Urea Cycle
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
How are AAs produced?
De novo synthesis, digestion of dietary proteins, and intracellular protein digestion.
What can AAs feed into?
Protein synthesis
Degratin/enery source - NADH/FAHD2 productions, TCA int, gluconeo, keton bodies
synthesis of other biomol - Pur/Pyr, phosphoatidyl serine, sphingosine, thyroxine epi, melatonin, Ach GABA, Heme , histamine, crestine, carnATiNE
Cell signaling - glycine/glutamate
Nirtrogen extcretion
Describe to your patient what a postive vs negative nitrogen balancce is?
Posititve — N intake >extretion (growth, infancy-ado, preg, rec from maltrutution)
Negative N intake < excretion (illness/mal/BURNS)
WHat is nitrogen seen as in the liver, kidney, and muscles?
urea cycle (liver)
glutanmine (kidney)
Creatine phos (muscle)
Also as purines
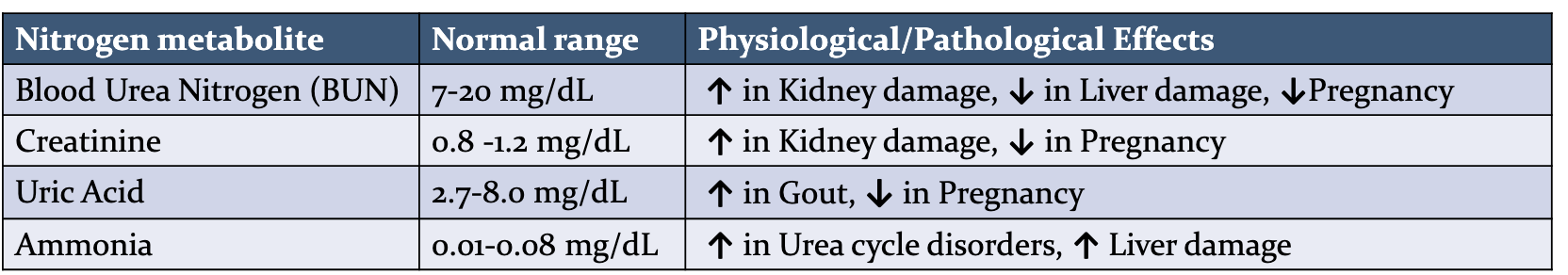
What do we see in patient A whose has kindey damamge and patient B who has liver damage and patient C who is pregnant, in term of blood urea nitrogen, creatine, uric acid, and ammonia?
What are the sources of ammonia in the body?
Glutamine, Monoanibes, purines/pyr, diet, transanmin rens, urea, other AAs, degration of neurotramsitters.
Describe the degration of AAs?
Removal of nitrogen
via transmination, deamination, or admidation
Clearnace of NH4+
urea ccyle ( ie ammonia is toxic)
Util of the carbon backbone
fed state - son of glcyogen fo trigly
fasting - enegery prod
***Urea cycle - one N comes for NH4, one from Asp, and carbon camones for CO2
How is nitrogen ripped away from the innocent AA
Denamination - removal of alpha amino of (glutamate, G, S, T, H) as NH4+
***Goes in the reductive direction in the liver and kindey
Occurs in the oxidative direction in other tissues
All done via glutamate dehydrogenase
Deadmidation - removal of amide form glutamine and aspragone as NH4+
Import in the kindey, most of the NH3 in urine, NH3 balances pH in urine
What is the main pathway of nitrogen removal?
Transamination - transfer of alpha amino from an aminot to a alpha keto
Generally on glutatmate, reverabale, cat via trabnsmainases (amintransases)
Uses PLP ie B6
Using aminotransferases as diagnostics.
Using AST or ALT in the liver , indicitaes liver damage, ALT more specific, AST also found in MI patients
What is the role of glutamate in nitrogen removal?
Collects N from AA via transmaination
Provides NH4 via deamination of glutmatated dehydrogenase
N to urea indirectly via transsmin oxaloacetate in Asp
Precur for allosteric act of the urea cycle
Glutamate Gathers, Gives, and Governs"
Gathers N via transamination
Gives N via deamination or aspartate
Governs urea cycle by making N-acetylglutamate
Where does the urea cycle take place and why is this the ulimate place of N?
