Comp Sci Exam 1 2025
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
What does a computer system consist of?
A computer system consists of hardware, software, people working with it or using it, and the immediate environment.
What are some methods of data gathering?
Interview (structure/unstructured), questionnaire(open/closed), document collections and observations.
What are the 4 types of cloud computing?
IaaS – Infrastructure as a Service (raw computing power)
PaaS – Platform as a Service (frameworks for developers)
SaaS – Software as a Service (e.g. Kognity, ManageBac) (hosted online apps like Google Docs)
NaaS – Network as a Service (virtual networking services)
Advantages of SaaS
Low initial cost and requires few investments in installation, maintenance, and upgrading.
Can be scaled dynamically. (e.g. It can be used in a 10 people workshop, or it can be scaled up to a 1000 people school)
Disadvantages of SaaS
Slow performance - depends on internet
Data loss risk
Hard to integrate with other solutions is hard
Legacy Systems: Meaning, Reasons for use, Risks.
Old technology, hardware, computer system, or application program still in use
Used because:
Can’t convert data to newer formats
Can’t upgrade application
Risks:
Incompatible
High maintenance cost
Security issues (easily exploited)
Outdated web server. (e.g. IIS 4.0)
Outdated operating system (e.g. Windows XP)
Outdated web browsers (e.g. IE 6)
On-Premise (Local) Software
On-premises software is installed and runs on computers on the premises of the person or organization using the software, rather than at a remote facility such as a server farm or cloud.
Pros: Security, Backups can be controlled, Legacy software, Software+Feature control
Cons: Cost of hardware, Technical support, Lack of collaboration.
Changeover
Changeover: In organizations, sometimes we changeover our systems. It is the process of putting the new system online and retiring old ones.
Choice of implementation (conversion, changeover) method includes following four methods:
Parallel: Both systems work in parallel for a short period of time.
Pros: low risk
Cons: training period is extended, adoption of new system takes longer, higher cost due to the maintenance of two separate systems
Direct (immediate/Big bang): Plugs in new system and unplugs the old one at the same time.
Pros: less cost
Cons: risky, dangerous when new one is not working, need to be trained properly
Pilot: New system is introduced in one of the sites and extended to other sites over time.
Pros: low risk, pilot sites serve as models for the rest
Cons: only work with multiple sites
Phased: Converts one module of the system at a time.
Pros: low risk
Cons: Training period is extended, Adoption of new system takes longer
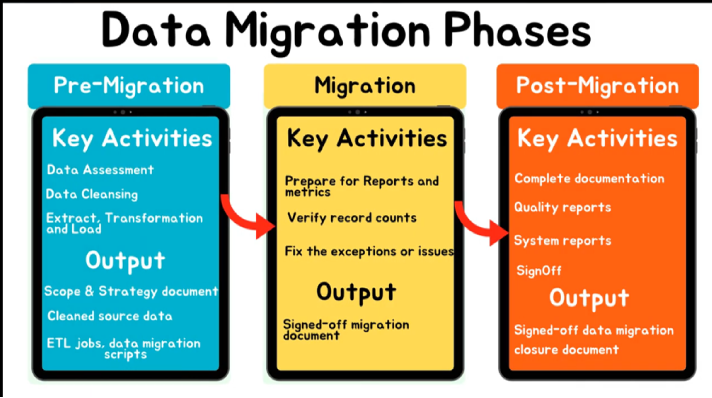
Data Migration
🔁 Data Migration
Moving data between formats/systems
Risks:
Data loss: Data may be lost or not transferred due to incomplete data transfer or errors during the process.
Security: ensure all the data is securely encrypted before migration
Compatibility: Incapability of moving the information due to parameters such as incompatibility. Data may also be misinterpreted due to incompatibilities. e.g. Change OS and unexpected file formats
Long Transfer Times: Connection speed or hardware restrictions
Unexpected Higher Cost: improper planning
Testing Types
Alpha Testing is done before the software product is made available to the general public. (Labratory - Developers)
Beta Testing includes comments and suggestions of the users. Unlike Alpha testing, users outside the company are involved in the testing. Their feedback is valuable and can be used to fix defects anderrors that were missed.
Black-box: Tests inputs/outputs, not code
White-box: Tests with access to internal code
User acceptance testing: Testing any new/updated system with its ultimate end users to see if it meets their expectation is very important.
User Documentation
A user documentation usually involves:
Minimum hardware and software requirements
Installation guide
How to start the system
How to use different features of the system
Screenshots explaining main features of the system
Example inputs and outputs
Explanations of error messages and troubleshooting guides
Information to contact the developer of the system if an undocumented question arises
Methods of Delivering User Training
Self-instruction: Users read a manual or watch a tutorial, or randomly do something in the system to figure out how it works. This type of training is only suitable for experienced computer users.
Formal classes: Users sit in a classroom, listen to an instructor who shows and explains how to use the system. This type of training is useful to train large amounts of staff as it is effective and relatively cheap, but if the size of the classes is too big, there is little time to deal with individual problems and questions.
Remote/Online training: An instructor trains a single user either by being in the same room or by some kind of remote connection (Skype, chat). This is the most effective way of training as it can be suited to user's needs and abilities but is very expensive compared to other.
