MKT 337 Miller Exam 3
1/136
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
137 Terms
Integrated Marketing Communications (IMC)
the careful coordination of all promotional messages to assure the consistency of messages at every contact point where a company meets the consumer
IMC Popularity Growth Factors
1. Proliferation (increase) of thousands of media choices
2. Fragmentation (breaking up) of the mass market
3. Slash of advertising spending in favor of promotional techniques that generate immediate response
Factors Affecting the Choice of Promotional Mix
1. Nature of product
2. Stage in PLC
3. Target market characteristics
4. Type of buying decision
5. Promotion funds
6. Push or pull strategy
Product Life Cycle and the Promotional Mix
Introduction, Growth, Maturity, Decline

Pre-Introduction (PLC)
light advertising, pre-introduction publicity
Introduction (PLC)
Heavy advertising, PR for awareness, sales promotion for trial
Growth (PLC)
Advertising, PR, brand loyalty, personal selling for distribution
Maturity (PLC)
Ads decrease, sales promotion, personal selling, reminder and persuasive
Decline (PLC)
Ad/PR decrease, limited sales promotion, personal selling for distribution
Advertising, Sales Promotion and Less Personal Selling
Target Market Characteristics for:
-widely scattered market
-informed buyers
-brand loyal repeat purchasers
Routine Buying Decision
advertising, sales promotion
Neither Routine nor Complex Buying Decision
advertising, public relations
Complex Buying Decision
personal selling, print advertising
Different Methods of Promotion
Personal selling
Mass selling (advertising and publicity)
Sales promotion
Who Must Plan, Integrate, and Manage the Promotion Blend
Sales Managers
Advertising Managers
Marketing Managers
Sales Promotion Managers
Promotion Objectives
Informing
Persuading
Reminding
The Traditional Communication Process
source, encoding, message channel, decoding, receiver, feedback & noise happens in the middle of it all
Push Strategy
manufacturer promotes to wholesaler, wholesaler promotes to retailer, retailer promotes to consumer, consumer buys from retailer
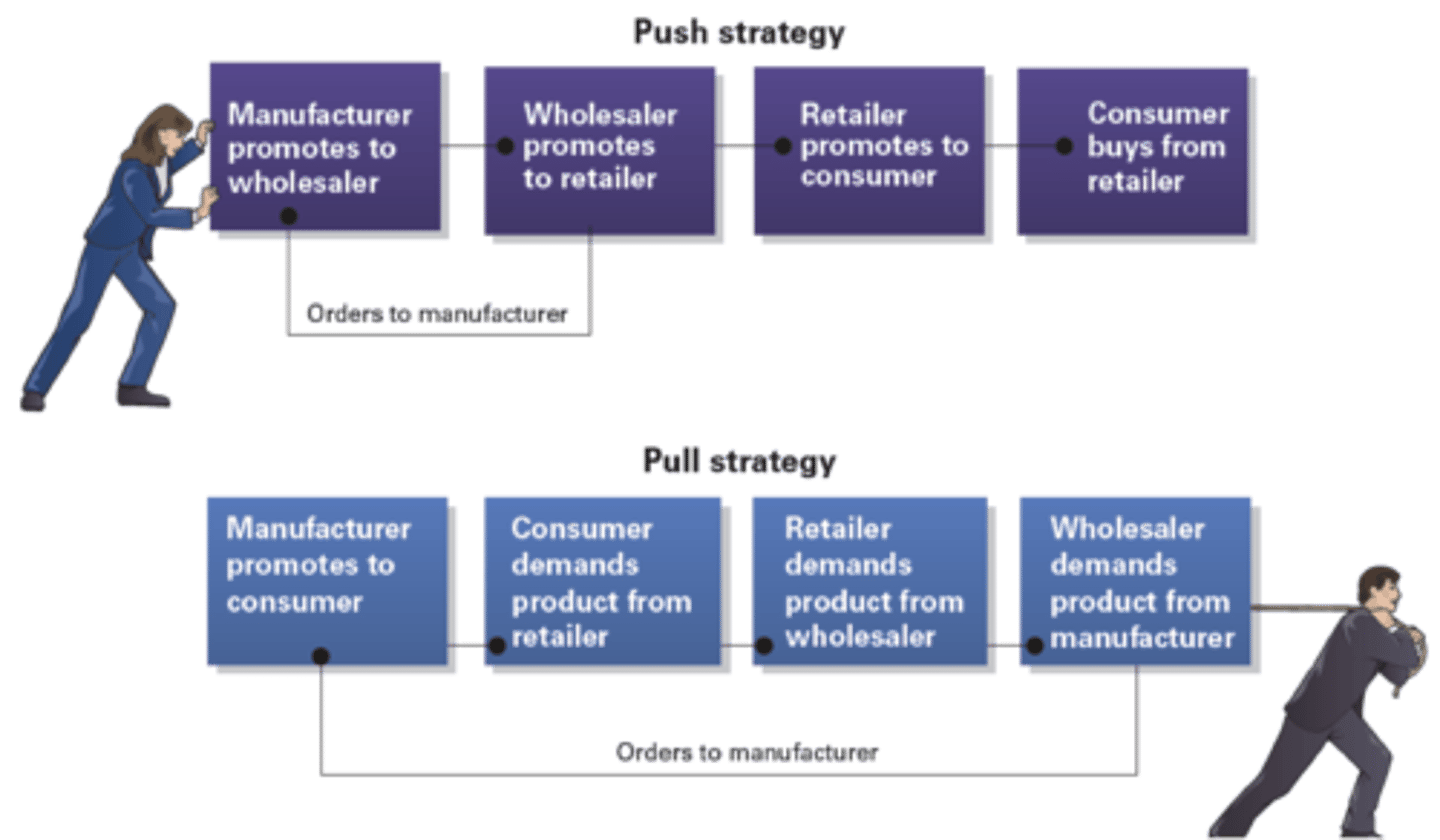
Pull Strategy
manufacturer promotes to consumer, consumer demands product from retailer, retailer demands product from wholesaler, wholesaler demands product from manufacturer

Promotional Strategy
a plan for the optimal use of the elements of promotion: advertising, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion
Promotional Mix
the combination of promotional tools used to reach the target market and fulfill the organization's overall goals