Only in the liver, AA N is carried to the liver via Alanine > glutamine and other AA to a lesser extent. —> urea then trasnported to the kidney and extreted in the urine (some via small intestines)
Who be using all the glutamate and who be making dis shit?
Using : Kidneys, gut, immune cells, and liver
Making: Muscle and brain
***NH4 used via glutamine syn, made via glutaminase and glutamate dehydro
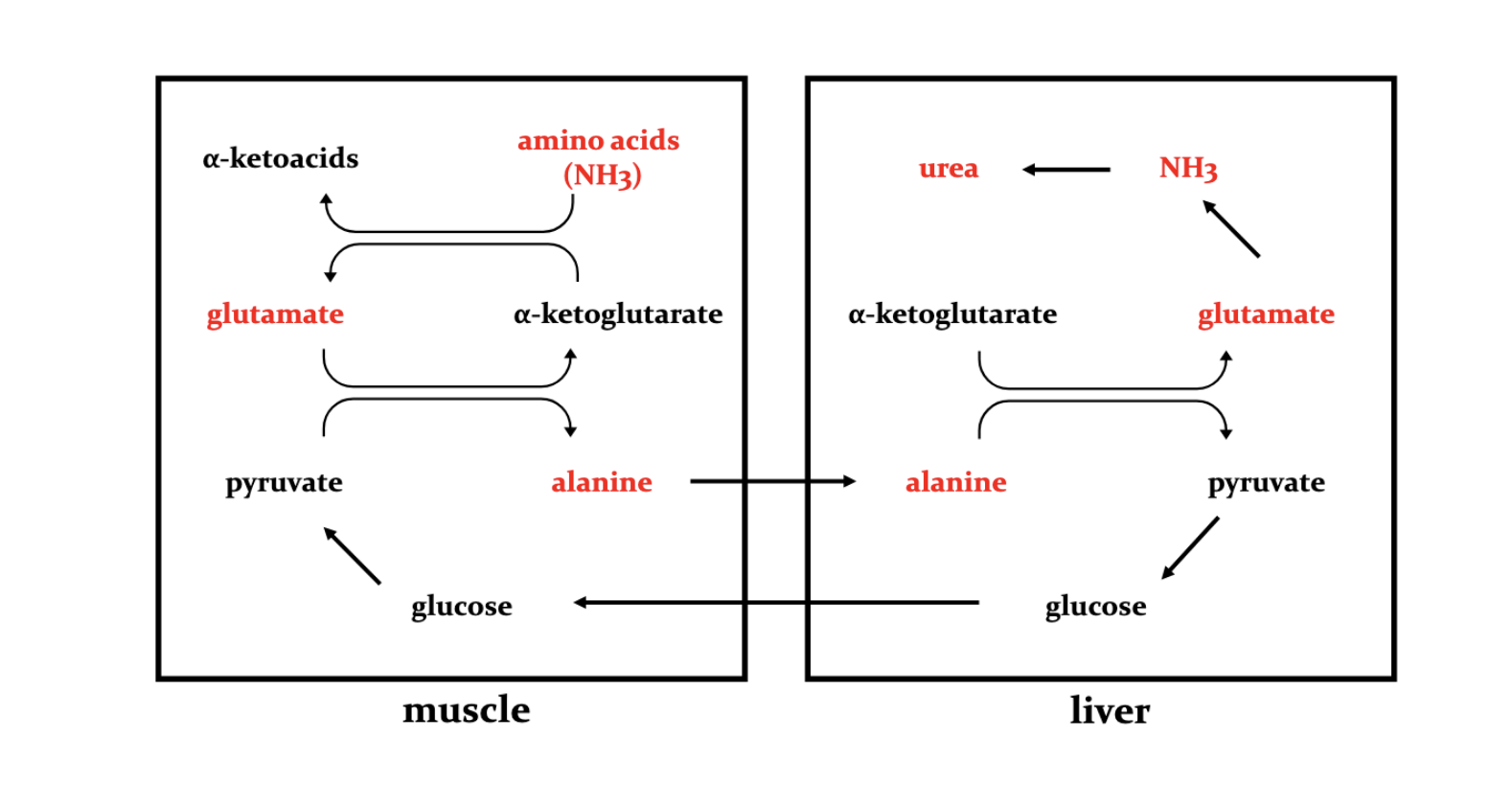
Why do we trasnport alanine to the liver?
