Ch 1
1/141
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
142 Terms
Geography
a discipline that examines Earth’s physical and human dimensions
Globalization
the increasing interconnectedness of people and places through converging economic, political, and cultural activities
Diversity
refers to the state of having different forms, types, practices or ideas, as well as the inclusion of distinct peoples, in a particular society
Describe the conceptual framework of world regional geography
Identify the different components of globalization, including controversial aspects, and list several ways in which globalization is changing world geographies.
Summarize the major tools used by geographers to study Earth’s surface.
Explain the concepts and metrics used to document changes in global population and settlement patterns.
Describe the themes and concepts used to study the interaction between globalization and the world’s cultural geographies.
Explain how different aspects of globalization have interacted with global geopolitics from the colonial period to the present day.
Identify the concepts and data important to documenting changes in the economic and social development of more and less developed countries.
Geography
A discipline inspired by our desire to explore and understand our world
What are the two puruits of geography?
physical and human geography
Physical geography
examines climate, landforms, soils, vegetation, and hydrology
Human geography
concentrates on the spatial analysis of economic, social, and cultural systems
What is thematic or systematic geography?
A geographic approach focused on a specific theme or topic
What is regional geography?
A geographic approach that focuses on a specific place or region
Place
Encompasses the characteristics of a location and the meaning people give to it
Cultural landscape
the tangible, material expression of human settlement, past and present
Space
represents a more abstract, quantitative, and model-driven approach to understanding how objects and practices are connected to and impact each other
Regions
Units of spacial similarity with a defined territory that share common characteristics
Formal region
Defined by some long term aspect of physical form, like climate or mountains
Functional region
Defined by the activities that take place within the area
World regions
12 regions defined by formal characteristics such as physical features, language groups, and religious affiliations, but also relying on functional characteristics such as trade groups and regional associations
What are the world regions?
North America, Latin America, the Caribbean, Sub-Saharan Africa, North Africa and Southwest Asia, Europe, Eurasia, Central South and East Asia, and Oceania
Explain the difference between place and space in geographic understanding and analysis
Place focuses on the meaning people place upon a location, such as cultural landscape, while space focuses on the more quantitative characteristics of an area, such as how income differs from location to location
How is the concept of the cultural landscape related to place?
Cultural landscape is a tool to help analyze a place. It reflects how people interact in a place and can be used to better understand that place.
How do functional regions differ from formal regions?
Functional regions are defined by the activities that take place within an area, formal regions are defined by the long term physical features of an area.
Globalization
the increasing interconnectedness of people and places
Glocalization
The process of modifying an introduced product or service to accommodate local tastes
Intraregional migration
Migration within a region
Interregional migration
Migration between regions
Human trafficking
the illegal trade of humans for the purpose of forced labor, sexual slavery, or commercial sexual exploitation that is often integrated into these illegal networks
World Trade Organization (WTO)
an institution that deals with the global rules of trade among nations
What is an argument for globalization?
Countries that have embraced the global economy generally enjoy more economic success than those that have sought economic self-sufficiency
What is an argument against globalization?
Globalization is a way for corporations and countries to maximize profits by moving capital and seeking low-wage labor
What is a middle-ground argument for globalization?
Globalization is unavoidable, and has drawbacks, but can be manged to reduce economic inequality and to protect the natural environment
Provide examples of how globalization impacts the culture of a place or region
Globalization in the U.S. has led to heightened cultural diversity. In Kenya most adults use M-Pesa, a cell phone based money transfer service
Describe and explain five components of economic globalization
Transportation systems that can quickly and inexpensively move goods by air, sea, and land. Global and regional trade agreements that promote more free trade. Market economies and private enterprises that have replaced state-controlled economies and services. Transnational business strategies that have created global corporations more powerful than many sovereign nations. An emphasis on producing more goods, services, and data at lower costs to fulfill consumer demand for products and information
Summarize three elements of the controversy about globalization
Globalization may not be a natural process, instead being an explicit economic policy. It may be a way for capitalist organizations to further profits through low wage work. Globalized economic systems may also be inherently unstable.
