Lecture 10: Gametogenesis, Fertilization and the Blastocyst
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
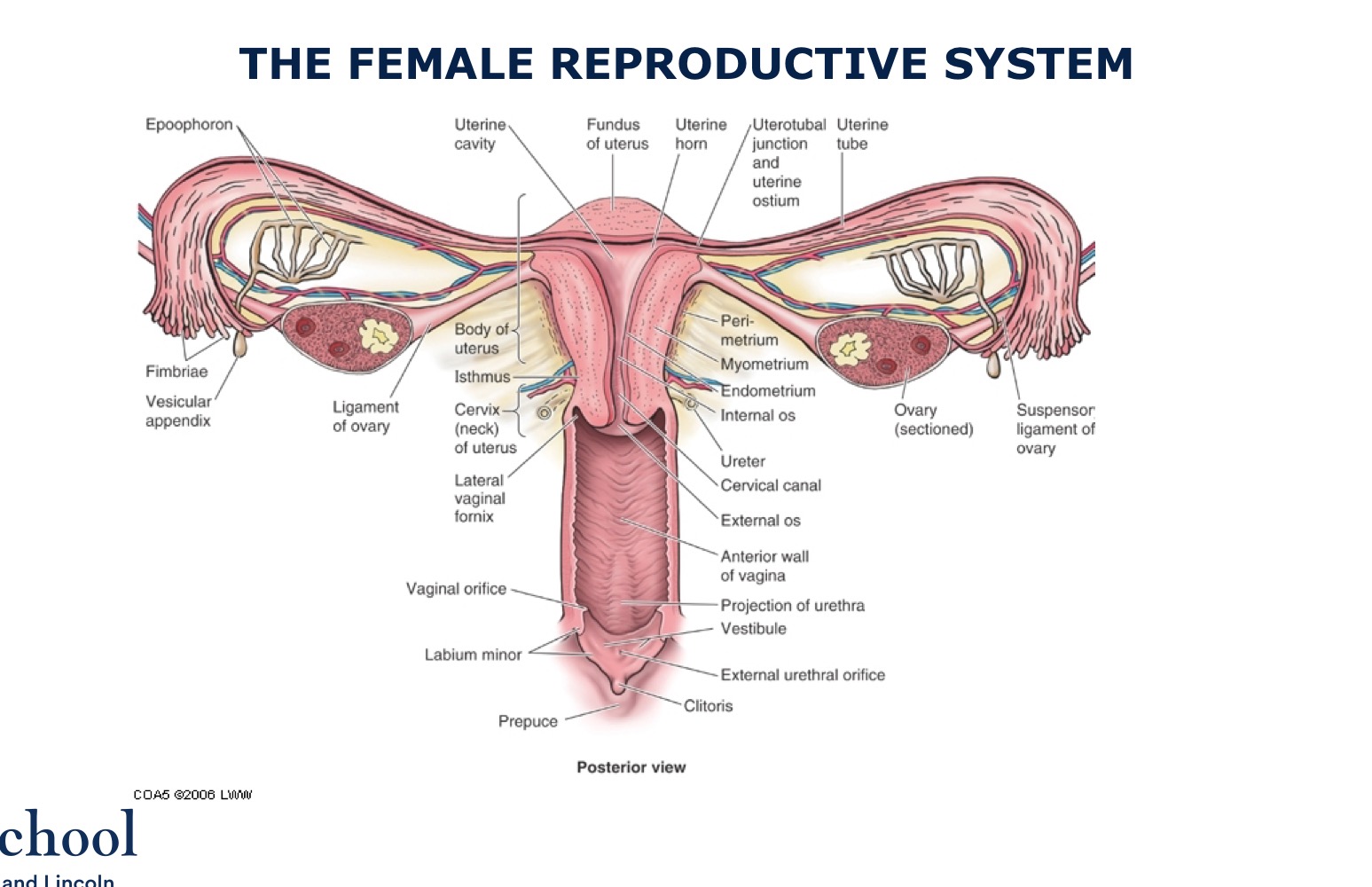
The female reproductive system
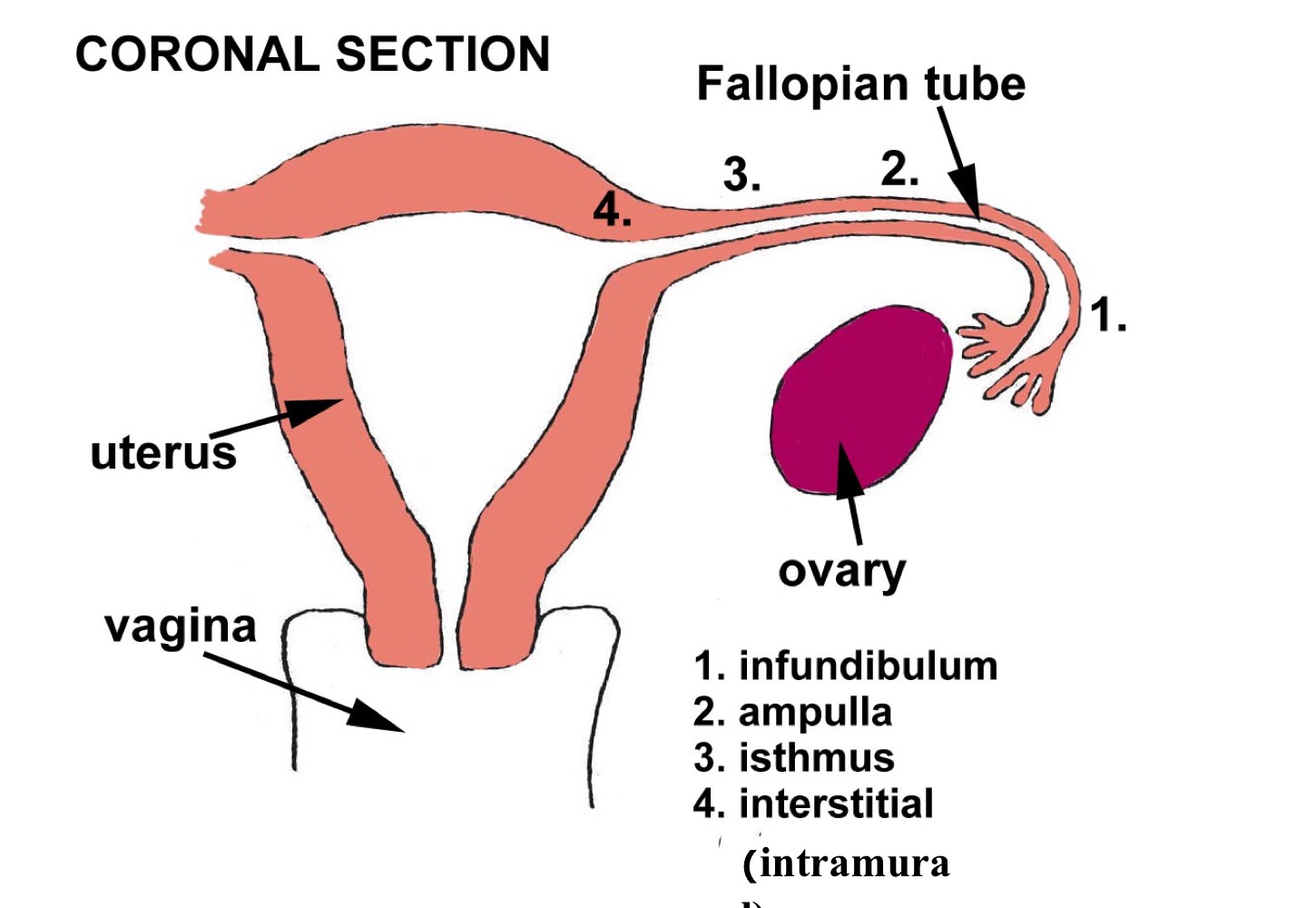
Coronal section of reproductive system
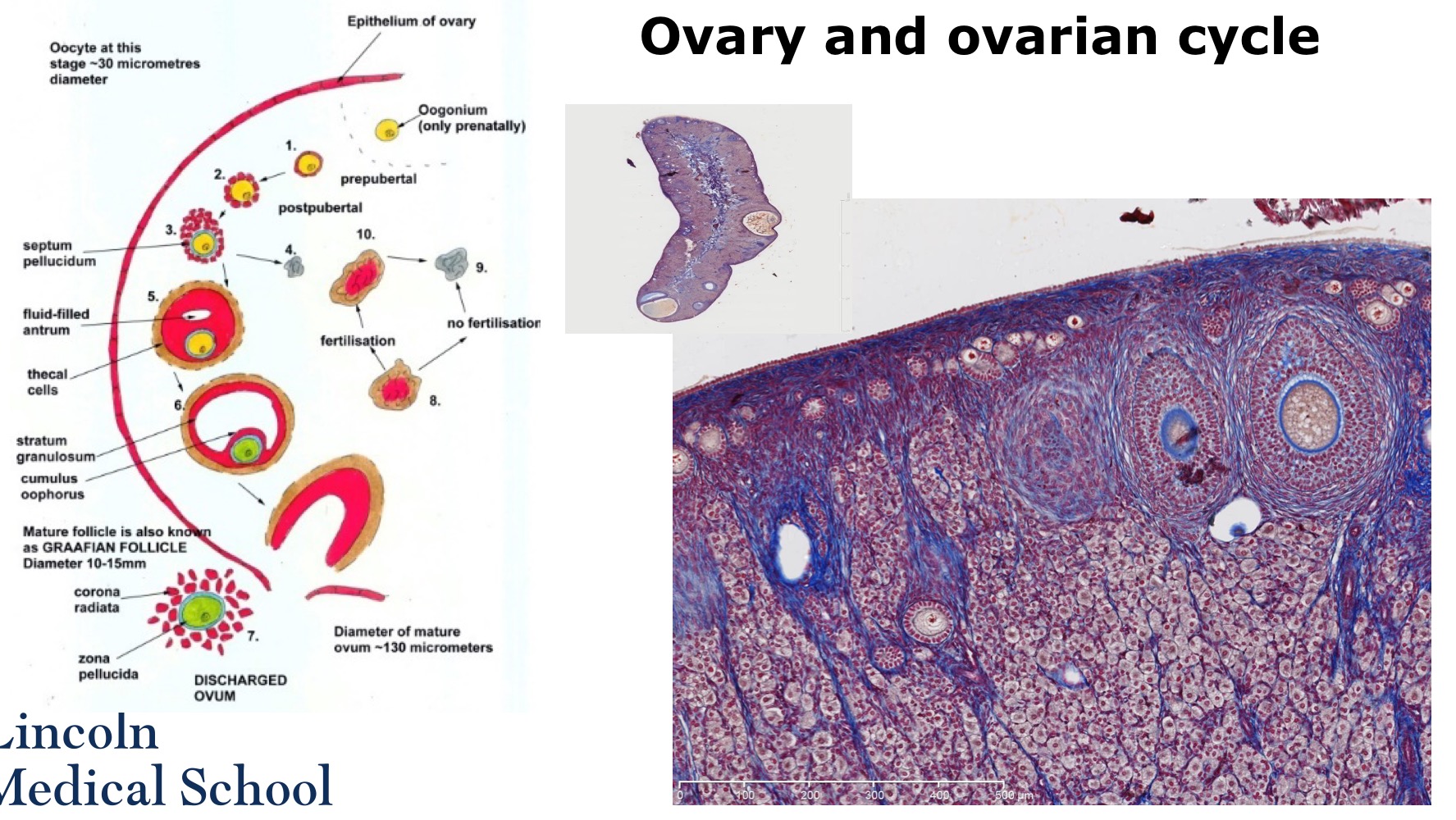
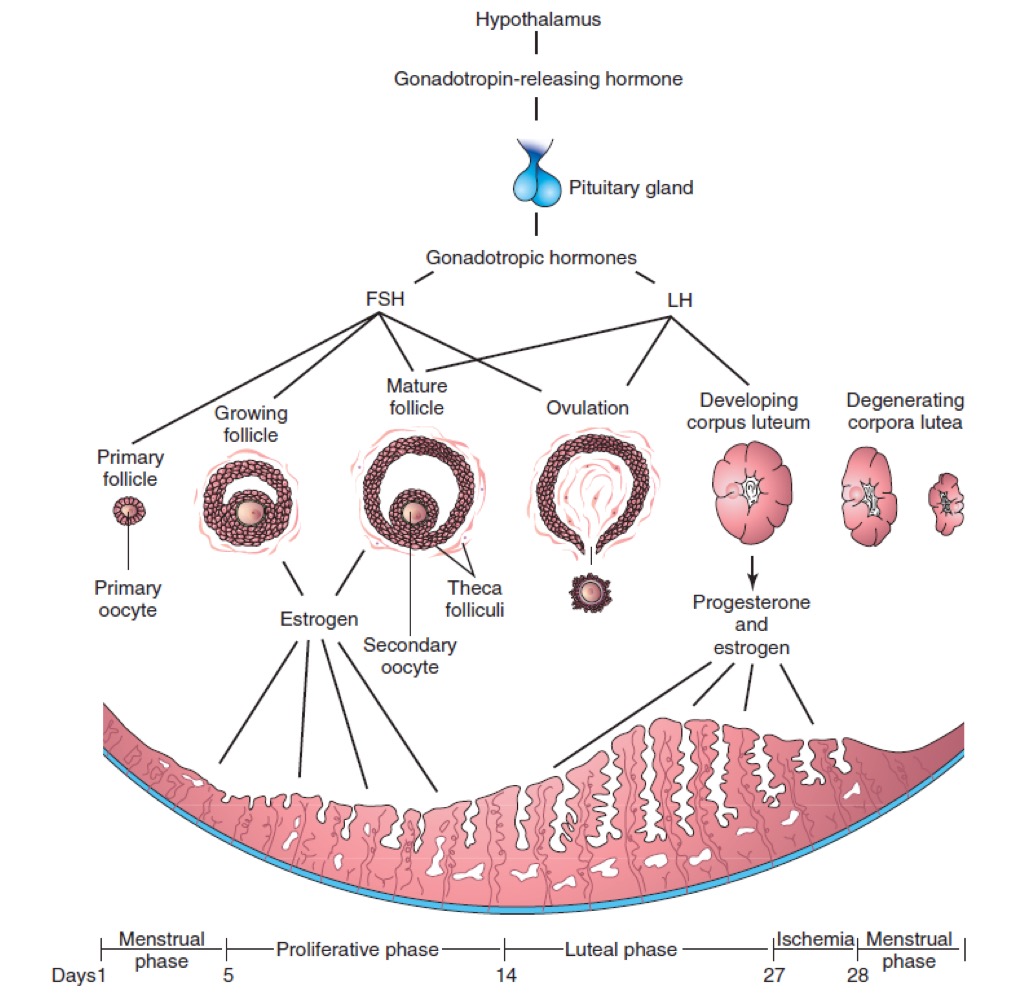
Ovary and the ovarian cycle
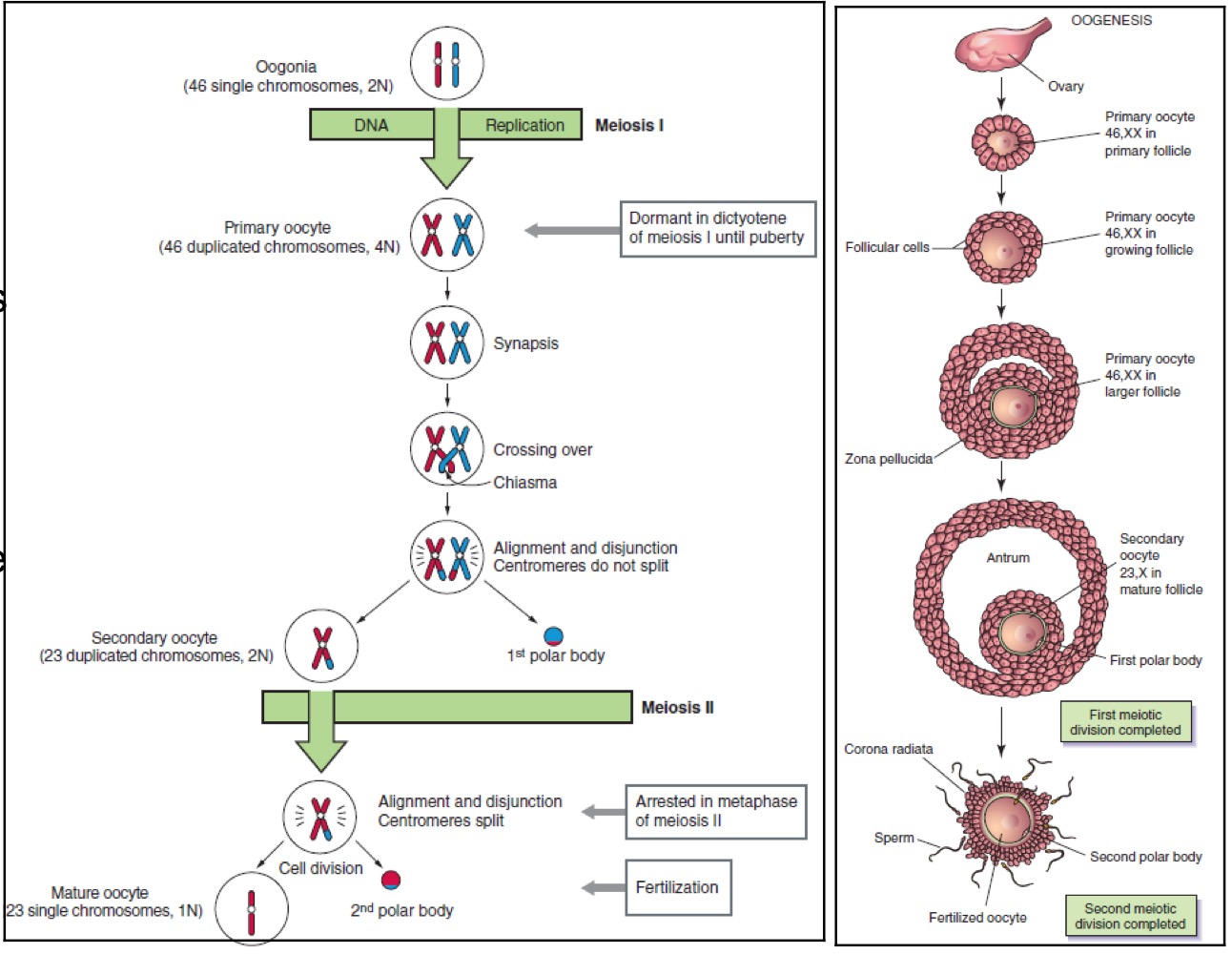
Gametogenesis
Gametogenesis in female is called oogensis
Surge in LH leads to completion of meiosis I to convert a 10 oocyte to 20 oocyte
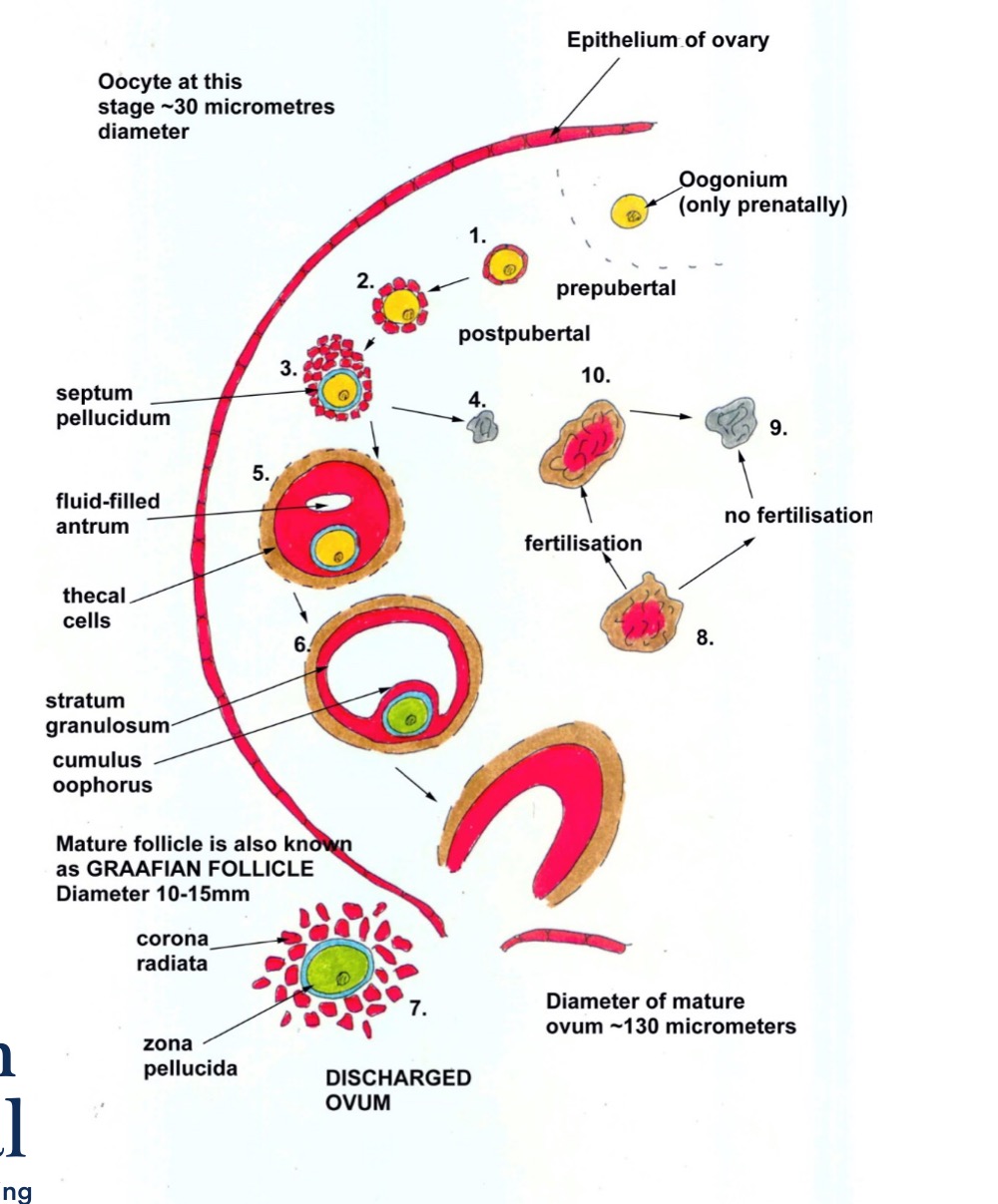
Step 1 of female gametogenesis
The primary oocyte is surrounded by a single layer of follicular cells (from the ovarian epithelium). Together they are known as the primary follicle
Step 2 of female gametogenesis
