14: Transcription regulation (prokaryotes)
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
at what points can you regulate genes
transcription initiation
post-transcription processing (splicing)
RNA stability
translational regulation
protein modification
protein transport
protein degradation
Core polymerase without sigma factor will initiate _
randomly
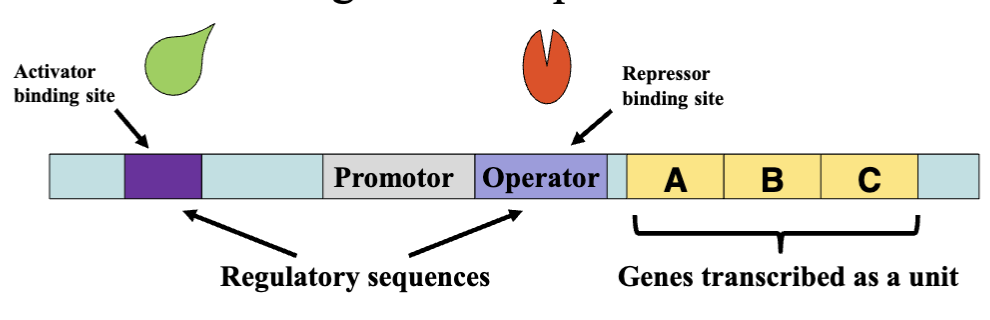
operons
clusters of co-regulated genes AND promotor and activating / repressor sites with related functions
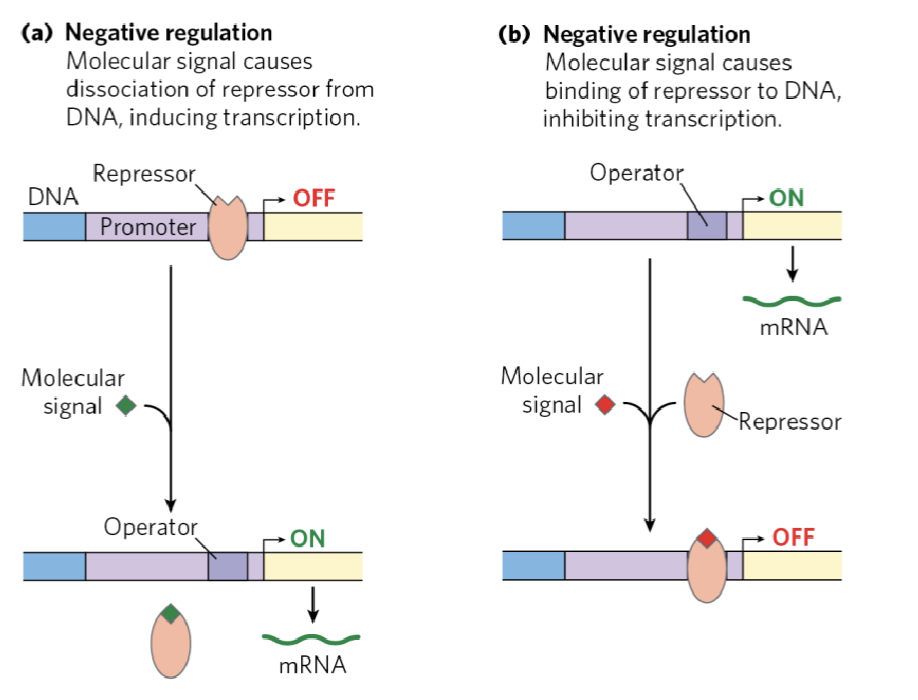
(positive / negative) regulation is a molecular signal that causes dissociation of repressor from DNA inducing transcription
negative
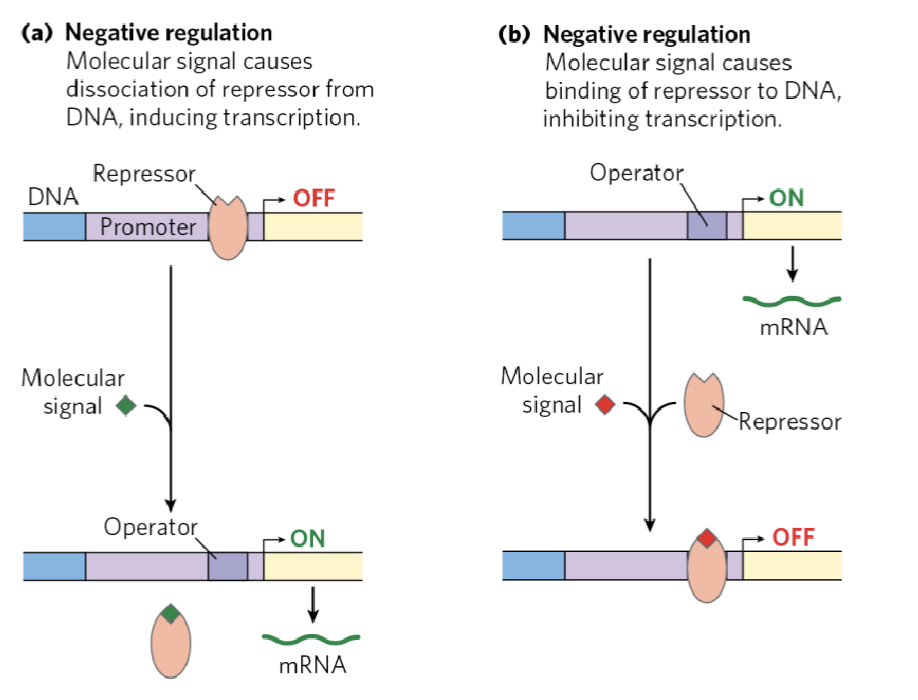
(positive / negative) regulation is a molecular signal that causes binding of repressor from DNA inhibiting transcription
negative
