Urinary System
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Name the strong transparent covering that encases the
kidney.
Fibrous capsule
Where does the ureter penetrate the
kidney
Hilum
The ureter, blood vessels, and nerves penetrate the kidney on its medial surface
True
The fibrous capsule is a layer of adipose tissue that surrounds the kidney.
False
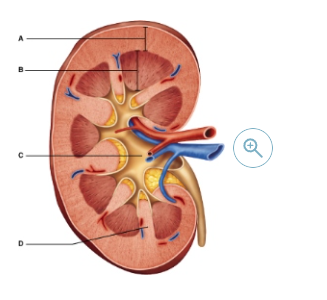
Which letter represents the region that combines several minor calyces to form two or three major calyces?
c
Which of the following is NOT a major urine formation process
micturition
The entire responsibility for urine formation lies with the nephron
False
Granular cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) regulate GFR indirectly through which mechanism?
renin-angiotensin mechanism
Through the tubuloglomerular feedback mechanism, how would an increase in filtrate NaCl concentration affect afferent arteriole diameter?
Afferent arteriole diameter would decrease.
What does a high concentration of NaCl in the renal tubule at the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) most likely indicate?
insufficient NaCl reabsorption due to high GFR
The myogenic mechanism of renal autoregulation primarily involves smooth muscle in which blood vessels?
afferent arterioles
Macula densa cells of the juxtaglomerular apparatus (JGA) regulate GFR through which intrinsic mechanism?
tubuloglomerular feedback
Which of the following are mechanisms of intrinsic control of glomerular filtration (renal autoregulation)?
myogenic mechanism and tubuloglomerular feedback
GFR regulation mechanisms primarily affect which of the following?
glomerular hydrostatic pressure (HPg)
Which of the following best describes glomerular filtration rate (GFR)?
the volume of filtrate created by the kidneys per minute
Patients with uncontrolled diabetes mellitus often have glucose in their urine. This is because the concentration of glucose in the filtrate exceeds the ____________ of the carrier proteins in the proximal tubule
Transport maximum
Reabsorption of which of the following drives the reabsorption of water and many other solutes in the proximal tubule?
Sodium
Through which pathway are most water and solutes reabsorbed in the kidney tubule?
Transcellular
Which of the following statements best describes the difference between the intrinsic and extrinsic controls of the kidney
Extrinsic controls have the greatest effect on systemic blood pressure while intrinsic controls have a greater effect on GFR.
What is the limiting factor for the reabsorption of most actively transported solutes in the proximal tubule?
number of transport carriers in the luminal membrane
Which of the following transporters in the luminal membrane results in secretion?
Na - H countertransport
The active transport of which ion out of proximal convoluted tubule cells causes the reabsorption of both water and solutes?
sodium
The decreased intracellular concentration of sodium in tubular cells during active transport is caused by which of the following mechanisms?
the sodium-potassium ATPase pump in the basolateral membrane
During reabsorption of water in the proximal convoluted tubule, what causes water to diffuse from the lumen into the interstitial space?
an increase in the osmolarity of the interstitium
Most solutes that are reabsorbed in the proximal convoluted tubule use which of the following pathways?
transcellular
In severe dehydration or blood loss, what would be the levels of ADH and what would be the urine flow rate?
ADH - high; low urine flow rate (0.25 ml/min)
In overhydration, what would be the levels of ADH (high, normal, or low) and what would be the osmolarity of the urine?
ADH - low; 100 mOsm (urine)
What is the osmolarity of the filtrate at the end of the proximal tubule?
isotonic - 300 mOsm
Which of the following statements about ADH (antidiuretic hormone) is correct?
ADH is released by the posterior pituitary gland.
Which of the following statements about aldosterone is NOT correct?
Aldosterone increases sodium reabsorption by increasing the number of Na+ -K+ ATPase pumps in the luminal membrane of the proximal tubule.
The rate of kidney filtrate formation would normally be dependent upon all of the following factors except __________.
blood calcium level
When given to a patient, which of the following substances would increase his or her urinary output?
intravenous saline
What hormone promotes active tubular secretion of potassium ions and reabsorption of sodium ions in the distal convoluted tubule (DCT) and collecting ducts?
aldosterone
Secondary active transport of solutes requires the presence of all of the following except __________.
ATP
Which of the following materials is NOT reabsorbed in the nephron loop?
glucose
The reabsorption of sodium in the DCT is regulated primarily by __________.
aldosterone and ANP
How are nutrient molecules such as glucose and amino acids reabsorbed through the apical surfaces of the tubule epithelia?
by secondary active transport
Filtrate in a typical healthy nephron will NEVER include
__________.
blood cells and proteins
Which of the following is NOT a property used to establish the medullary osmotic gradient?
the blood flow through the ascending and descending portions of the vasa recta