Lifespan Development Chapters 7-10
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/100
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 1:34 PM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
1
New cards
Childhood Obesity
Having a BMI above the 95th percentile
2
New cards
Asthma
a chronic disease of the respiratory system in which inflammation narrows the airways from the nose and mouth to the lungs
3
New cards
Concrete Operational Thought
Piaget’s term for the ability to reason logically about direct experiences and perceptions
4
New cards
Classification
the logical principle that thins can be organized into groups according to characteristics
5
New cards
Seriation
The concept that things can be arranged in a logical series
6
New cards
Working memory
Memory that is active at any given moment
7
New cards
Knowledge Base
A body of knowledge in a particular area that makes it easier to master new information in that area
8
New cards
English Language Learners
Children in the US whose proficiency in English is low
9
New cards
Immersion
a strategy in which instruction in all school subjects occurs in the second language that a child is learning
10
New cards
Bilingual education
a strategy in which school subjects are taught in both the learner’s original language and the second language
11
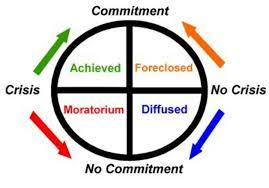
New cards
English as a Second Language (ESL)
US approach to teaching English that gathers all of the non-English speakers together
12
New cards
Neurodiversity
Idea that each person has neurological strengths and weaknesses that should be appreciated
13
New cards
Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD)
A condition characterized by persistent pattern of inattention and/or hyperactive or impulse behaviors
14
New cards
Specific learning disorder
A marked deficit in a particular area of learning that is not caused by an apparent physical disability, or intellectual disability, or by an unusually stressful home environment
15
New cards
Dyslexia
Unusual difficulty with reading; thought to be the result of neurological underdevelopment
16
New cards
Dyscalculia
Unusual difficulty with math; probably originating from a distinct part of the brain
17
New cards
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
A developmental disorder marked by difficulty with social communication and interaction
18
New cards
Family sturcture
The legal and genetic relationships among relatives living in the same home
19
New cards
Standard North American Family
A family with a mother and a father and their biological children
20
New cards
Extended Family
A family of relatives in addition to the nuclear family, usually three or more generations living in one household
21
New cards
Puberty
The time between the first onrush of hormones and full adult physical development. Usually last 3-5 years
22
New cards
Menarche
A girl’s first menstrual period. Pregnancy is now biologically possible
23
New cards
Spermarche
A boy’s first ejaculation of sperm
24
New cards
Pituitary
A gland in the brain that responds to a signal from the hypothalamus by producing many hormones
25
New cards
Adrenal glands
two glands located above the kidneys, respond to the pituitary, producing hormones
26
New cards
HPG (hypothalamus-pituitary-gonad) axis
a sequence of hormone production originating in the hypothalamus and moving to the pituitary and then the gonads
27
New cards
Gonads
The paired sex glands. They produce hormones and mature gametes
28
New cards
HPA (Hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal) axis
a sequence of hormone production originating in the hypothalamus and moving to the pituitary then the adrenal glands
29
New cards
circadian rhythm
A day-night cycle of biological activity that occurs approx. every 24 hours
30
New cards
Growth spurt
the relatively sudden and rapid physical growth that occurs during puberty
31
New cards
body image
a person’s idea of how their body looks
32
New cards
Anorexia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by starvation
33
New cards
Bulimia nervosa
An eating disorder characterized by binge eating and subsequent purging
34
New cards
Binge eating disorder
Frequent episodes of uncontrollable eating
35
New cards
Primary sex characteristics
The parts of the body that are directly involved in reproduction
36
New cards
Secondary sex characteristics
Physical traits that are not directly involved in reproduction but may indicate sexual maturity
37
New cards
Child sexual abuse
Any erotic activity that arouses an adult and excites, shames, or confuses a child
38
New cards
Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI)
A disease spread by sexual contact
39
New cards
Adolescent Egocentrism
A characteristic of adolescent thinking that leads young people to focus on themselves to the exclusion of others
40
New cards
Imaginary Audience
The other people who, in an adolescent’s egocentric belief, are watching
41
New cards
Personal fable
An aspect of adolescent egocentrism characterized by an adolescent’s belief that they are more unique and wonderful than anyone else
42
New cards
Invincibility Fable
An adolescent’s idea that they cannot be overcome or harmed by anything that might be dangerous
43
New cards
Formal operational thought
Piaget’s fourth and final stage, characterized by more systematic logical thinking and the ability to understand abstract concepts
44
New cards
Hypothetical thought
reasoning that includes propositions and possibilities that may not reflect reality
