Chap 8A - Chemical equilibria
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Define irreversible reaction
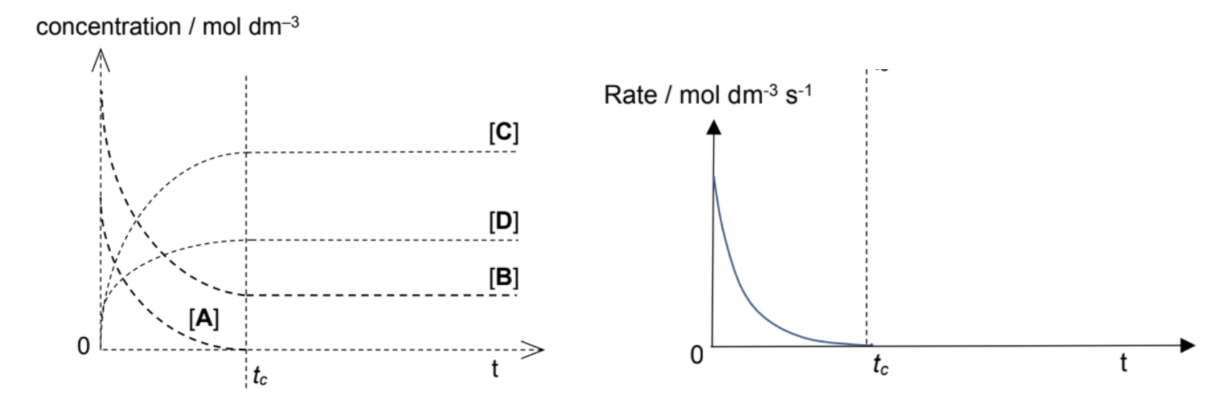
(Def.): Irreversible reactions are chemical reactions that proceed to completion. These chemical reactions take place in one direction almost exclusively and are denoted by a single–headed arrow (→). The limiting reagent is completely used up in an irreversible reaction
Draw concentration time and rate time graph for irreversible reactions (aA + bB → cC + dD)
Define reversible reaction
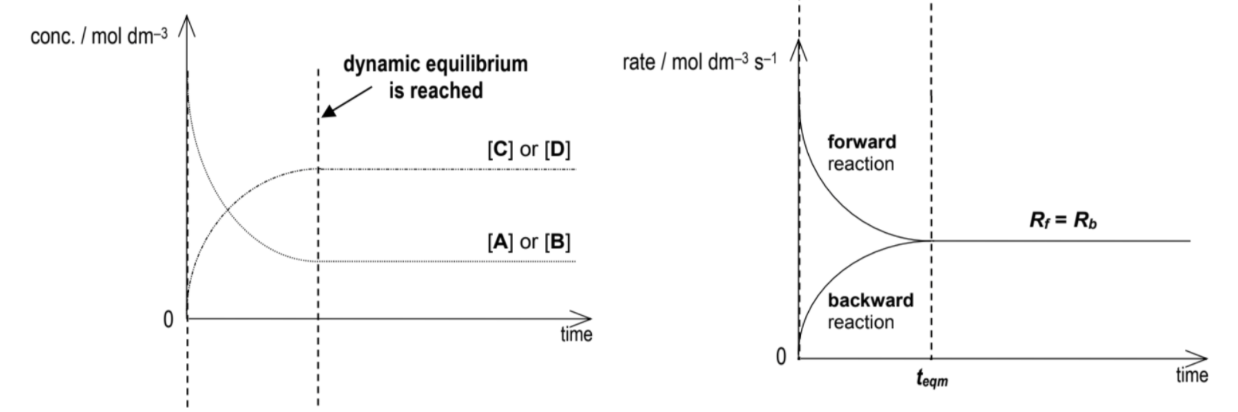
Definition : A reversible reaction is one which can occur in both direction, denoted by a double-headed arrow ‘⇌’ is used to denote a reversible reaction, they are incomplete and reach a state of dynamic equilibrium containing a mixture of both reactants and products
There is no excess or limiting reagents as they are never completed
Draw conc time and rate time graph for reversible reactions
Describe and define dynamic equilibrium
(Def.) : A state of dynamic equilibrium is said to have reached when the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction in a reversible reaction and the concentrations of both reactants and products are constant
System is closed (does not allow matter to enter or leave but allow free transfer of energy)
Forward and backward reactions are still taking place!
