Nucleic Acids: Structure, Function, and Key Concepts in Biology
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
What are nucleic acids?
Biomolecules that code for all proteins in living organisms, primarily DNA and RNA.
What is the primary function of DNA?
To code for hereditary information.
What is the primary function of RNA?
To translate the genetic code from DNA into proteins.
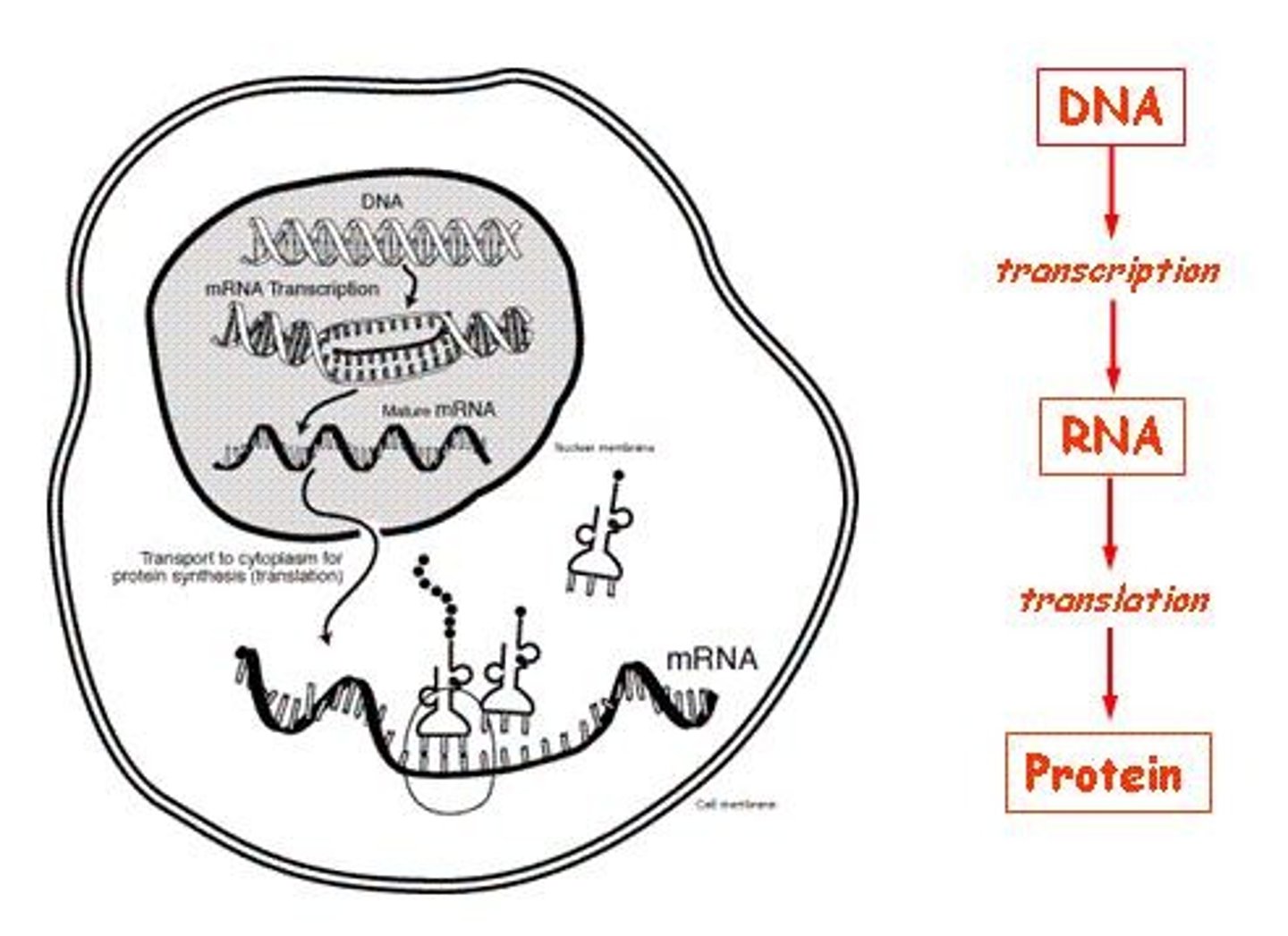
What is the flow of genetic information in cells?
