Strategy and Decision Making Exam 1
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
Average Returns
returns equal to those an investor expects to earn from other investments possessing a similar amount of risk
Strategic Management Process
the full set of commitments, decisions, and actions firms take to achieve strategic competitiveness and earn above-average returns
The Strategic Management Process
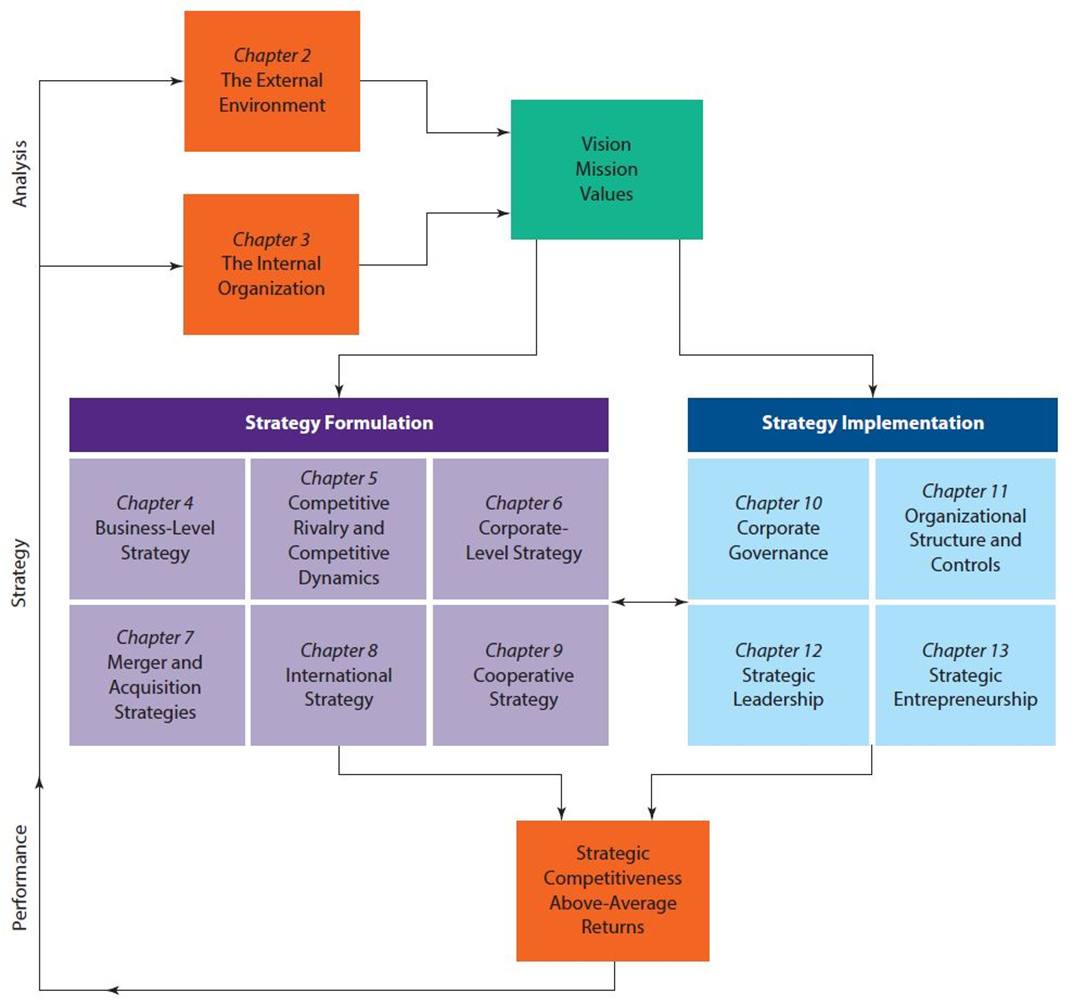
An organization can be confident that its strategy yields a competitive advantage after:

competitors efforts to duplicate it have ceased or failed
Digitilization
the process of converting something to digital form, is a competitive dimension that is affecting competition in multiple industries throughout the world
Hypercompetition
a condition where competitors engage in intense rivalry, markets change quickly and often, entry barriers are low
2 primary drivers of hypercompetition
the emergence of a global economy
rapid technological change
global economy
one in which goods, services, people, skills, and ideas move freely across geographic borders
tariff
a tax imposed by a government on goods imported into their country. sometimes used as a weapon against a country in an effort to gain concessions in other areas.