At the beginning of each cycle, 5-12 primary follicles begin to develop and become growing follicles.
Step 3 of FG
The follicular cells multiply and become several-layered. They also become separated from the ovum by an acellular mucopolysachharode layer, the septum pellucidum
Step 4 of FG
Usually all but one of the growing follicles degenerate to form a small corpus atreticum or scar
Step 5 of FG
The follicular cells of the remaining growing follicle secrete a fluid which produces a fluid-filled antrum within the follicle.
The ovarian non-gamete cells surrounding the follicle also become altered and form a thecal layer around the follicle.
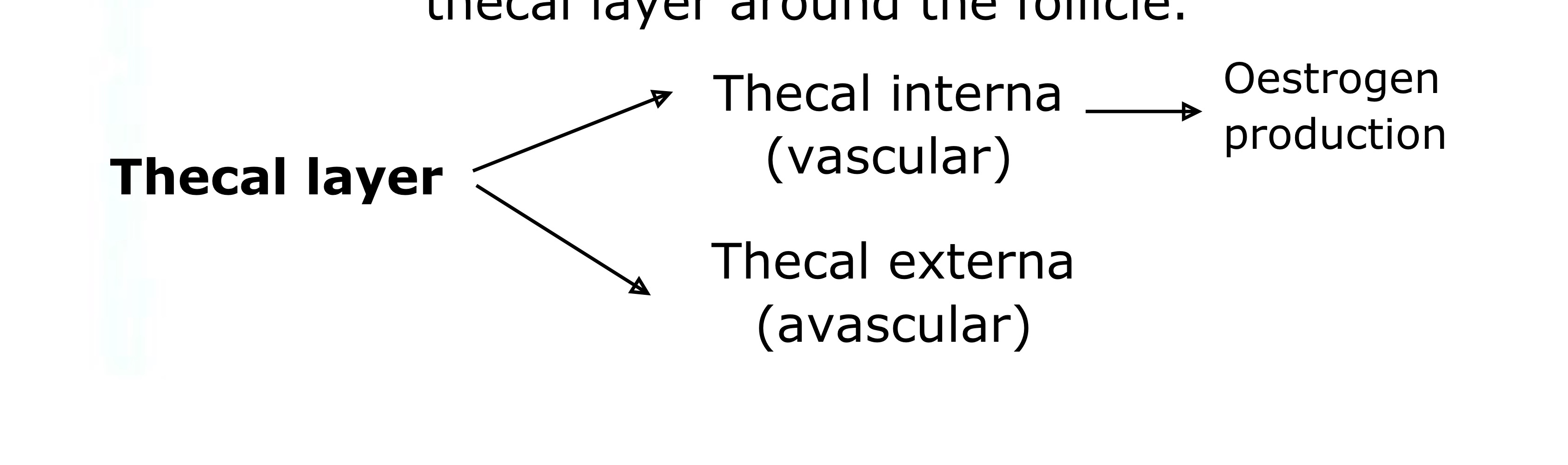
Step 6 of FG
In the mature or Graafian follicle, the majority if the follicular cells form the stratum granulosum, which will produce progesterone.