DNA → RNA → Protein.
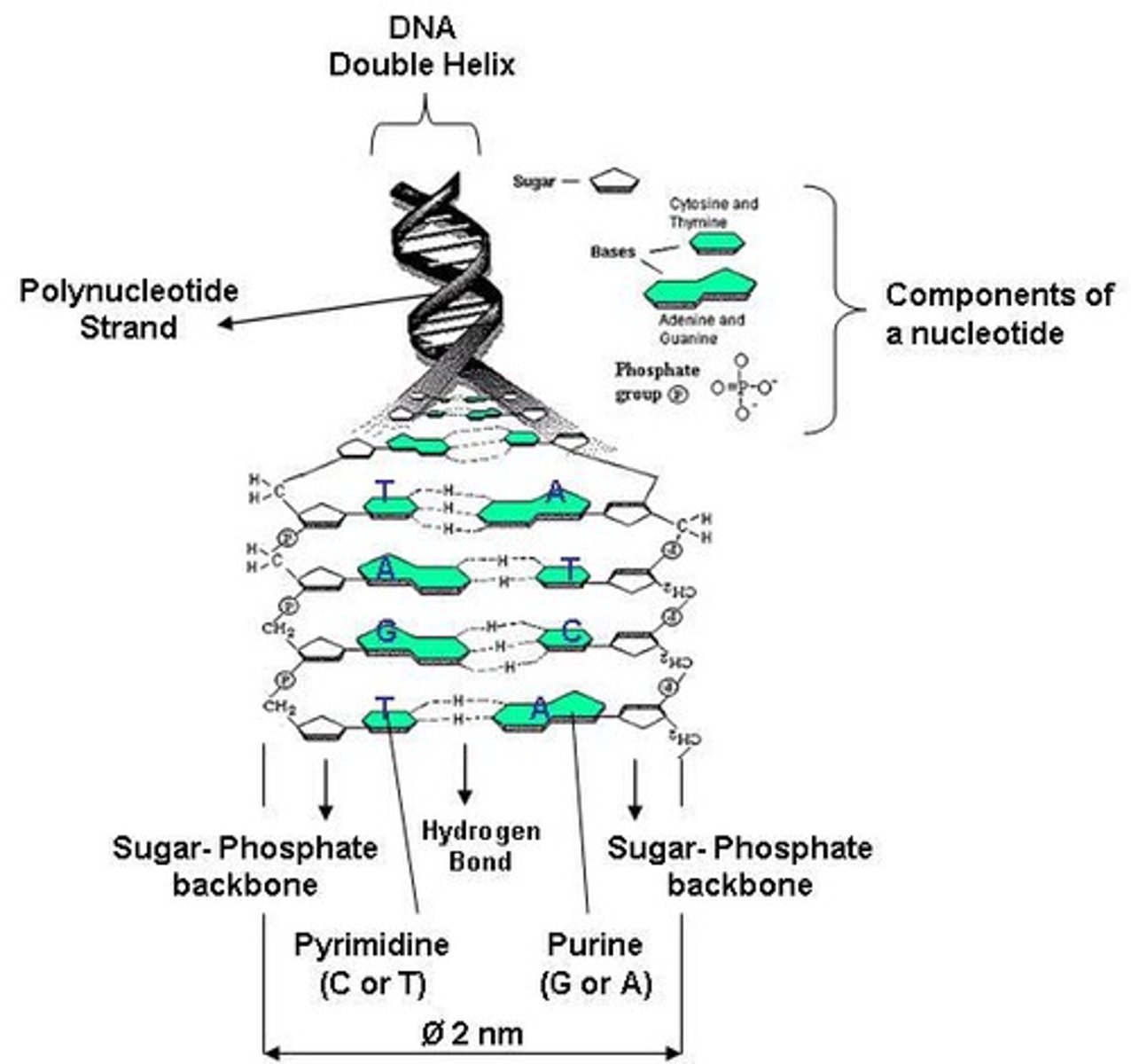
Describe the structure of DNA.
