Applications of Molecular Genetics
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
What is a somatic cell gene therapy?
Somatic cell gene therapy is when wild type genes are introduced into and expressed in cells of the person’s body
What was the first protein to be produced commercially in bacteria?
Human insulin
One method for the production of a transgenic mouse involves the culturing and transfer ion of ________ from the inner cell mass of the blastula
Embryonic stem cells
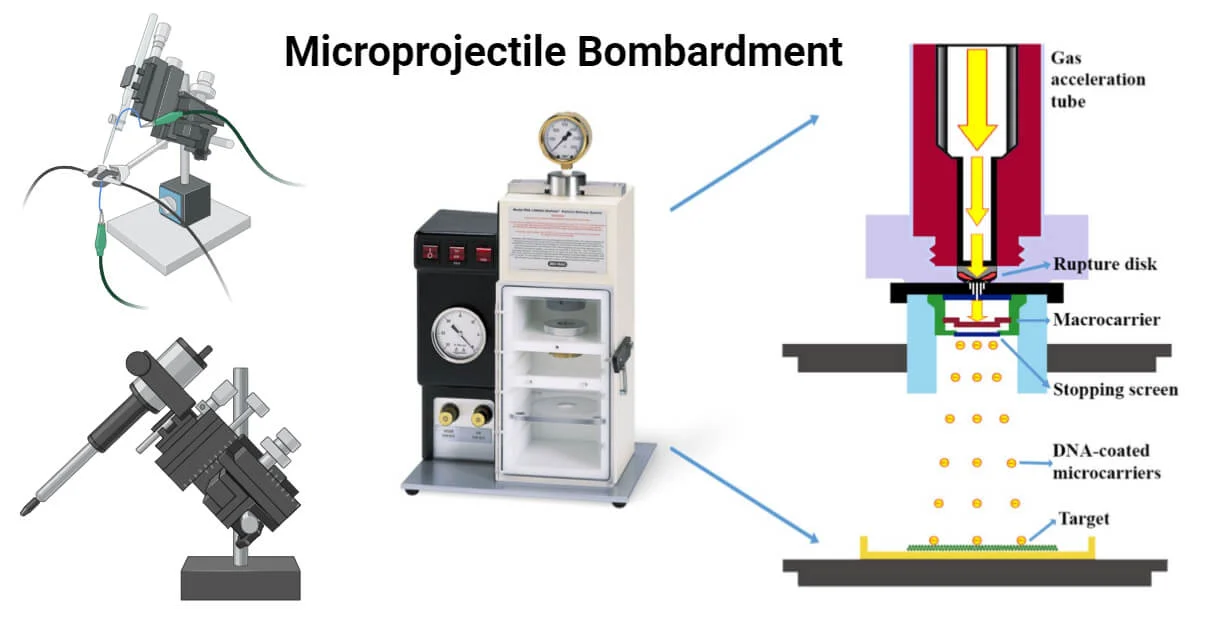
________ involves the shooting of DNA-coated tungsten or gold particles into plant cells
Microprojectile bombardment
What is a consequence of antisense RNA present in a cell?
The complementary antiparallel RNA sequence will bind to the mRNA and stop translation
The human growth hormone gene requires what additional sequences to be expressed in E. coli?
The promoter and ribosome-binding site are required in the human growth hormone
What does totipotency mean?
This is the ability of a single cell to produce all of the differentiated cells
What is true regarding the production of a knock-out mouse gene targeting vector?
