PH 111 - Final Exam
1/71
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Waldron Spring 2025
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
72 Terms
Negative
Consider the vector C = A + B. The x component of C is …
Positive
Negative
Zero
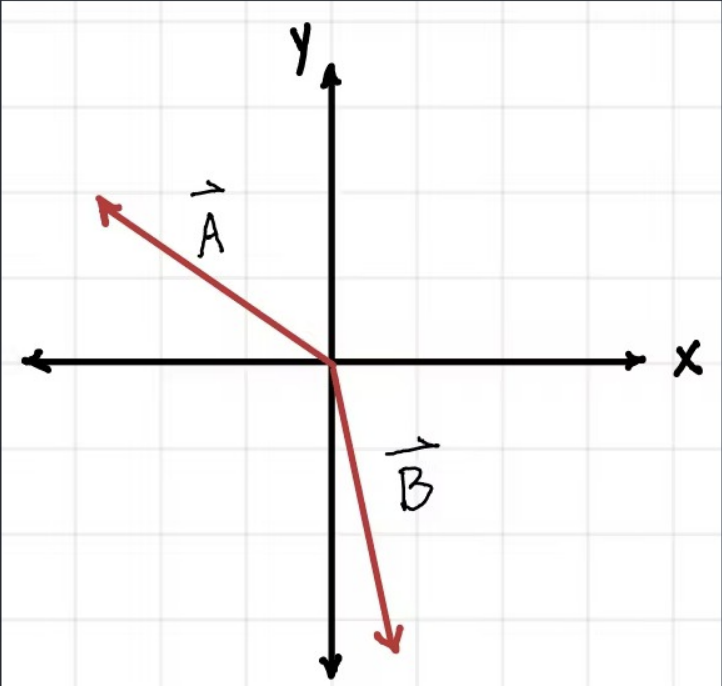
Negative
Consider the vector C = A + B. The y component of C is …
Positive
Negative
Zero
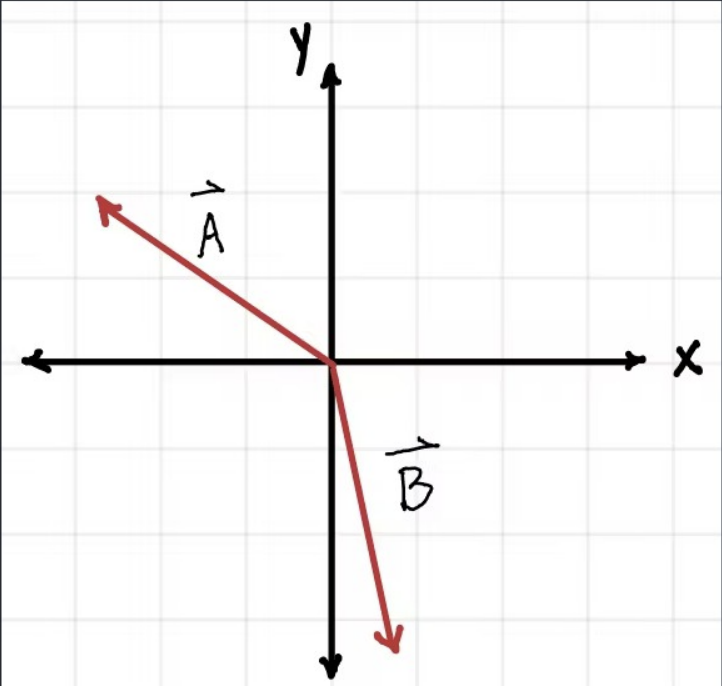
Negative
Consider the vector C = A - B. The x component of C is …
Positive
Negative
Zero
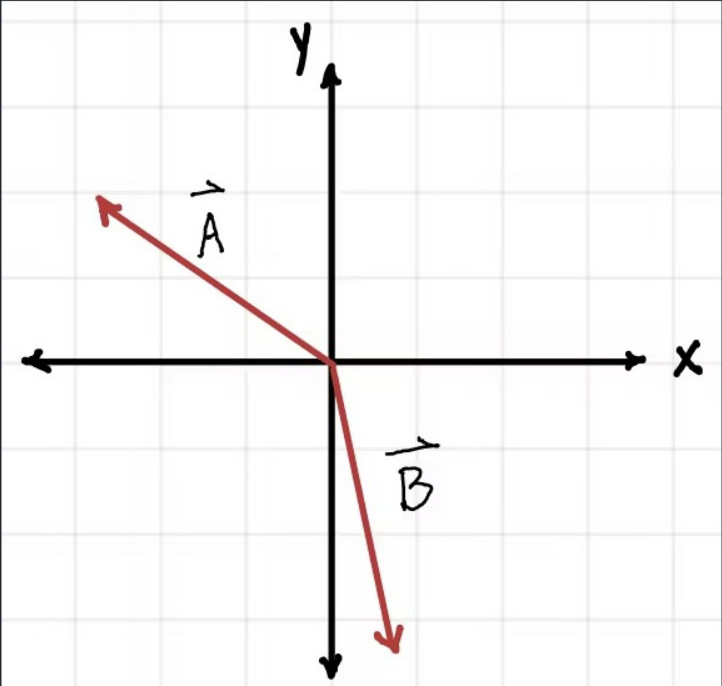
Positive
Consider the vector C = A - B. The y component of C is …
Positive
Negative
Zero
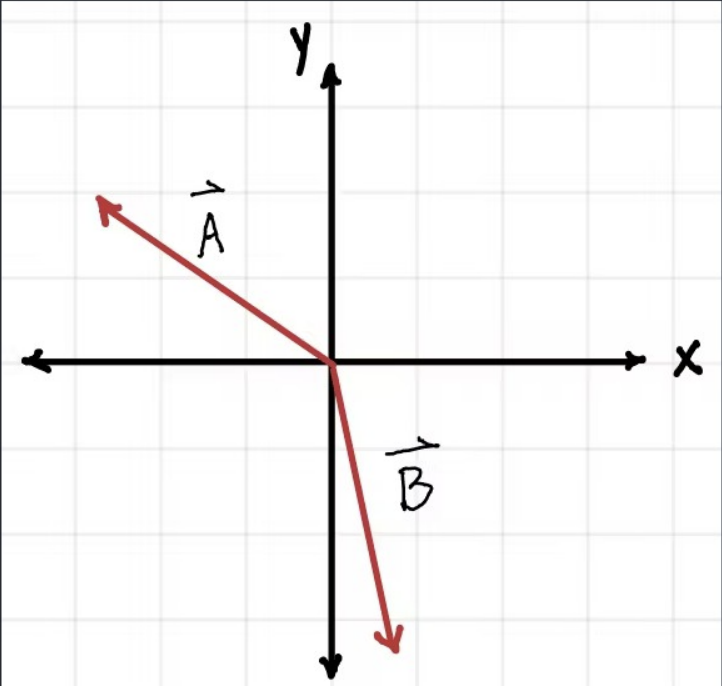
When the magnitude of k is less than 1
Vector B=kA where k is a scalar. When does B have a smaller magnitude than A?
When the magnitude of k is less than 1
When the magnitude of k is equal to 1
When the magnitude of k is greater than 1
False
True or False: When vectors are added together, the order of addition matters
Zero
A football player receives a kickoff at the front of his end zone. He runs to the 50 yd line and is chased back to his starting position where he is tackled. What is his total displacement along the length of the field?
(Assume he begins on the left end of the field, and the right is positive. Also, assume that he only runs along the long axis of the field.)
Greater than zero
Less than zero
Zero
Cannot be determined
Greater than zero
A football player receives a kickoff at the front of his end zone. He runs to the 50 yd line and is chased back into his end zone where he is tackled. What distance is he from his original starting position?
(Assume he begins on the left end of the field, and the right is positive. Also, assume that he only runs along the long axis of the field.)
Greater than zero
Less than zero
Zero
Cannot be determined
100 yards
A football player receives a kickoff at the front of his end zone. He runs to the 50 yd line and is chased back to his starting position where he is tackled. What is his total path length that he runs?
(Assume he begins on the left end of the field, and the right is positive. Also, assume that he only runs along the long axis of the field.)
0 yards
50 yards
100 yards
Cannot be determined
Zero
A football player receives a kickoff at the front of his end zone. He runs to the 50 yd line and is chased back to his starting position where he is tackled. What is his average velocity along the length of the field?
(Assume he begins on the left end of the field, and the right is positive. Also assume that he only runs along the long axis of the field.)
Greater than zero
Less than zero
Zero
Cannot be determined
False
True or False: Acceleration and velocity must always be in the same direction
True
True or False: In one dimension, it is possible for an object to be slowing and its acceleration be positive.