DNA is an anti-parallel, double helix.
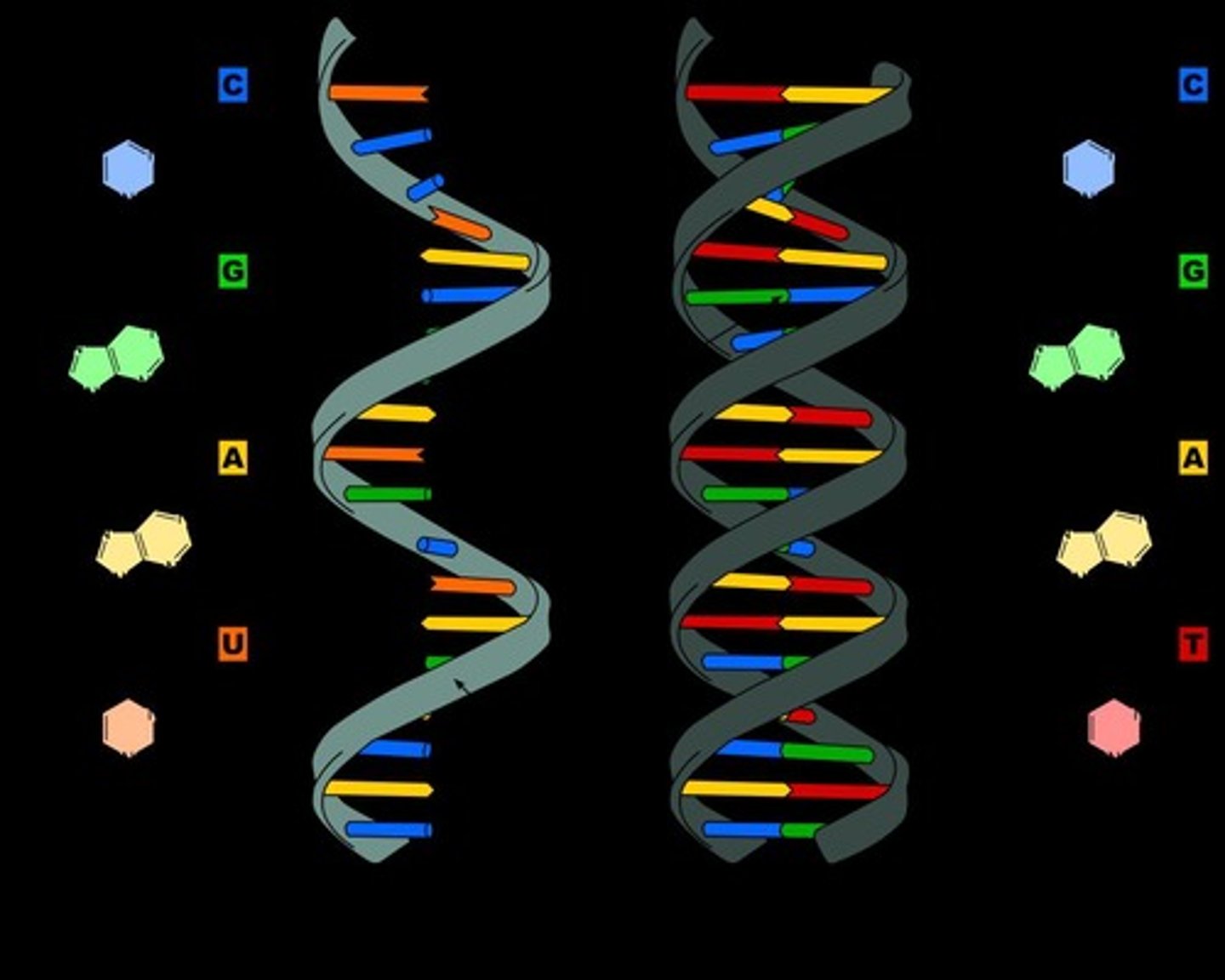
Describe the structure of RNA.