The tkHSV gene is used to eliminate cells that show targeted integration
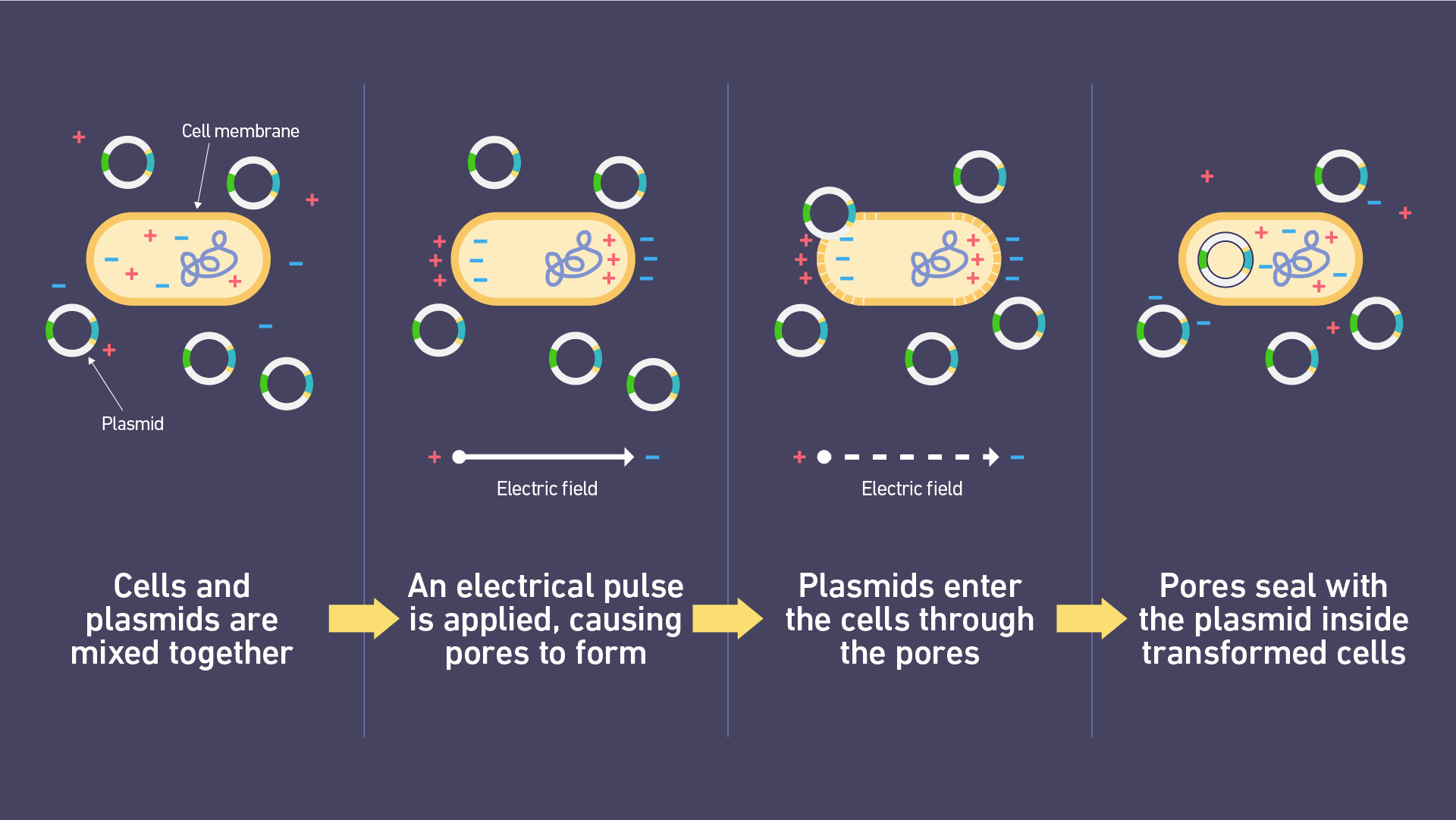
________ uses a short burst of electricity to get DNA into cells
Electroporation
What is electroporation?
This is a technique that uses electrical pulses to temporarily create pores in cell membranes, allowing substances like DNA, drugs, or proteins to enter cells
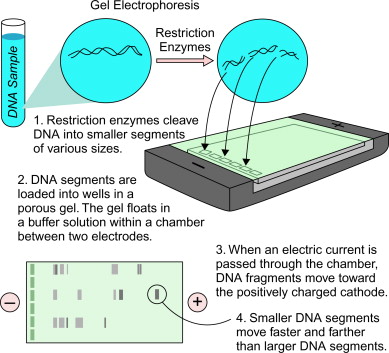
What is electrophoresis?
The movement of charged particles in a fluid or gel under the influence of an electric field
What is microprojectile bombardment?
