ib econ- 2.5: demand elasticity
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
credits https://www.econinja.net/microeconomics/2-5-demand-elasticity
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
what is elasticity of demand?
how responsive the quantity demand is for a good/service when price or income changes.
demand is elastic when a change in price/income leads to a larger change in quantity demand, and vice versa for inelastic.
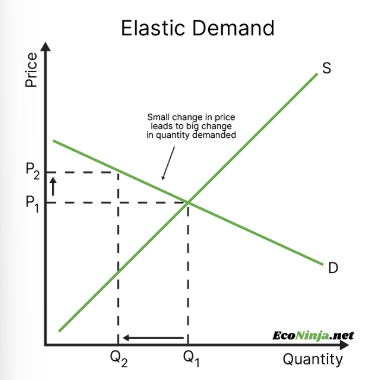
draw an elastic demand curve and give an example of a demand elastic product
sweets are demand elastic because there are many substitutes and competing brands, so if the price of one increases, consumers will turn to other options
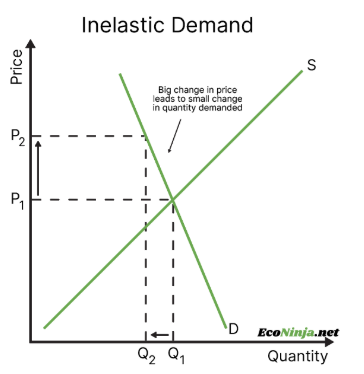
draw a demand inelastic curve and give an example of such a product
gasoline is demand inelastic because people need it even if prices rise, so demand will not change significantly
what is price elasticity of demand (PED)?
how responsive the quantity demanded is for a good/service when price changes
how do you calculate PED?