RNA is a single helix or chain of molecules that can fold upon itself.
What are the monomers of nucleic acids?
Nucleotides.
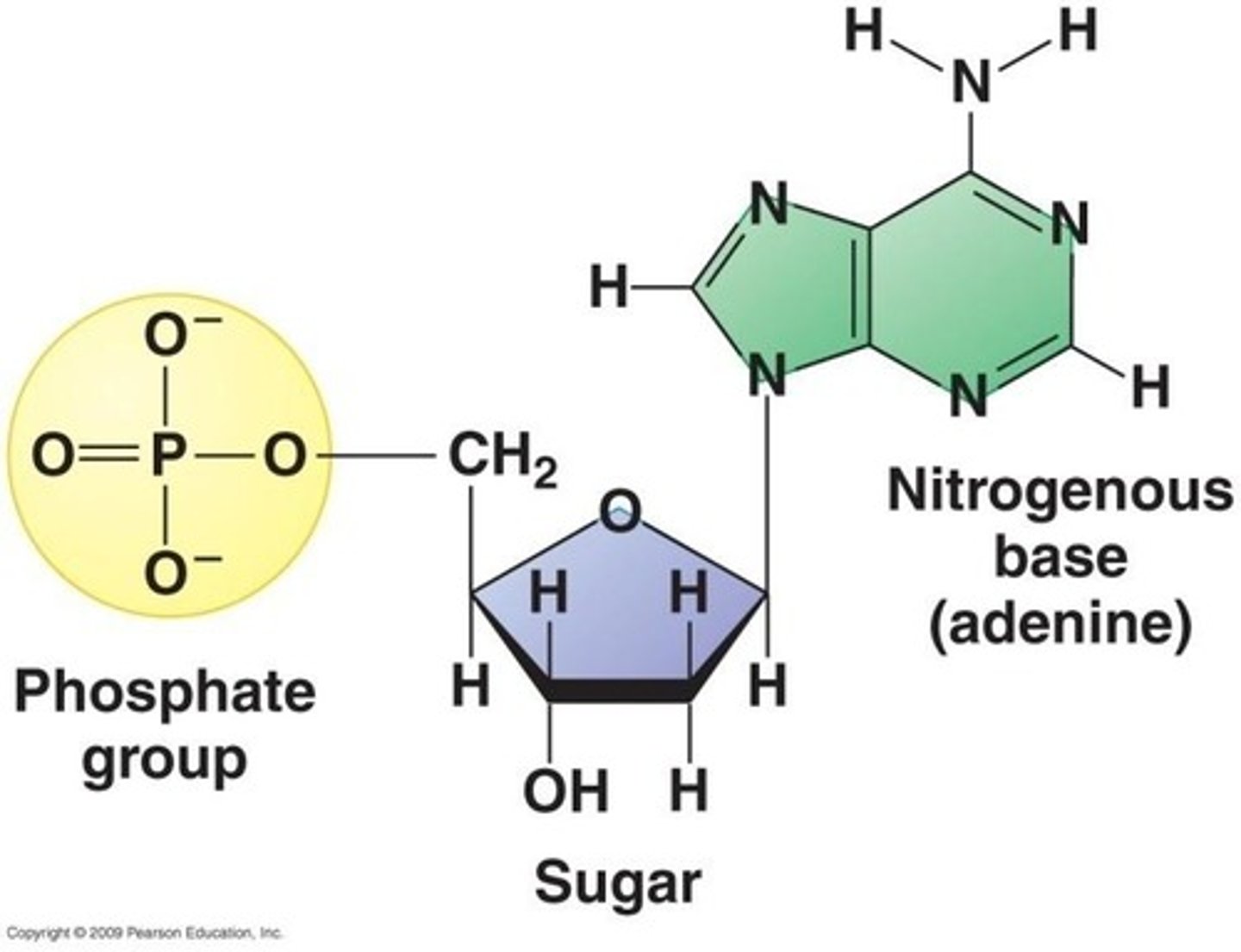
What are the components of a nucleotide?