The remainder surround the oocyte as the cumulus oophorus. It is now a secondary oocyte.
Step 7 of the FG
The mature follicle ruptures to release the ovum. This retains a covering of follicular cells which form the corona radiate. The septum pellucidum has expanded to become the zona pellucida.
Step 8 of the FG
The cells of the theca interna and the stratum granulosum enlarge, turn yellowish and form the corpus luteum. It secrets large amounts of progesterone (and also oestrogen). Prior to ovulation the follicle produced mainly oestrogen.
Step 9 of FG
If fertilisation does not occur the corpus luteum has a life of only 12 days after which it degraded into the corpus albicans. The cessation of its hormonal output leads to menstruation
Step 10 of FG
If pregnancy occurs the corpus luteum is sustained by the HCG produced by the conceptus and forms a large corpus luteum of pregnancy. This will eventually form a large corpus albicans.
Female Gametogenesis overview
1,2,3 : Primary oocyte to primary follicle to growing follicle
4,5 : Growing follicle and corpus atreticum
6 : Graafian follicle and secondary oocyte
7: Release of oocyte
8,9,10 : Corpus luteum and corpus albicans
Female reproductive system overview
Male reproductive system
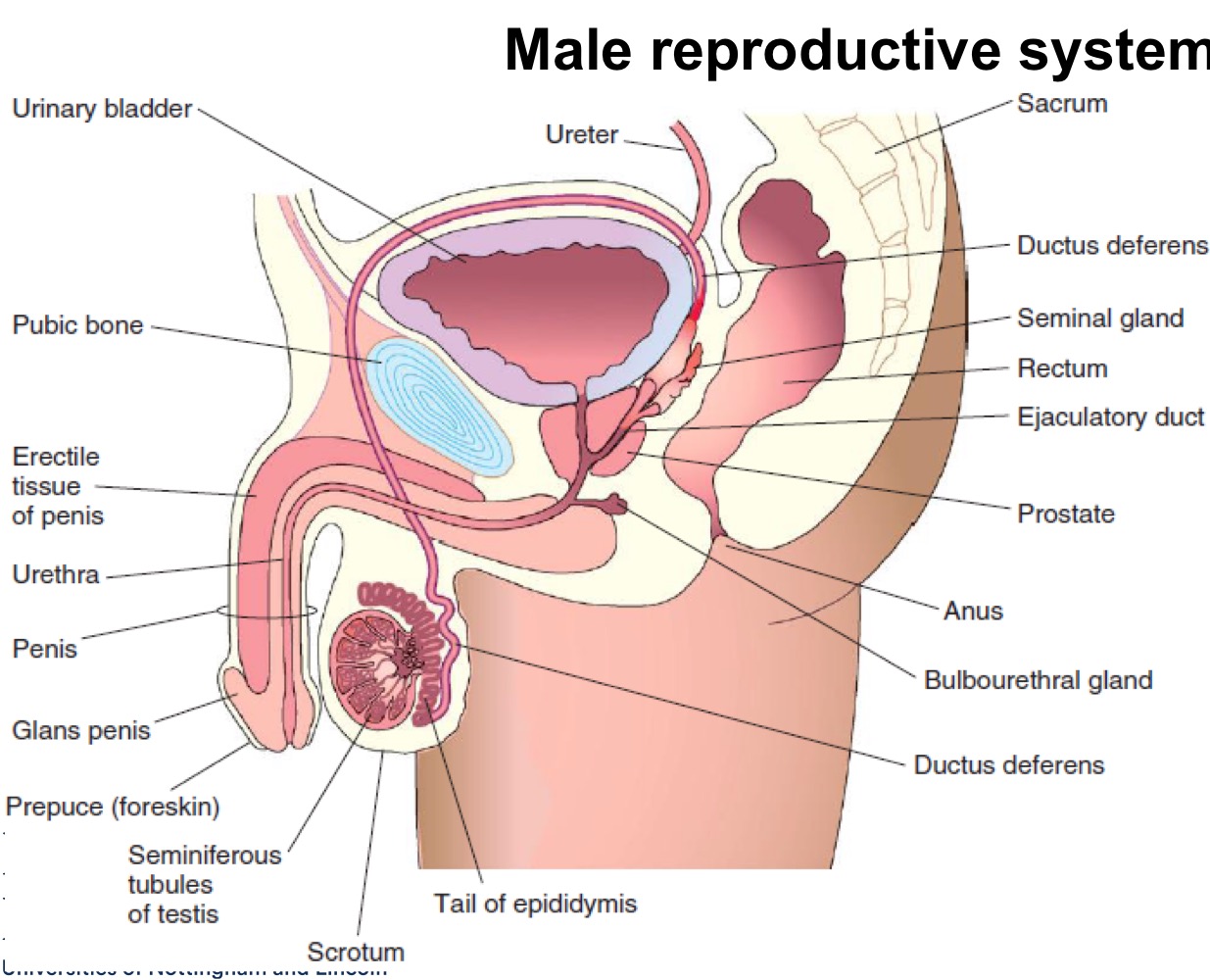
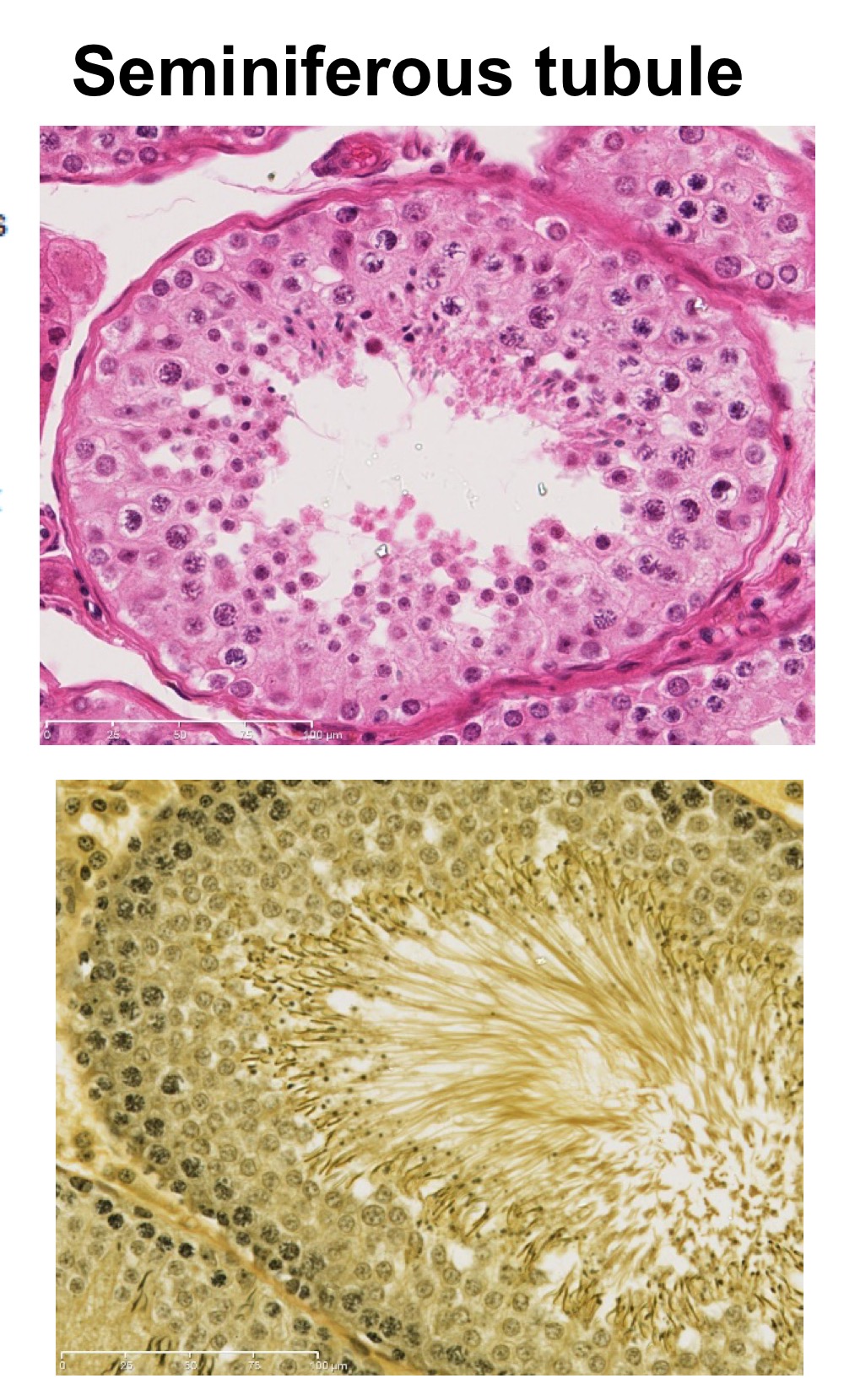
Seminiferous tubule overview
Gametogenesis in males overview