PED = (% change in Q)/(% change in D)
to calculate percentage change, remember “new minus old over old”
price is always on the bottom “you Q before you P”
IGNORE ANY NEGATIVES
if the value is less than 1, the product is inelastic (change in P = less change in Q)
if the value is greater than one, the product is elastic (change in P = greater change in Q)
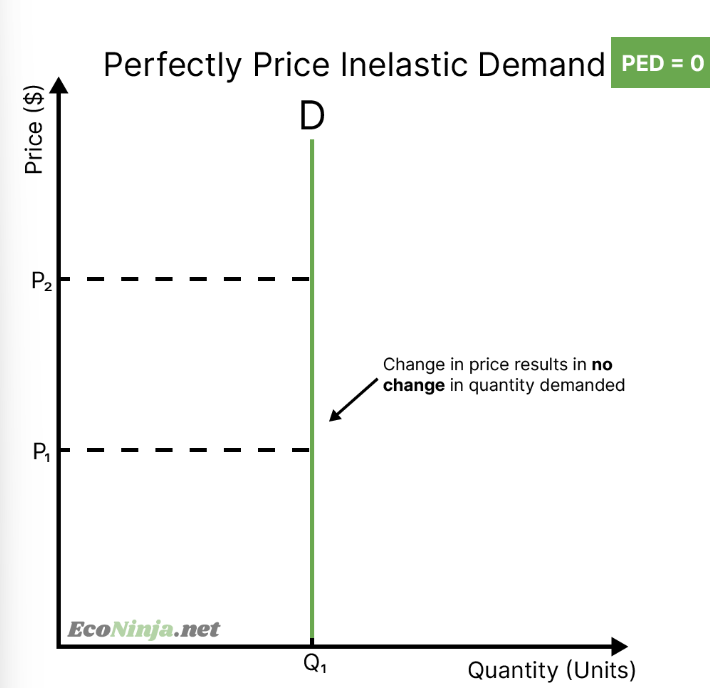
what is the PED for a product with perfectly price inelastic demand? draw the diagram
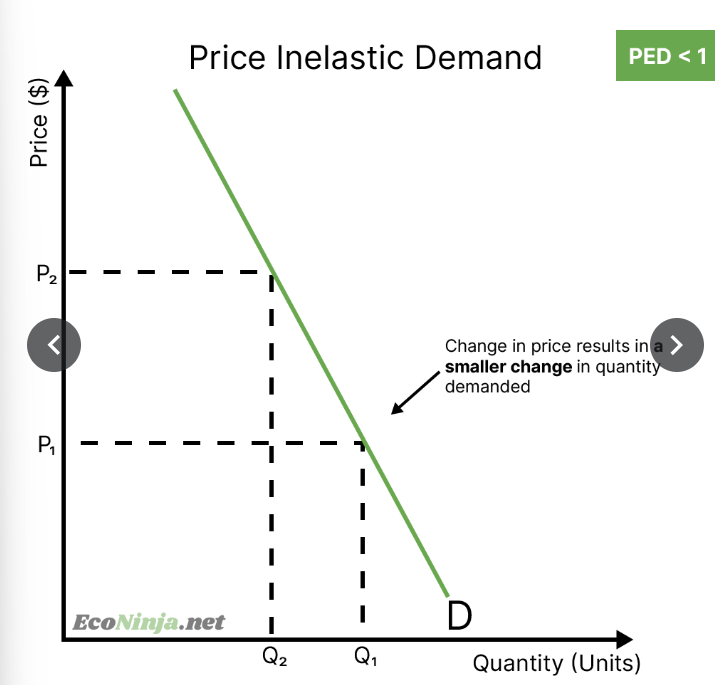
what is the PED for a product with price inelastic demand? draw the diagram
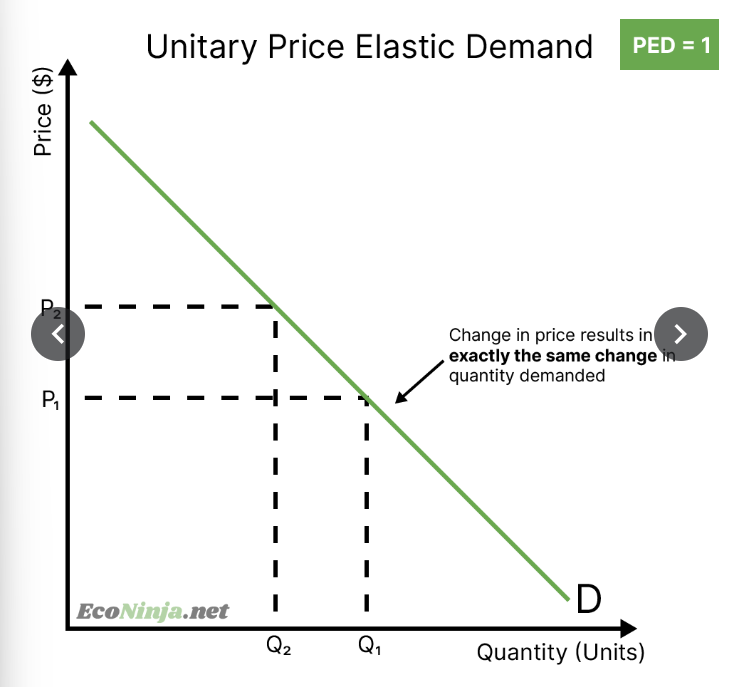
what is the PED for a product with unitary price elastic demand? draw the diagram
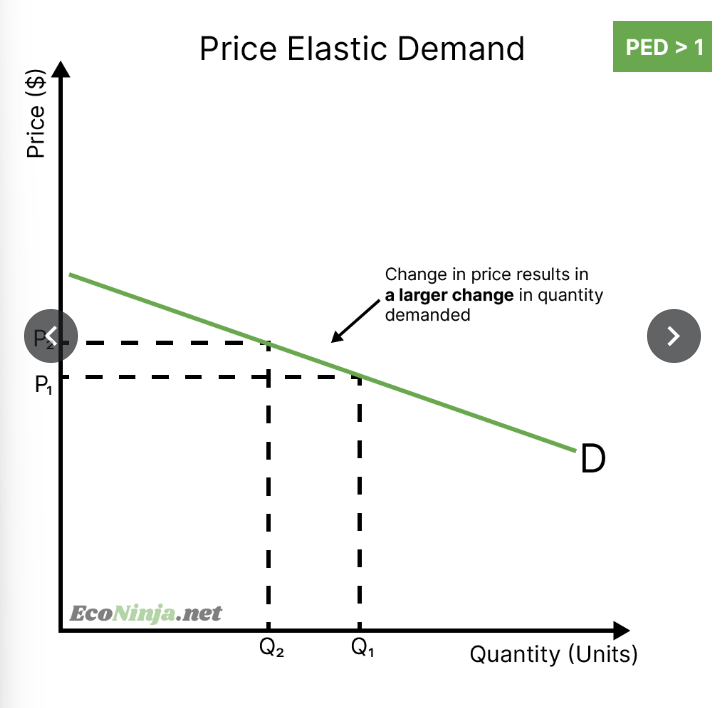
what is the PED for a product with price elastic demand? draw the diagram
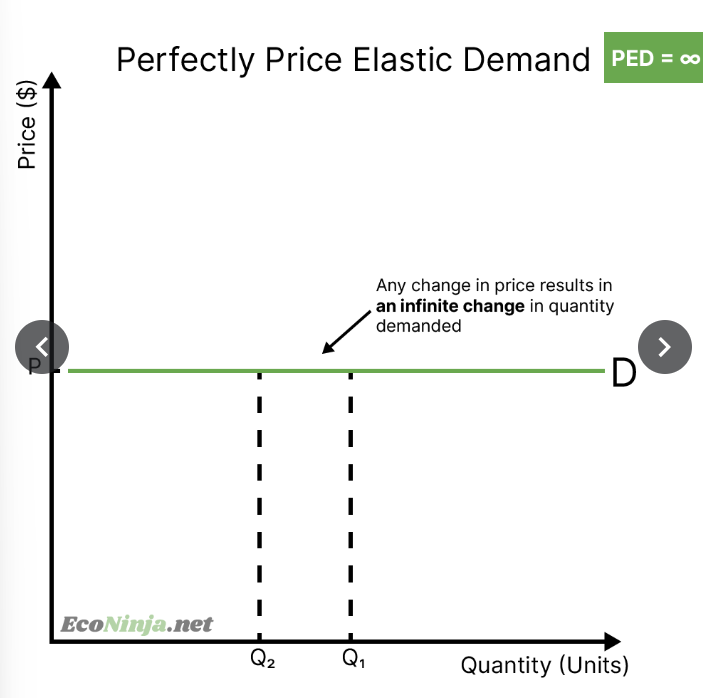
what is the PED for a product with perfectly price elastic demand? draw a diagram
what are the determinants of PED?
number and closeness of substitutes
degree of necessity
proportion of income spent on good
time
how does number and closeness of substitutes affect PED?