Relative locations
A mental map of an area used to locate places based on their relationship to other landscape features
Absolute location
A map that draws on a universally accepted coordinate system that gives every place on Earth a specific numerical address based on latitude and longitude
Latitude
Also called parallels, run east–west around the globe and are used to locate places north and south of the equator
Longitude
Also called meridians, run north-south around the globe an are used to locate places east of west of the prime meridian
Prime meridian
located at 0 degrees longitude at the Royal Naval Observatory in Greenwich, England. Divides the world into the east and west hemispheres
Equator
Located at 0 degrees latitude, divides the world into north and south hemispheres
Global positioning system (GPS)
Systems that use signals sent from your location to satellites and back to you to calculate your precise lat-long coordinates
Map projections
The different ways to project a spherical image onto a flat surface
Mercator projection
Square projection of earth, distorts features in high latitudes
Robinson projection
Oval shaped projection which minimizes distortion
Map scale
the mathematical ratio between the map and the surface area being mapped
Representative fraction
the ratio between the map and the area being mapped, maps are categorized as having either large or small scales
graphic or linear scale
visually depicts distance units such as feet, meters, miles, or kilometers on a horizontal bar
reference map
shows the location of certain features
thematic map
displays data such as religious affiliations or popular tourist attractions in a city
Chloropleth map
color shades represent different data values, with darker shades generally showing larger average values
remote sensing
electromagnetic images taken from aircraft or satellites
geographic information systems (GIS)
A spacial database which compiles multiple map layers to show spacial patterns and relationships
Explain the difference between latitude and longitude, and describe how they are used to locate a place
Latitude lines run east-west and measure distance north and south of the equator. Longitude lines run north-south and measure distance east and west of the prime meridian. Used together they produce a universally accepted coordinate system which gives every place on earth a specific numerical address
What does a map’s scale tell us?
The mathematical ratio between the map and the surface area being mapped
What is a choropleth map, and what might it depict?
A map in which color shades represent different data values. Per capita income and population density are often represented by these maps
What are geographic information systems (GIS), and how are they used today to address societal needs?
These are programs that compile multiple map layers into one map. They can be used for city planning, environmental science, public health, and real-estate development
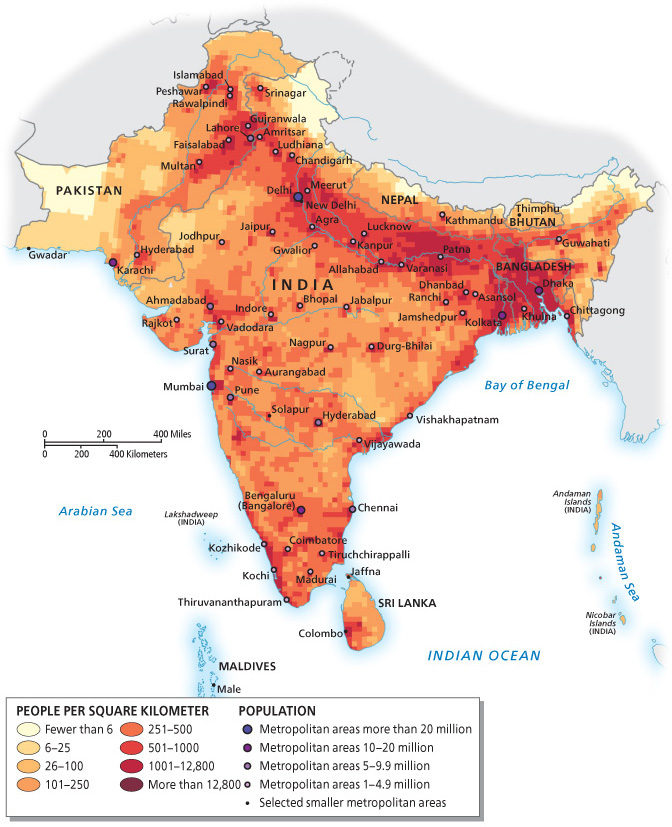
Population density
the average number of people per square kilometer
rate of natural increase (RNI)
provides the annual growth rate for a country or region as a percentage
total fertility rate (TFR)
the average number of live births a woman has in her lifetime
replacement rate
A TFR of 2.1, which suggests that it takes two children per woman, with a fraction more to compensate for infant and child mortality, to maintain a stable population
population pyramid
depicts the percentage of a population (or, in some cases, the raw number) that is male or female in different age classes, from young to old. A pyramid with a narrow base represents slow to negative growth
demographic transition model
a conceptualization that tracks the changes in birth rates and death rates over time
economic migrants
immigrants who migrate for employment opportunities
remittances
money sent by individuals working abroad to families in the origin country
refugees
migrants fleeing a well-founded fear of persecution
net migration rate
The amount of immigration (people entering a country) and emigration (those leaving a country)
megacities
a city with more than 10 million inhabitants
Urbanization
The percentage of people living in cities compared to rural areas
urban primacy
Where a primate city (often the capital) is three or four times larger than the country’s next largest city
What is the rate of natural increase (RNI), and how can it be a negative number?