Spermatogenesis
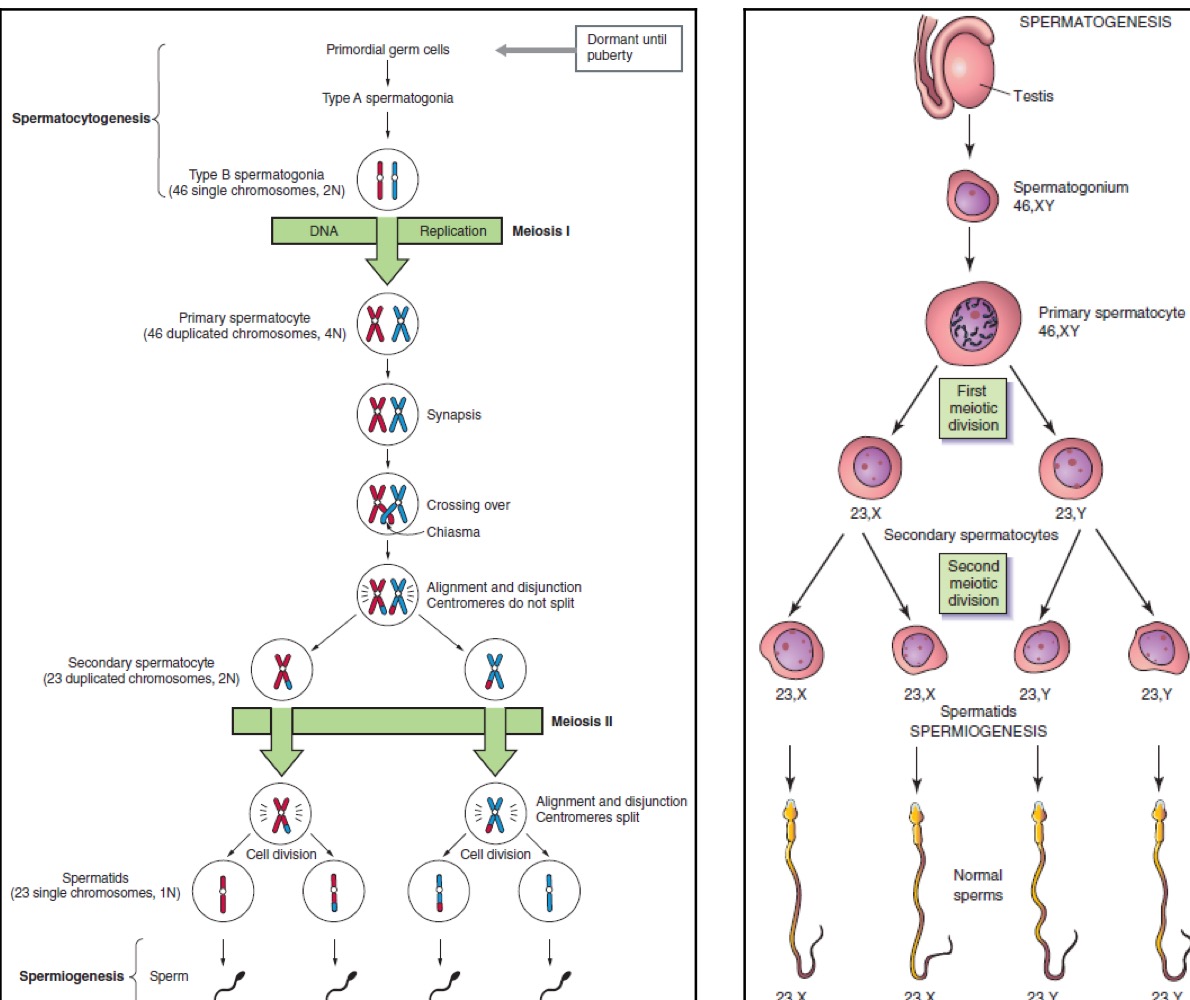
Spermatogenesis
Rounded spermatic differentiates to become the tadpole-shaped sperm via a process called Spermiogenesis
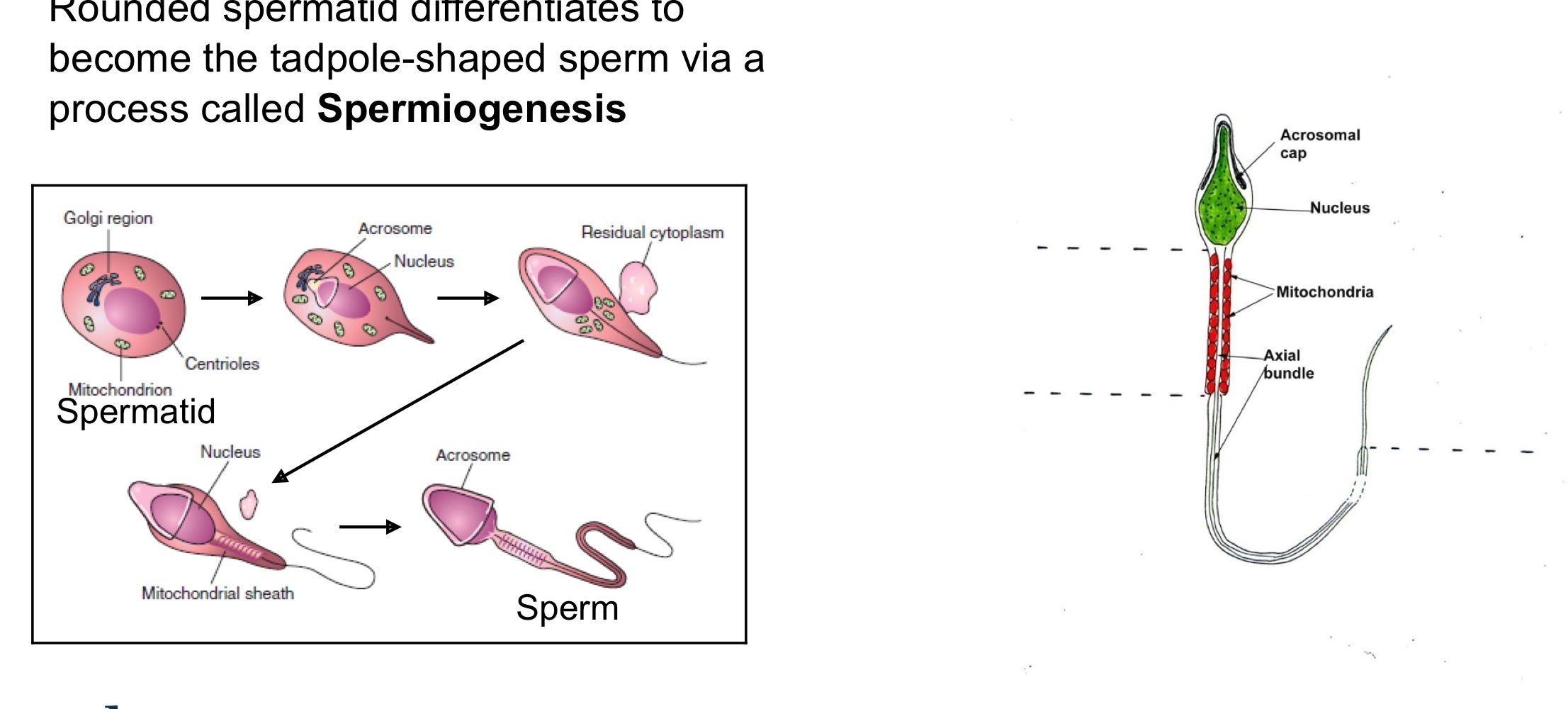
Comparison of male and female gametogenesis
Female reproductive system
The ovum is shed into the abdominal cavity and is caught by the fimbria of the fallopian tube. So, just for a moment it is ‘outisde’ the reproductive system.
Note that in the female the abdominal cavity communicates with the exterior (vagina, fallopian tube, abdominal cavity)
In the male, the abdominal cavity is closed.
Fertilisation process
Only 1% of the sperm deposited go past the cervix, several hours later sperm reach isthmus - become less motile - chemoattractants released from cumulus cells on ovulation make sperm motile again - swim to ampulla - fertilisation.
Why do sperm require capacitation
Condiitoning in female reproductive tract during which across all region loses glycoprotein coat.
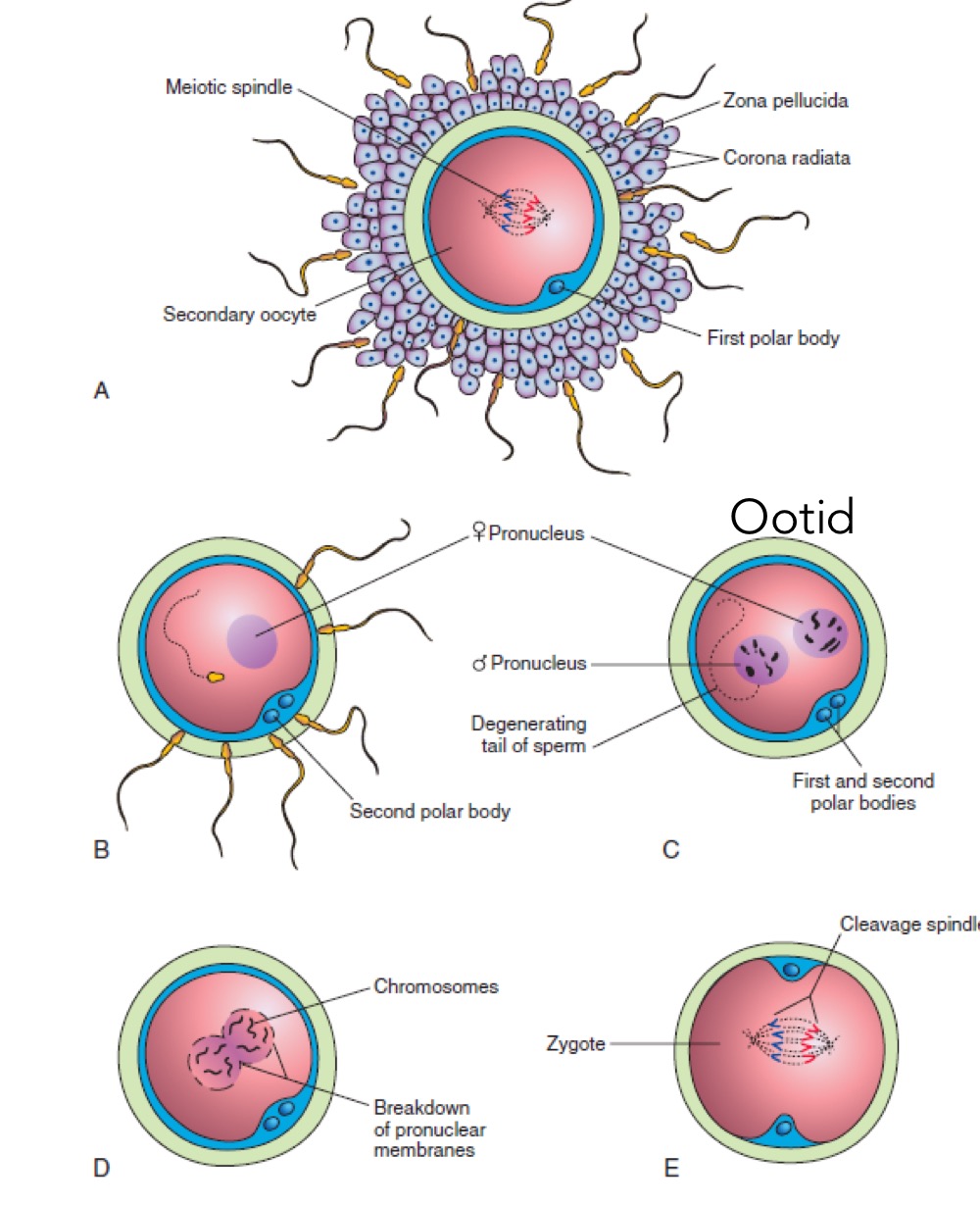
Overview of fertilisation (3 phases)
Sperm penetration of corona radiata
Sperm binding and penetration of the zona pellucida
Fusion of sperm and oocyte cell membranes (syngamy)
Fertilisation & cleavage
Secondary oocyte halted part way through 2nd meiosis division
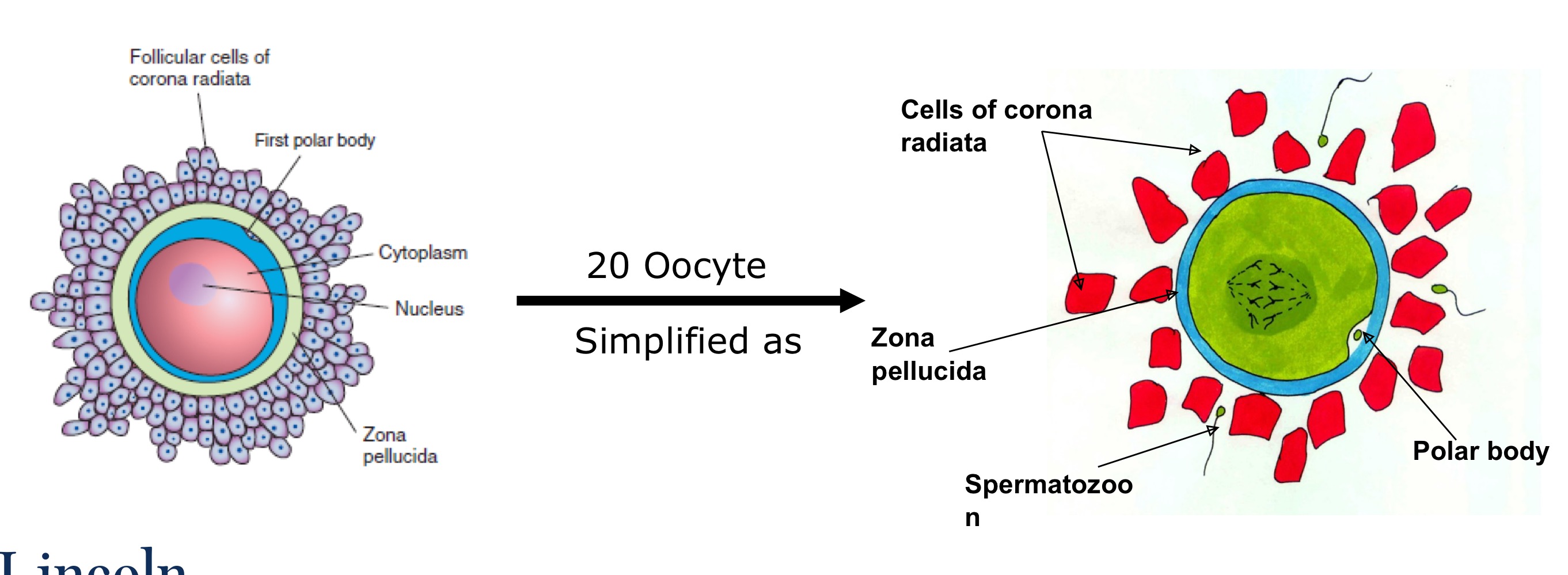
Fertilisation - What are acrosomal enzymes for?