A nitrogenous base, a sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate functional group.
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases?
Pyrimidines (thymine, cytosine, uracil) and Purines (adenine, guanine).
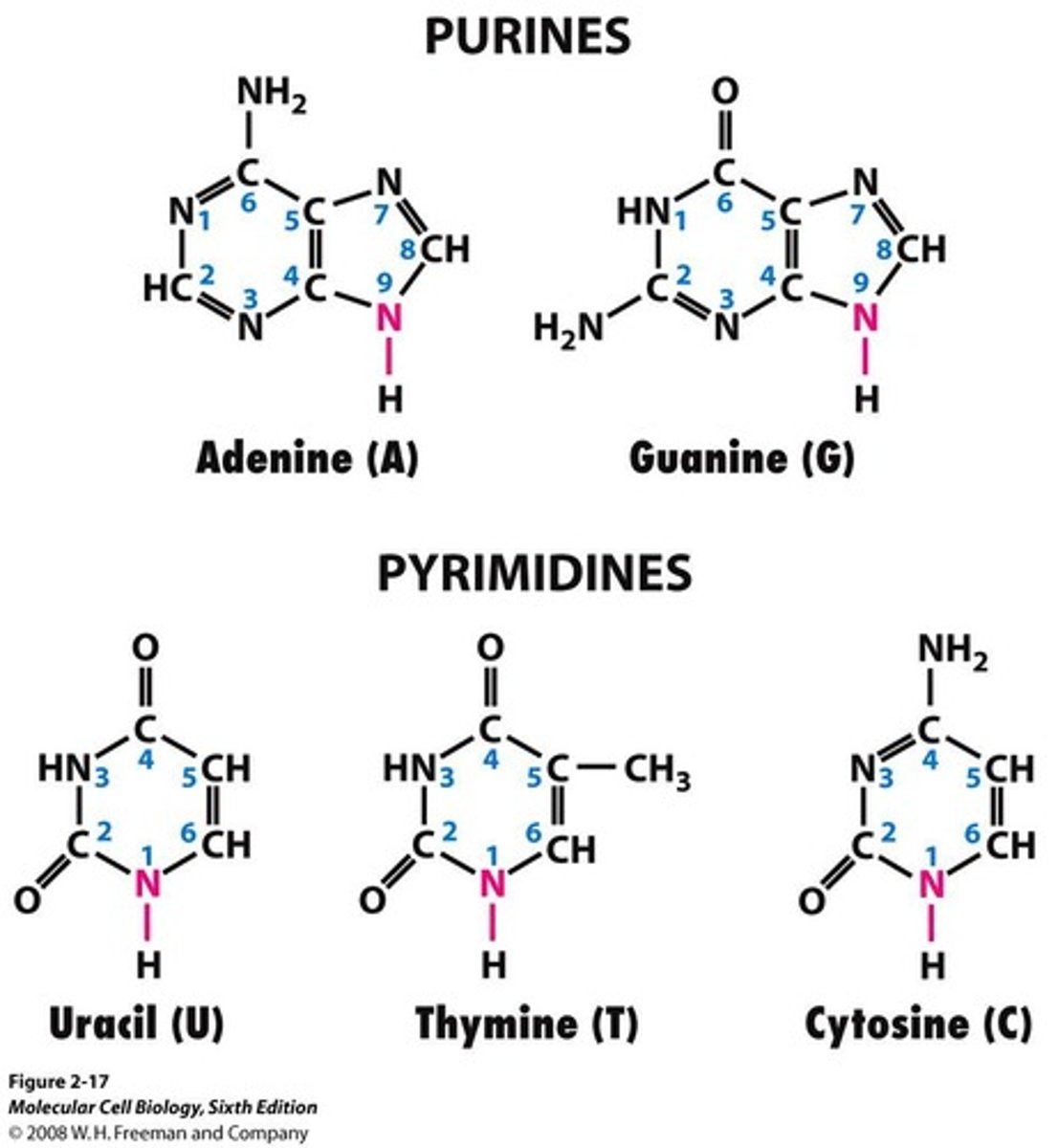
What is the structure of nitrogenous bases?
