Exothermic and endothermic reactions
1/29
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
Law of conservation of energy
Energy cannot be created or destroyed but can be transferred or dissipated to the surroundings.
How to measure heat content
Thermometer
Two types of energy created
1) Exothermic Reactions
2) Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic reaction
They release energy, and the temperature of the surroundings increases.
Examples of exothermic reaction
Combustion Reactions (fires/burning)
Many oxidation reactions
Most neutralisation reactions
Everyday example of exothermic reaction
Self-heating cans and hand warmers.
Endothermic reaction
Absorbs energy, the temperature of the surroundings decreases.
Example of endothermic reaction
Thermal decomposition reactions
The reaction of citric acid and sodium hydrogen carbonate
Everyday example of endothermic reaction
Instant ice packs which can be used to treat sports injuries.
Some diagrams of an exothermic and endothermic reaction
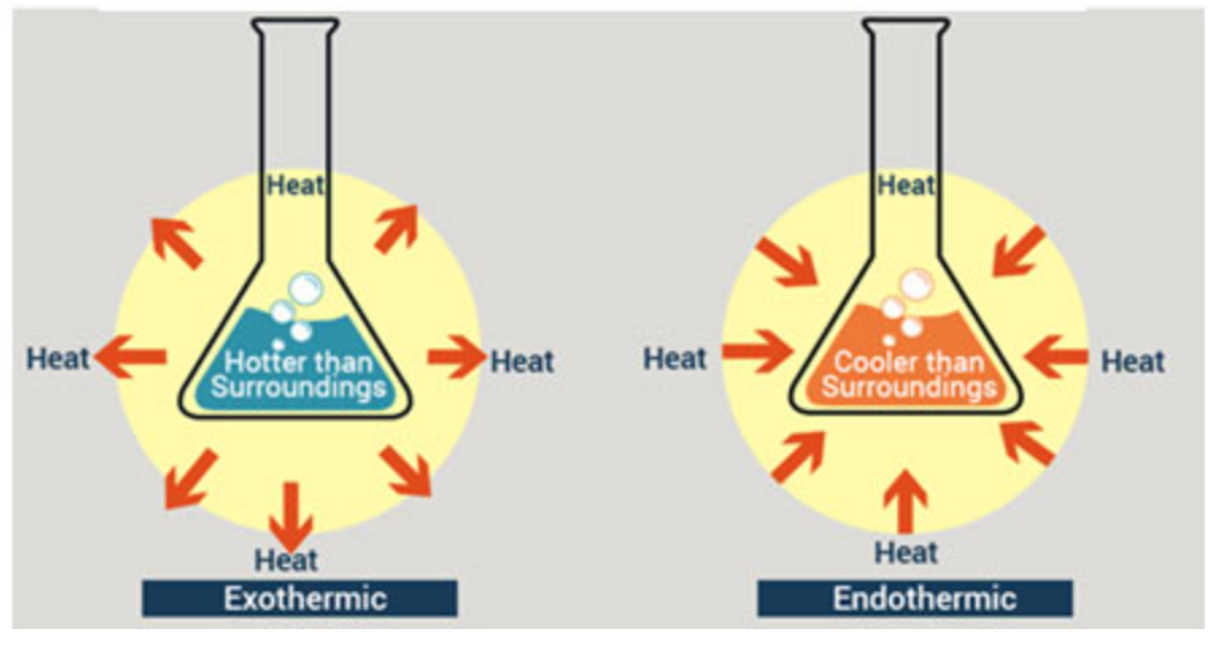
Good way to show exothermic/endothermic reactions
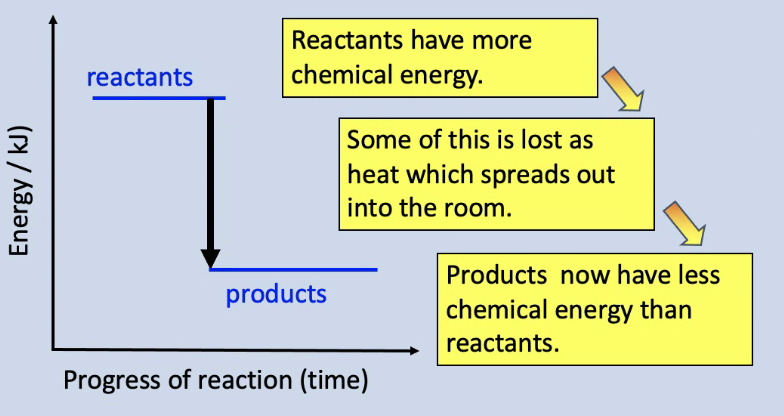
Energy level diagram
Energy level diagram for an exothermic reaction
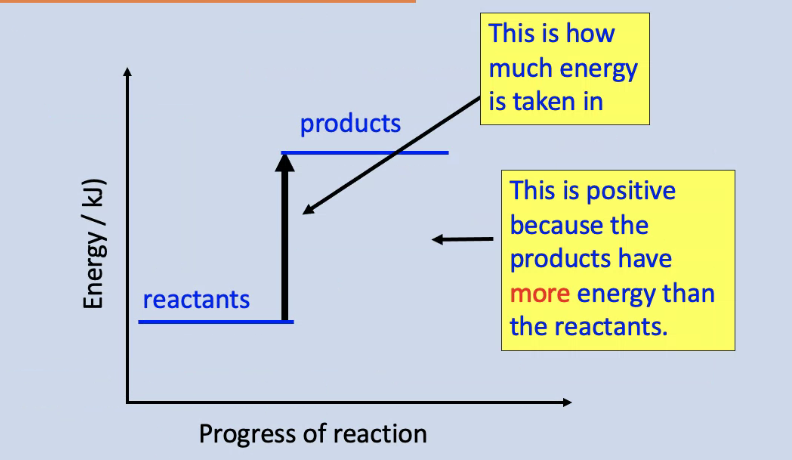
Energy level diagram for an endothermic reaction
