Anatomy and Procedures of the Alimentary Canal Large Intestine
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
intestine vs colon
The large intestine and colon are not synonymous.
• The colon does not include the cecum and rectum
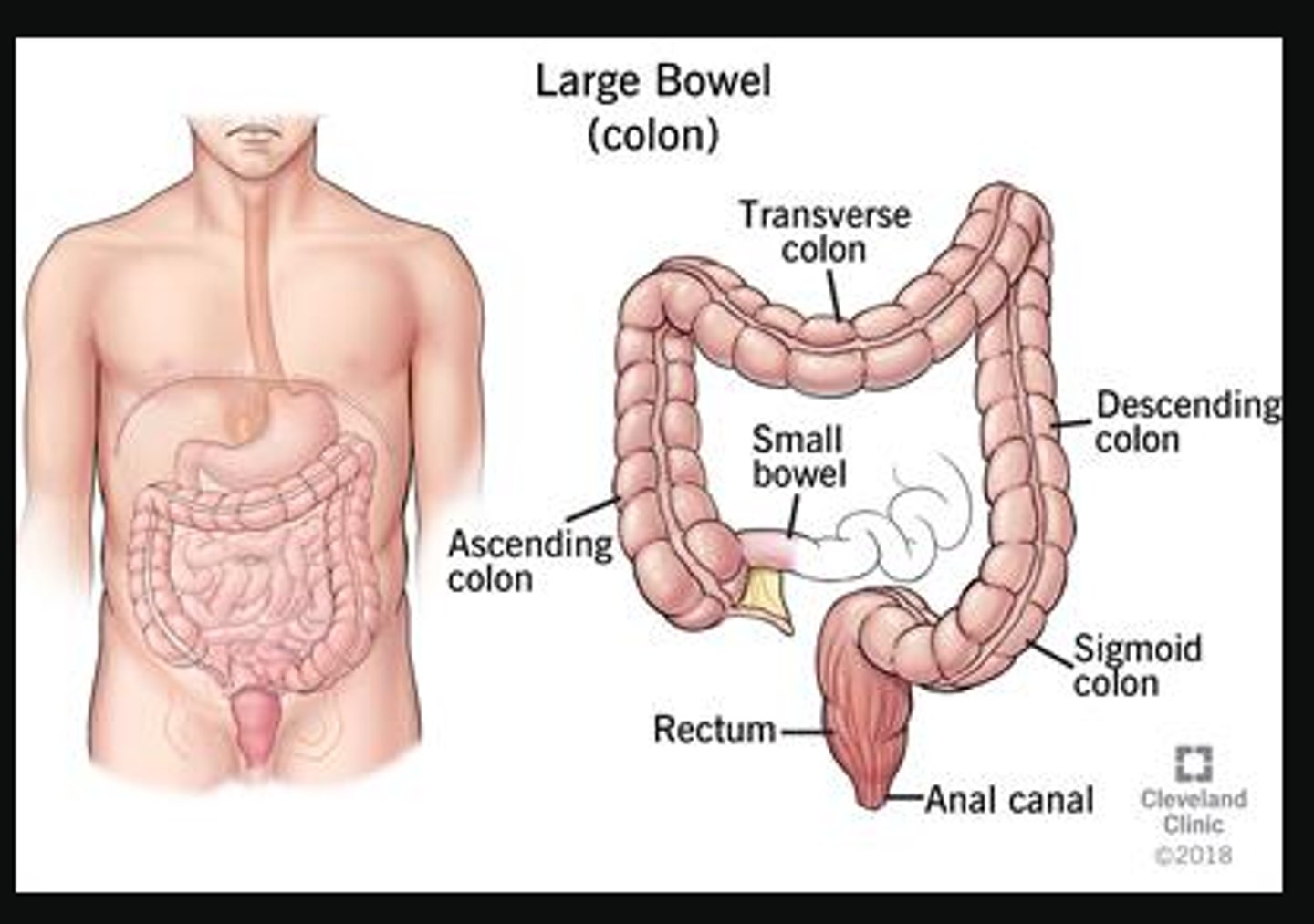
Where does the large intestine begin?
