IMC Unit 2: Macro Economics
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
What are the Key Economics Indicators in the US
Average weekly hours of production workers
Initial claims for unemployment insurance
New orders in manufacturing
New private housing permits
Yield curve slope shifts
Money supply
Consumer sentiment
Personal income
Data releases, e.g. non-farm employment (payroll
What are Economic and Financial Cycles
Economy-wide fluctuations in economic activity observed via
• GDP/Income/Employment/Industrial production
• Boom and contraction
How long do Business Cycles tent to last
3-5 Years
What do Keynesisan Ideas suggest are the causes of Business Cycles
• Fluctuations in demand
• The cycle of net credit creation suggests easy credit leads to
speculative bubbles
What is the circular flow of money thoey
Economy comprised of ‘households’ and ‘firms’
‘Government’ and ‘foreign factors’ are IGNORED temporarily
National income accounting is a way to measure GDP (Y)
In the Circular flow theory are households and firms inputs and outputs equal?
Yes
What are Leakages and Injections in the Circular Flow
Leakages: savings, tax, imports
• Injections: investment, government spending, exports
If Households either save or consume what does Y equal
Y = C + S
In the Circular flow theory are savings and investments equal?
Yes
Deposits are lent to businesses and used to invest
How is GDP(Y) equal
Y= C+I+G+(X-M)
What is GDP
The value of output produced by factors of production which are
located within the domestic economy
Ignoring foreign factors
What is GNP
This is GDP plus the net income from abroad
What is the consumption function
C= a +cYD
a is autonomous spending
c is the ‘marginal propensity to consume’ (MPC)
YD is disposable income
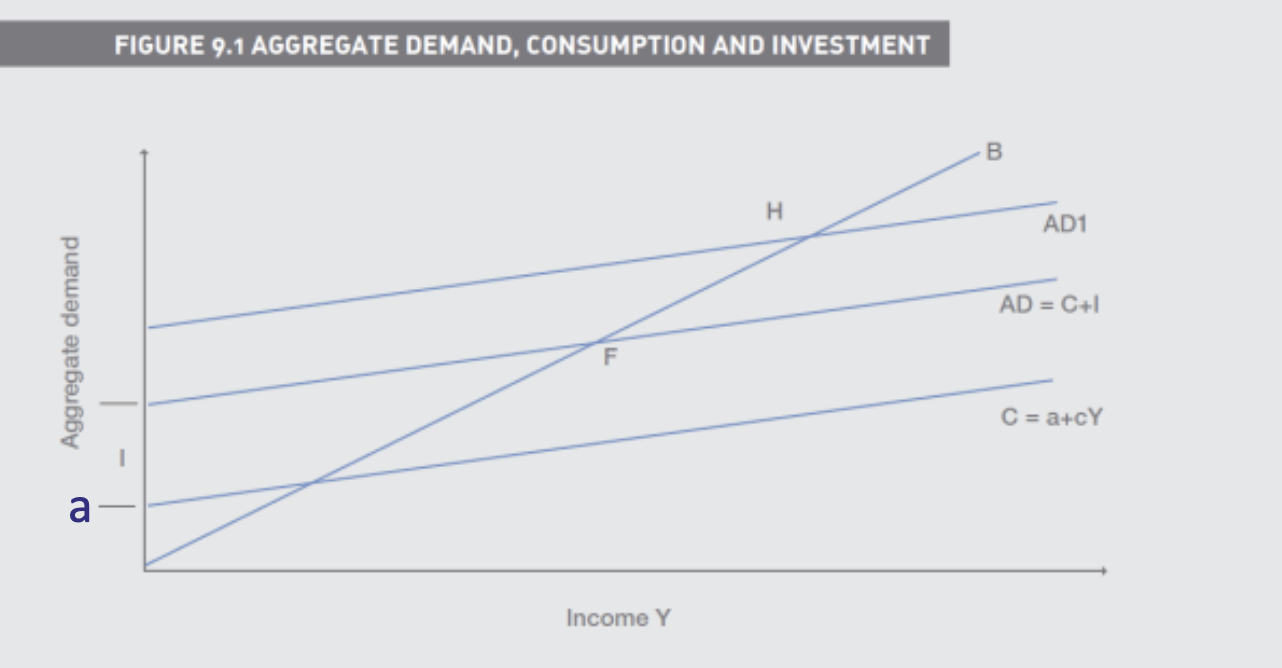
What is the Multiplier
1/(1-c)
(1-c) = the marginal propensity to save (MPS
What is the Multiplier when the Government is factored in
Tax reduces our ability to consume:
• C = a + c(1-t)YD
Hence adjusted for tax the multiplier becomes:
• 1/(1 - c(1-t))
What is the Multiplier when Foreign Trade is factored in