_ help recruit sigma factors to enhance transcription
activators
(activators / repressors) bind to operators
repressors
(positive / negative) regulation is a molecular signal that causes dissociation of activator from DNA inhibiting transcription
positive
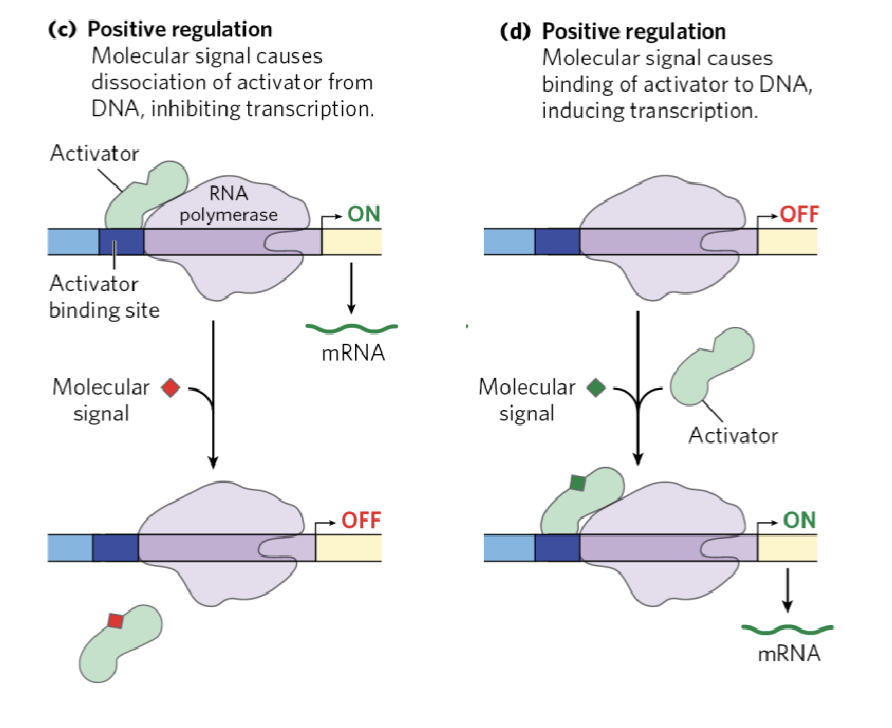
(positive / negative) regulation is a molecular signal that causes binding of activator from DNA incuding transcription
positive
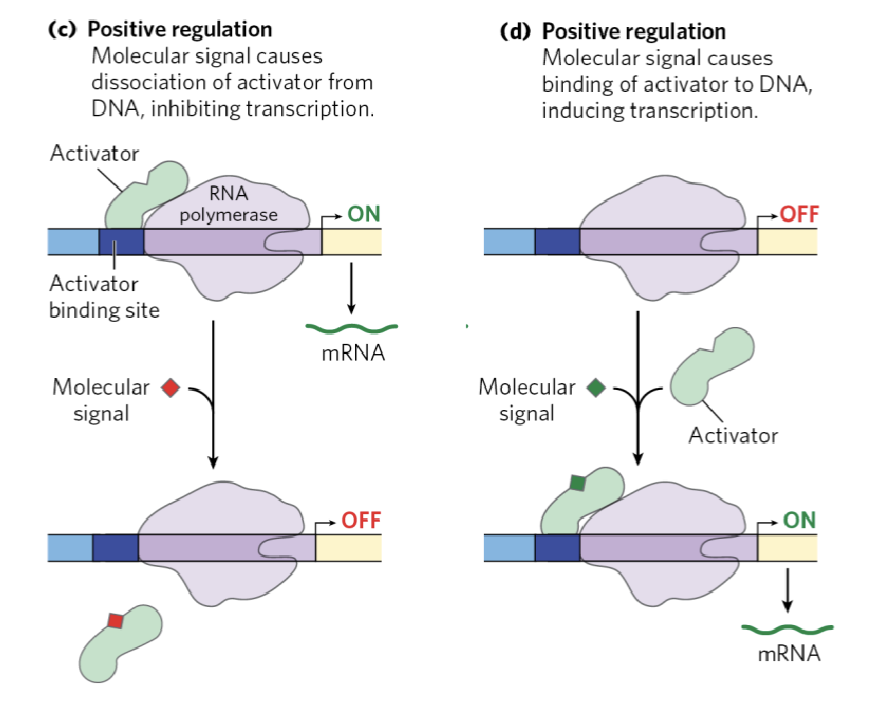
negative regulation involves (activators / repressors)
repressors
positives regulation involves (activators / repressors)
activators
T or F. E. coli lac operon goes under both positive and negative regulation
true
function of lac Z
convert lactose → glucose + galactose or allolactose
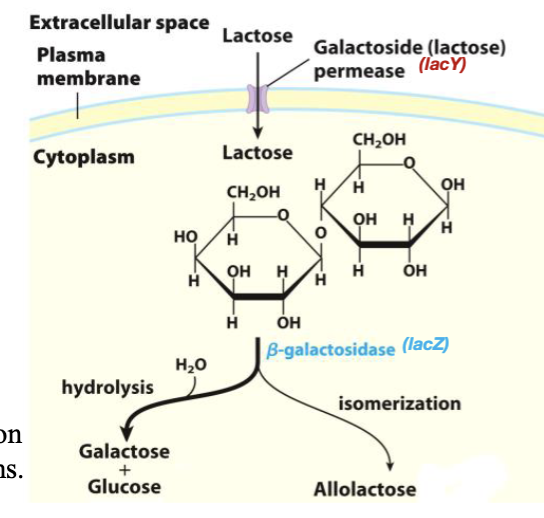
_ enzyme converts lactose to allolactose
b-galactosidease
activators bind to the _