Includes:
advertising, public relations, personal selling, sales promotion, social media
Advertising
most commonly distributed by traditional media, though increasingly through non-traditional media, such as websites, email, blogs, and interactive video kiosks in malls and supermarkets
Traditional Advertising Media
Television
Radio
Newspapers
Magazines
Books
Direct mail
Billboards
Transit cards
New Advertising Media
Internet
Banner ads
Viral marketing
E- mail
Interactive video
Advertising Advantages
1. Reach large number of people
2. Low cost per contact
3. Can be micro-targeted
Advertising Disadvantages
1. Total cost is high
2. National reach is
expensive for
small companies
Public Relations
Evaluates public attitudes, identifies areas within the organization that public may be interested in, and executes a program to earn public understanding
The Function of Public Relations
1. Maintain a positive image
2. Educate the public about the company's objectives
3. Introduce new products
4. Support the sales effort
5. Generate favorable publicity
Communication
the process by which meanings are exchanged or shared through a common set of symbols
Marketing Communication As Senders
1. Inform
2. Persuade
3. Remind
Marketing Communication As Receivers
1. Develop messages
2. Adapt messages
3. Spot new communication opportunities
Traditional Advertising Model
1. impersonal
2. numbers driven
3. unquantifiable consumer behavior
Internet and Social Media Advertising
1. Personal
2. Direct communication
3. Feedback driven
4. Highly visible communication
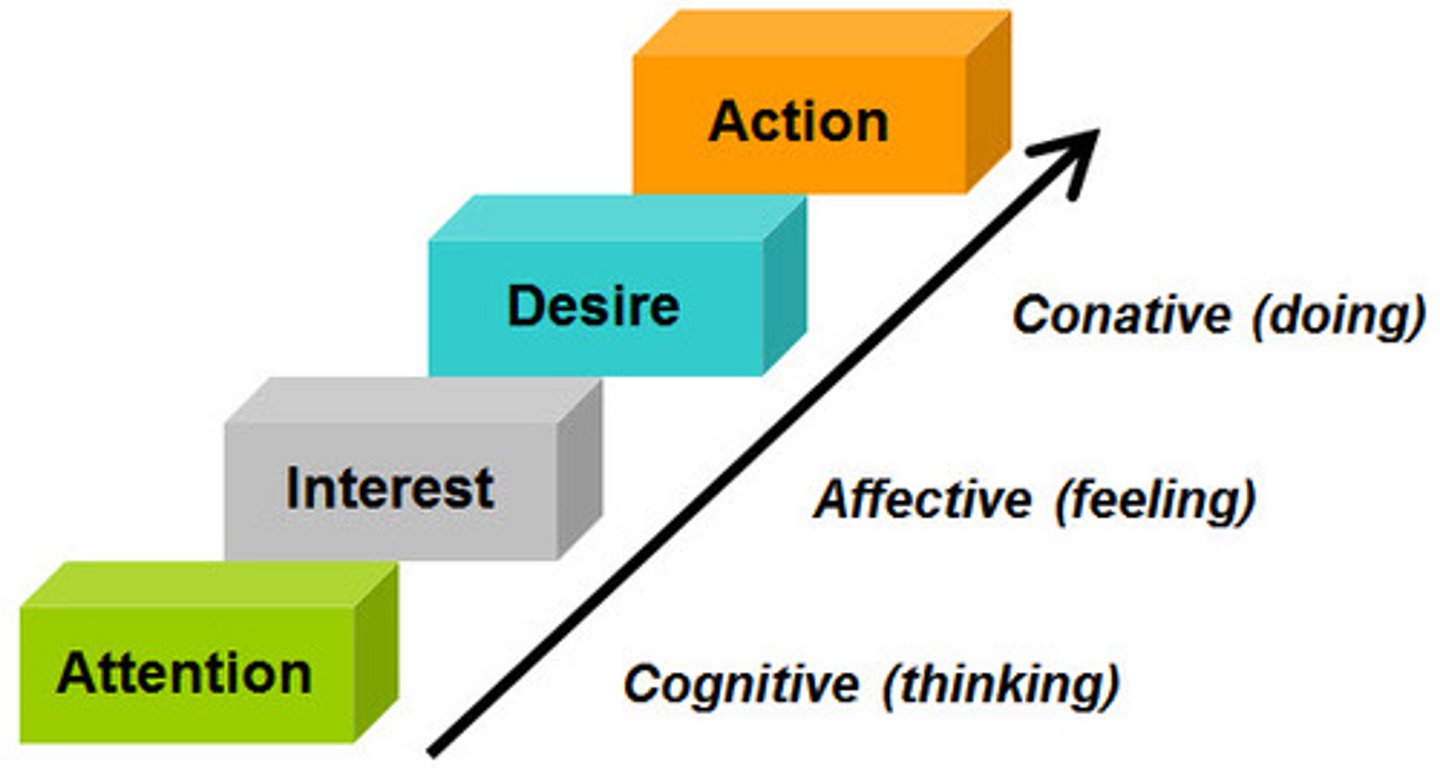
The AIDA Concept
a model that outlines the process for achieving promotional goals in terms of stages of consumer involvement with the message; the acronym stands for attention, interest, desire, and action
PLC Stages: Informing
Introduction
Early Growth
PLC Stages: Reminding
Maturity
PLC Stages: Persuading
Growth
Maturity
Informative Promotion
Increase awareness
Explain how product works
Suggest new uses
Build company image
Persuasive Promotion
Encourage brand switching
Change customers' perceptions of product attributes
Influence immediate buying decision
Persuade customers to call (to see what its like)
Reminder Promotion
Remind customers that product may be needed
Remind customers where to buy product
Maintain customer awareness
Sales Promotion
marketing activities - other than personal selling, advertising, and public relations - that stimulate consumer buying and dealer effectiveness
Personal Selling