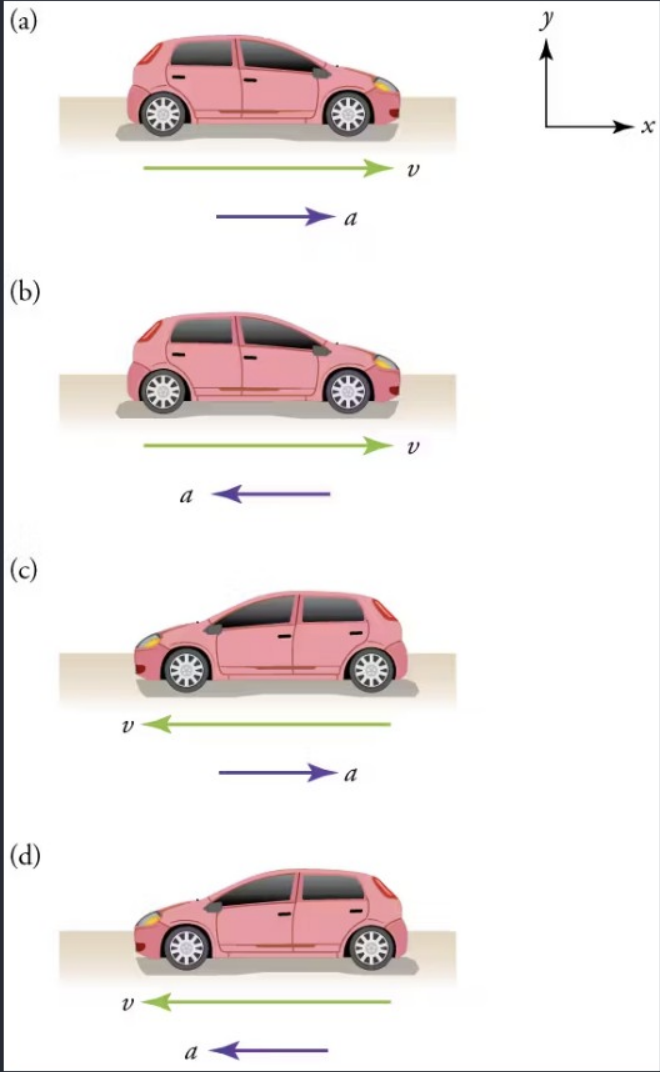
Car B & Car C
Which of the cars is slowing down?
State all that apply
Car A
Car B
Car C
Car D
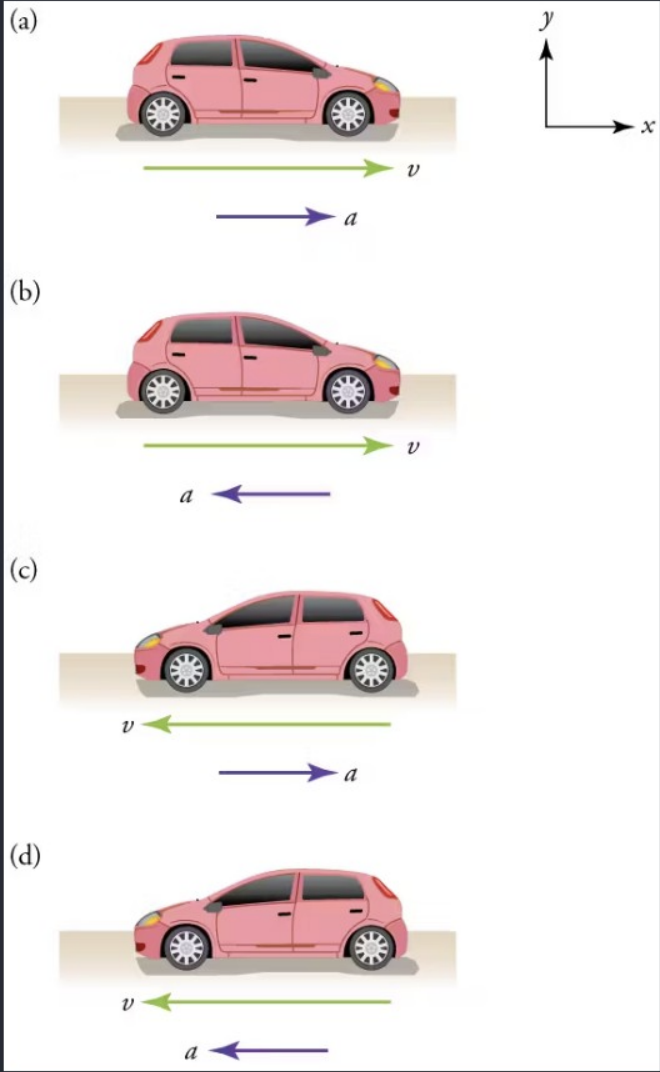
Car B & Car D
Which of the cars has negative acceleration?