activator binding site
lac operon has # promoters
2
(activators / repressors) help bind sigma factors
activators
lacI is (activators / repressor)
repressor
in lac operon, there is / is not always some repression happening
is
allolactose binds to
repressor
lacZ takes place (inside / outside ) cytoplasm
inside
outline positive regulation of lac operon
starvation → cAMP
camp → CRP (cAMP receptor protein)
CRP binds to activator binding site
enhance gene expression (ON)
outline negative regulation of lac operon
lacI binds o2 and o1 to repress transcription
allolactose binds repressor
o1 is not repressed → ON
riboswitch
switches when responding to signals that creates poly U termination to terminate transcription
binding of mRNA riboswitch to TPP ligand results in conformational change and _
inhibits transcription
binding of mRNA riboswitch to _ ligand results in conformational change and inhibits transcription
TPP
when glucose is high, camp is (high / low)
low
when glucose is low, cAMP is (high / low)
high
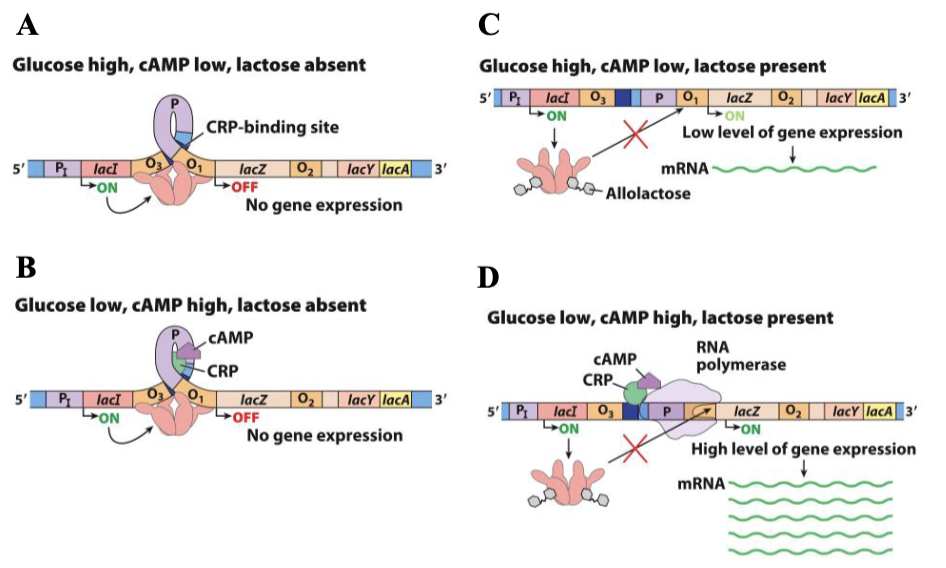
glucose high / camp low + lactose absent =
no gene expression

glucose low / camp high + lactose absent =
no gene expression
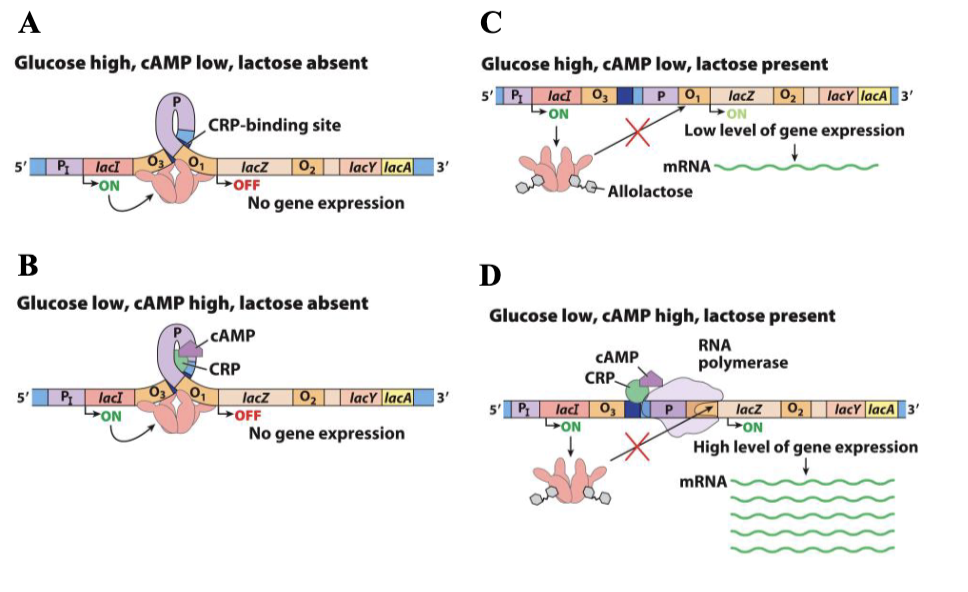
glucose high / camp low + lactose present
low gene expression
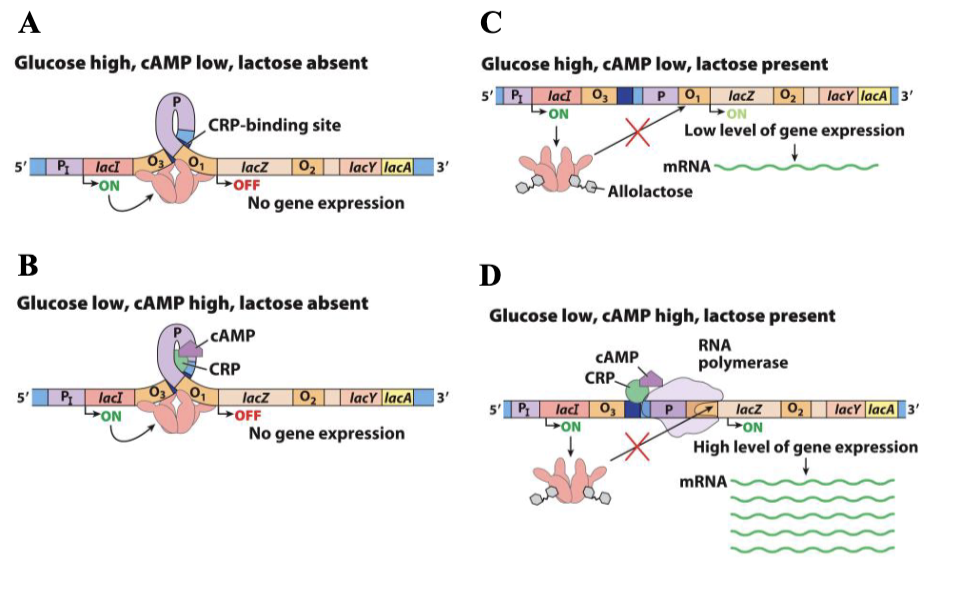
glucose low / camp high + lactose absent =
no gene expression
when lactose is absent, lac repressor binds to _
operator (lacZ)
when lactose is present, lac repressor binds to _
allolactose
high levels of gene expression when glucose is __ and lactose is _
low, present
galactoside permease (lacY)
transports lactose from extracellular space into cytoplasm
allolactose releases _ from operator
lac repressor