05 - Complex plant tissues
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
80 Terms
Complex plant tissues and function
Often more than one function per tissue
Specialization for protection, exchange, uptake, transport, support and storage
types of Complex plant tissues
epidermis, periderm, xylem, phloem, ground tisssue
Epidermis function
protection, exchange, uptake
parts of epidermis
epidermis cells
cuticle
stoma
glands
hair
chracteristics of epidermis
Non-woody plants, one cell layer thick, alive
function of epidermis cells
protection
function of cuticle
protection
Cuticle
waxy layer: fatty substance (cutin)
Thickness ≈ water permeability → resistance to bacteria and other pests
function of stoma
2 guard cells; H2O & gas exchange
stoma
Stoma: two bordering guard cells (specialized epidermis cells)
stoma pressure
Dry conditions, low H2O pressure
Wet conditions, High H2O pressure
when are guard cells swollen or shrunken
when open they swollen
when closed they shrunken
function of glands
protection
example of glands
female canabis plants have glands with poison to keep away insects
what are hairs also known as
trichome
what are glands also known as
glandular trichome
what are platelet also knwon as
flatteneted trichome
difference between gland and hair
glands have a tip contining something
what is a platelet
more specilized hair
enlarging into umbrella
funtion of hair -
defense against herbivores and heat
sometimes modified into stinging hairs
how do hair protect against heat
its white which reflects light so less heat
how do stringing hairs work
outer layer is made from silica (glass material ) which is very brittle, so when it breaks it release poison
purpose of platelets
Defense against heat
plants covered by platelets aka silver berry, it shades the plants so it can grow in higher heat
Hairs on roots:
root hairs
root hair purpose
vital for water uptake
life span of root hairs
short lived
one or two weeks and then root need to grow more and new hair forms there
Conical epidermis
epidermis cells breaks ligh in different way which creates a nice sheen attracting insects
H2O-repellent epidermis
some leafs want to be kept dry as stoma are on top and if covered theres no gas exchaneg
h20 repeelant epidermis makes it so watwr cant touch the botton layer

Water and dirt repellent epidermis
in the lotus
h20 repellent and also pickes up dirt
Epidermal sensing hairs
in the venus fly trap
grows specilaized leaf not for photosynthesisi but to catch food
hairs responds to touch twice in 20 secs cuz it it touched once it could be dirt or anythig but life things move and would touch twice
Epidermal adaptations
Outer epidermis of the trap: helpful to climb up
Rim epidermis: directional, slippery grooves
Rim edge: downward pointing teeth and glands
Glands at the inner rim edge: Alluring sweet treat Slippery wax
Interior: slippery, overhanging epidermal cells (going down easy but up almost impossible )
Glands produce enzymes for insect digestion
unique epidermis
Conical epidermis
H2O-repellent epidermis
dirt repellent.
hair sensning
unique traits of the pitcher plant
function of periderm
protection and exchange
second most specialized
why is permiderm needed
Growth of stem → ripping-apart of epidermis
Needed: NEW sealing (beyond epidermis)!
where can perimederms be found
parennials
function of periderm in parrenials
like epidermis
what is the periderm made out of
Made up from two cell types:
● Cork cambium (meristem; source of new periderm)
● Cork cells (protection)
cork cambium
secondary meristem
not present in seedling but developes later on
Cork cells
dead at maturity,
walls with lignin (anti-microbial (hard for bacteria to get in))
suberin (wax-like (good for protecting cell), against desiccation)
function of xylem
(transport, support, storage)
what is the xylem
Continuous system transporting water and minerals from roots to rest of the plant
part of xylem
• Tracheids (transport, support)
• Vessel members (transport, support)
• Fibers (support)
• Parenchyma (storage)
which parts of xylem are dead at maruity and which are not and is this a bad thing
dead at maturity
• Tracheids (transport, support)
• Vessel members (transport, support)
• Fibers (support)
not dead