The large intestine begins in the right lower quadrant of the abdomen
parts of the large intestine
• Right colic (hepatic) flexure
• Ascending colon
• Ileocecal valve
• Cecum
• Appendix (vermiform process)
SLIDE 4
digestive system organs
Large Intestine
• Cecum
• Ascending colon (posterior to transverse colon)
• Hepatic flexure (Rt. Colic)
• Transverse colon
• Splenic flexure (Lt. Colic) (most patients are higher than hepatic flexure)
• Descending colon (posterior to transverse colon)
• Sigmoid colon
• Rectum
• Anus
SLIDE 5

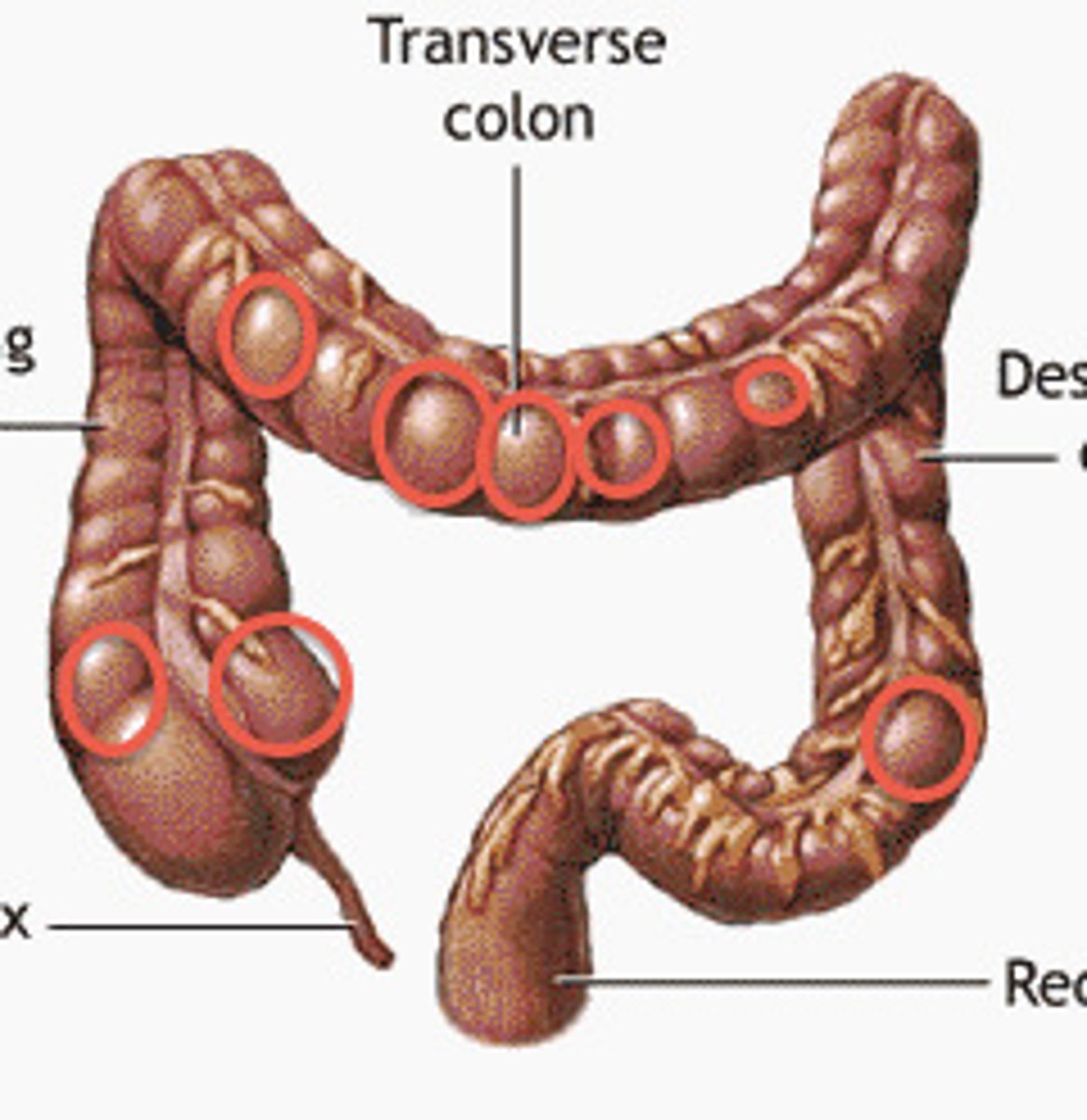
Haustra
• The haustra are sac-like pouches along the length of the large intestine.
• They are formed by bands of muscle termed taeniae coli
routine barium enema
• A fluoroscopic and radiographic examination of the colon
• Scout is obtained before contrast administration
• Check anatomy and preparation efficacy
• Barium is instilled under fluoroscopy
• Radiographs of the contrast-filled colon are obtained
• The patient evacuates the barium
• Post-evacuation radiograph is obtained
patient preparation
There are many methods used to prep the patient.
Ultimately, the objective is to have an empty bowel.
A combination of these three methods are most often utilized.
• Low-residue diet
• Cathartics
• Cleansing enema's
• NPO after midnight/last meal
contrast media
• BaSO4 is used unless contraindicated.
• The water temperature used is debatable.
• Cold water is recommended by some. It is supposed to have an anesthetic effect
• Some critics argue that it may cause colonic spasm.
• Most agree that room temperature water works best
what drug will prevent colic spasms/muscle relaxer?
glucagon
BE appartus
Disposable soft plastic enema tips and enema bags are commercially available indifferent sizes
Smaller enema tips necessary for patients with strictures, fissures, inflamed hemorrhoids, or other anal abnormalities
Retention tips have balloon cuff at end
• Balloon inflated with air after insertion to aid in retention of enema
retention balloon, enema tip, air inflater
SLIDE 12
patient prep and preparation
Patient cooperation is key to success
Explain the patient's role and examination required
Instruct patient on ways to minimize discomfort during filling
• Relax abdomen
• Deep oral breathing
• Communicate cramping so that filling may be slowed or stopped
SLIDE 14
what is the recommended height of the enema bag above the rectum?