The multiplier adjusted for the marginal propensity to import ‘e’ is:
• 1/1 – (c-e)
What is Fiscal Policy
The totality of the government’s decisions about spending and
taxation
What is the Budget Surplus
The difference between government revenue (t) and spending (G
What is stabilisation policy
Adjusting ‘G’ or ‘t’ to boost or slow down the economy is know a
How does fiscal policy slow down a boom
Increasing taxation (t) decreases consumption by decreasing
disposable income (YD)
Decreasing government spending (G) delivers less stimulus
How does fiscal policy stimulate growth
Decrease taxation (t) increases consumption by increasing
disposable income (YD)
Increasing government spending (G) delivers more stimulu
What is monetary policy
When Central Bank’s influence the price and quantity of money and credit available in the economy
What is the M0 Measure of the money supply
Publication ceased in 2006. Replaced by publication of
‘reserve balances’ (bank and building society deposits at the Bank
of England)
What is the M1 Measure of the money supply
Notes and coins outside of banks, together with private sector non-interest bearing sight deposit
What is the M3 Measure of the money supply
M1 plus private sector interest bearing sight and time
deposits (excluding Building Societies)
What is the M4 Measure of the money supply
M3 plus CDs, repos and securities with a maturity of less than
five years
What is the M4ex Measure of the money supply
M4 excluding the deposits of international offshore
financial centres
What is the system of fractional reserve banking
A small proportion of deposits are held by the bank (the majority
is used to create credit)
What is the monetary base (the stock of high-powered money)
The quantity of notes and coins in private hands and held by the banking system
What is the Money multiplier
The relationship between the different definitions of money and changes in the monetary base

What does the Quantity Theory of Money relate to
The supply of money to inflation
What is the equation for the Quantity Theory of Money
MV = PT
• M is money
• V is velocity
• P is the price level