45
New cards
deductive reasoning
reasoning from a general statement to figure out specifics
46
New cards
inductive reasoning
reasoning from one or more specifics to reach a general conclusion
47
New cards
Dual processing
the notion that two networks exist within the human brain, one for emotional processing of stimuli and one for analytical reasoning
48
New cards
intuitive thought
thought that arises from an emotion or hunch
49
New cards
analytical thought
thought that results from analysis
50
New cards
Identity vs Role confusion
Erikson’s fifth stage of development
51
New cards
Identity achievement
Erikson’s term for the attainment of identity
52
New cards
Role confusion
When adolescents have no clear identity
53
New cards
Foreclosure
Erikson’s term for premature identity formation, when adolescents adopt roles without analysis
54
New cards
Gender identity
A person’s acceptance of the roles and behaviors that society associates with a particular gender
55
New cards
Parental monitoring
Parent’s ongoing knowledge of what their child is doing
56
New cards
Familism
The belief that family members should support one another, sacrificing individual freedom and success in order to preserve family unity
57
New cards
peer pressure
encouragement to conform to friends or contemporaries
58
New cards
Coercive joining
when others strongly encourage someone to join in their activity
59
New cards
Sexual orientation
a person’s romantic or sexual attraction
60
New cards
Cyberbullying
when people try to harm others via electronic means
61
New cards
Sexting
Sending sexual messages or photographs
62
New cards
Major depressive disorder
feelings of hopelessness, lethargy, and worthlessness that last two or more weeks
63
New cards
Suicidal ideation
serious thinking about suicide
64
New cards
parasuicide
any potentially deadly self-harm that does not result in death
65
New cards
Cluster suicides
Several suicides committed by members of a group within a brief period of time
66
New cards
Middle Childhood
The period between early childhood and adolescence, approx. ages 6-11
67
New cards
Common Causes of Death in Middle Childhood
Drowning, car accidents, firearms
68
New cards
Metacognition
thinking about thinking, or the ability to evaluate a cognitive task in order to determine how best to accomplish it, and then to monitor and adjust one’s performance on that
69
New cards
Industry vs. Inferiority
continual need to be advancing in arenas. Within the mastery of chosen skills, they find them selves to be competent or incompetent.
70
New cards
G factor intelligence
general and global intelligence; the idea that some people are lower or higher on IQ
71
New cards
Alfred Binet
Developed the average intelligence for each age after being hired by French government to determine which kids should go to school
72
New cards
IQ
Intelligence quotient; mental age/actual age
73
New cards
Perfect normal IQ score
100
74
New cards
Aptitude
the potential to master a specific skill or to learn a certain body of knowledge
75
New cards
IQ test
a test designed to measure intellectual aptitude, or measure ability to learn in school
76
New cards
Flynn effect
People are getting smarted all the time, so the IQ scale has to be readjusted
77
New cards
Range of reaction
range of IQ possible for a child based on their parents’ IQ
78
New cards
Gardner’s multiple intelligence theory
There are 8 different intelligences that someone can succeed in: intrapersonal, naturalist, linguistic, logical-mathematical, spatial, bodily-kinesthetic, musical, interpersonal
79
New cards
Andrew Wakefield
Published study that MMR vaccine caused Autism, lost credentials
80
New cards
Family process/function
the way a family works to meet the needs of its members (respect)
81
New cards
5 needs of a child from their family
Material necessities, learning, self-respect, peer relationships, harmony and stability
82
New cards
Hormone
An organic chemical substance; produced by one body tissue and conveyed via the bloodstream to another to affect some physiological function
83
New cards
Fluctuation of hormones
Approximately around age 8-9
84
New cards
Estradiol
sex hormone, considered the chief estrogen
85
New cards
Testoterone
sex hormone, the best known androgen
86
New cards
Genes and gender
2/3 of variation in age of puberty is genetic
87
New cards
Body fat
most girls reach at least 100 pounds before they can experience their first period
88
New cards
Stress
The link between stress and puberty is known, but not agreed that stress causes early puberty
89
New cards
Amenorrhea
stopping of a period that you once had
90
New cards
Visible onset of puberty
age 11-12
91
New cards
precocious puberty
sexual development before the age of 8
92
New cards
Lina Medina
Gave birth at age 5, after beginning menstrual cycles at age 2
93
New cards
Leptin
hormone that affects appetite and is believed to be involved in the onset of puberty
94
New cards
Early maturing girls
more at risk, treated like they are older
95
New cards
Early maturing boys
Positive psychology, but still at risk
96
New cards
Logic shut down
when emotions are intense, the logic part of the brain shuts down
97
New cards
Amygdala
controls emotions, threats, aggression and is developed by age 13
98
New cards
Prefrontal cortex
Controls reasoning and logic; developed in early 20s
99
New cards
James Marcia
Inspired by Erikson, developed 4 identity achievement arenas
100
New cards
Identity achievement arenas
Achieved, foreclosed, moratorium, diffused