Calorimetry
A technique used to measure changes in enthalpy of chemical reactions (how much heat is released/absorbed by a chemical reaction)
Enthalpy change?
The amount of heat as a result of a chemical reaction, such as combustion and neutralisation.
Two calorimetry experiments
Enthalpy changes of reactions in solution
Enthalpy changes of combustion
What is the enthalpy changes of reactions in solution suitable for?
Dissolving, displacement and neutralisation
Things you have to do to make sure the experiment is accurate for enthalpy changes of reactions in solution
That the specific heat capacity of the solution is the same as pure water, i.e. 4.18 J g-1 K-1
That the density of the solution is the same as pure water, i.e. 1 g cm-3
The specific heat capacity of the container is ignored
The reaction is complete
There are negligible heat losses
What do you test enthalpy changes of reactions in solution in
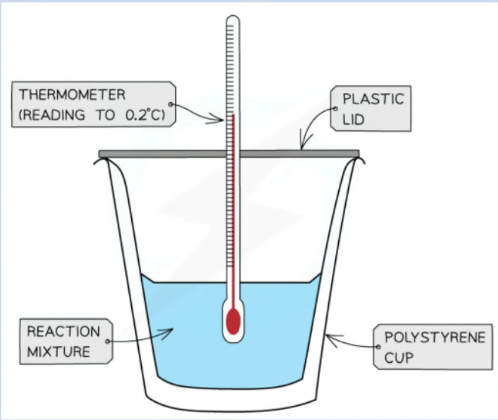
A calorimeter (can be made up of a polystyrene drinking cup, a vacuum flask or a metal can), It will have an in
How to test for enthalpy changes of reactions in solution
A fixed volume of one reagent is added to the calorimeter and the initial temperature taken with a thermometer
An excess amount of the second reagent is added and the solution is stirred continuously