planned presentation to one or more prospective buyers for the purpose of making a sale
Traditional Selling
Attempts to persuade the buyer into a specific point of view; creates a win-lose outcome.
Relationship Selling
Long-term relationships; creates a win-win outcome.
Social Media
promotion tools used to facilitate conversations among people online
Social Media allows marketers to:
1. manage brand images
2. engage with consumers
3. generate interest
Predictive Analytics
the process of using historical data to make assumptions about future results
software is typically based on a big data analytics engine
How is predictive analytics used in sales?
Lead scoring and prioritization
Sales process optimization
Accurate forecasting
Eliminating uncertainty
Hiring and HR
Employee Training
Predictive Analytics: Key Players
infer
IBM
SAP
dataxu
Oracle
insidesales.com
Marketo
Tableau
Predictive Analytics: Customer Use Cases & Application
Analytical CRM
Child Protection
Cross Selling
Customer Retention
Direct Marketing
Fraud Detection
PA: Analytical CRM
Uses predictive analysis in applications for marketing campaigns, sales, and customer services
PA: Child Protection
Child welfare agencies have started using predictive analytics to flag high risk cases
PA: Cross Selling
Organizations collect and maintain abundant data (e.g. customer records, sale transactions) as exploiting hidden relationships in the data can provide a competitive advantage
PA: Direct Marketing
Identify the most effective combination of product
versions, marketing material, communication channels and timing that should be used to target a given consumer
PA: Fraud Detection
Identify high-risk fraud candidates in business or the public sector through big data
PA: Customer Retention
Maintaining continuous customer satisfaction, rewarding consumer loyalty and minimizing customer attrition
PA in Sales: Lead Scoring and Prioritization
When you know which deals are the most likely to close, you can ensure that sales reps are spending their time on the right opportunities
PA in Sales: Sales Process Optimization
When you know which activities and content lead to more closed deals, you can structure your sales process for repeatable success
PA in Sales: Accurate Forecasting
When sales opportunities are scored and weighted based on historical success rather than gut feelings, managers can be confident in their forecasts
PA in Sales: Eliminating Uncertainty
Being able to make choices with a higher measure of assurance changes the entire workplace
PA in Sales: Hiring and HR
Predicting your headcount needs. Ebbs and flows in employee retention.