They are ring-shaped structures rich in nitrogen.
What type of chains are DNA and RNA?
Polynucleotide chains.
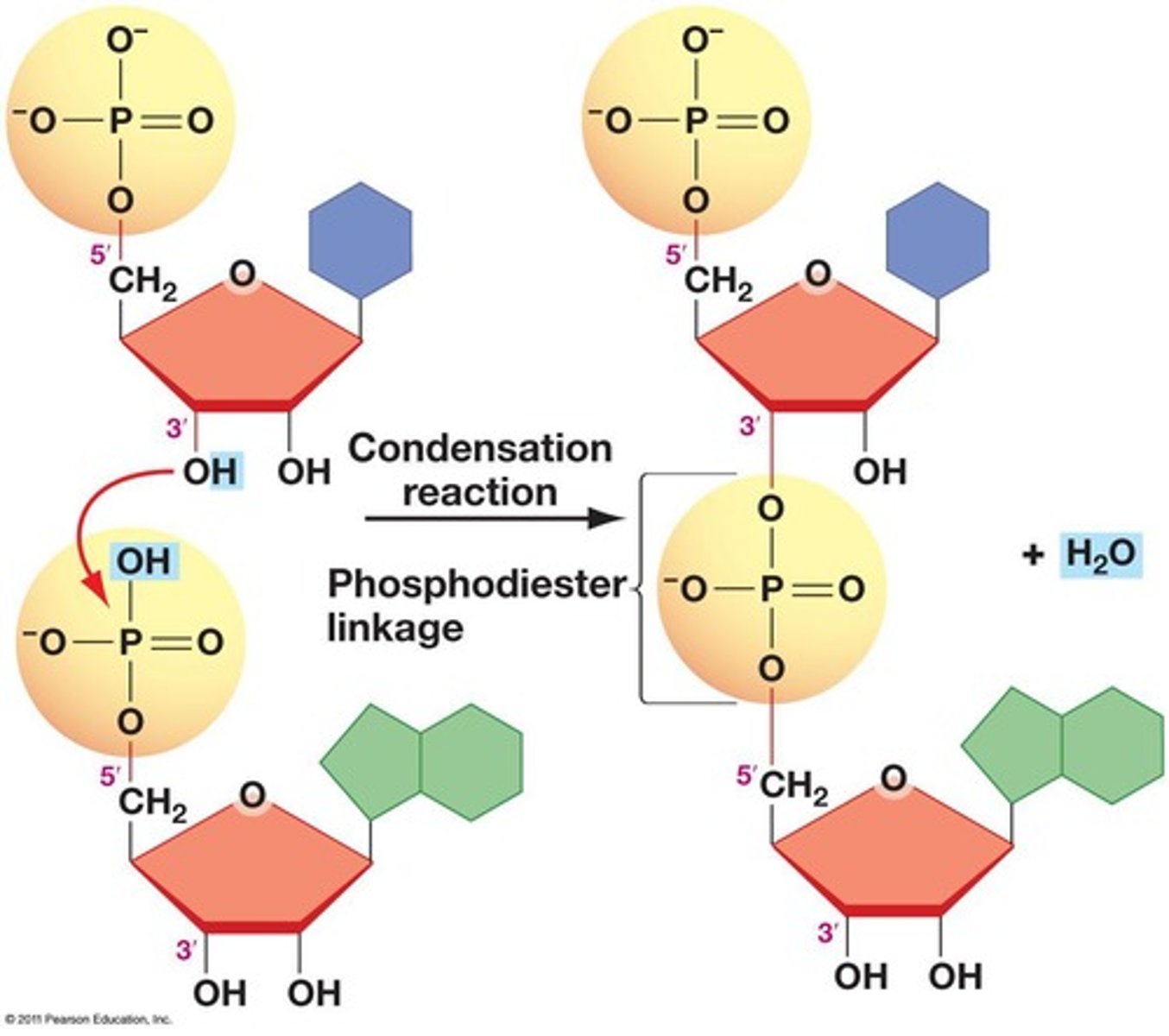
What type of bonds form the sugar-phosphate backbone of DNA?