Acromomal enzymes (acrosin) released via acrosomal reaction help disperse corona radiate and aid penetration of zona pellucida. Plasma membranes of gametes fuse and male nucleus is injected.
What results in completion of the 2nd meiotic division
Mature ovum, penetration by spermatozoon results in completion of 2nd meiotic division
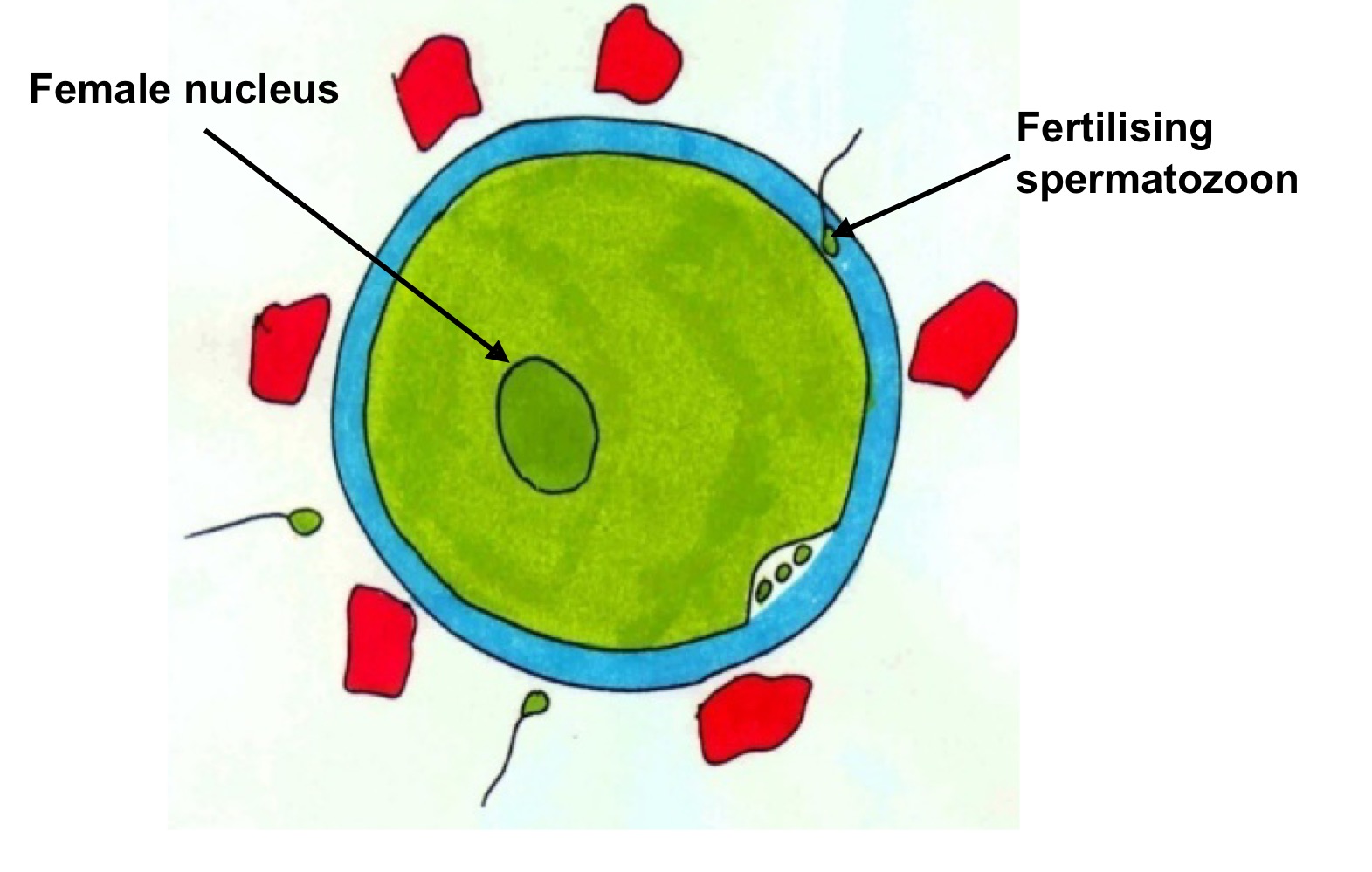
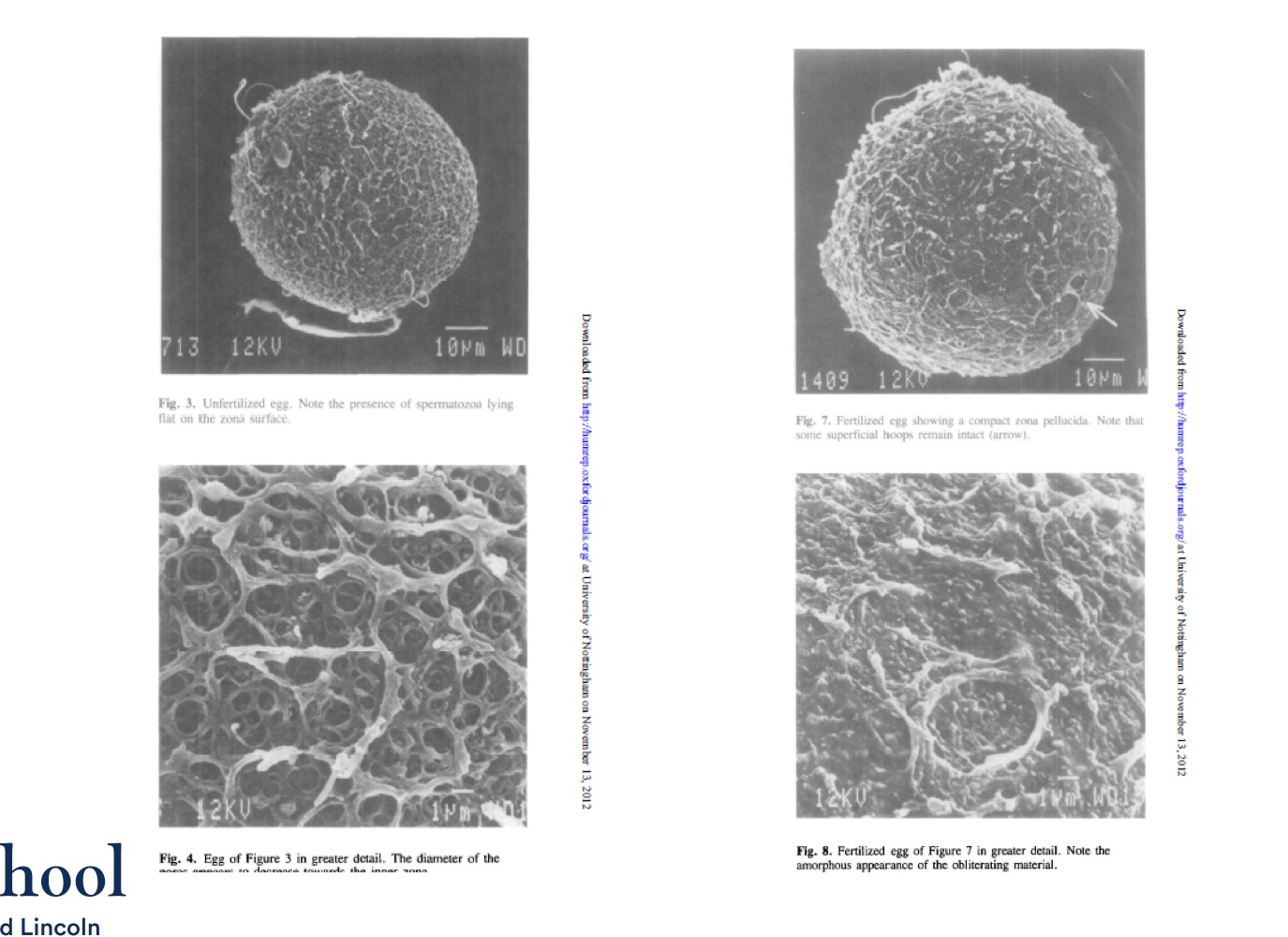
Role of enzymes released by cortical granules
Digest sperm receptor proteins ZP2 and ZP3 so that they can no longer bind sperm.