Removal of N via the urea cycle
Gluconeo
Sources: Main muscle (via protein degration and transanim and kidney +intenstine
glutamine —>glutamate —Alanine
………Glutaminase …..ALT……..
A patient comes in with toxic amount of ammoina in thei blodd, descibre the mechanism which would normally be in work to keep these ammonia levels in check.
Transaniation rxn collect N on glutamate (safe if not free)
Glutamate dehydrogenase (NADH/NADPH), glutamine synthesis (ATP) main brain detox, carbamoyl phos synthesis 1 (ATP)1 step in urea syn
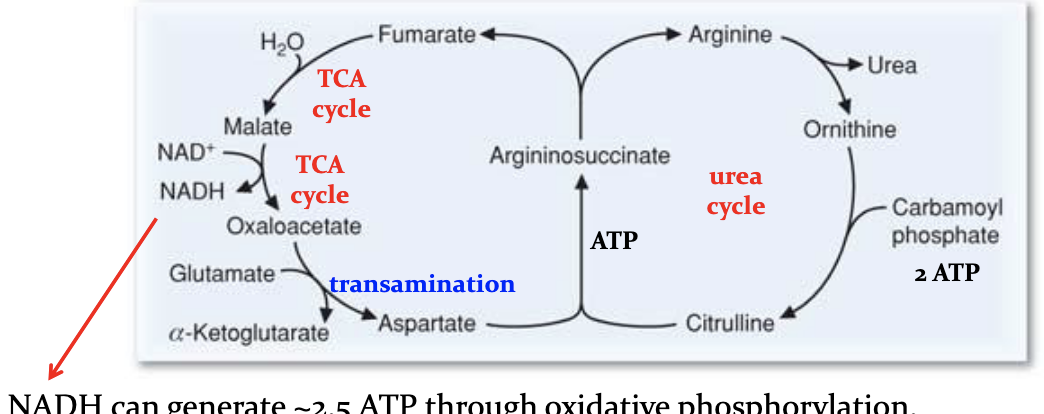
Where is the location of the urea cycle start and finish?
Starts in the mito and finished in the cytosol
Describe carbamoyl phos synthesis?
Cat via carbamoyl phos synthetase I ( CPSI) —> RL and commitment step
in the mito, uses 2 ATP (irreversible), allos reg via N acetylgutamate (NAG) (act via arginine)
Act via agrinine and N acetyl glutamate
Clinical sig : Type I hyperammonemia
**Also can be syn from glutatmine and CO2 via CSPII in the cyctol —>pyrimidine synthesis
Describe citrullinne synthesis
Cat by ornithine transcarbmoylase (OTC)
In the mito, transpofrted via ornithine translocatase —>cytosol
Clinical rel: Ornithine transcarbamoylase —> T2 hyperammonemia
orithine translocase —>hyperorithemia hyperammonemia - Homocitrullinuria (HHH) syndrome
Describe argininosuccinate synthesis?
Cat via arginosuccinate sythetase
in the cytosol, req 1 ATP, Asp—>ammonia
Clinical rel: Def = cirtullinemia T1
**T2 is caused by def citrin which is a mito glutamate/aspartate shuttle
Describe arginine synthesis.
Cat via. argininosuccinate lyase
in the cytosol, only way its produced the human body, released furmarate —→OAA—>Asp
Clinical Rel: Def = argininosuccinyl acidemia
What happens when arginine is cleaved?
Cleaved into urea and ornithine, Cat via arginase in the cytosol, orthinine moves back to mito and reacts with carbmoyl phosphate.
Clinical rel: Def causes argininemia
Arginine can go to protein syn or NO syn
How is this complicated ass cycle funded in terms of energy?
4 phosphate bonds are broken making this irreversible
Energy remvoed if furmurate —>malate—>OAA
What are some regulation steps of the urea cycle?
N acetyl glutamate is a alloesteric ac t of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CSPI)
Itself act via high arginine levels
High protein diet and excess degradation ie fasting will increase urea syn (increased Arg and ssyn of urea cycle enzymes)
Conc of subs and inter
How is the urea cycle used during fasting?