• T is the level of transactio
What are the 3 typical assumptions of the Quantity Theory of Money
V and T are fixed with respect to the money supply
Supply of money is exogenous
Causation runs from left (MV) to right (PT
What do the assumptions of the Quantity Theory of Money mean
An increase in the supply of money will lead to an exactly
proportionate increase in the price level
Thus money supply expansions only cause price inflatio
How do Central Banks control money supply
By changing interest rates
What are the different types of Uneployment
Frictional
Structural
Classical
Keynesian
What is Inflation
Sustained price rise
Measured by the year-on-year change in the consumer price index (CPI)
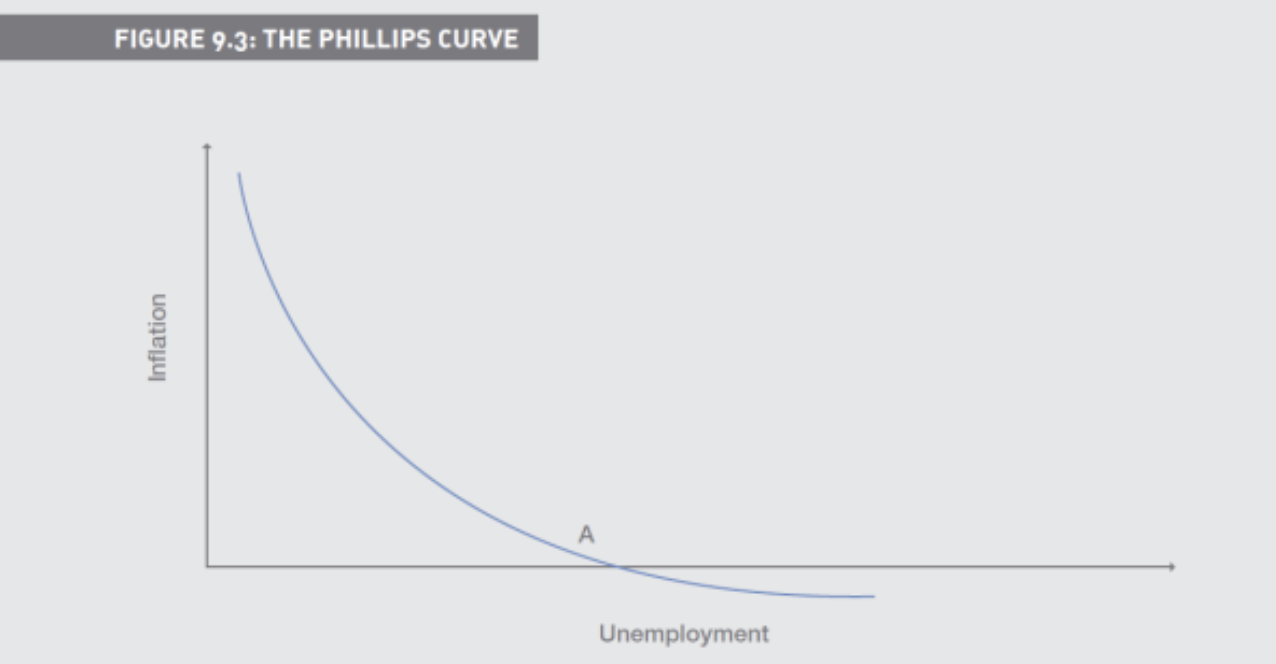
What is the Phillips Curve
Shows the relationship between inflation and unemployment
More inflation Less unemployment
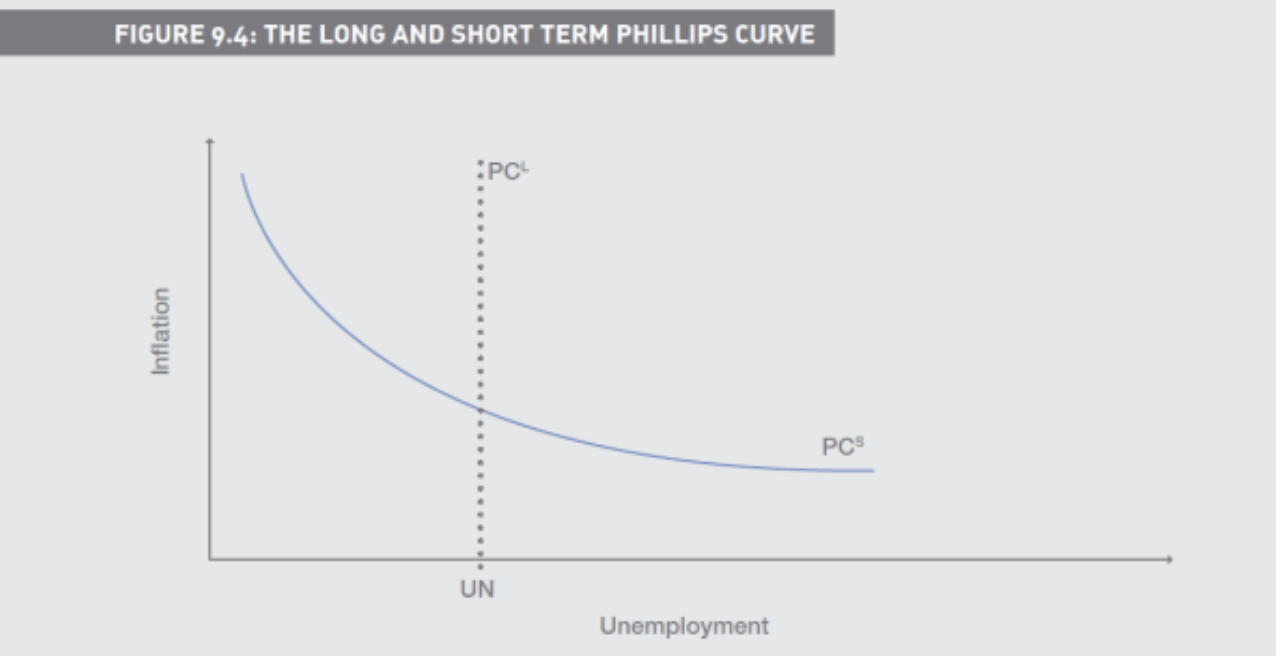
How is the Phillips Curve in the Long Run
Trade-off between unemployment and inflation was found to be
temporary, rather than permanent
Over the long-term when the economy is expanding in equilibrium there was found to be a natural rate of unemployment, full employment
What are the other Central Bank Tools for managing the Economy
Open market operations
• Quantitative easing
Reserve ratio
Forward guidance
How does the MPC set interest rates
to influence aggregate demand to keep inflation within ±1% of the CPI target level of 2%
What are the Bank liquidity requirements
Banks must hold a percentage of their risk-adjusted assets in high quality assets (cash, government bonds)
Securitising assets lowers this requirement
What are the features of the FOREX Market
No physical market place
Major players: international banks and brokerage house
What are the features of the Spot Market
Transactions for ‘immediate delivery’
Normal settlement: T+2
Market makers quote rates as bid-offer spread
What is a Bid Price
Price at which a market maker or dealer is willing to buy an asset from you.
What is a Offer (Ask) Price
Price at which a market maker or dealer is willing to sell an asset to you.