Microprojectile bombardment is one of the physical methods of gene transfer used to introduce foreign genetic materials directly into cells or tissues using high-velocity particle
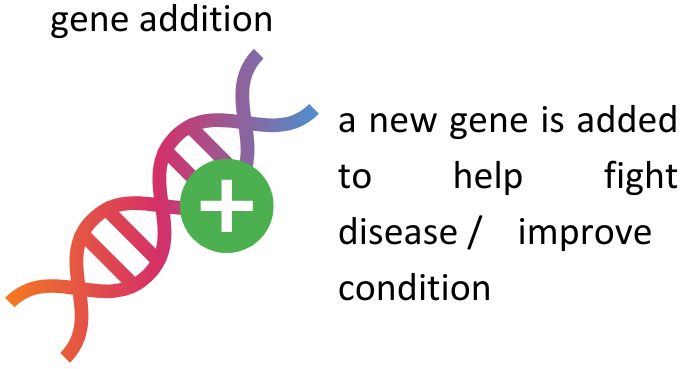
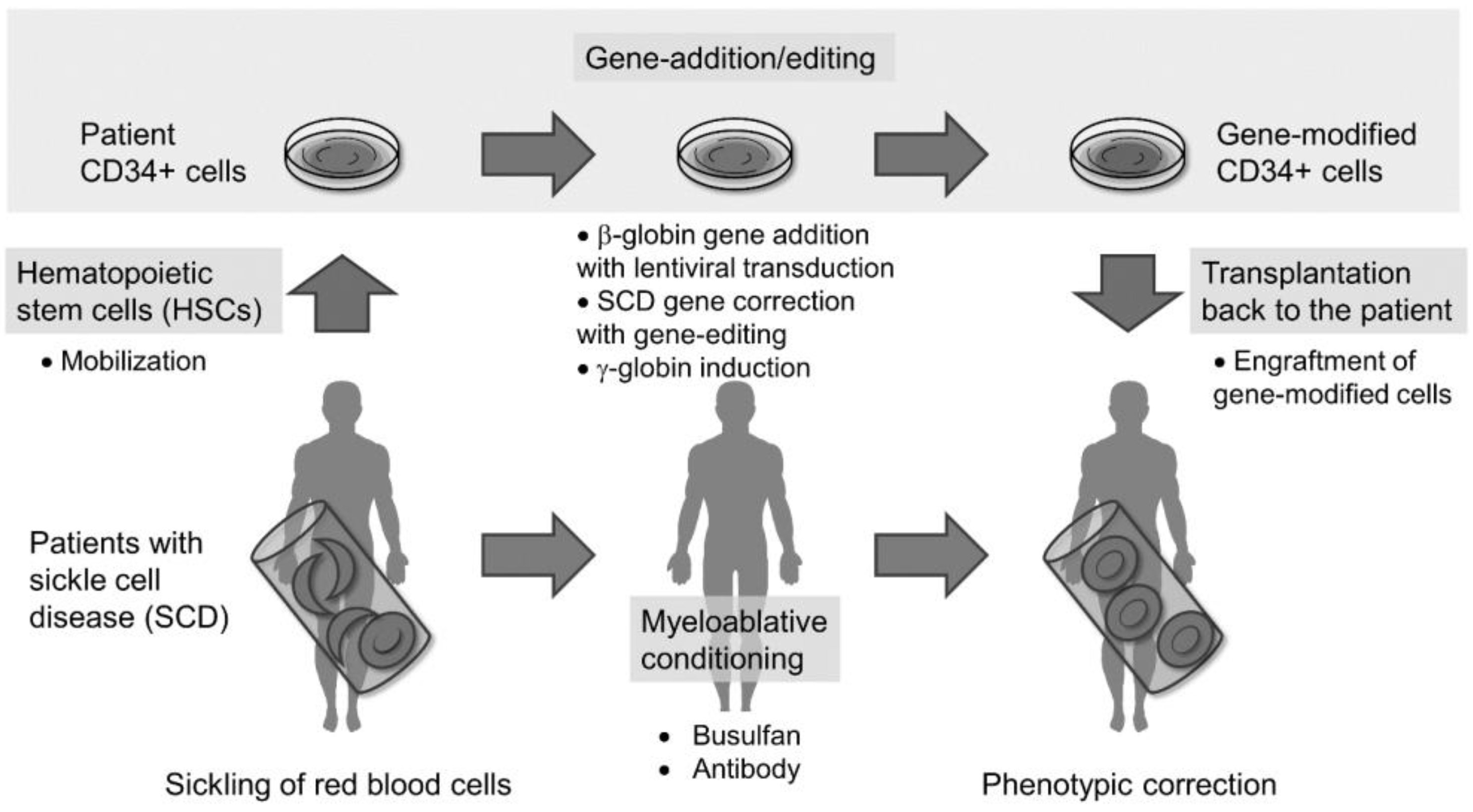
What is a gene addition procedure?
gene addition procedure is the process of adding functional copies of the gene that is defective into the genome of the patient. A working copy of a gene is inserted into a cell to compensate for a missing or faulty gene