective tissue functions
Framework
fluid transport
organ protection
interconnecting tissues
energy storage
defense
Connective tissue classifications
connective tissue proper
fluid connective tissues
supporting connective tissues
CTP cell types
fibroblasts
fibrocytes
adipocytes
mesenchymal cells
melanocytes
mast cells
lymphocytes
macrophages
CTP fiber types
collagen fibers
reticular fibers
elastic fibers
Loose connective tissue
act as a packing material of the body