State all that apply
Car A
Car B
Car C
Car D
An object has constant acceleration & An object is not accelerating
The kinematic equations derived at the beginning of the semester apply when:
An object is accelerating
An object has constant acceleration
An object is not accelerating
Never
Remains constant
When an object is tossed in the air, the object’s acceleration _____ while it is in free fall.
Increases
Decreases
Increases then decreases
Decreases then increases
Remains constant
Decreases then increases
When an object is tossed in the air, the object’s speed _____ while it is in free fall.
Increases
Decreases
Increases then decreases
Decreases then increases
Remains constant
Increases
An object is dropped into free fall. Five seconds later a second object is dropped into free fall. While they are falling, the distance between them:
Increases
Decreases
Remains constant
The object has constant velocity
The acceleration of an object is zero when:
The object moves at constant speed
The object moves in a straight line
The object has constant velocity
None of these
North, South, East, & West
If an object is moving toward the west at some instant, in what direction could its acceleration be?
State all that may apply
North
South
East
West
Driving up a long straight incline at a constant speed
The acceleration of a car is zero when it is:
Turning right at a constant speed
Driving up a long straight incline at a constant speed
Traveling over the crest of a hill at a constant speed
Bottoming out at the lowest point of a valley at a constant speed
Speeding up as it descends a long straight decline
True
True or False: Imagine objects A and B are moving in the same direction at the same speed. The relative velocity between these two objects is zero.
Nowhere along the path
As a projectile moves in its parabolic path with non-zero velocity in the x direction, the velocity and acceleration are parallel when?
At the peak
Everywhere along the path
Nowhere along the path
Not enough information
False
True or False: If an object is moving, then there must be a force acting on that object.
Second
The statement, "an object experiencing a net force has an acceleration inversely proportional to its mass," align to which of Newton’s Laws?
First
Second
Third
Fourth
Third
The statement, “forces come in pairs,” aligns to which of Newton’s Laws?
First
Second
Third
Fourth
True
True or False: If a single force acts on an object, the object accelerates.
First
The statement, "objects tend to maintain their current state of motion," aligns to which of Newton’s Laws?
First
Second
Third
Fourth
The net force acting on the truck is zero
A truck moves directly away from you at a constant velocity (as observed by you while standing in the middle of the road). It follows that …
No forces act on the truck
A constant net force acts on the truck in the direction of its velocity
The net force acting on the truck is zero
The net force acting on the truck is equal to its weight
True
True or False: If two external forces that are both equal in magnitude and opposite in direction act on the same object, the two forces can never be a N3L pair.
False
True or False: Objects in orbit do NOT experience gravity from the body they orbit.
True
True or False: Objects in orbit DO experience gravity from the body they orbit.
False
True or False: Two forces of a N3L pair are equal only if the objects involved are not accelerating.
The person’s gravity pulling up on the Earth
What is the reaction force to the Earth’s gravity pulling down on a person according to N3L?
The upward force exerted by the ground on the person
The person’s gravity pulling up on the Earth
The Earth’s gravity pulling up on the person
The person pushing down on the ground
They have the same magnitude force
A motorcycle and a truck collide head on. Which experiences the greater magnitude force?
Motorcycle
Truck
They have the same magnitude force
Motorcycle
A motorcycle and a truck collide head on. Which experiences the greater magnitude acceleration?
Motorcycle
Truck
They have the same magnitude acceleration
Zero
What is the apparent weight of someone in free fall?
Less than their weight, but not zero
Equal to their weight
Greater than their weight
Zero
False
True or False: The normal force always points up.
True
True or False: The normal force always points perpendicular to the surface an object is in contact with.
False
True or False: The normal force is always equal and opposite to the force of gravity.
Out of the board
I press the board’s eraser into the vertical plane of the board such that it does not fall. In which direction is the normal force of the board?
Upward
Downward
To the left
To the right
Out of the board
Into the board
Upward
I press the board’s eraser into the vertical plane of the board such that it does not fall. In which direction is the static friction on the eraser?
Upward
Downward
To the left
To the right
Out of the board
Into the board
Pulling with a string forward and upward
You slide a friend on a cardboard sled down the dorm hallway. Which case would make your job easiest?