• Parenchyma (storage)
not a bad thing cuz they do their jobs even as dead
whta is used for tansport in xylem
tracheids and vessel membranes
are trahcied and vessels the same
same function but evolutionary very different
Tracheids vs. vessel shape
Tracheids:
• narrow, long
• tapered (pointy)
vessel shape
• wider, shorter
• flattened
Tracheids vs. vessel evolutionary
Tracheids:
• evolutionary old
• gymnosperms and angiosperms
vessel shape
• evolutionary newer
• angiosperms
Tracheids vs. vessel movemetn of water
Tracheids:
• water moves between tracheids only through pits
- H2O flows through adjacent pits from cell to cell
• less efficient water transport
vessel shape
• water moves from one vessel ement to the next through performations and pits
• more efficient water transpor
why are wallas of vessel and tracied lined with ligin
high force of water
which are stronger vessels or tracieds
vessels Generally more strongly enforced than tracheids (bc wider: need to withstand more water pressure)
what would the xylem in soft wood be made out of
tracheids
what would the xylem in hard wood be made out of
both trachieds and vessesl
how do xylem act as support
Most ± lignified = hard, sturdy
function of phloem
transport
what does the Phloem consist of
• Sieve tube members (transport) • Companion cells (“control center")
purpose of Phloem
Continuous system transporting dissolved primarily sugars from leaves to the rest of the plant
how does Phloem work
Sugar flows through sieve tube members, divided by sieve plates Companion cells: control both themselves and sieve tube members
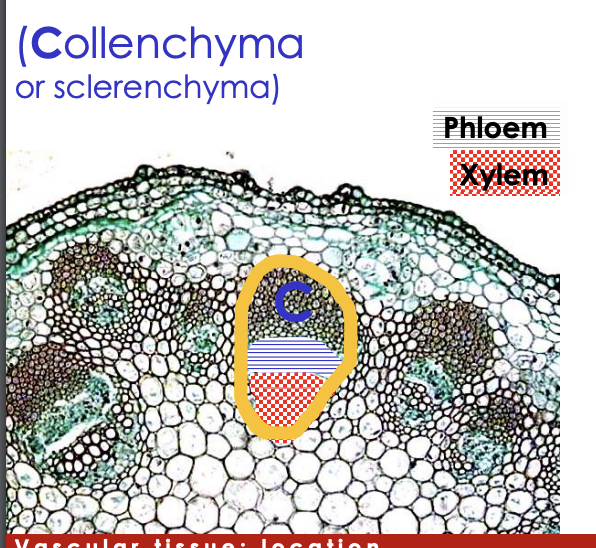
Vascular tissue: non-woody plants
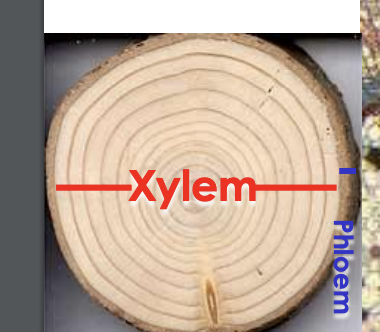
Vascular tissue: trees
function of Ground tissue
support, storage
Ground tissue (non-woody plants)
Tissues other than dermal and vascular tissue systems
what is ground tissue made out of
Ground tissue is made up by parenchyma >>> collenchyma >>>> sclerenchyma
use of ground tisse
Use: photosynthesis, store nutrients, fill space
When guard cells are well hydrated, they are much wider than high
true
Which complex tissue can be made up of the following components? Epidermal cells, cuticle, glands, hairs, stomata
epidermis
is epidermis alive or dead at maturity
alive
How many guard cells are there per stoma?
2
The outer wall of a guard cell is ____ compared to the ____ inner wall.
thinner
more enforced
When guard cells take up water and hence have to accommodate this higher volume, the outer walls of the two guard cells ___ and hence become more ___ , while the inner walls become more __ . This turns the two guard cells into something like _, and thus _ the stoma.
expand
convex
concave
two curved sausage
opening
when do the outer walls of stoma become more convex
when the the outer walls of the two guard cells expand
when do the iner walls of stoma become more concave
when the the outer walls of the two guard cells expand
Which complex tissue can contain all of tracheids, vessel members, fibers and parenchyma cells?
xylem
In the following is a description of one part of the epidermis. Which one?
This cell type, being part of the epidermis, has various roles: on leaves, it can act to deter herbivory mechanically (insects do not like to mess with it) or even chemically (when it is full of toxic chemicals), it can shield a leaf from too much sun and when on roots, water and nutrients are taken up through it.
Trichome
Which complex tissue consists of two cell types only, of which one is a secondary meristem and the other is dead at maturity and the cell walls are enriched by suberin and lots of lignin?
Periderm
At what developmental stage does the periderm take over from the epidermis in its activity of sealing the stem?
In year 2
To which complex tissue is the periderm functionally analogous?
Epidermis
This cell type, as a part of the epidermis, is typically used uniquely for chemical warfare to deter herbivores. Which part of the epidermis is this?
Gland
Which member of the epidermal tissue produces THC?
Gland
Epidermal hairs only occur on above-ground plant organs
false
Which complex tissue is mostly made up of parenchyma cells, followed by some collenchyma and sometimes sclerenchyma?
Ground tissue