globalization
the increasing economic interdependence among countries and their organizations as reflected in the flow of products, financial capital, and knowledge across country borders.
global supply chain
a network of firms that spans multiple countries with the purpose of supplying goods and services
deglobalization
a reduction in participation in global supply and value chains
technology diffusion
the speed at which new technologies become available to firms and when firms choose to adopt them
perpetual innovation
a term used to describe how rapidly and consistently new, information-intensive technologies replace older ones
disruptive technologies
technologies that destroy the value of an existing technology and create new markets
knowledge
consists of information, intelligence, and expertise
information technology
the key to acquiring and managing knowledge flows
big data
refers to the data retrieved by firms that are increasing in volume, variety, and frequency
big data analytics
the process of examining huge amounts of data to uncover hidden patterns and other information that can be used to improve decision making
strategic flexiblity
a set of capabilities firms use to respond to various demands and opportunities existing in today’s dynamic and uncertain competitive environment
involves coping with uncertainty and its accompanying risks
requires developing the capacity for continuous learning and adapting to a changing environment
sustainability
a firm that should not deplete or destroy natural elements upon which it depends for survival
logic of the I/O (industrial organization) model
the profitability potential of an industry or a segment of it as well as the actions firms should take to operate profitably are determined by a set of industry characteristics, including:
economies of scale
barriers to market entry
diversification
product differentiation
the degree of concentration of firms in the industry
market frictions
The I/O (industrial organization) Model of Above-Average Returns

The industrial organization (I/O) model assumes that
The external environment imposes pressures and constraints that determine the strategies that would result in above-average returns.
resources
inputs into a firm’s production process, such as capital equipment, the skills of individual employees, patents, finances, and talented managers
capability
the capacity for a set of resources to perform a task or an activity in an integrative manner
core competencies
capabilities that serve as a source of competitive advantage for a firm over its rivals
Resources and capabilities have the potential to be the foundation for a competitive advantage when they are:
−Valuable (allow a firm to take advantage of opportunities or neutralize threats in its external environment)
−Rare (possessed by few, if any, current and potential competitors)
−Costly to imitate (are difficult for other firms to obtain)
−Non-substitutable (have no structural equivalents)
Which of the following is an assumption of the resource-based model?
Organizational decision makers are assumed to be rational individuals who are committed to acting in the firm's best interests, as shown by their profit-maximizing behaviors.
stakeholders
individuals, groups, and organizations that can both influence and are affected by the objectives, actions, and outcomes of a firm.
primary stakeholders
directly involved in the value-creating processes of the firm and include: suppliers, employees, customers, the communities in which the firm operates, financiers such as the firm’s shareholders and banks
secondary stakeholders
can both influence and are influenced by what the firm does, but they do not contribute directly to the value the firm creates.
distributional justice
means that stakeholders feel as though they are receiving value through their relationship with their firm that is commensurate with what they contribute to the firm
procedural justice
means that the firm listens to stakeholders and considers their positions when making important decisions that are likely to affect them
interactional justice
means that all stakeholders are treated with honesty, respect, and integrity
vision
a picture of what the firm wants to be and, in broad terms, what it wants to achieve
a vision statement:
articulate the ideal description of an organization and gives shapes to its intended future, tends to be relatively short and concise
an effective vision
stretches and challenges people, and is consistent with the decisions and actions of those involved with developing it.
mission
specifies the businesses in which the firm intends to compete and the customers it intends to serve
a mission is:
more concrete than a firms vision, should establish a firms individuality, should be inspiring and relevant to all stakeholders, deals more directly with product markets and customers, has a higher profitability of being effective when employees have a strong sense of ethics.