What does the zona (cortical) reaction
Leads to polyspermy block to prevent more than one sperm penetrating/ fertilising the ovum. The mechanism is not foolproof making diandric triploidy quite a common phenomenon.
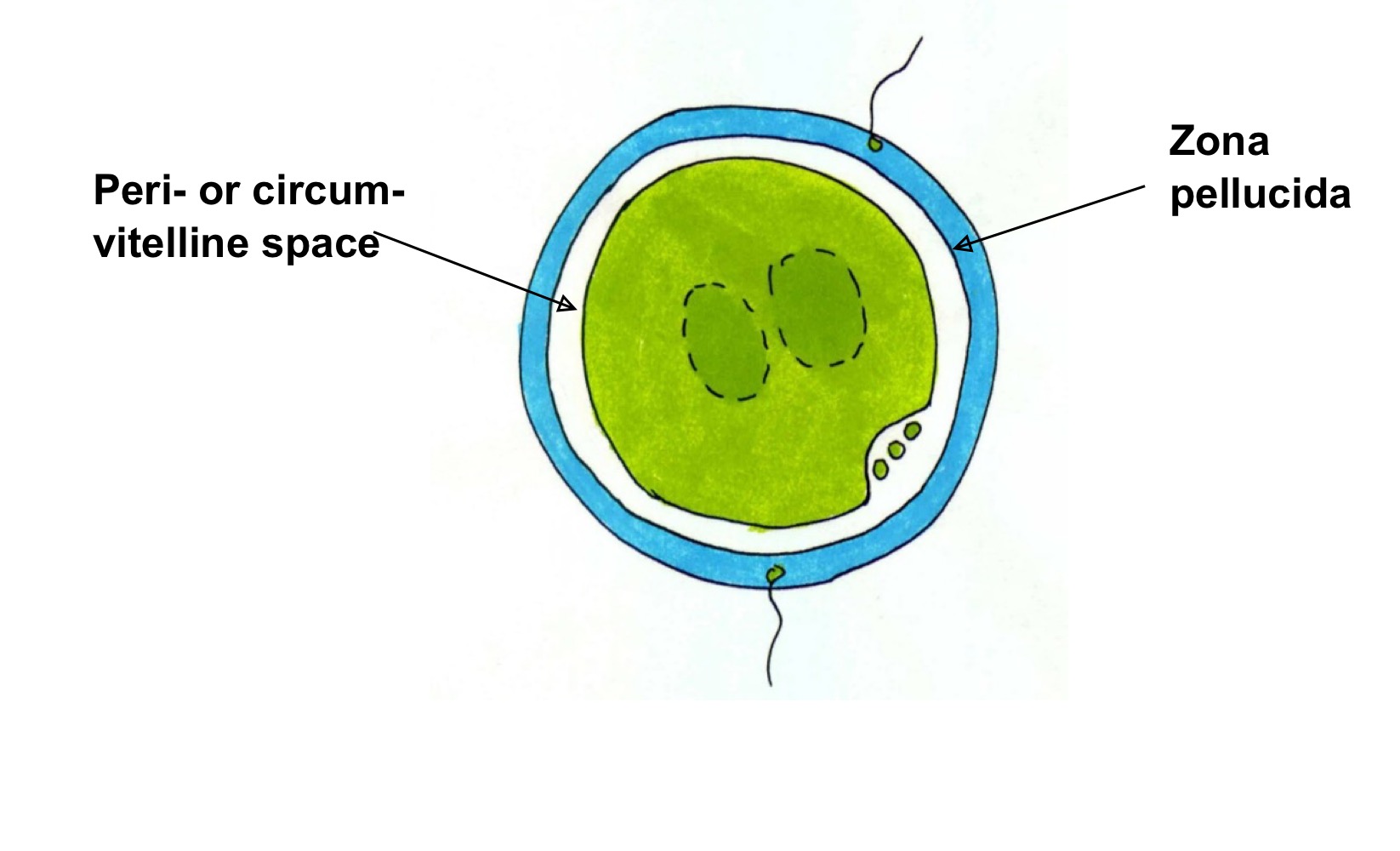
Zona reaction overview
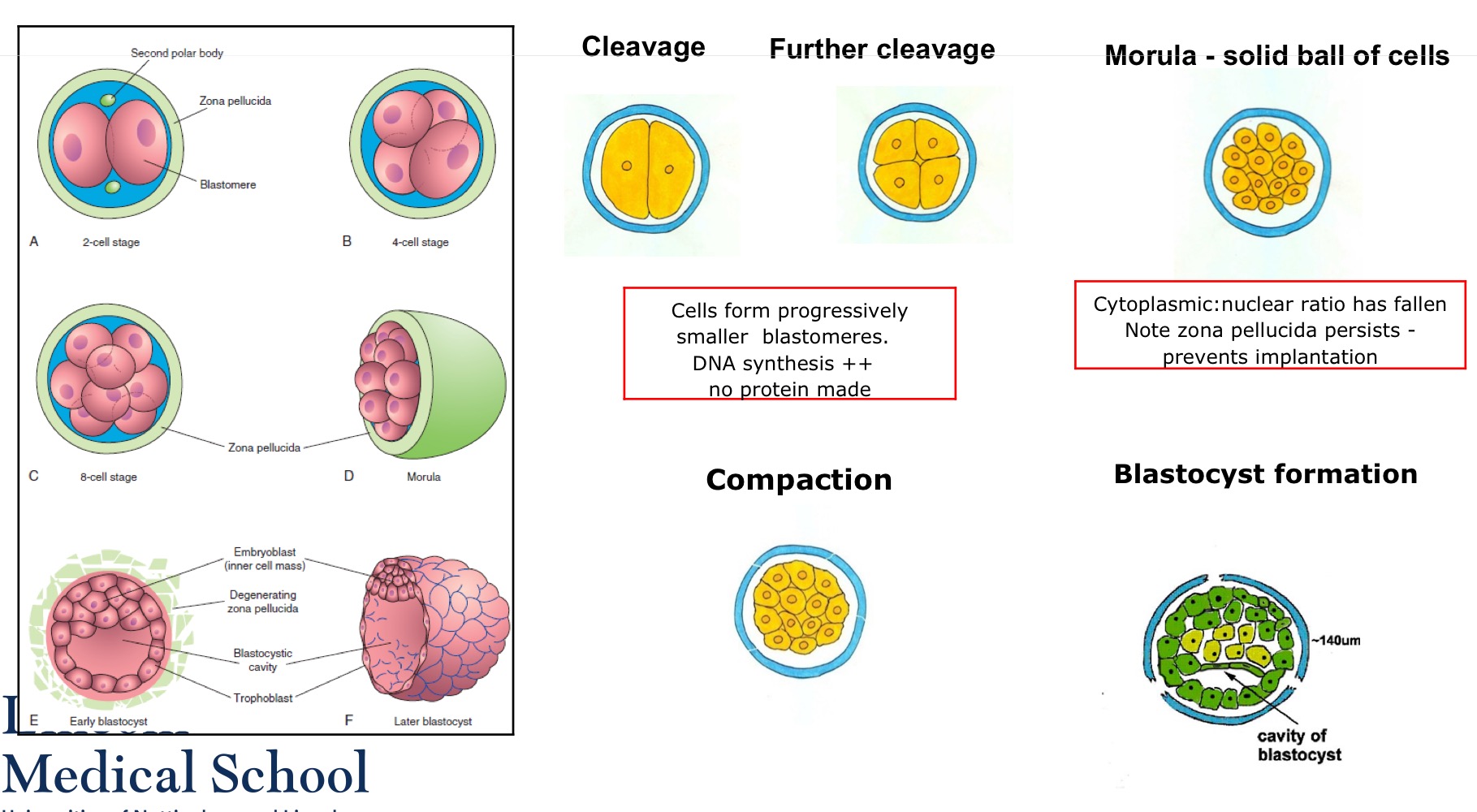
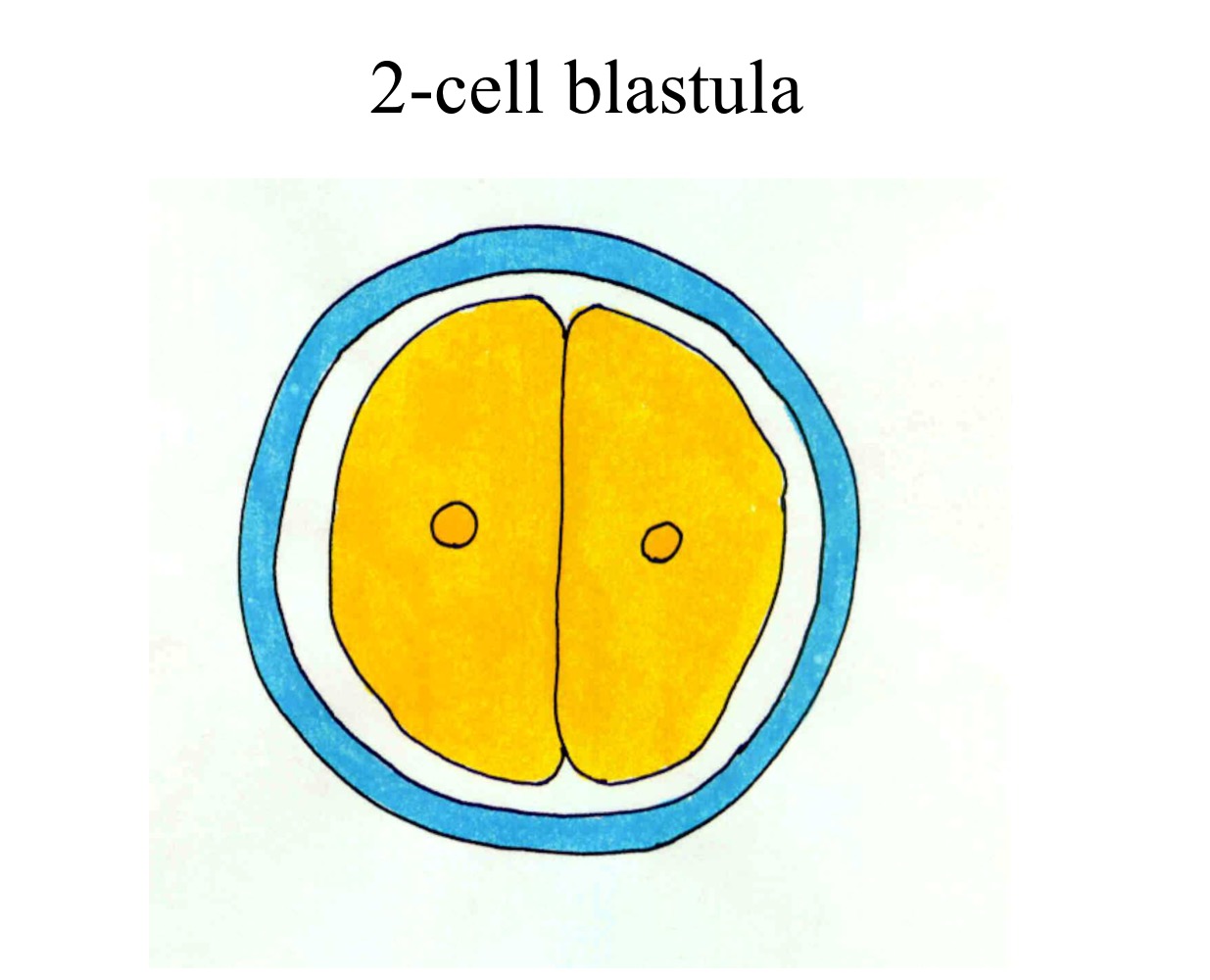
2-cell blastula
4-cell blastula
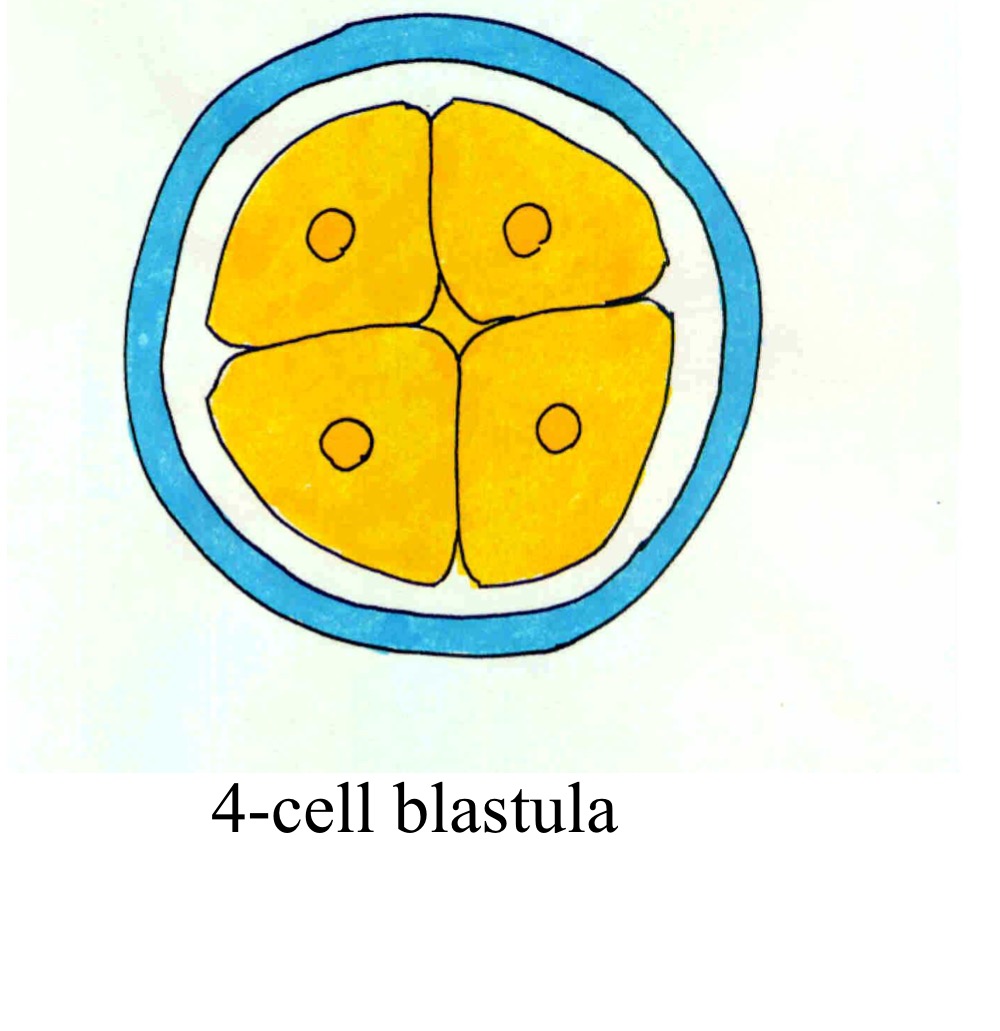
Blastomeres are totipotent up to
The eight-cell stage
A cluster of 16-32 blastomeres forms a