The annual growth rate for a country or region. A negative RNI means a declining population, which could be bad for an area.
Explain a high versus a low total fertility rate, and give examples
A high fertility rate is one above a TFR of 2.1, such s Nigeria at 5.5. A low fertiliy rate is one below a TFR or 2.1, such Russia at 1.6
Describe and explain the demographic transition model
A model that tracks birth rate over time. In Stage 1, population growth is low because high birth rates are offset by high death rates. Rapid growth takes place in Stage 2, as death rates decline. Stage 3 is characterized by a decline in birth rates. Stage 4 the birth rate and death rate reach a relative balance. Stage 5, growth stops or growth goes negative.
How is a population pyramid constructed, and what kind of information does it convey?
The pyramid shows the percentage of a population that is male or female in different age classes from young to old. The pyramid can inform you about population growth depending on the shape (pyramid: rapid growth, top heavy: slow to no growth).
Culture
A learned, not innate, behavior shared by a group of people, empowering them with what is commonly called a “way of life.”
cultural imperialism
The active promotion of one cultural system at the expense of another
nationalism
The process of protecting and defending a cultural system against diluting or undesirable cultural expressions, while at the same time actively promoting national and local cultural values
cultural syncretism
The most common product of cultural exchange. Forms a new, synergistic form of culture
cultural assimilation
the adoption of the language, customs, or norms of the host society by an immigrant
language families
Language groups based on common ancestral speech
lingua franca
A third language used by different cultures to communicate when they cannot use their native language
secularism
An ideology where people consider themselves either nonreligious or outright atheistic
Gender
A sociocultural construct, linked to the values and traditions of specific cultural groups that differentiate the characteristics of the two biological sexes, male and female