Pressing on the shoulders forward and down
Pressing on the back parallel with the floor
Pulling with a string forward and upward
The component of gravity down the ramp is equal to friction
Objects that slide down a ramp can do so with constant speed. In this case, we expect …
The component of gravity down the ramp is less than friction
The component of gravity down the ramp is equal to friction
The component of gravity down the ramp is greater than friction
True
True or False: A force that is always perpendicular to the velocity of a particle never does work on the particle.
Equal to zero
You hold your book bag in your hand and carry it along level ground. In this case the word you do on the bag is …
Greater than zero
Equal to zero
Less than zero
True
True or False: Work can be negative.
Postive
As a block slides down a ramp, gravity does ____ work.
Positive
Negative
Zero
Zero
As a block slides down a ramp, the normal force does ____ work.
Positive
Negative
Zero
Positive
A block slides down a ramp subject to gravity, the normal force of the plane, and friction. If the object speeds up, the net force does ___ work.
Positive
Negative
Zero
They all have the same speed when they strike the ground
Three objects are thrown with the same initial speed from the same rooftop. One thrown slightly upward, one horizontal, and one slightly downward.
Which one will have the highest speed when they hit the ground?
The one thrown slightly upward
The horizontally thrown object
The one thrown slightly downward
They all have the same speed when they strike the ground
4x
A spring is compressed some distance. By what factor does the stored energy change when the compression instance is doubled?
1x (its constant)
2x
4x
1/2x
1/4x
The object falls at constant speed
For an object that is falling, the drag force can eventually the gravitational force. In this case …
The object stops moving
The object moves upward
The object falls at constant speed
The object falls with speed g
True
True or False: If two people lift identical boxes to the same height but one does it faster, the person who lifts the box faster uses more power.
True (think boomerang)
True or False: The center of mass of an object can lie outside the object.
Both balls will have the same change in momentum
If a tennis ball and bowling ball experience the same impulse, which of the following is true?
Both balls will have the same change in momentum
The tennis ball will have a greater change in momentum
The bowling ball will experience a greater change in momentum
Neither ball will change its momentum
They have the same magnitude momentum change
A motorcycle and a truck collide head on. Which experiences a greater change in its momentum?
Motorcycle
Truck
They have the same magnitude momentum change
Motorcycle
A motorcycle and a truck collide head on. Which experiences a greater change in its velocity?
Motorcycle
Truck
They have the same magnitude velocity change
Perfectly inelastic collision
Objects that collide and stick together experience a(n) _____
Elastic collision
Inelastic collision
Perfectly elastic collision
Perfectly inelastic collision
Always
In a collision, momentum is ____ conserved.
Always
Sometimes (rarely)
Never
Sometimes (rarely)
In a collision, kinetic energy is ____ conserved.
Always
Sometimes (rarely)
Never
It remains stationary
Two ice skaters, one heaver than the other, push off from each other while standing still. What happens to the center of mass of the skater system?
It moves in the direction of the heavier skater
It moves in the direction of the lighter skater
It remains stationary
It moves halfway between the two skaters
Moves to the right
A toddler stands on a sled that is on ice on the driveway. The toddler walks to the left, therefore the sled ____.
Moves to the left
Moves to the right
Remains stationary
Their angular velocity is the same
Two students are on the same rotating merry-go-round. Student A is 1m from the center, and Student B is 2m from the center.
Which has the higher angular velocity?
Student A
Student B
Their angular velocity is the same
Cannot be determined
Student B
Two students are on the same rotating merry-go-round. Student A is 1m from the center, and Student B is 2m from the center.
Which has the higher tangential velocity?
Student A
Student B
Their angular velocity is the same
Cannot be determined
Student B
Two students are on the same rotating merry-go-round. Student A is 1m from the center, and Student B is 2m from the center.
Which has the higher centripetal acceleration?
Student A
Student B
Their angular velocity is the same
Cannot be determined
Increases linearly with angular speed
The motor of a merry-go-round exerts a constant torque on it. As it speeds up from rest, the power output of the motor:
Is constant
Increases linearly with angular speed
Is zero
None of these
False
True or False: A particle moving in uniform circular motion has constant velocity.
False
True or False: A particle moving in uniform circular motion has constant acceleration.
They are the same
As the ISS orbits the Earth, which experiences the greater gravitational force?
The Earth
The ISS
They are the same
Need to know their masses
They are the same
As the ISS orbits the Earth, which experiences the greater acceleration?
The Earth
The ISS
They are the same
Need to know their masses
Satellite 2
Satellite 1 is in a certain circular orbit while satellite 2 is in a larger circular orbit. Which has the longer period?
Satellite 1
Satellite 2