PA in Sales: Employee Training
Tracking employee performance as they complete training modules. Assess value of training.
PEPSICO Tips
1. Merchandise more clearly
2. Advanced Planning
3. Pay attention to core competencies
4. Iconic Brands: make, move, sell!
5. Industry requires flexibility
6. DSD System ( continue to look for ways to improve )
The Life Stage
of a company will in many ways dictate the most effective supply chain strategy to employ
What should a companies Supply Chain strategy support/accentuate?
its core competencies
Cost Savings
NOT a strategy, nor should it be the sole purpose of choosing a supply chain process ( customer value and organizational agility need to be considered as well )
Marketing Channels
A combination of organizations and individuals who perform the required activities to link producers of products to users of those products to accomplish marketing objectives
Channel Objectives
specifically stated, measurable, and consistent with firm's marketing objectives
Channel Strategy
an expression of a general action plan and guidelines for allocating resources to achieve the channel objective
Factors in Channel Strategy
1. buyer preference
2. relationship orientation
3. market coverage
Buyer Preference
letting the customers buy the way they want to
Relationship Orientation
building strong relationships with customers
Market Coverage
number of outlets marketing the product
Specialization and Division of Labor
1. Creates greater efficiency
2. Provides lower production costs
3. Achieves economies of scale
4. Aids producers who lack resources to market directly
5. Builds good relationships with customers
Retailer
a channel intermediary that sells mainly to customers
Merchant Wholesaler
an institution that buys goods from manufacturers ,takes title to goods, stores them and resells and ships them
Agents and Brokers
wholesaling intermediaries who facilitate the sale of a product by representing channel members
Factors suggesting type of wholesaling intermediary to use
1. Product characteristics
2. Buyer Considerations
3. Market Characteristics
Some reasons for choosing direct channels
1. greater control
2. lower cost
3. internet makes direct distribution easier
4. direct contact with customers
5. no suitable intermediaries (gotta sell it yourself)
Direct Channel
a distribution channel in which producers sell directly to customers
When Indirect Channels are Best
1. convenience
2. store loyalty
3. lower initial investments
channel
1
Key Issues in Channel Management
1. Choosing the type of relationship
2. Whole-channel product-market commitment
3. Conflict handling
4. Role of channel captain
Discrepancy of Quantity
the difference between the amount of product produced and the amount an end user wants to buy
Discrepancy of Assortment
the lack of all the items a customer needs to receive full satisfaction from a product or products
Conflicts may occur if channel members:
Have conflicting goals
Fail to fulfill expectations of other channel members
Have ideological differences
Have different perceptions of reality
Channel Partnering/Cooperation
the joint effort of all channel members to create a channel that serves customers and creates a competitive advantage
By COOPERATING, channel members can:
speed up inventory replenishment, improve customer service, and reduce the total costs of the marketing channel
Intensive Distribution
selling a product through all responsible and suitable wholesalers or retailers who will stock or sell the product
Selective Distribution
selling through only those intermediaries who will give the product special attention
Exclusive Distribution
selling through only one intermediary in a particular geographic area
Logistics or Physical Distribution
how to get RM to factory and finished product to customer
increase profit, cut prices, improve customer service
Factors Affecting Physical Distribution Service Levels
1. info on product availability
2. order processing time
3. backorder procedures
4. inventory storage
5. order accuracy
6. damage in transit
7. online status info
8. advance info on delays
9. delivery time and reliability
10. compliance with customers
11. defect-free deliveries
12. handling adjustments/returns
Just In Time (JIT) Inventory
seamless process of getting a product or service from manufacturer to consumer
Areas Where Computers Help Physical Distribution Service
1. Continuously updated information systems
2. Electronic data interchange
Ethical issues may arise: Product Availability
1. false expectations about delivery speed
2. selling products that are not available
3. running out of popular products
Ethical issues may arise: Coordination of Physical Distribution
1. intentional delays in order confirmation
2. shifting of burden of holding inventory (take responsibility)
Supply Chain
the connected chain of all of the business entities, both internal and external to the company, that perform or support the logistics function
Supply Chain Management
a management system that coordinates and integrates all of the activities performed by supply chain members into a seamless process, from the source to the point of consumption, resulting in enhanced customer and economic value
The philosophy behind supply chain management
by visualizing the entire supply chain, supply chain managers can maximize strengths and efficiencies at each level of the process to create a highly competitive, customer driven supply system that is able to respond immediately to changes in supply and demand