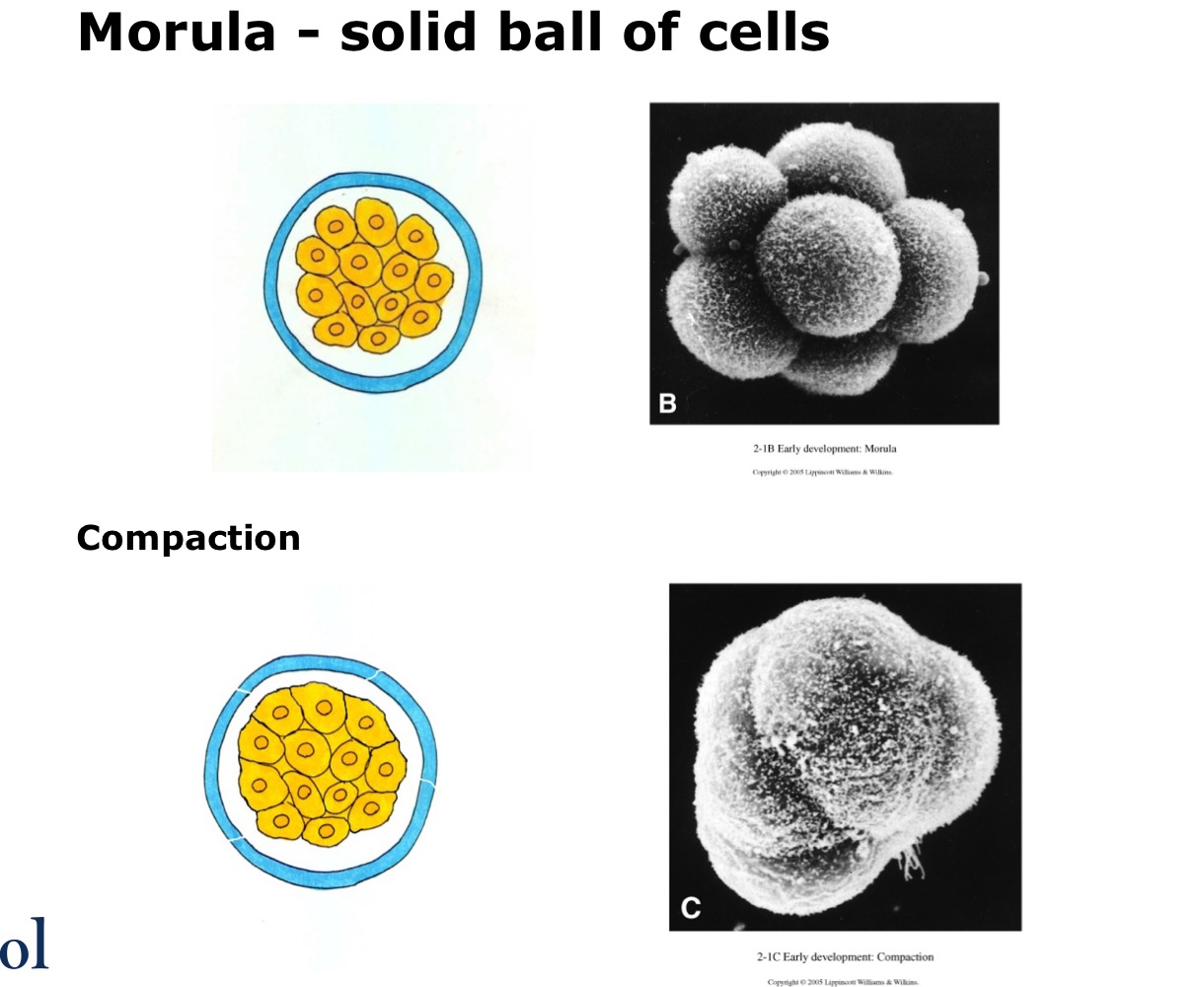
Morula
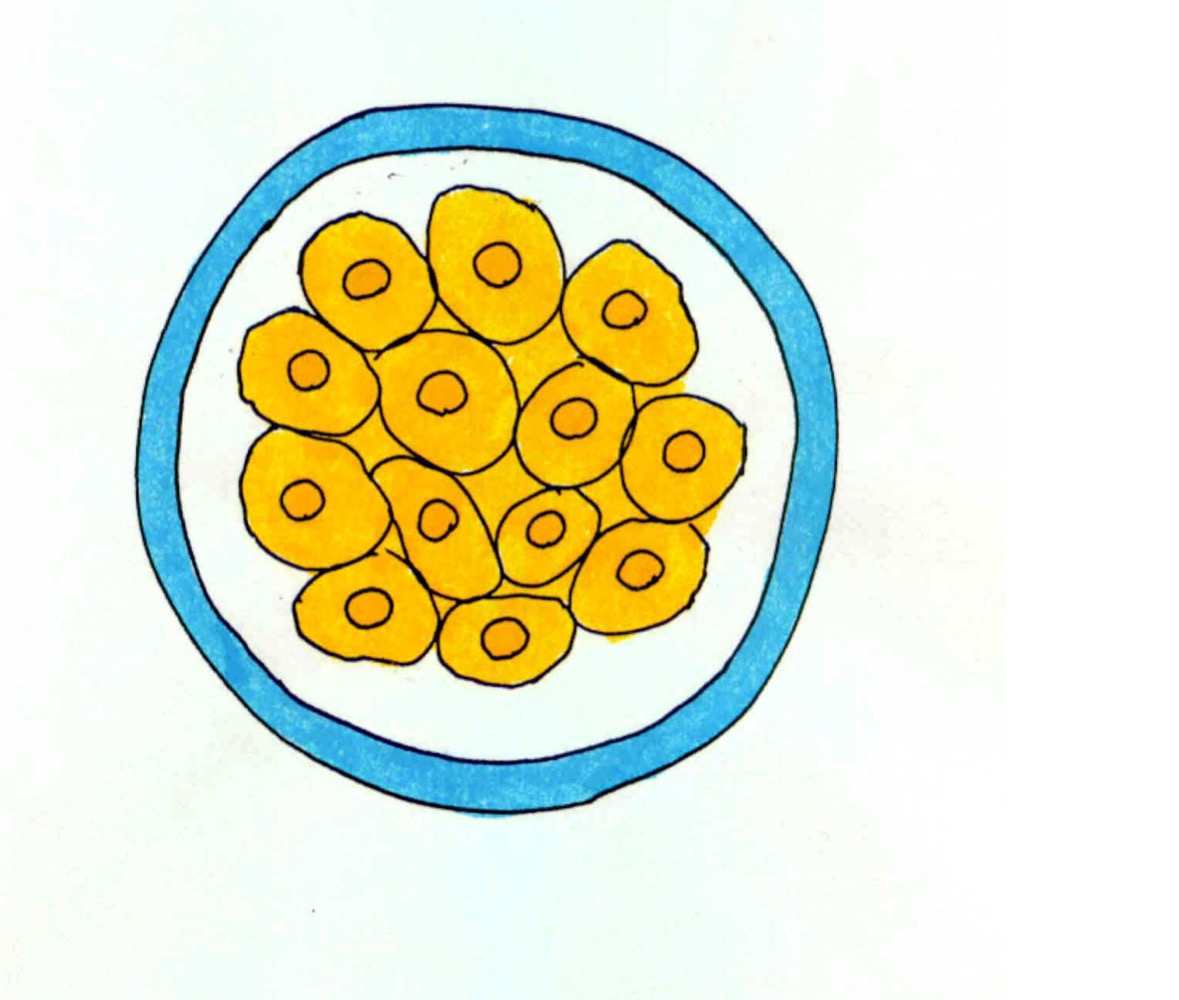
In the second week, the morula is
Still surrounded by the zona pellucida free within tubal/ uterine cavity. Still a solid ball of cells
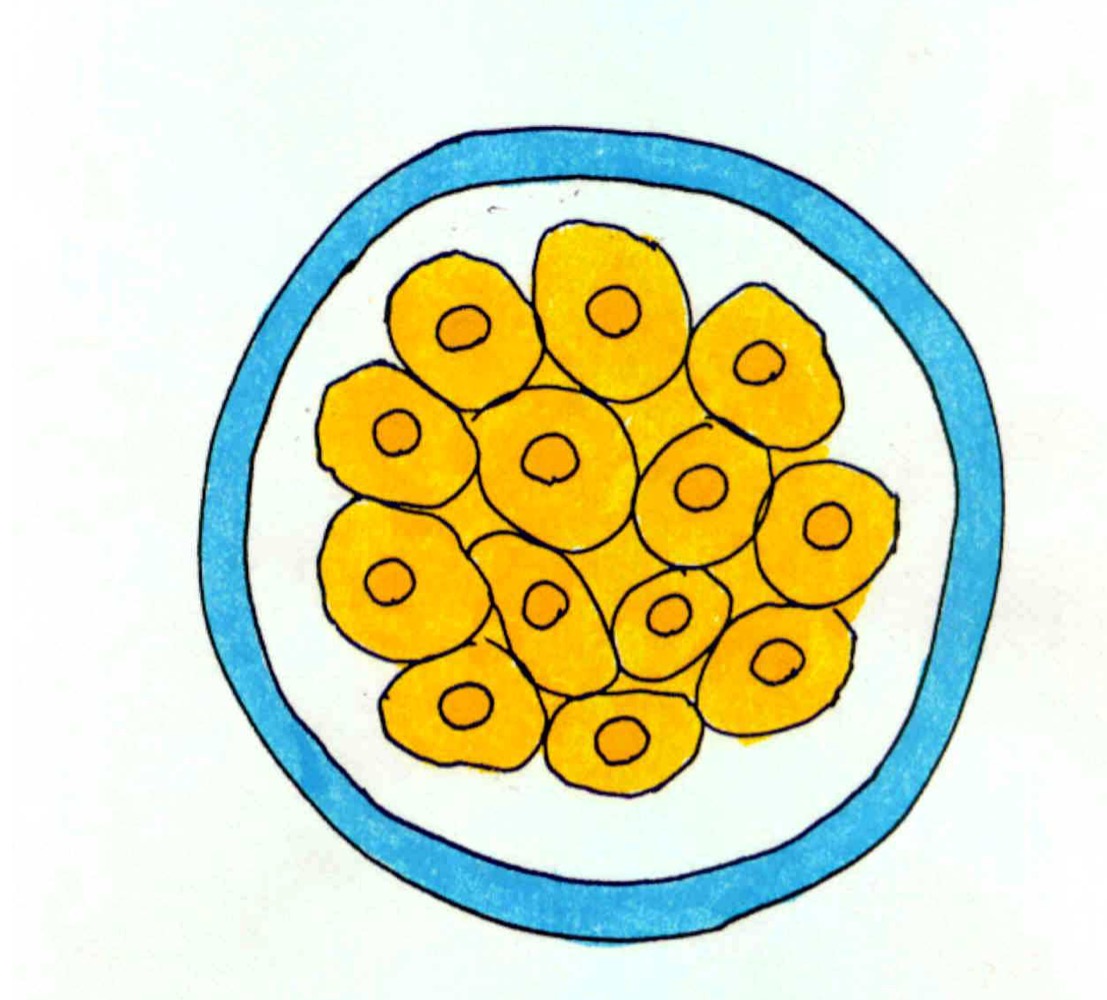
Morula cells undergo what in the second week
Compaction - Establishment of tight junctions between surface cells
Zona pellucida starting to split
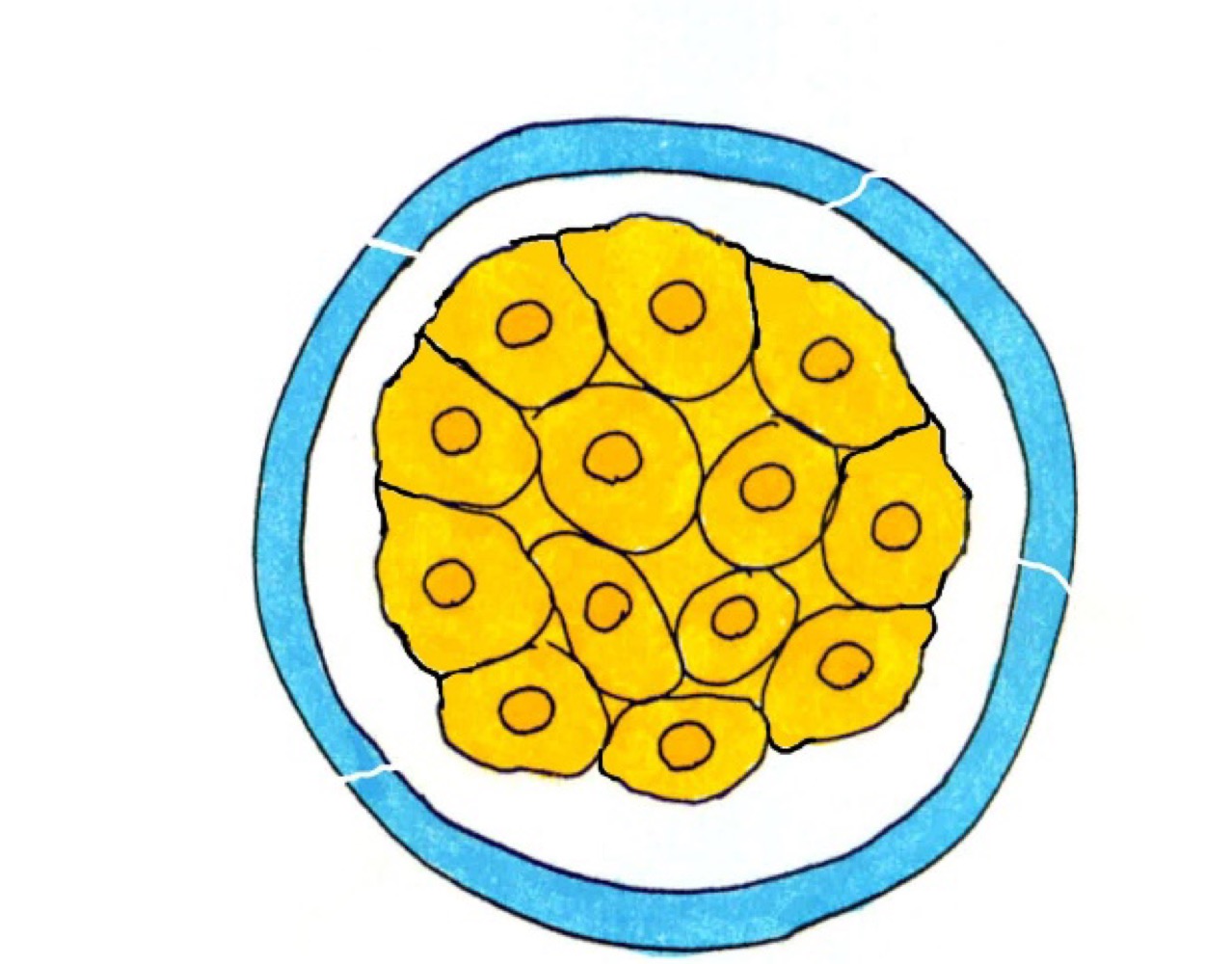
Morula and compaction images
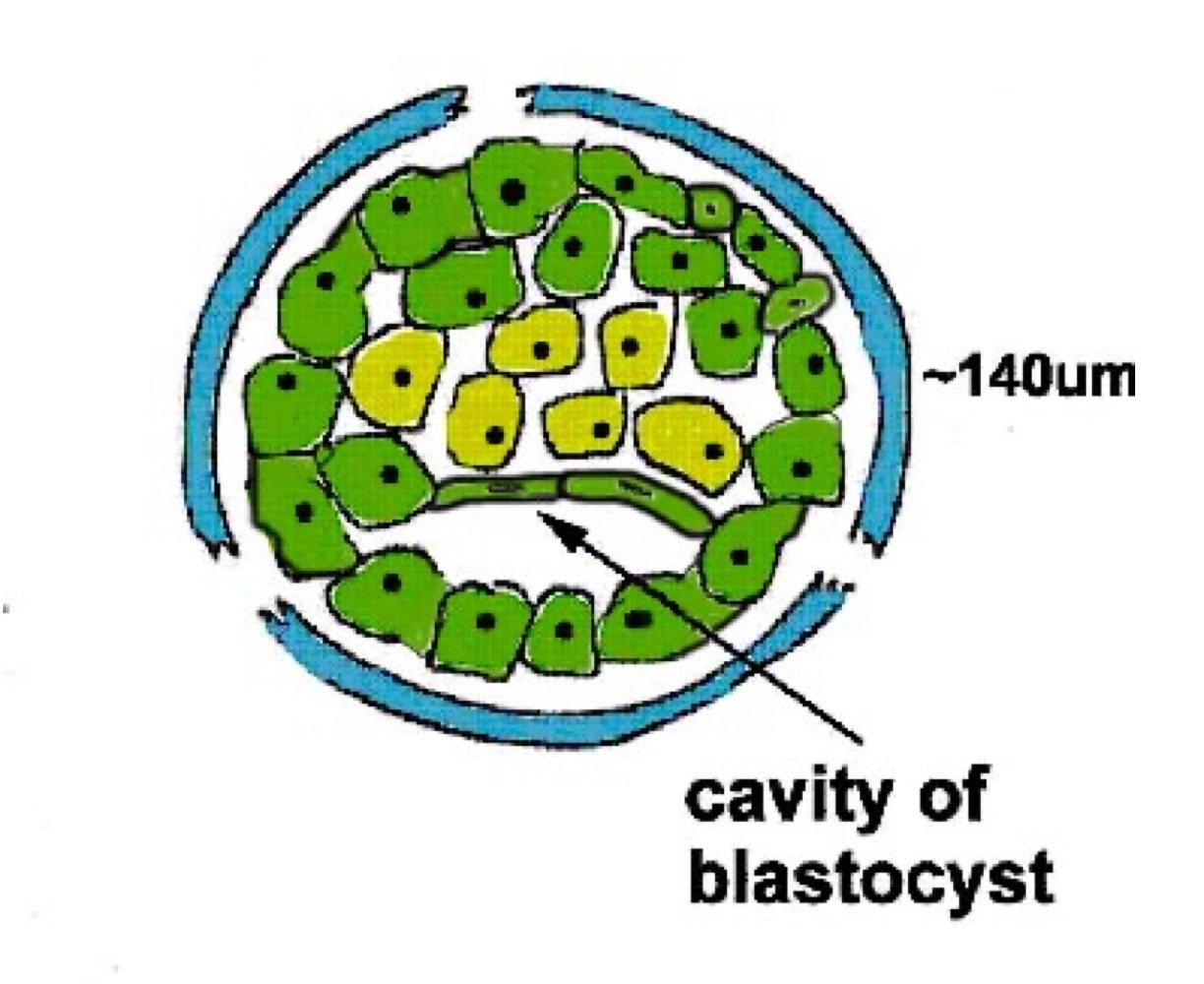
How does a blastocyst form