if there are many similar alternatives to a good, it is easier to switch, making it more price elastic
how does degree of necessity affect PED?
if it is necessary to survival, people will buy a product regardless of its price, making it more price inelastic
how does proportion of income spent on good affect PED?
if people only spend 0.1% of their income on a good and it doubles to 0.2%, consumption is unlikely to dramatically change, if this figure were to double from 25% to 50%, demand is likely to drop significantly
how does time affect PED?
humans take time to reduce their consumption behaviour. in a short timeframe, demand for any good is unlikely to dramatically change
what is the relationship between PED and total revenue?
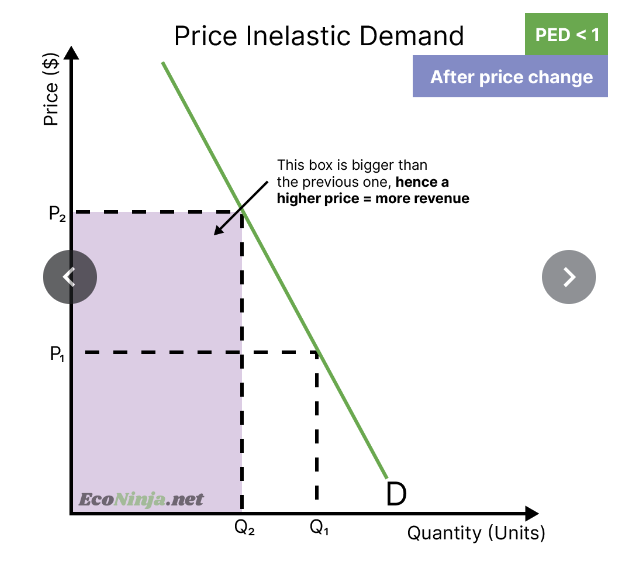
if you’re selling a good that is price inelastic of demand, it means that increasing the price by 10%, for example, will lead to a decrease of sales less than 10% - you can increase price to increase revenue
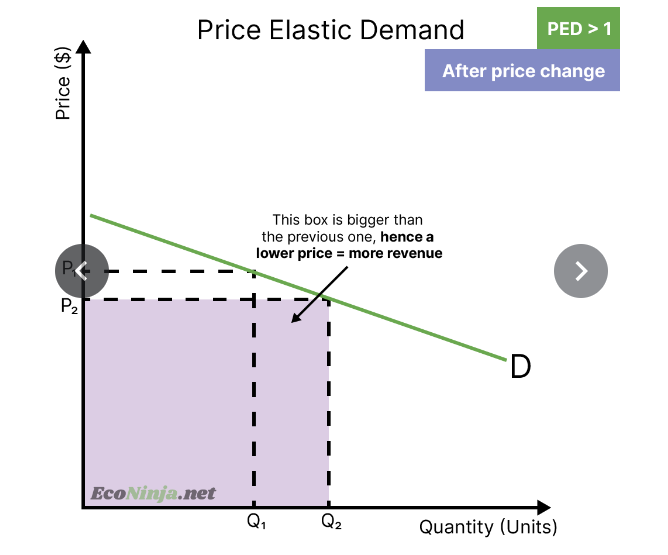