Things still happening but cannot be seen as all macroscopic properties remain constant
Describe and define static equilibrium
Static equilibrium (Def.): state in which there is no change in both macroscopic and microscopic (molecular scale) properties in a system
Equilibrium can be achieved “from either direction” : Equilibrium can be established starting with either the reactants or products
Describe A + B ⇌ C + D reaction
At time = 0 (start of reaction), forward reaction occurs to form C and D
Since C and D commences, backward reaction commences to form A and B
At teqm, the forward and backward reactions are still occurring
A state of dynamic equilibrium is attained where Rf = Rb = constant (NOT 0)
At this point, there is no net change in the amount of reactants and products
At equilibrium, the reaction is incomplete (reactants are still present in the system at equilibrium)
Once equilibrium is reached, the system will remain in this state, until conditions affecting the rates are introduced
Define and describe reaction quotient
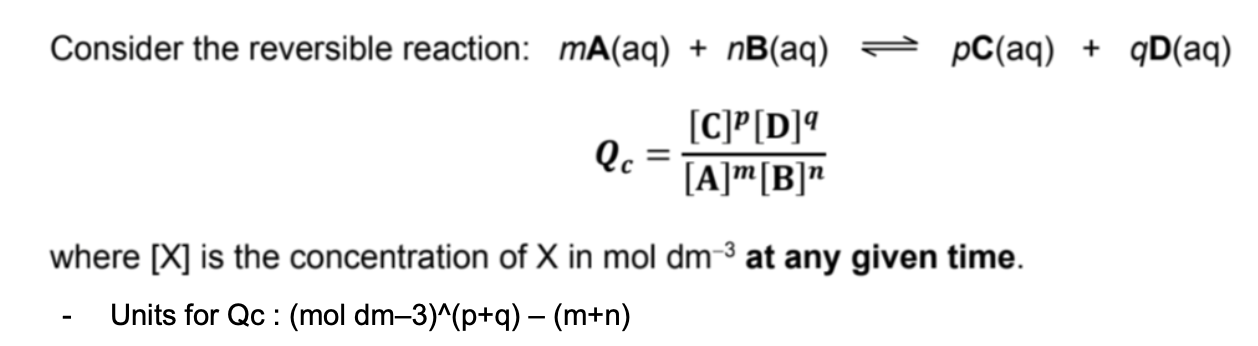
(Def.): For a reversible reaction, it is the ratio of the concentrations of products to reactants raised to their stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced equation
Qc is not constant (Changes with time until the reaction reaches equilibrium)
State Qc equation and its units
Explain Qc < Kc and vice versa
Qc < Kc | Qc > Kc |
|
|
Define and describe Kc (words)
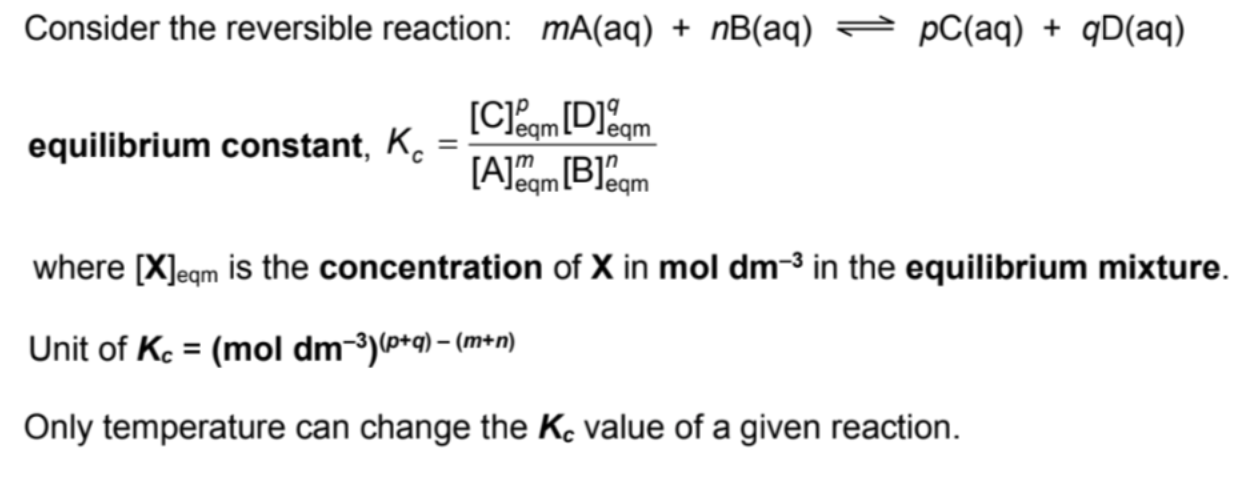
Kc (Def.): Measures the extent to which reactants are converted to products at equilibrium at a given temperature
At equilibrium: forward = backward rate
Equilibrium law: When reaction is at equilibrium, Qc = Kc
Constant at constant temperature
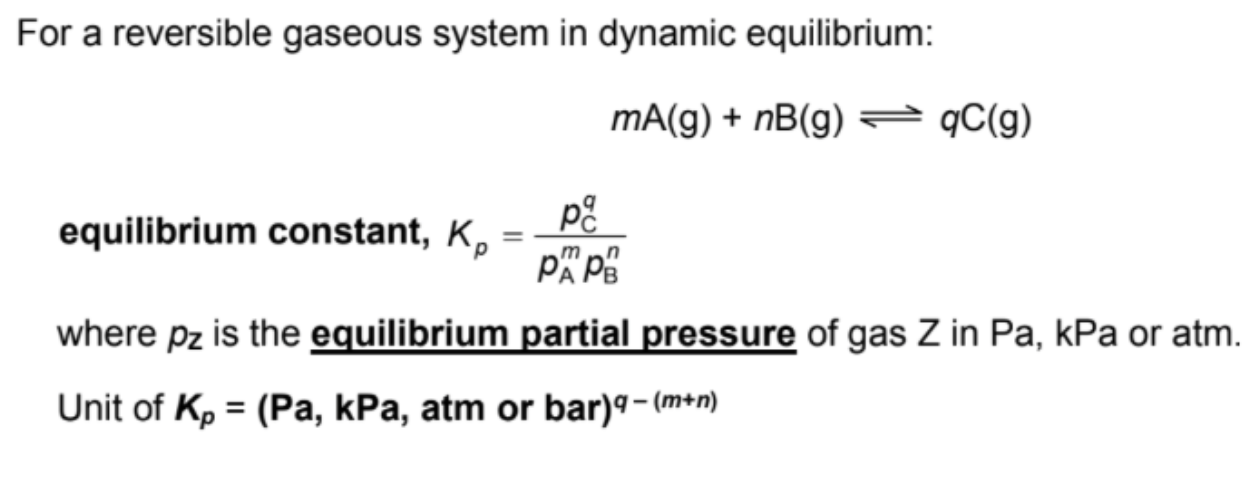
Describe units of K