Common Causes of Data loss
Human Error
Viruses & Malware
Hard Drive Damage
Power Outages
Computer Theft
Liquid Damage
Disasters
Software Corruption
Hard Drive Formatting
Hackers and Insiders
Software and Development
Data Loss prevention techniques
Back up: By copying all sensitive information on to a different medium than the one used in the system, like a second hard disk or CDs, chance or information loss can be reduced significantly. By storing these media physically separated from the system, data loss due to malicious activities can be prevented as well.
Hard Copies: In some cases, information can also be printed out to be archived, like books, texts, important contracts or scientific papers. However creating hard copies can be expensive and take up a large amount space. Hard copies are also liable to data loss, as in the case of print outs getting burned in fire
Strategies for managing releases and updates
Automatic updates: The system checks automatically for updates over the internet from time to time. If updates are available, they are downloaded and installed automatically.
Advantages:
Updates get installed automatically. Inexperienced users have an easy chance to get the updates.
No need for software manufacturer to contact every user about the new software.
Disadvantages:
Users miss updates if they are not connected to the internet.
If updates bring a major change of system functions, users might not be informed about it.
Manual update: The software manufacturer contacts every user about the new update and supplies the installation package to him to be installed.
Advantages:
Users have more control what updates they want to install
Users get to know if an update brings major changes to how the system works
Disadvantages:
Users might miss an update fixing security issues
Users might not know how to install the update
Users might harm system by wrongly installing update
Users might lose medium containing the update
Prototype
Prototypes are abstract representations of the system, often focusing on only one or two key aspects of the system. They are important in testing as each component of the system can be tested before implementing, and to illustrate the working of the future system to the client. (early versions of the system)
Benefits:
Attracts the attention of the client, since it encourages them to use it and "get a feel for it“
Provides just enough of the concept for the investors to decide if they want to fund the full production or not
Encourages active participation between users and developers
Gives an idea of the final product
Helps in the identification of problems with the efficiency or the design
Increases system development speed
Accessability
Accessibility refers to the potential of a service, product, device or environment to serve and meet the needs of as many individuals as possible.
A system characterized by high accessibility can meet the needs of many people, while a system with low accessibility presents barriers to specific groups of people.
Frequently, accessibility is studied in parallel with disabled people (people with special needs) and the use of various assistive technologies.
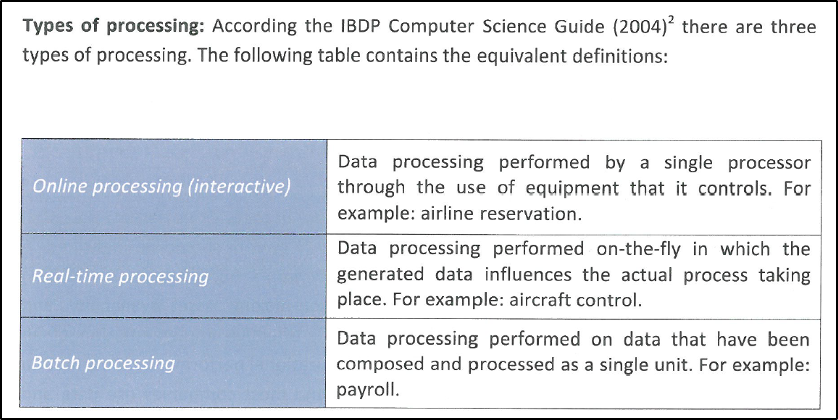
Types of Processing
Ergonomics
designing and arranging things people use for users to interact most efficiently and safely.
Usability
Usability refers to the potential of a product, application or website to accomplish user goals.
Usability relates to effectiveness, efficiency and satisfaction in a specified context of use.
Usability is the property of a system that determines how easy and self-explanatory the use of the system is for unexperienced end-users. It usually measures ergonomics and accessibility of the system.
Methods that can be used to improve the accessibility of systems
Touch screens
Voice recognition
Text-to-speech
Braille keyboards
Braille printers
Simpler interface with fewer buttons
Common Usability Issues
Complex navigation
Poor feedback
Inconsistent design
High cognitive load
Bad error messages
No accessibility
Slowness / crashes
Confusing interface
Overcrowded design
No help section
👉 All People Seem To Need Data Processing
That’s the 7 layers, in order:
Application
Presentation
Session
Transport
Network
Data Link
Physical
Why layers matter:
Easier to manage
Manufacturers can make compatible stuff
Tech updates can happen in one layer without breaking others
5. Protocols (Communication Rules)
What is a protocol?
A set of rules that governs:
What is sent
How it’s sent
When it’s sent
Examples to memorize:
TCP: Sends data reliably (e.g. websites)
FTP: File Transfer Protocol
SMTP: Email sending
3. Types of Networks
Just know these terms and what they stand for:
LAN: Local area (e.g. school)
WLAN: Wireless LAN
VLAN: Virtual LAN — divides network virtually
WAN: Wide Area (e.g. internet)
SAN: Storage network
VPN: Secure connection over internet
PAN: Personal (e.g. Bluetooth earbuds)
P2P: Peer-to-peer (no central server)
A hub consists of multiple ports. When a network device wishes to send data to some other device on the network, it sends the data to the hub. The hub then copies the data and sends it to all devices connected to its ports. The device waiting to receive the data accepts the data. All the other devices just ignore it.
A switch is also the connection point for multiple devices on a single network. However, unlike a hub, the switch can identify which network device is connected to which part. This allows the switch to transmit data to the exact port and network device for which it is intended.
Router is a more sophisticated device than both a hub and a switch. Its use is to join multiple networks and serve as an intermediary between these networks so that data can be exchanged effectively and efficiently between network devices of those networks.