if you’re selling a good that is price elastic of demand, then increasing the price by 10% will lead to a decrease in sales of more than 10%- however it also conversely means that decreasing the price by 10% will lead to an increase in sales of more than 10% - meaning that you can lower price to increase revenue
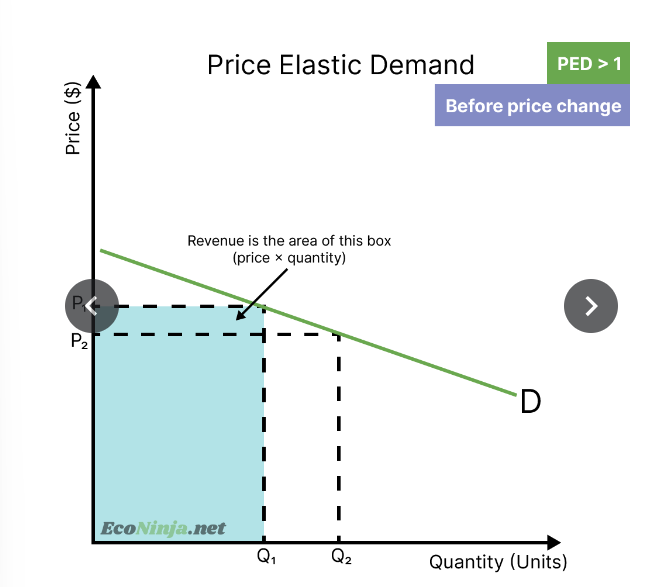
draw the impact of a price decrease on a product that is price elastic of demand
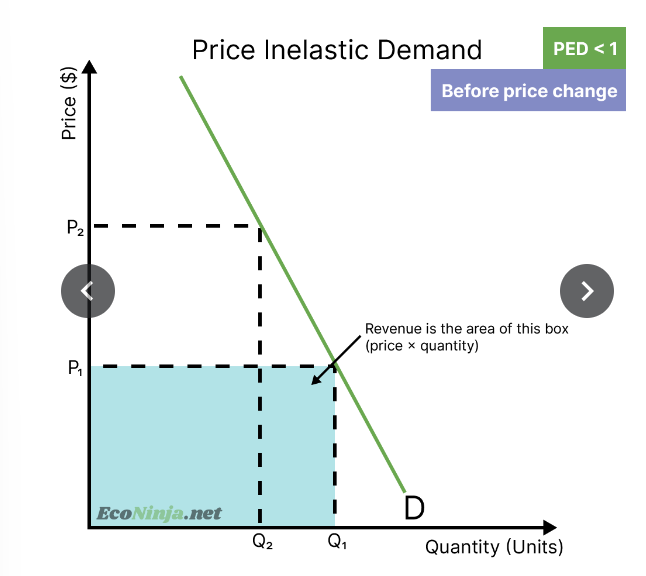
draw the impact of a price increase on a product that is price inelastic of demand
why is PED important for governments and firms?
taxes on inelastic goods will do little to reduce demand, but are very effective on elastic goods
subsidies on inelastic goods will do little to increase demand, but will be very effective on elastic goods
for firms who want to increase revenue, they could determine their good’s PED and see that way whether they should increase or decrease prices
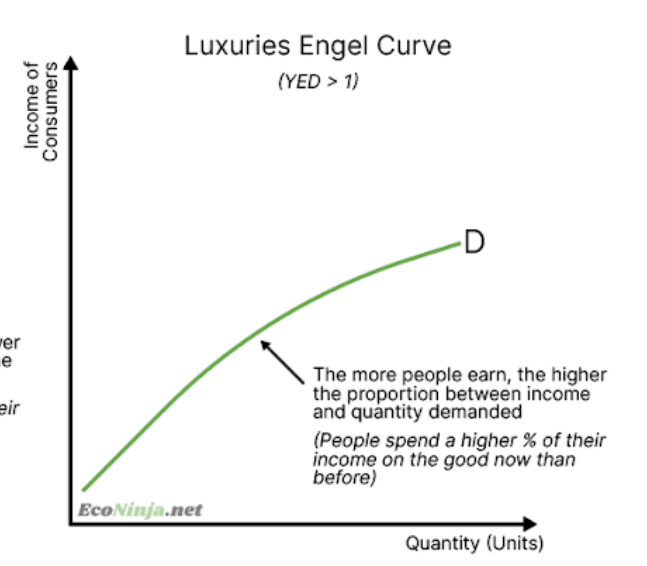
what is income elasticity of demand (YED)?
how responsive the quantity demanded is for a good or service when income of consumers changes
how do you calculate YED?