Units dependent on chemical equation (ALWAYS state it) (possible to have no units)
K can be expressed in terms of:
Concentration (in mol dm–3), denoted by Kc
For gaseous reactions, partial pressure (usually in Pa or atm), denoted by Kp
The value of Kc or Kp is unaffected by changes in the conc or pressure of reactants or products, or the presence of a catalyst (affected by temperature only)
Define Kc (the equation one)
Define Kp (the equation one)
Describe homo and hete mixtures
Homogeneous | Heterogeneous |
The reaction mixtures contain reactants and products in the same phase or physical states | The reaction mixtures contain reactants and product in different phases or physical states |
Describe 3 species to exclude from Kc/Kp expressions
[Pure solids]
Exclude solids in all equilibrium expressions for all mixtures because concentration of a pure solid = its density is constant and independent of the mass of the solid present.
[Pure liquids]
Exclude pure liquids in expressions for heterogeneous equilibria because concentration of a pure liquid calculated from its density is a constant in heterogeneous mixtures and independent of the mass of liquid present
[Solvents]
Exclude solvents in all equilibrium expressions as they are present in excess
Being pure liquids, their concentrations calculated from their densities is a constant
Describe position of equilibrium
Refers to the composition of an equilibrium mixture (the relative proportion of products to reactants in an equilibrium mixture)
May lie on the right (towards the products) or lie on the left (towards the reactants)
Magnitude of Kc or Kp indicates the extent of the forward reaction at equilibrium at a given temperature
Magnitude of Kc or Kp gives no information about the ROR
Describe small VS large K
Small K | Large K |
|
|