The maximum temperature is recorded and the temperature rise calculated
To see this reaction in action and how to set up (Optional)
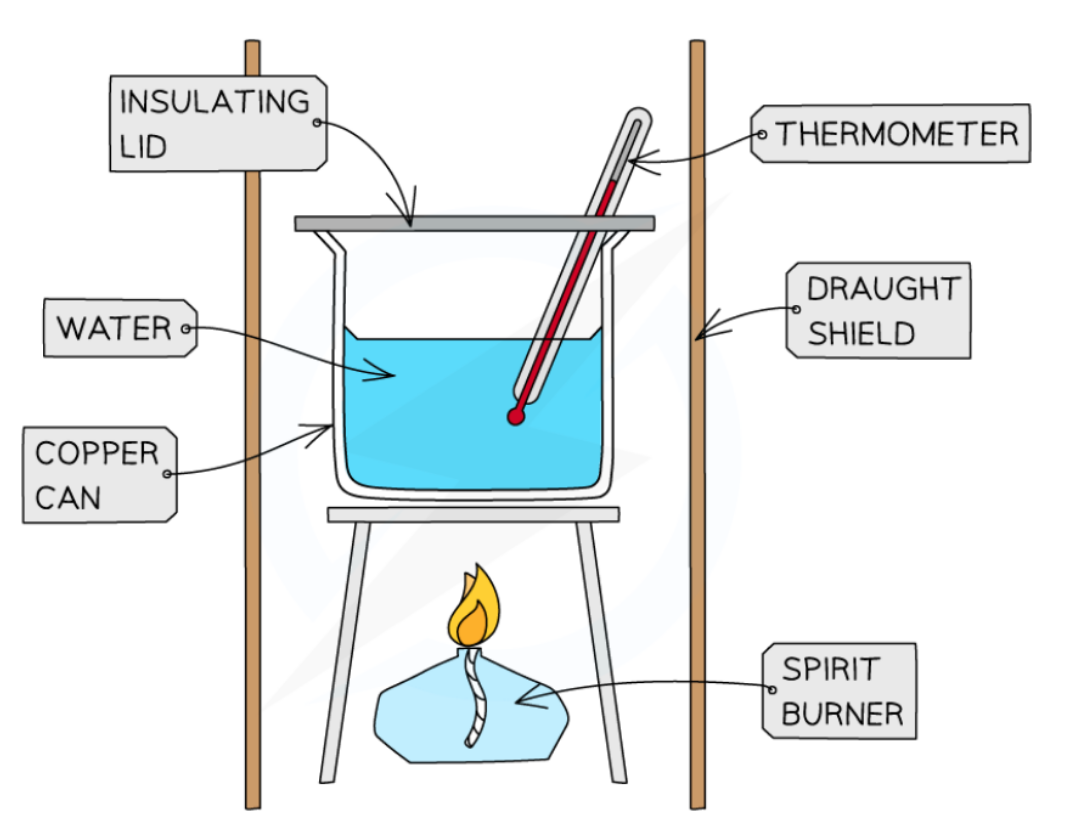
What do you need to test for Enthalpy of Combustion
Thermometer
Draught shield
Spirit burner
Typical calorimeter
Setup for an Enthalpy of Combustion experiment
Other calorimeter setup
Possible faults in either experiment
Not all the heat produced by the combustion reaction is transferred to the water
Some heat is lost to the surroundings
Some heat is absorbed by the calorimeter
To minimise the heat losses the copper calorimeter should not be placed too far above the flame and a lid placed over the calorimeter
Shielding can be used to reduce draughts
In this experiment the main sources of error are
Heat losses
Incomplete combustion
What is specific heat capacity
Describes how much energy it takes to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
Specific heat capacity of 1kg water?
4200J
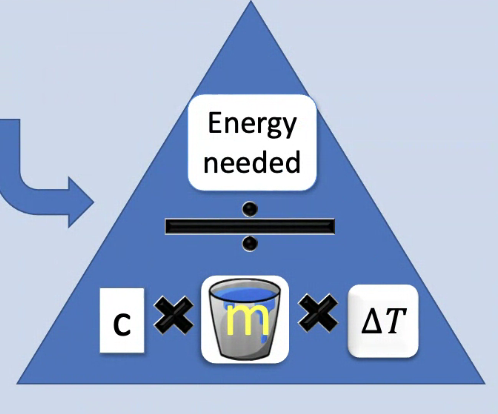
How to work out energy needed?
Energy = Mass x heat capacity x change in temperature
or
M x c x △T
Work out the energy needed to make 3kg of water rise in temperature by 5°C
(M x c x △T)
63,000 J
Formula triangle for specific heat capacity