Chemistry 6.2 - Bonding Between Nonmetals
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
How do nonmetals obey the Octet Rule?
In this way nonmetals obey the Octet Rule which asserts that atoms will attempt to achieve a full outer shell by sharing electrons with other atoms when they react to from compounds.
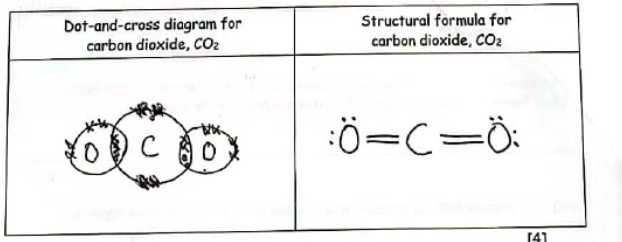
Explain, with the help of a dot-and-cross diagram, why the element hydrogen exists as diatomic molecules.
Two chlorine atoms bond by sharing a pair of electrons. Both atoms now have a full outer shell.
When is a Covalent bond formed?
A covalent bond is formed when two atoms share a pair of electrons.
What is a diatomic molecule?
A diatomic molecule is a molecule formed when two atoms covalently bond with each other.
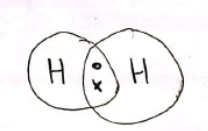
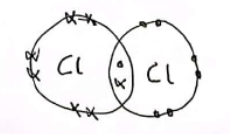
Explain, with the help of a dot-and-cross diagram, why the element chlorine exists as diatomic molecules.
Two chlorine atoms bond by sharing a pair of electrons. Both atoms now have a full outer shell.
What does the term lone pair mean?
The term lone pair is used when refering to a pair of electrons in the outer shell of an atom that is not shared with another atom.
How can nonmetal atoms gain a full outer shell?
Nonmetal atoms may gain a full outer shell by sharing two or more pairs of electrons.
When is a double bond formed?
A double bond is formed when two atoms share two pairs of electrons to form two covalent bonds between the atoms.
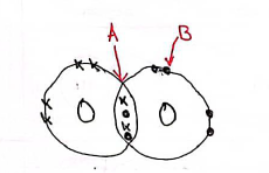
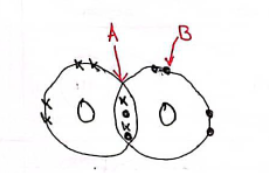
A dot-and-cross diagram showing the bonding in a molecule of oxygen is shown below. Use the dot-and-cross diagram to explain why oxygen exists as diatomic molecules.
(A is a double bond & B is a lone pair)
Two oxygen atoms bond by sharing two pairs of electrons. Both atoms now have as full outer shell.
When is a triple bond formed?
A triple bond is formed when two atoms share three pairs of electrons to form three covalent bonds between the atoms.
What is a molecular formula?
The molecular formula for a compound contains the atoms in one molecule of the compound.
What is the structural formula?
The structual formula for a molecule can be used to quickly and clearly show how the atoms in a molecule are connected by:
using a line between two atoms to represent shared pair of electrons
a pair of dots (••) to represent each lone pair of electrons.
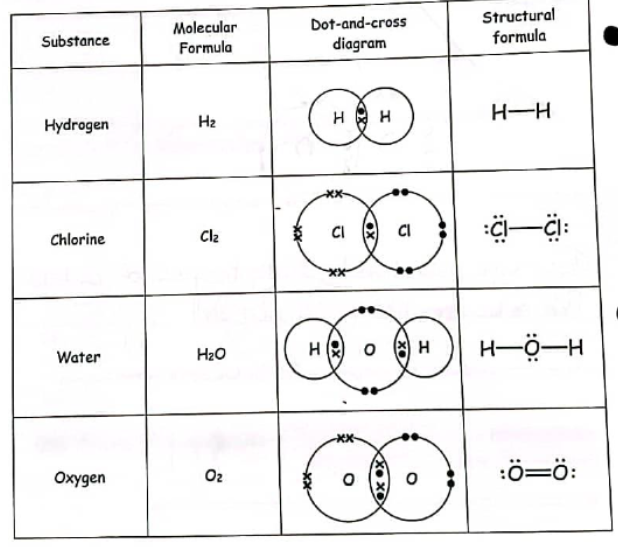
What are some examples of molecular and structual formulas?
Hydrogen, Chlorine, Water, Oxygen

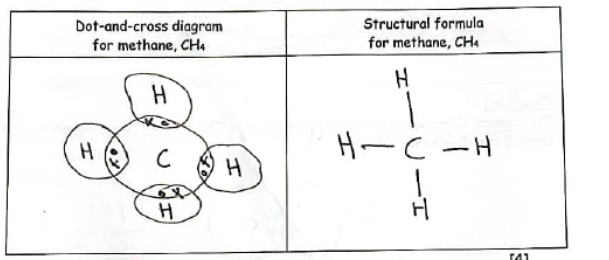
Complete the table by drawing a dot-and-cross diagram, and a structural formula, for a molecule of methane CH4.
Do these drawings.

Complete the table by drawing a dot-and-cross diagram, and a structural formula, for a molecule of carbon dioxide, CO2.
Do these drawings.