gender roles
the cultural guidelines that define appropriate behavior within a specific context
Define cultural imperialism and cultural assimilation. How are they similar and how are they different?
In cultural imperialism the non-dominant culture is degraded. In cultural assimilation, the cultures blend to form a new culture
What is a lingua franca? Provide two examples
A go between language when two cultures cant use their native languages to communicate. Swahili is an example for the many tribes of eastern Africa. French historically was the lingua franca for international correspondance
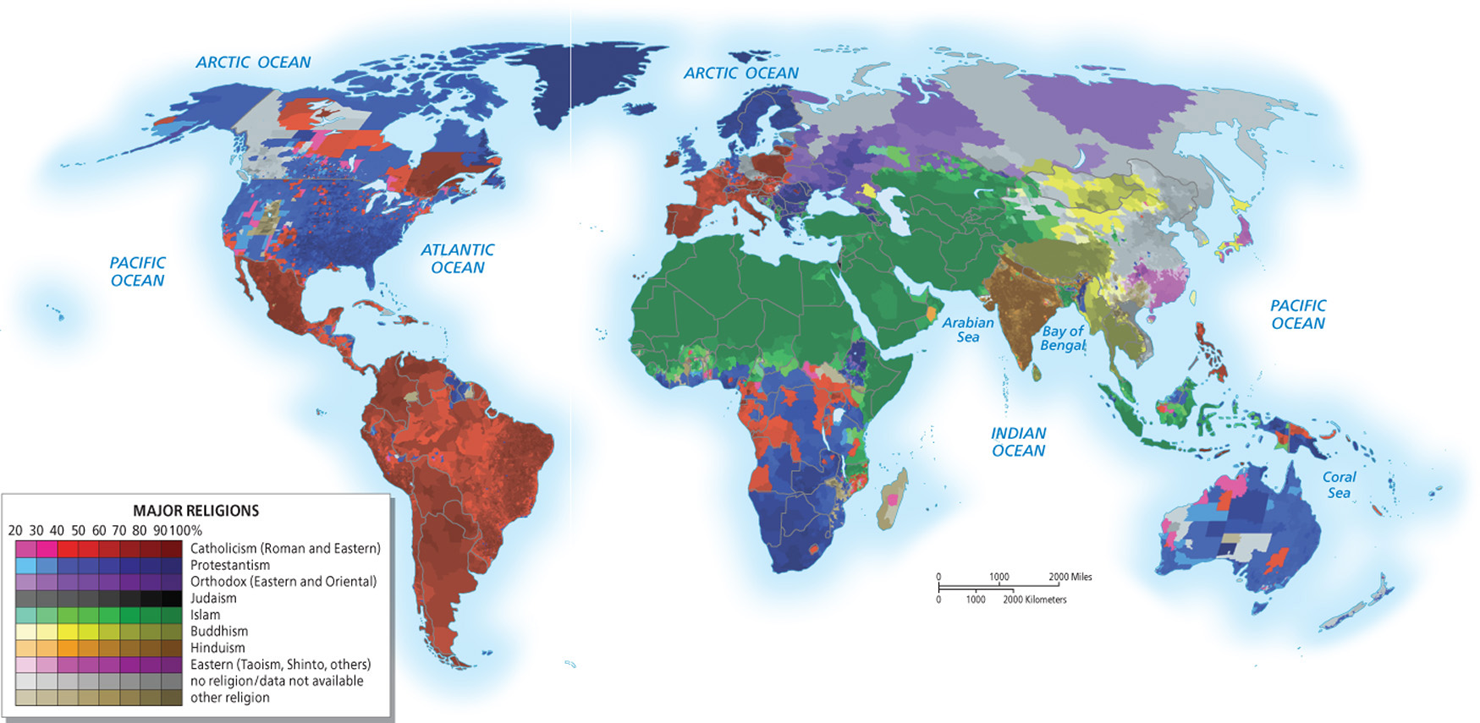
Describe the geographies of Catholicism and Protestantism shown in Figure 1.32. What would explain these distinct realms of influence?
Religion is heavily tied to culture. These religious boundaries represent cultural boundaries
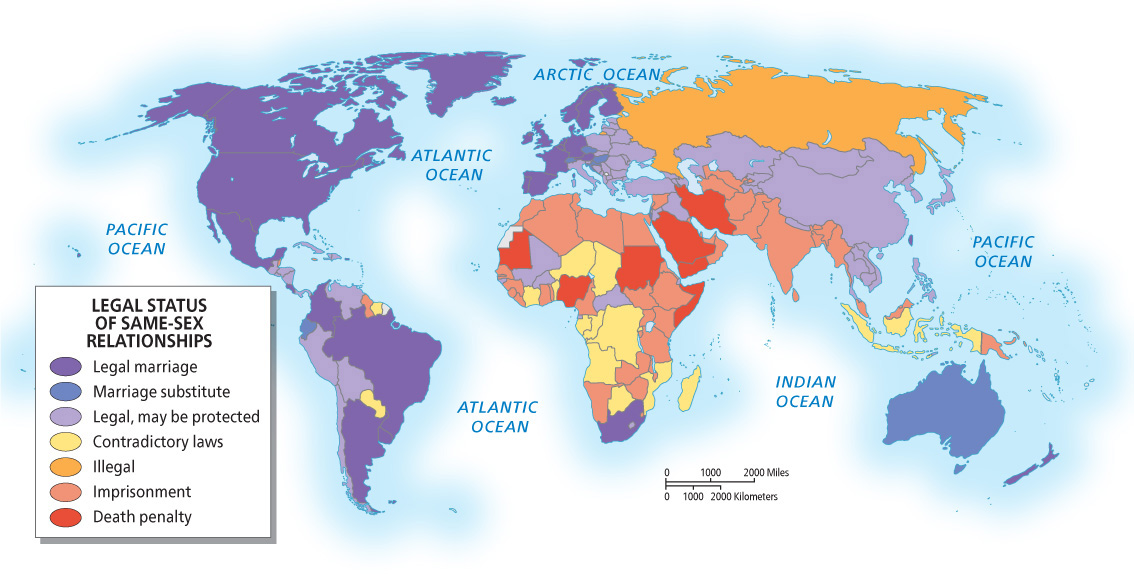
Discuss the patterns of acceptance and exclusion shown in Figure 1.34 with regard to gay rights
More globalized countries are more accepting of gay rights
geopolitics
used to describe the close link between geography and politics
sovereignty
the ability (or inability) of a government to control activities within its borders
territory
the delimited area over which a state exercises control and which is recognized by other states
nation-state
Nation describes a large group of people with shared sociocultural traits, such as language, religion, and shared identity. State refers to a political entity that has a government and a clearly delimited territory that is maintained and controlled
ethnicity
a social group with a common or distinctive culture, religion, language, or history
autonomous areas
An area of a country that has a degree of autonomy, or has freedom from an external authority
Colonialism
the formal establishment of rule over a foreign population
Decolonialization
the process of a colony gaining (or, more correctly, regaining) control over its own territory and establishing a separate, independent government