Chapter 17: Revenue Recognition
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
Revenues are:
Inflows or other enhancements of assets
and/or settlements of liabilities
from delivering or producing goods, rendering services, or other activities constituting the enterprise’s ongoing major or central operations
What are the 5 steps to recognizing revenue?
Identify the contract: legal rights of seller and customer established.
Identify the performance obligation(s): could be single or multiple.
Determine the transaction price: under single/multiple performance obligation(s), it’s the amount seller is entitled to receive from customer.
Allocate the transaction price: under a single PO, no allocation required. under multiple PO’s, allocate a portion to each performance obligation.
Recognize revenue when (or as) each performance obligation is satisfied: under a single PO, at a point in time or over a period of time. Under multiple PO’s, at whatever time is appropriate for each performance obligation.
When is a performance obligation satisfied?
When control has transferred from the seller to the customer. Control means that the customer has direct influence over the use of the good or service and obtains its benefits.
When is a customer more likely to control a good or service?
If a customer has:
An obligation to pay the seller
legal title to the asset
physical possession of the asset
assumed the risks and rewards of ownership
accepted the asset
What does it mean when a seller is a principal and what method is used?
A principal has primary responsibility for delivering a product or service. The gross method is used: record sales revenue and cost of goods sold (if selling a product) E.g.: Target, BestBuy, United Airlines
What does it mean when a seller is an agent and what method is used?
An agent facilitates the sale and earns a commission for assisting the seller. Net method is used: sales commission is the only revenue earned. E.g.: eBay, Groupon, Priceline
Why is Consignment Sales an issue with revenue recognition?
The consignor physically transfers the goods to another company (the consignee), but the consignor retains legal title.
Goods on consignment are part of the consignor’s inventory. Consignor recognized revenue only when the actual sales happen (not when it moves the inventory to consignee’s location).
Consignee makes a commission on the sale at the point of the sale.
Why is time value of money an issue with revenue recognition?
Time value of money is when a contract (sales transaction) involves a significant financing component. Recognize sales revenue at the point of sale and recognize interest revenue over the period of the loan.
Why is warranty an issue with revenue recognition?
Assurance-type warranty: warranty is included in sales price. not a separate performance obligation.
Extended warranty: a separate performance obligation.
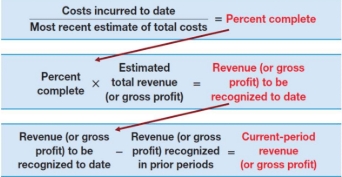
When accounting for long-term contracts, which steps of recognizing revenue are critical?
step 2: identify the performance obligations. Long-term contracts usually have a single PO, because they don’t meet the “separately identifiable” criterion necessary for goods and services to be viewed as distinct.
step 5: recognize revenue when (or as) each performance obligation is satisfied. When recognizing revenue over time according to the process toward completion (use the percentage-of-completion method). When recognizing revenue upon contract completion, use the completed-contract method.
What is the percentage of completion: cost-to-cost method?