values of an organization
define what should matter most to managers and employees when they make and implement strategic decisions
values:
help guide what is rewarded and reinforced in the organization,
are a practical application of business ethics
can help a firm define its purpose and answer the fundamental question of what the firm stands for
should help determine the way stakeholders are treated and their priority in important decisions.
strategic leaders
people located in different areas and levels of the firm using the strategic management process to select actions that help the firm achieve its vision and fulfill its mission
organizational culture
refers to the complex set of ideologies, symbols, and core values that individuals throughout the firm share and that influence how the firm conducts business
the social energy that drives- or fails to drive- the organization
how can a firm avoid managerial hubris (overconfidence) at the top of the organization
delegate strategic responsibilities
A-S-P process
The Analyses (A) firms use to develop strategies
the firms analysis provide inputs that are the foundation for choosing one or more strategies (S) and deciding with one/s to implement.
the strategic management process calls for disciplines approaches to serve as the foundation for developing a competitive advantage
the process has a major effect on the performance (P) of the firm
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Define strategic competitiveness, strategy, competitive advantage, above-average returns, and the strategic management process.
1. Strategic Competitiveness – When a firm uses a strategy that helps it succeed against rivals.
2. Strategy – A plan of actions and choices to reach goals and compete.
3. Competitive Advantage – When a company does something rivals can’t easily copy.
4. Above-Average Returns – Profits greater than what investors expect for similar risks.
5. Strategic Management Process – The steps a firm takes to choose, apply, and review strategies to stay competitive.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Describe the competitive landscape and explain how globalization, technological changes, and expectations of socially responsible behavior shape it.
The competitive landscape is shaped by globalization, which increases worldwide competition; rapid technology, which forces constant innovation; and rising expectations for social responsibility, which push firms to act ethically and sustainably.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: Use the industrial organization (I/O) model to explain how firms can earn above-average returns.
The I/O model says a firm’s success depends mostly on the external environment (industry it competes in). To earn above-average returns, firms:
Study the industry to see what drives profits.
Pick an attractive industry.
Choose a strategy suited to that industry.
Develop skills to carry out the strategy.
Use those skills to compete and earn higher returns.
In short: Pick the right industry, match strategy to it, and execute well.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: 1.4 Use the resource-based model to explain how firms can earn above-average returns.
The resource-based model says a firm’s success depends on its internal resources and capabilities. To earn above-average returns, a firm must have resources that are:
Valuable – help exploit opportunities or neutralize threats.
Rare – not widely available to competitors.
Costly to Imitate – hard or expensive for rivals to copy.
Organized – effectively used to create value.
👉 In short: Use unique, valuable resources well to outperform rivals.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: 1.5 Use the stakeholder model to explain how firms can earn above-average returns.
The stakeholder model says firms earn above-average returns by managing relationships with all key stakeholders (customers, employees, suppliers, investors, communities). By meeting stakeholders’ needs and creating mutual value, firms gain loyalty, support, and a strong reputation, which drives long-term success.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: 1.6 Describe vision, mission, and values, and explain why they are important.
Vision – A long-term goal showing what the firm wants to become.
Mission – The firm’s purpose and approach to reach its vision.
Values – Core principles guiding behavior and decisions.
LEARNING OBJECTIVE:1.7 Describe strategic leaders and what they do.
Strategic leaders are people located in different areas and levels of the firm using the strategic management process to select actions that help the firm achieve its vision and fulfill its mission.
They are : decisive, committed to nurturing those around them, and committed to helping the firm create value for all stakeholder groups
LEARNING OBJECTIVE: 1.8 Explain the strategic management process.
a rational approach firms use to achieve strategic competitiveness and earn above-average returns.
ASP process
the analyses (A )and use to develop strategies
the firms analyses provide inputs that are the foundation for choosing one or more strategies (S) and deciding which ones to implement
the process has a major effect on the performance (P) of the firm.