Your muscles are broken down and AA —> Liver —> converted to glucose
N of used AA —> urea
When starving brain —> switches glucose —>ketone bodies(from FAs)
Decreased AA utilization —> decreaaed urea
What are the differecnes between primary and secondary type of hyperammonemias?
Primary - enyzmes in the urea cycle are defective
Secondary - main cause is liver failure (cirrhosis, hep, hepatoxins), heaptocyctes are fucked up, genetic defects can cause this ie beta oxi def
Expand on primary hyperammonemias? Also how can we really distuingish between these diseases?
Type 1: (CPSI or N acetylgltamate synthease def)
Type 2: (ornithine transcarbmoylase ) (X linked)
Citrullinuria T1: arginosuccinate synthetase def
Arginosuccininic acidemia:arginosuccinate lyase def
Argininemia: arginase def
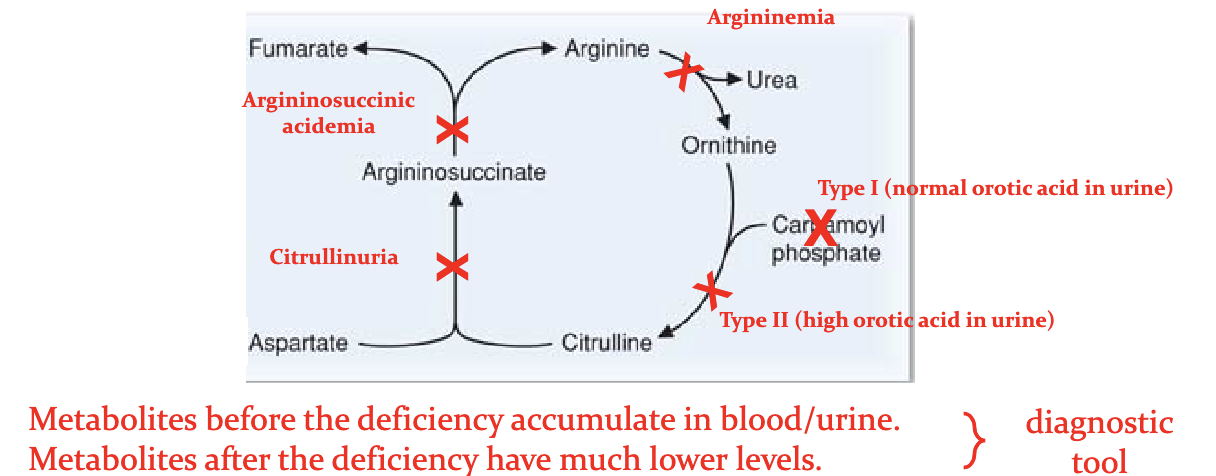
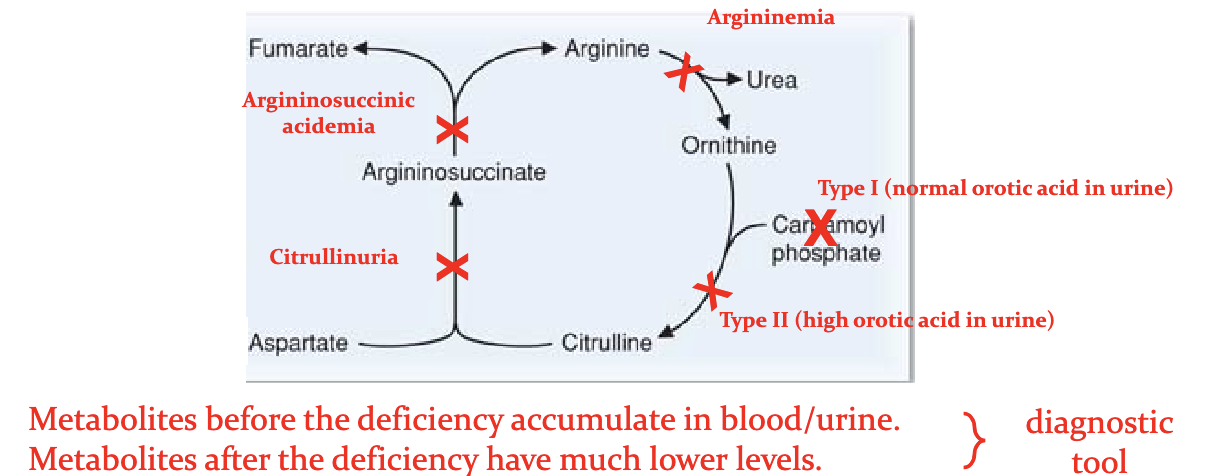
How do we distinguish between the different causes for primary hyperammonemias?