A market maker is quoting a price for GB pounds in US dollars GBP/USD 1.5244-1.5284. How many dollars will you receive if you sell £500,000 to the market maker?
500,000 × 1.5244 = 762,200
What are the Features of the Forward Market
Transactions to trade currencies at a future date at a fixed price
agreed now
Forward quotes are at a premium or discount to spot
Question on premiums on discount
xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz xyz
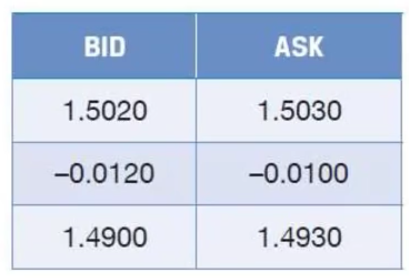
Sterling spot against the dollar is GBP|USD 1.5020-1.5030, and the three- month rate is quoted as a premium of 1.2c-1.0c
How much sterling will you receive if you sell $500,000 forward
Since you are selling, you’re looking for the Ask Price
You must subtract the premium
Therefore, the answer is 500,000 / 1.4930
= 344,896
What is Purchasing power parity (PPP)
The ‘law of one price’
• Explains the relationship between spot rates and forward rates
• Relies on the principle of zero arbitrage
What is the rationale of PPP
an exchange rate will change by a proportion that
reflects the inflation differential between two countries
What is the Formula for PPP

A good costing £1 in the UK currently costs $1.4471 in the US. Inflation is 2.0%pa in the UK and 2.5%pa in the US.
Calculate the expected 12 month forward rate
1.4471 * ((1+ 0.025) / (1+ 0.02))
= 1.454
What is Interest rate parity (IRP)
Starting from a point where exchange rates are at their
equilibrium, an increase/(decrease) in domestic interest rates will
cause that country’s currency to appreciate/(depreciate
What is the rationale of IRP
1. Converting a £ sum to $s today (at the spot rate), depositing in the US (at the US interest rate) and re-converting at the forward rate
should generate the same sterling value as;
2. Depositing the same £ sum in the UK for the same period
What is the Formula for IRP

The £/$ exchange rate is £1/$1.4471 in the US. Interest rates are 2.0%pa in the UK and 2.5%pa in the US.
Calculate the three-month forward rate
3 months = 0.25 years
1.4471 * ((1+ 0.025 ×0.25) / (1+0.02×0.25))
1.4471 * (1+ 0.00625) / (1+ 0.005)
= 1.4489