YED = (% change in Q)/(% change in Y)
NEGATIVES ARE IMPORTANT HERE
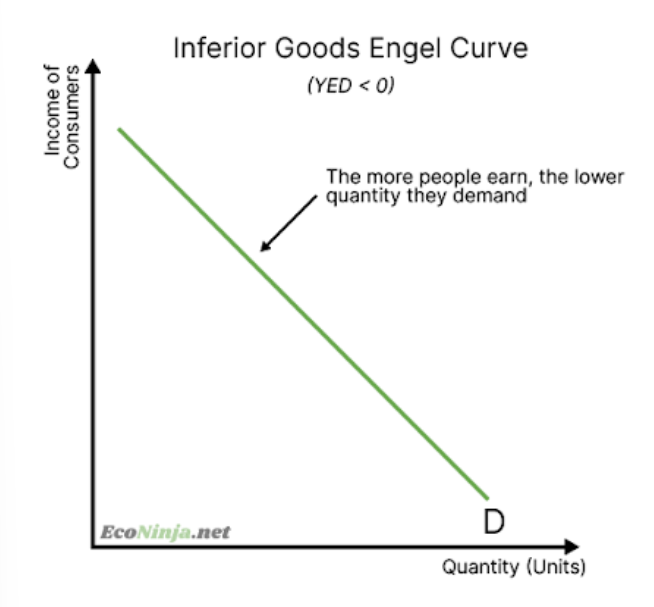
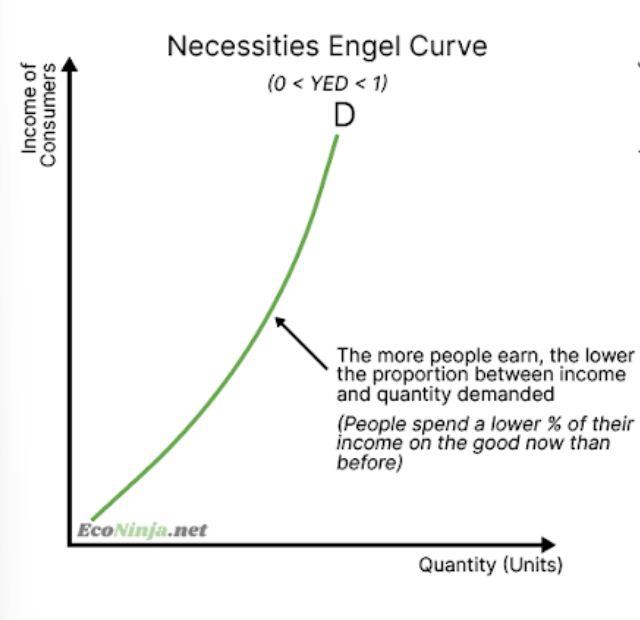
what are the three types of YED and how are they linked to its value?
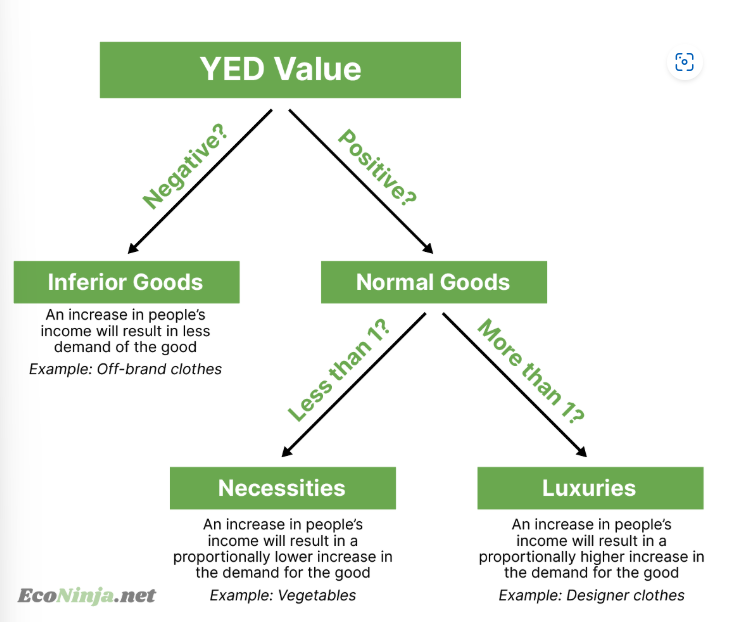
draw the inferior goods engel curve
draw the necessities engel curve
draw the luxuries engel curve?