Phosphodiester bonds.
What is the role of DNA in heredity?
DNA carries genetic information that is passed from one generation to the next.
What is the role of RNA in protein production?
RNA translates the genetic code from DNA to synthesize proteins.
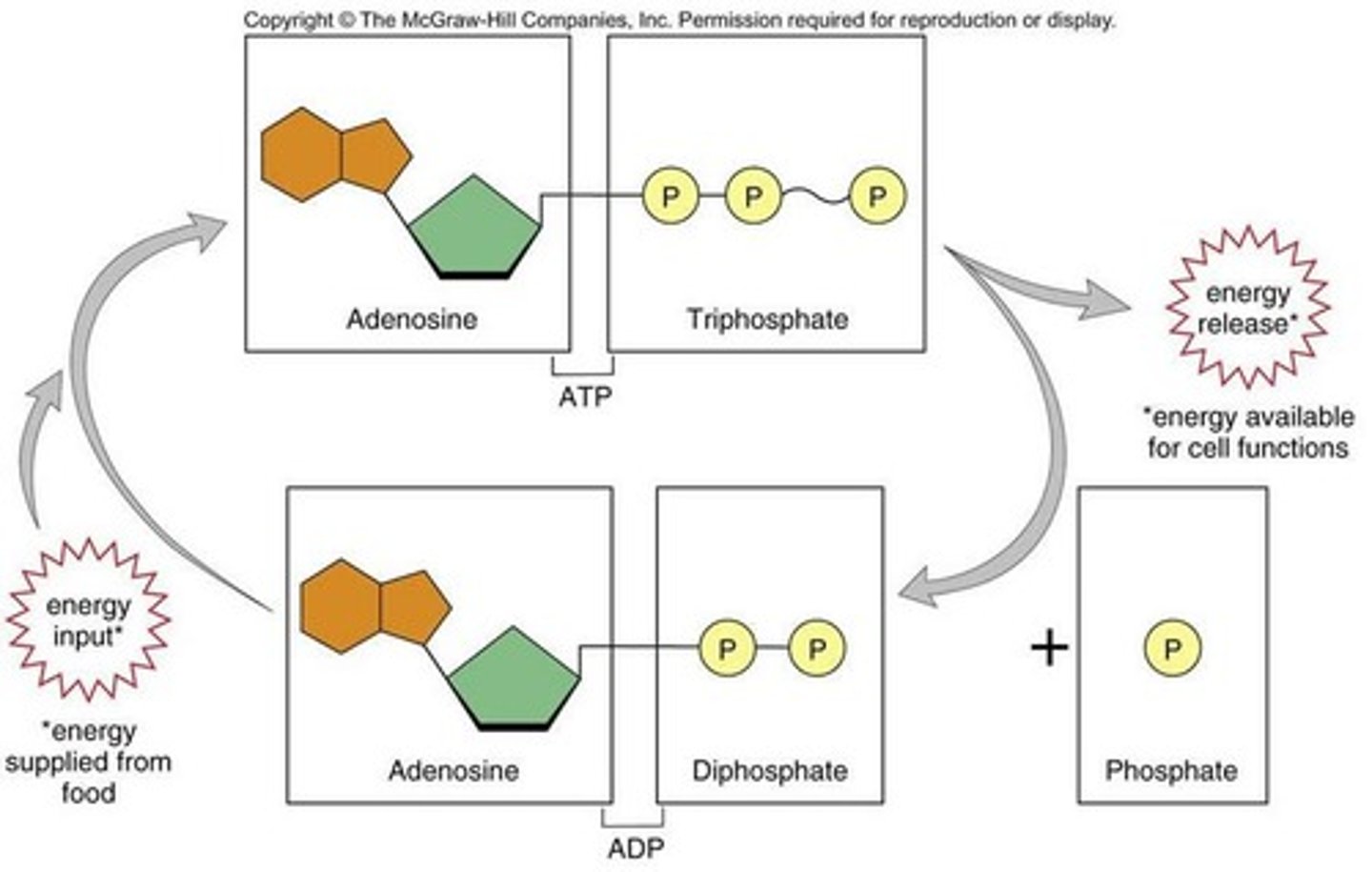
What is ATP and its components?