High urine orortate in CPSII
HHH with extremem high blood ornithine nad homocituiline levels.
WHat are some exmaples of AA supplementation?
Arginine - All primary hyperamm will result in low Arg expect for arginase def
Promtes prod of N aacetyl glut so CPSI can he lp for second ammon
Citrulline - T1 and T2 hyperammonemia. Captures Asp so one N can be excreted
N carbamoylgluatamate - angonist for CSPI in case of N acetylglutamtate synthetase def
How do we reduce the N load on the urea cycle?
Low protein diet, avodi fastin - limit AA degrad
Scavanger drugs - conjugate AAs and taeget for excretion
Benzote + glycine —> hippuric acid —>exc
Phenylbutyrate + glutamine —> phenylacetylglutamine —> exc
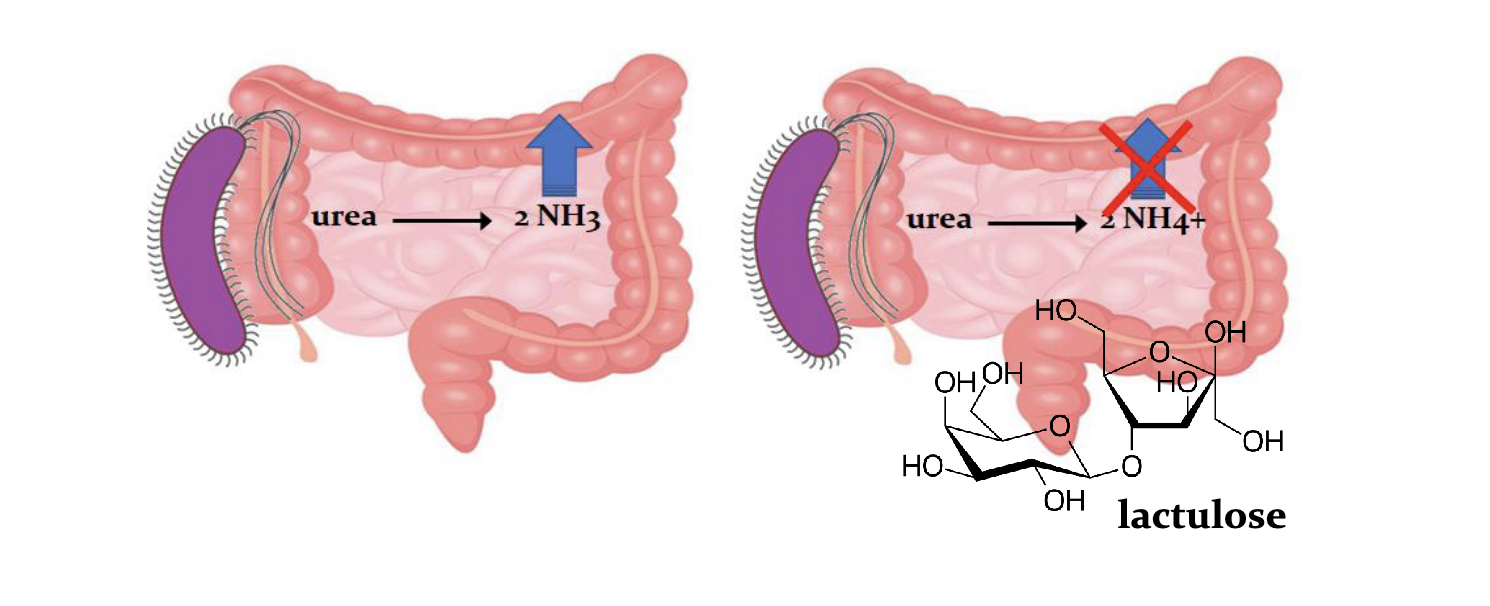
Reducing ammonia from micro flora
Bat ureases in gut generates ammonia
Lactolose laxactive decreases pH so ammoina connot be absorbed, *** ureases inhale red N via this source.