5 days post fertilisation, a cavity develops in the morula and blastocyst is formed.
The zona pellucida is beginning to degenerate ‘hatching’
Has probably been responsible for preventing implantation up to now
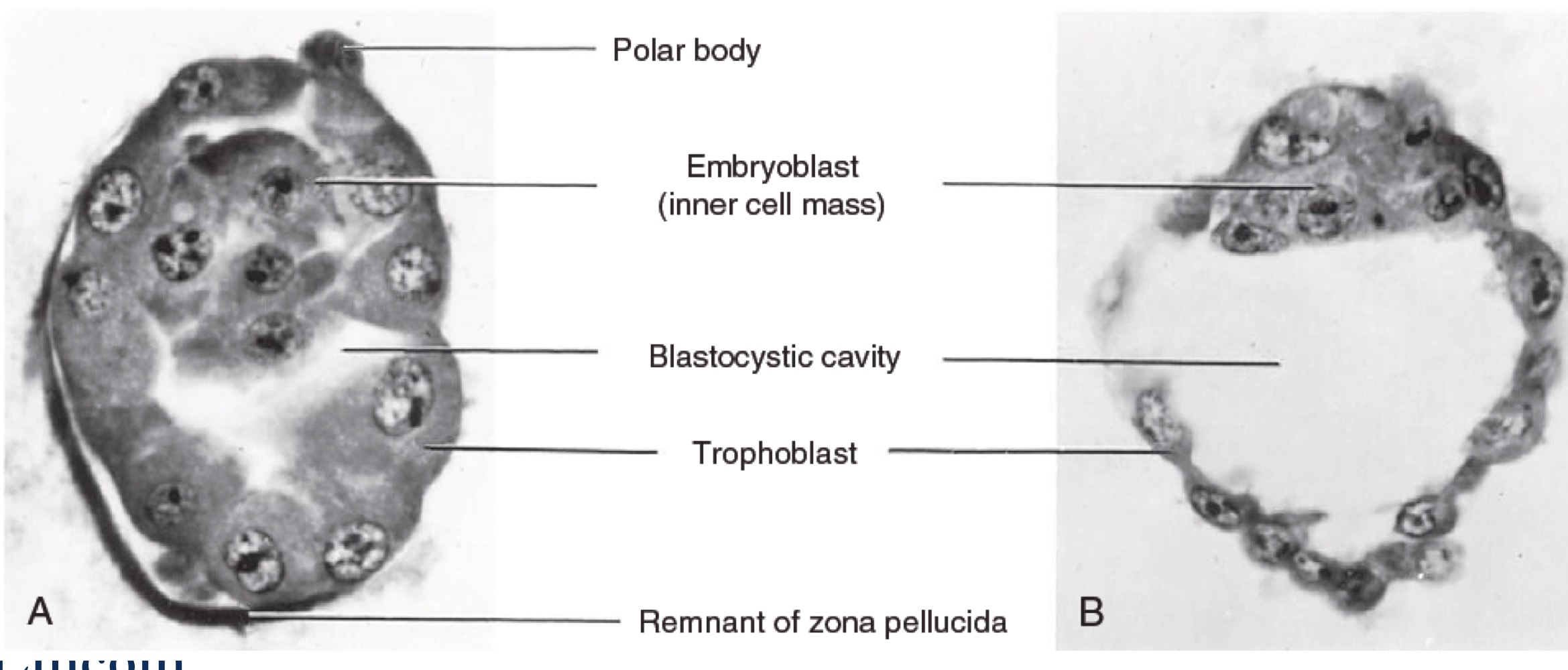
Photomicrographs of sections of human blastocysts
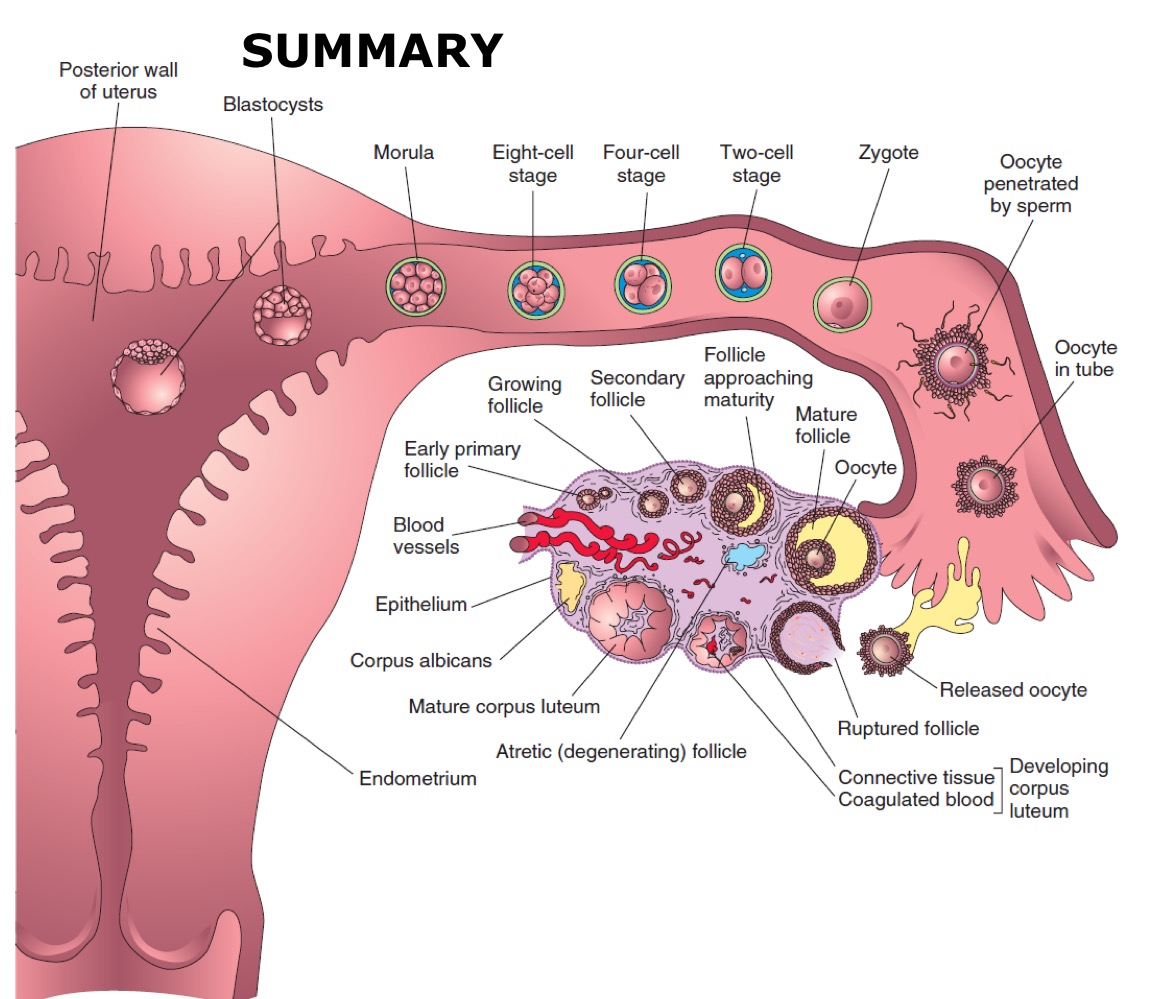
Summary of female fertilisation
Secondary oocyte halted part way through 2nd meiotic division
Penetration by spermatozoon triggers completion of 2nd meiotic division.
Summary of early cleavage and blastocyst formation