18-24 inches
NO GREATER THAN 24 INCHES
Higher the bag, higher the chance of spasm/cramps
how to get air in large intestine
lower bag to remove barium from large intestine to make room for air
colostomy

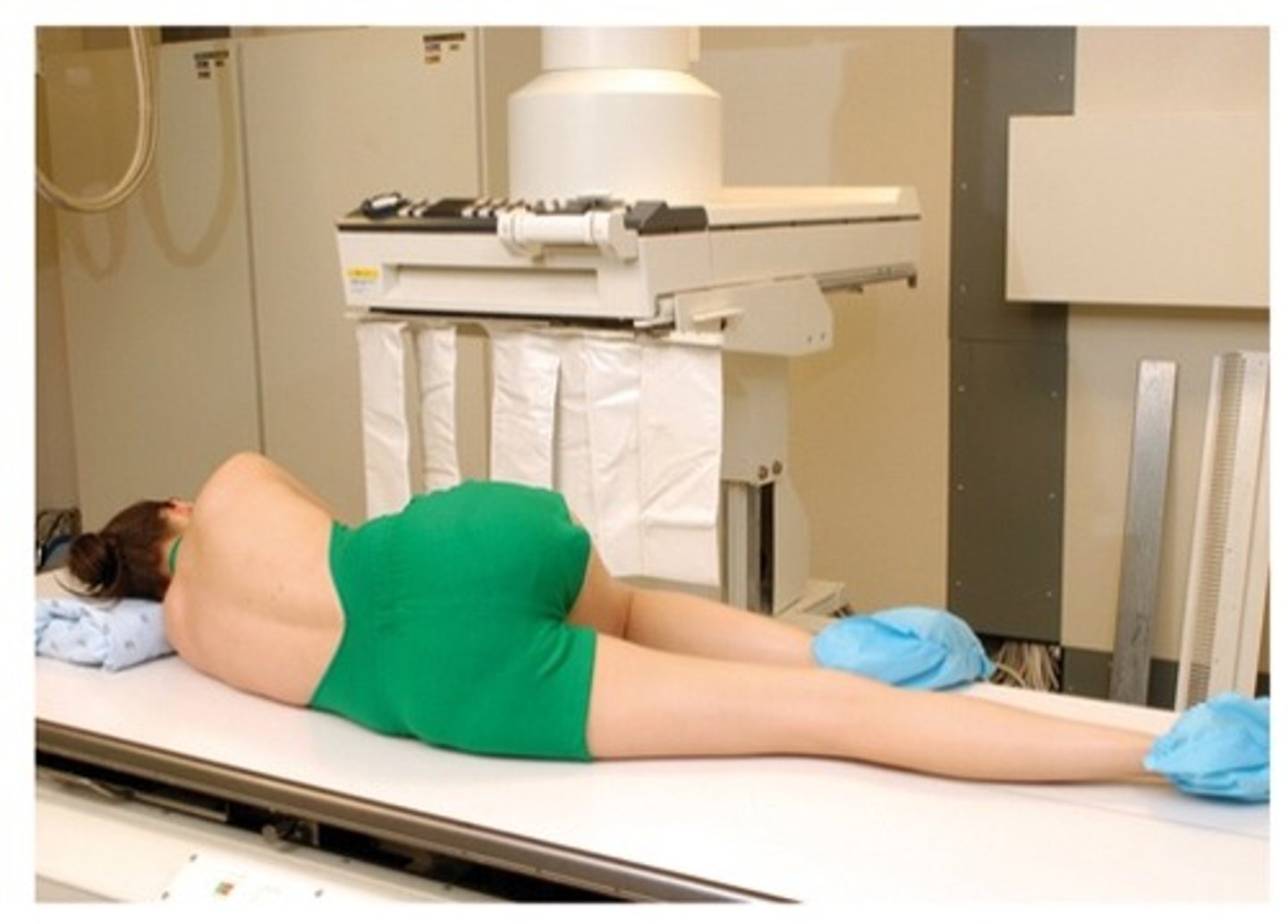
enema tip insertion position
The patient should first be placed in the Sims position
• Lying on their left side, the right leg flexed and lying in front of the left. The left knee is just comfortably flexed.
• This position relaxes abdominal muscles and decreases abdominal pressure
air-contrast vs single contrast large intestine
SLIDE 17
examination protocol (BE)
• Introduce patient to radiologist
• On request, release clip to allow barium to flow
• Single-Contrast (barium only): flow of barium is suspended periodically to reduce cramping and defecation impulse
• Double-Contrast (barium and air): examinations flow of barium first, then air or other gas after barium is evacuated
• Filling is viewed on fluoroscope
• Radiologist instructs patient to rotate to visualize all portions of bowel