Adenosine Triphosphate, composed of ribose sugar, adenine, and three phosphate groups.
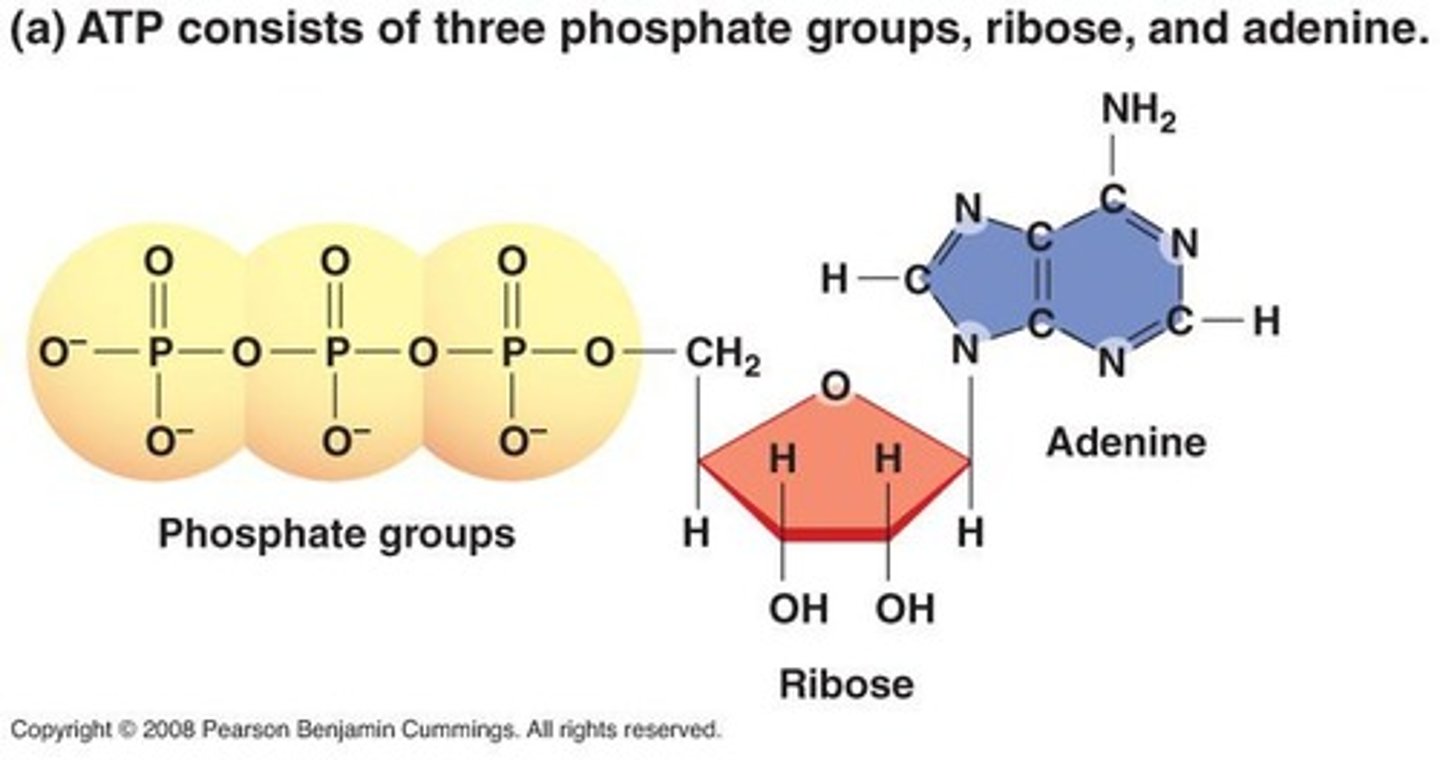
How does ATP release energy?
By removing the last phosphate group, which transfers energy to cellular processes.